Слайд 2
The Origins of English Words
Слайд 3
Definitions
A native word is a word which belongs
to the original English word stock, as known from
the earliest available manuscripts of the Old English period.
A borrowed word (a borrowing, or a loan word) is a word taken over from another language and modified in phonemic shape, spelling, paradigm or meaning according to the standards of the English language.
Слайд 4
Words of Native Origin
Words of the Indo-European origin
(IE)
Words of common Germanic origin
English words proper
Слайд 5
Words of the Indo-European origin
Family relations: father,
mother, brother, son, daughter
Parts of the human body: foot,
nose, lip, heart, tooth
Animals and plants: cow, swine, goose, tree, birch, corn
The most important objects and phenomena of nature: sun, moon, star, wind, water, wood, hill, stone
Adjectives: hard, quick, slow, red, white, new
Numerals from 1 to 100: one, two, twenty, eighty
Pronouns – personal, except they (Sc.): I, you, he; demonstrative : that; interrogative: who
Some of the most frequent verbs: bear, do, be, sit, stand
Слайд 6
Words of common Germanic origin
Nouns denoting parts of
the human body: head, arm, finger
Periods of time: summer,
winter, time, week
Natural phenomena: storm, rain, flood, ice, ground, sea, earth
Artefacts and materials: bridge, house, shop, room, coal, iron, lead, cloth
Animals, plants and birds: sheep, horse, fox, crow, oak, grass
Adjectives denoting colours, size and other properties: broad, dead, deaf, deep, grey, blue
Verbs: see, hear, speak, tell, say, make, give
Слайд 7
Historical causes of borrowing
The Roman invasion (1st c.
B.C.),
The introduction of Christianity (7th c. A.D.),
The
Danish conquests (11th – 13th c. A.D.),
The Norman conquest (1066 A.D.),
The Renaissance period (14th – 16th c. A.D.),
Direct linguistic contacts and political, economical and cultural relationship with other nations.
Слайд 8
The Etymology of Borrowed Words
Celtic: 5th – 6th
A. D.
Latin:
1st layer: 1st c. B. C.
2nd layer: 7th c. A. D. (the introduction
of Christianity)
3rd layer: 14th – 16th c. (the Renaissance period)
Scandinavian: 8th – 11th c. A. D.
French:
Norman borrowings: 11th – 13th A. D.
Parisian borrowings: the Renaissance period
Greek: the Renaissance period
Italian: the Renaissance period and later
Spanish: the Renaissance period and later
Russian: the Renaissance period and later
German, Indian and other languages
Слайд 9
Celtic borrowings
Place names: Avon, Exe, Esk, Usk,
Ux (Celtic “river”, “water”); London (Llyn “river”+ dun “a
fortified hill”) - “a fortress on the hill over the river”
cradle, cross, iron, flannel, tweed, lake (C. loch)
Слайд 10
The earliest Latin borrowings (1st c. A.D.)
words denoting
things connected with war, trade, building and domestic life:
pound, inch, cup, kitchen, pepper, butter, cheese, milk, wine, cherry
Слайд 11
Latin words borrowed into English through the Christianization
of England (7th c. A.D.)
persons, objects and ideas
associated with church and religious rituals: priest, bishop, monk, nun, candle, temple, angel
words connected with learning: grammar, school, scholar, decline, master, magister
Слайд 12
Latin borrowings of the Renaissance period (14th –
16th c. A.D.)
abstract words: major, minor, filial, moderate,
intelligent, permanent, to elect, to create.
Слайд 13
Scandinavian borrowings (8th - 11th c. A.D.)
Verbs: call,
take, cast, die, want
Nouns: law, egg, husband (Sc. hūs
+ bōndi “inhabitant of the house”), window (Sc. vindauga “the eye of the wind”)
Adjectives: ill, loose, low, weak
Pronouns and pronominal forms: they, their, them, same, both, though.
Слайд 14
Scandinavian borrowings (place names)
Derby, Tremsby (-by: Sc.
“village, town”);
Zinthorp, Altharp (-thorp: Sc. “village”);
Eastoft, Nortoft (-toft:
Sc. “a plot of land covered with grass”);
Troutbeck (-beck: Sc. “brook”);
Inverness (-ness: Sc. “cape”);
Applethwait, Crossthwait (-thwait: Sc. “forest glade”)
Слайд 15
Norman borrowings (11th – 13th c. A.D.)
Government and
administration: state, country, government, parliament, prince, baron
Legal terms: court,
judge, justice, crime, prison, jury
Religious terms: saint, sermon (проповедь), prayer, parish (приход), chapel
Military terms: army, war, soldier, officer, battle, enemy
Educational terms: pupil, lesson, library, science, pen, pencil
Artistic and literary terms: image, character, figure, volume, design
Terms of everyday life: chair, table, plate, saucer, dinner, supper, breakfast
Слайд 16
Parisian borrowings: the Renaissance period and later
regime, routine,
police, machine, ballet, matinée, scene, technique, bourgeois, etc.
Слайд 17
The Renaissance period borrowings (14th – 16th c.
A.D.)
Italian: piano, violin, opera, alarm, colonel
Spanish: potato, tomato, cargo,
banana, cocoa.
Greek: direct (e.g. atom, cycle, ethics, esthete), or through Latin (datum, status, phenomenon, phenomenon, philosophy, method, music).
Слайд 18
Other borrowings
Japanese: karate, judo, hara-kiri, kimono, tycoon;
Arabic: algebra,
algorithm, fakir, giraffe, sultan
Turkish: yogurt, kiosk, tulip
Persian: caravan, shawl,
bazaar, sherbet
Eskimo: kayak, igloo, anorak
Amerindian languages: toboggan, wigwam, opossum
Russian: bistro, tsar, balalaika, tundra, sputnik
Слайд 19
Classification of borrowings according to the aspect which
is borrowed
Borrowings proper
Translation borrowings (translation loans)
Semantic borrowings
Слайд 20
Classification of borrowings according to the aspect which
is borrowed
Translation borrowings (translation loans) are words and expressions
formed from the material already existing in the English language but according to patterns taken from another language, by way of literal morpheme-for-morpheme translation.
E. g. masterpiece < Germ. Meisterstück; Wonder child < Germ. Wunderkind; wall newspaper < Rus. стенная газета; collective farm < Rus. колхоз.
Слайд 21
Classification of borrowings according to the aspect which
is borrowed
Semantic borrowing is understood as the development in
an English word of a new meaning under the influence of a related word in another language.
E. g. Eng. pioneer ‘explorer’, ‘one who is among the first in new fields of activity’:: Rus. пионер ‘a member of the Young Pioneers’ Organization’.
reaction, deviation, bureau
Слайд 22
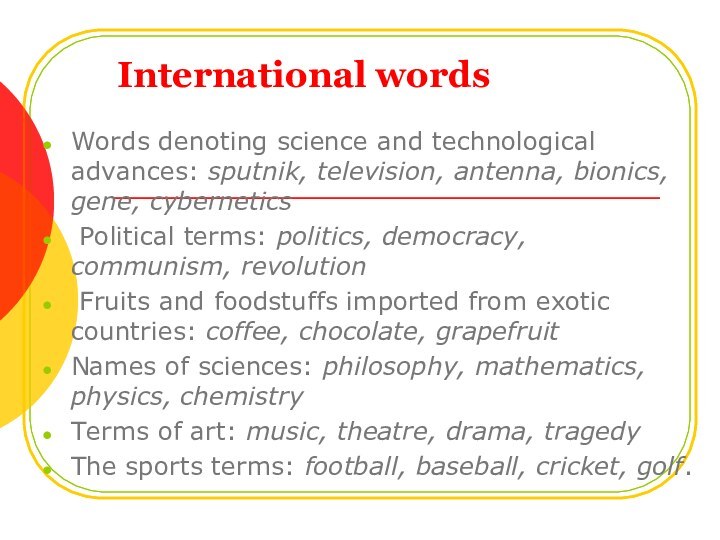
International words
“Words of identical origin that occur in
several languages as a result of simultaneous or successive
borrowings from one ultimate source” (I. A. Arnold, p. 260).