Слайд 2
Forensics, pertaining to the courts either criminal or
civil
Forensics DNA analysis is the use of DNA evidence
Used
in:
paternity suites
victim identification
identifying suspects
Слайд 3
Originally identification was limited to:
Physical attributes such as;
ethnicity, gender, height, weight, hair color, etc.
Friction-ridge identification or
fingerprinting
Blood-antigen & serum proteins, ABO blood groups
Слайд 4
Even though two unrelated humans differ in their
DNA only by 0.1 to 0.2% there are still
up to 6 million basepair differences
It is these differences that are used to create a unique DNA “fingerprint” also known as DNA profile
Слайд 5
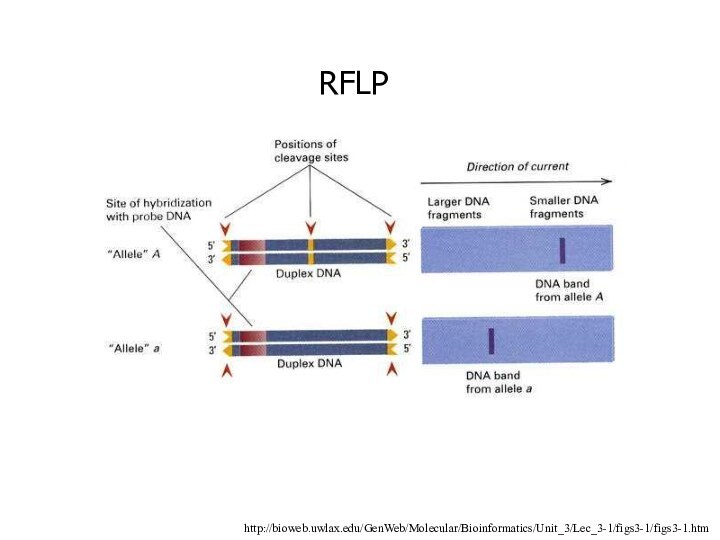
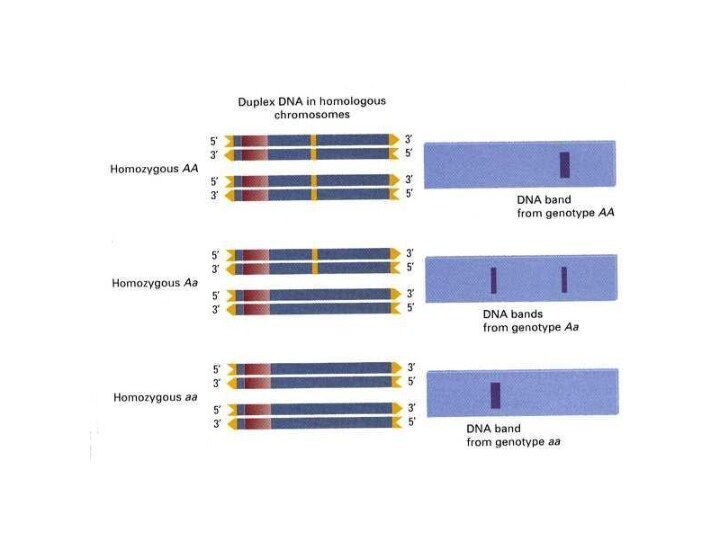
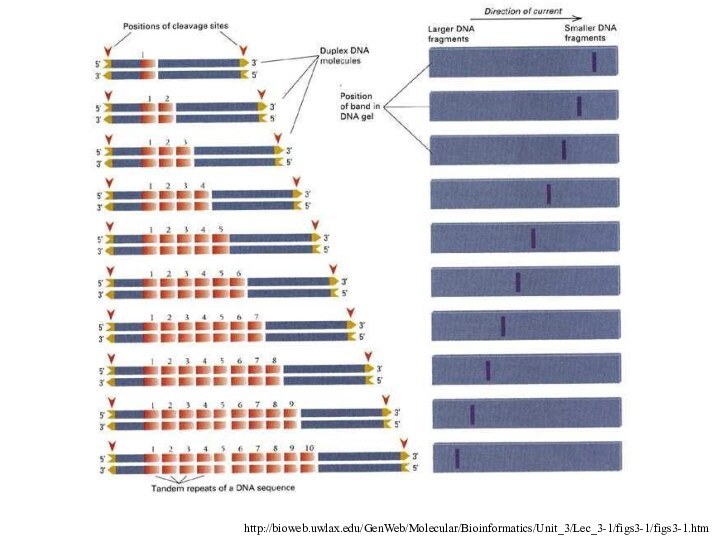
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
Detects a single basepair
change in DNA
Must occur within a restriction enzyme cleavage
sequence to be visible
Often used in disease screening such as in the detection of sickle cell anemia
DNA fragments are often visualized by Southern Blot
Слайд 6
http://bioweb.uwlax.edu/GenWeb/Molecular/Bioinformatics/Unit_3/Lec_3-1/figs3-1/figs3-1.htm
RFLP
Слайд 8
DNA Fingerprinting
First described in 1985 by Alec Jeffreys
as a method for identifying individuals by their unique
pattern of DNA banding
First use of DNA fingerprinting was in a 1985 immigration case in the UK. It identified a child as being the offspring of a British citizen
It was then used to rule out a suspect in a rape/murder case in England in 1986
Слайд 9
During the late 80s/early 90s US courts questioned
the validity of DNA profiling
The debates centered on evidence
collection procedures, training of technicians, & the statistics used to establish a match
By the mid 1990s DNA profiling was shown to be scientifically valid and DNA evidence became admissible
Слайд 10
What creates this unique pattern?
Satellite DNA: repetitive DNA
sequence.
Macrosatellite: core sequence 100 to 6500bp
Minisatellite: core sequence of
10-20bp repeated multiple times
Microsatellite: small arrays of tandem repeats of 2 to 4bp in length
(AT)n account for 0.3% of the human genome
(CATG)n accounts for 0.5% of the human genome
Слайд 11
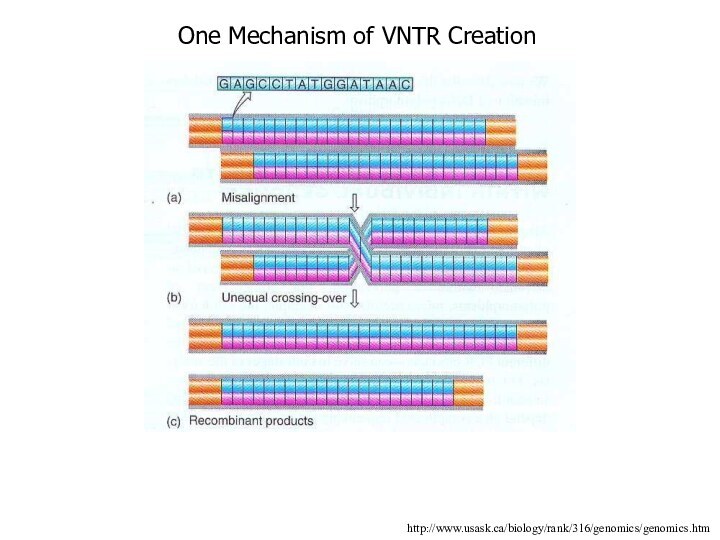
Repeats of Satellite DNA
Repeat units vary in length
from 2bp to long stretches of 6000bp or more
These
repeat units are lined up head to tail and compose satellite DNA and are interspersed throughout the genome
The number of units varies person to person
Thus these sequences are called VNTRs (variable number of tandem repeats)
A VNTR is a locus that is hypervariable due to a large number of alleles each characterized by a different number of repeat units
Слайд 12
http://www.usask.ca/biology/rank/316/genomics/genomics.htm
One Mechanism of VNTR Creation
Слайд 13
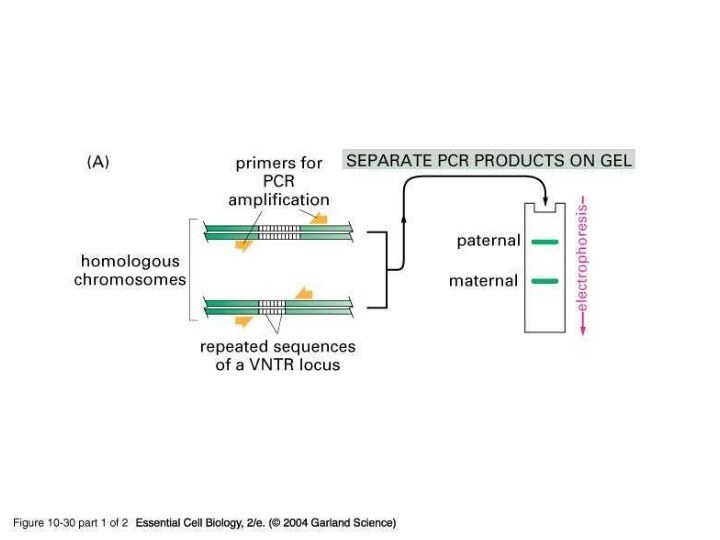
Southern blotting can be used to visualize the
variation
Probes specific to the repeat unit are hybridized to
DNA cut with a restriction enzyme that cuts just outside the VNTR
This allows for the difference in VNTR length to be detected
Two common probes are known are:
33.6 (AGGGCTGGAGG)18
31.5 (AGAGGTGGGCAGGTGG)29
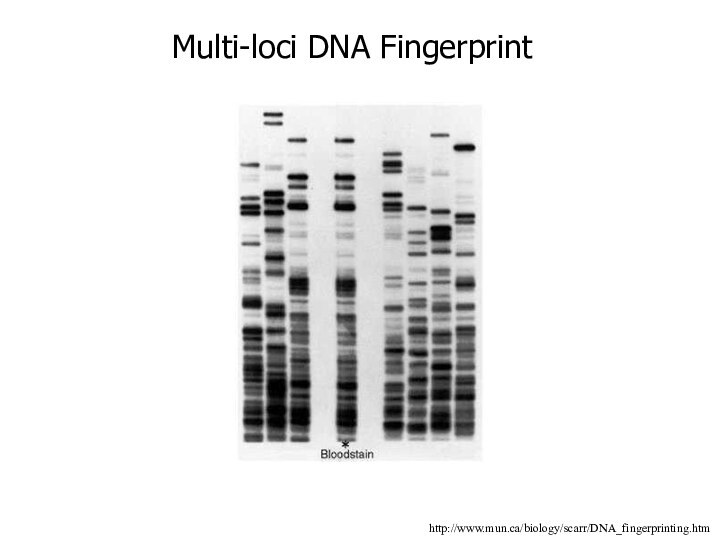
These are multi-locus minisatellite probes and show about 17 different DNA bands for each individual
Слайд 14
http://bioweb.uwlax.edu/GenWeb/Molecular/Bioinformatics/Unit_3/Lec_3-1/figs3-1/figs3-1.htm
Слайд 15
http://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/DNA_fingerprinting.htm
Multi-loci DNA Fingerprint
Слайд 16
Multi-locus analysis of Dolly used to prove she
was a clone
1 –12 are control sheep
U is original
udder cells
C is cells from culture
D is Dolly blood cells
Слайд 17
http://www.genelex.com/paternitytesting/paternityslide2.html
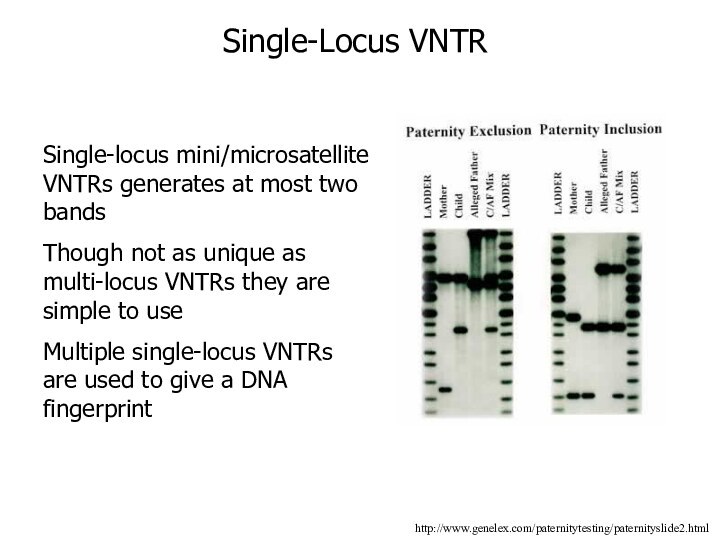
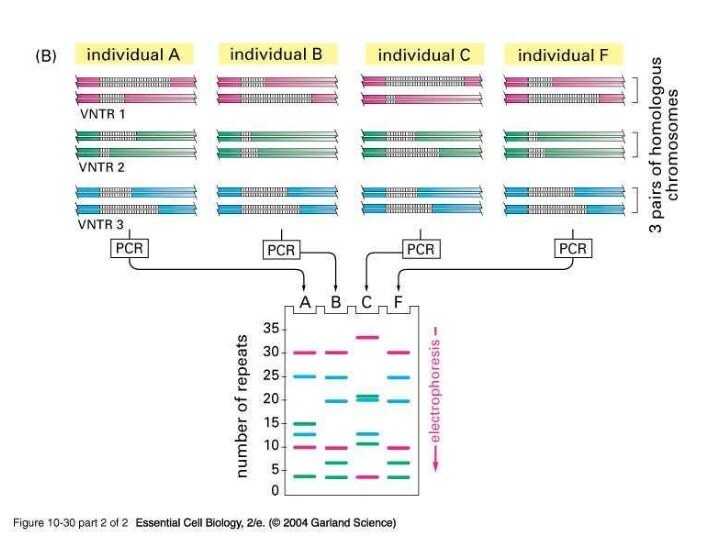
Single-Locus VNTR
Single-locus mini/microsatellite VNTRs generates at most two
bands
Though not as unique as multi-locus VNTRs they are
simple to use
Multiple single-locus VNTRs are used to give a DNA fingerprint
Слайд 18
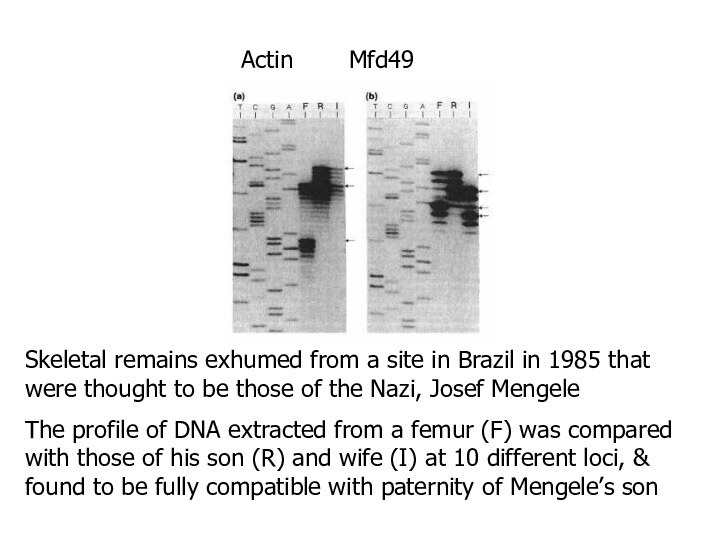
Skeletal remains exhumed from a site in Brazil
in 1985 that were thought to be those of
the Nazi, Josef Mengele
The profile of DNA extracted from a femur (F) was compared with those of his son (R) and wife (I) at 10 different loci, & found to be fully compatible with paternity of Mengele’s son
Actin Mfd49
Слайд 19
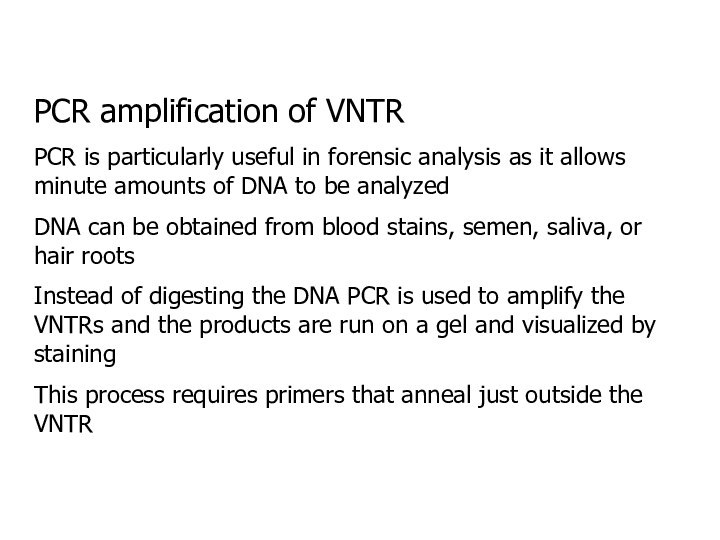
PCR amplification of VNTR
PCR is particularly useful in
forensic analysis as it allows minute amounts of DNA
to be analyzed
DNA can be obtained from blood stains, semen, saliva, or hair roots
Instead of digesting the DNA PCR is used to amplify the VNTRs and the products are run on a gel and visualized by staining
This process requires primers that anneal just outside the VNTR
Слайд 22
Short Tandem Repeats (STR)
Are a variation on VNTRs,
but use the smallest repeats units often only 2
to 4 bp in length
aatttttgtattttttttagagacggggtttcaccatgttggtcaggctgactatggagt
tattttaaggttaatatatataaagggtatgatagaacacttgtcatagtttagaacgaa
ctaacgatagatagatagatagatagatagatagatagatagatagatagatagacagat
tgatagtttttttttatctcactaaatagtctatagtaaacatttaattaccaatatttg
13 core loci of tetrameric repeats are tested together to make a DNA profile
The sequence above is locus D7S280 which is located on chromosome 7
Слайд 23
STRs are isolated using PCR
Primers have been developed
to allow amplification of multiple STR loci in a
single reaction mixture
Each primer set has been optimized such that its product, no matter the number of STRs, is not the same size as any of the other products
Each primer set has unique fluorescent molecules covalently linked to them so that they may be visualized immediately by a computer
Слайд 24
Following the PCR reaction, internal DNA length standards
are added to the reaction mixture
The DNAs are separated
by length in a capillary gel electrophoresis machine
As DNA peaks elute from the gel they are detected with laser activation
The results are then graphed by a computer which compares them to a standard
Слайд 25
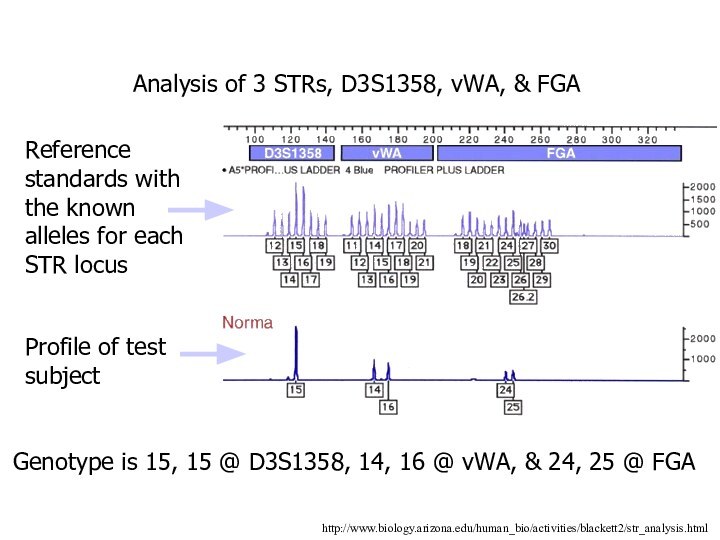
http://www.biology.arizona.edu/human_bio/activities/blackett2/str_analysis.html
Analysis of 3 STRs, D3S1358, vWA, & FGA
Reference
standards with the known alleles for each STR locus
Profile of test subject
Genotype is 15, 15 @ D3S1358, 14, 16 @ vWA, & 24, 25 @ FGA
Слайд 26
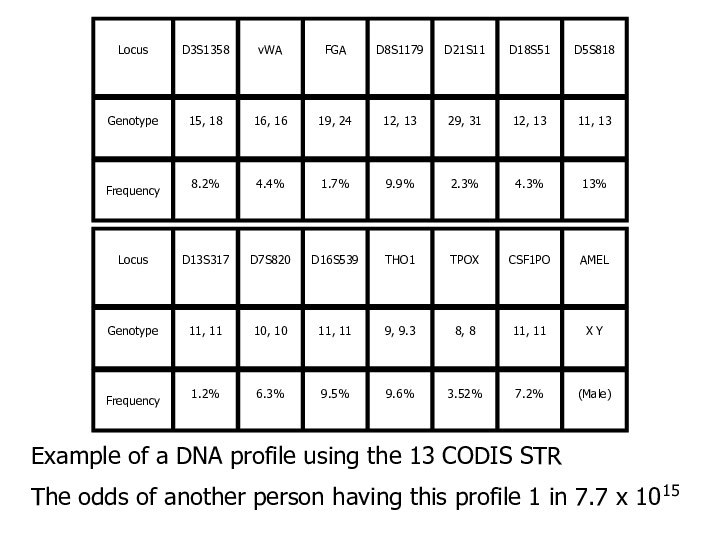
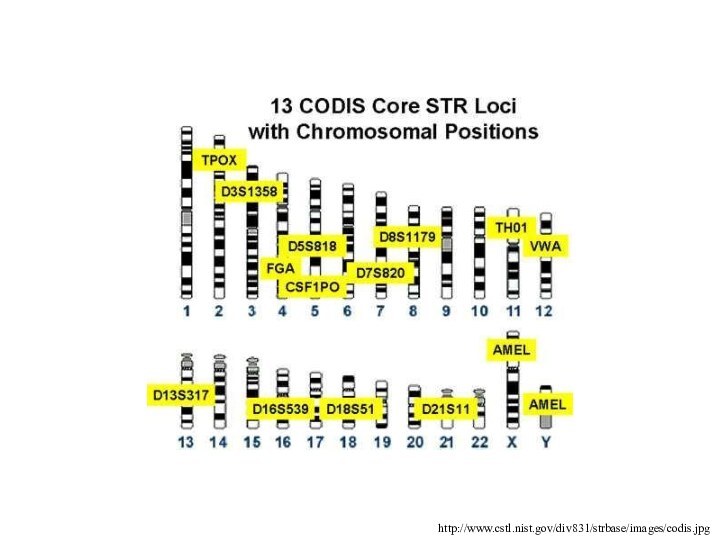
Example of a DNA profile using the 13
CODIS STR
The odds of another person having this profile
1 in 7.7 x 1015
Слайд 27
CODIS (Combined DNA Index System)
In 1997, the FBI
announced the selection of 13 STR loci to constitute
the core of the United States national database, CODIS
All forensic laboratories that use the CODIS system can contribute to the national database
The STRs alleles are easily genotyped using commercial kits
All data from these analyses are digital thus easily placed in the database
Слайд 28
http://www.cstl.nist.gov/div831/strbase/images/codis.jpg