- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему The Alimentary tract
Содержание
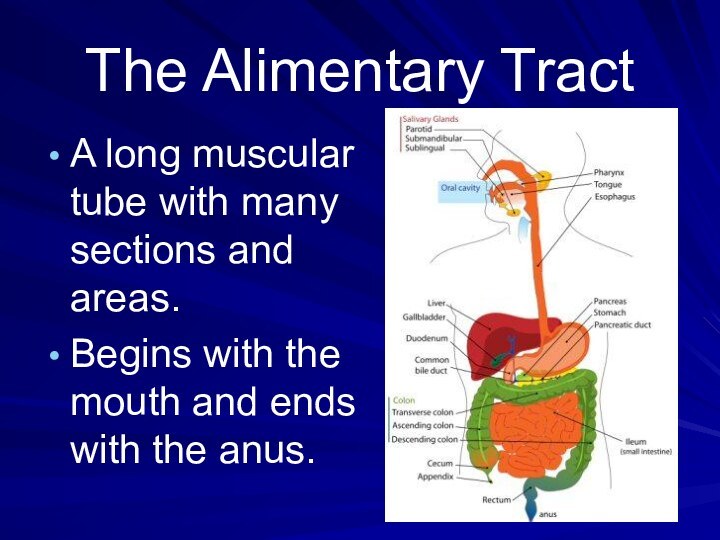
- 2. The Alimentary TractA long muscular tube with
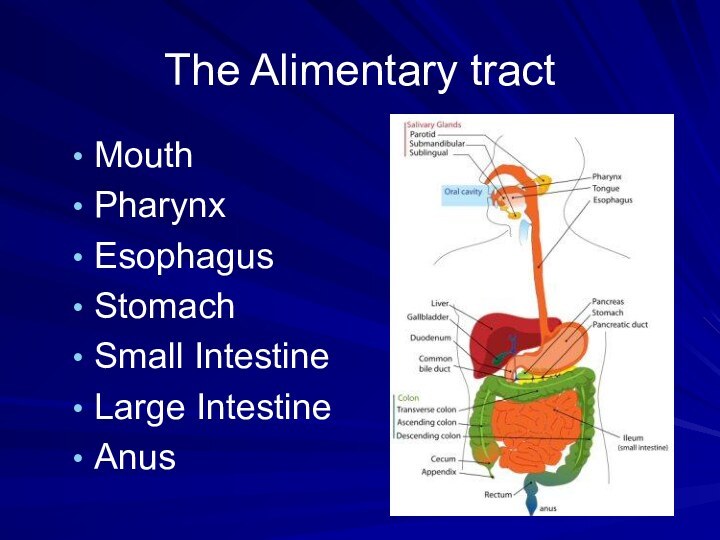
- 3. The Alimentary tract MouthPharynxEsophagusStomachSmall IntestineLarge IntestineAnus
- 4. Accessory PartsOrgans that are not in the
- 5. MouthFunctions: Food enters in the mouth or
- 6. MouthStructures in the mouth that aids digestion:
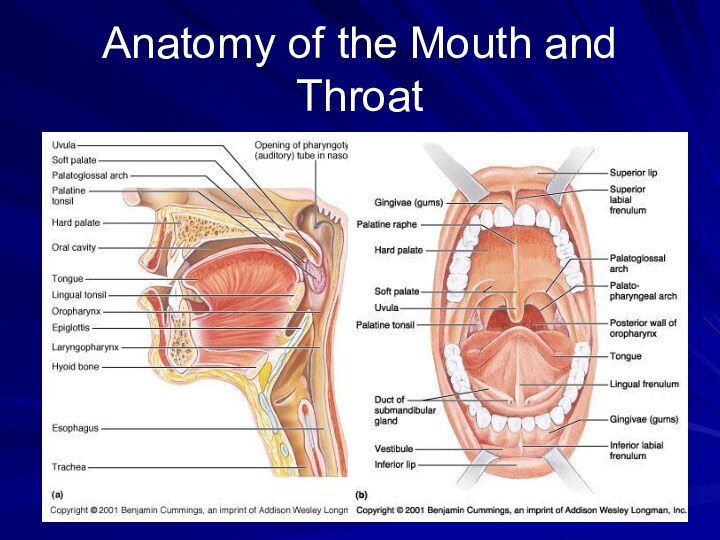
- 7. Mouth Tongue Mixes and rolls food into
- 8. Anatomy of the Mouth and Throat
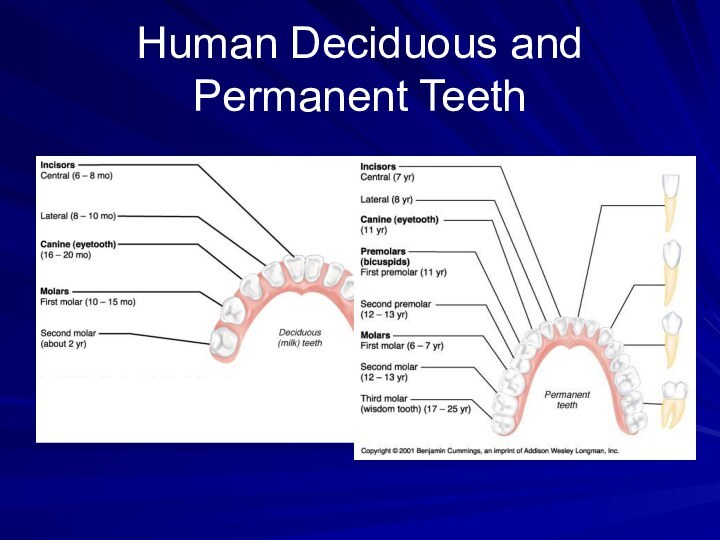
- 9. Human Deciduous and Permanent Teeth
- 10. Mechanism of SwallowingSwallowing is a coordinated activity
- 12. EsophagusA straight muscular tube that is about
- 13. Peristalsis
- 14. StomachJ-shaped muscular sacHas inner folds (rugae) that
- 15. Stomach
- 16. StomachPepsin – major enzyme; converts proteins into
- 17. Movements in Stomach
- 18. Small IntestineLong (20 ft), coiled tube beneath
- 19. Small IntestineSite of greatest amount of digestion and absorption
- 20. Small IntestineTakes about 4 – 8 hrs
- 21. Small IntestineHas folded inner walls covered with
- 22. Movement in small intestine:Mixing: Segmental contraction that
- 23. Large Intestinea.k.a. Colonlarger diameter, but shorter (5
- 24. Large Intestine
- 25. Large IntestineWaste is pushed into the expanded
- 26. Accessory OrgansProduce or store enzymes that helps
- 27. Accessory OrgansGall bladder Stores bile in between
- 28. Accessory OrgansPancreas Produces a juice that contains
- 29. Скачать презентацию
- 30. Похожие презентации
The Alimentary TractA long muscular tube with many sections and areas.Begins with the mouth and ends with the anus.



















Слайд 4
Accessory Parts
Organs that are not in the Alimentary
tract but helps in the digestion
Teeth
Tongue
Salivary glands
Liver
Gall bladder
Pancreas
Слайд 5
Mouth
Functions:
Food enters in the mouth or oral
cavity
Tasting
Mechanical breakdown of food
Secretion of salivary
glands (salivary amylase)
Слайд 6
Mouth
Structures in the mouth that aids digestion:
Teeth
– cut, tear, crush and grind food.
Salivary glands
– produce and secrete saliva into the oral cavity. Parotid (beneath the cheeks)
Submaxillary (below the jaw bone)
Sublingual (below the tongue)
– saliva moistens the food and contains enzymes (ptyalin or salivary amylase) that begins digestion of starch into smaller polysaccharides.
Слайд 7
Mouth
Tongue
Mixes and rolls food into tiny
mashed up bits (Bolus)
Pushes the bolus toward
the pharynx and into the esophagus when swallowing.
Слайд 10
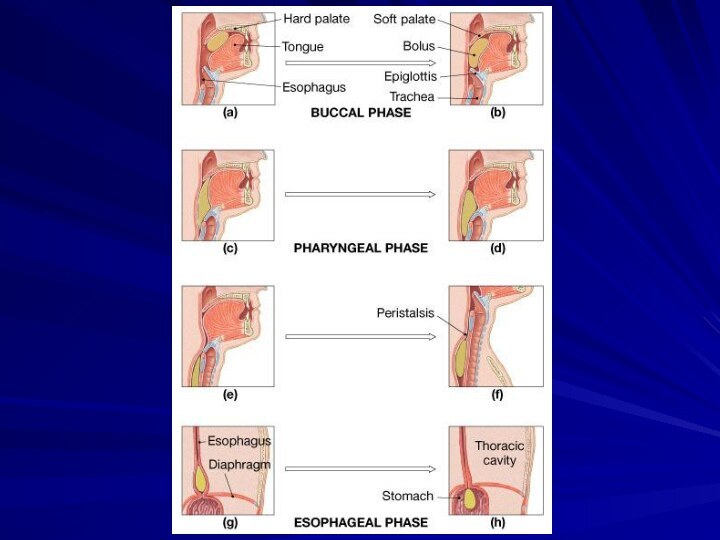
Mechanism of Swallowing
Swallowing is a coordinated activity of
the tongue, soft palate, pharynx and esophagus.
Phases
Food is pushed
into the pharynx by the tongue. (voluntary) Tongue blocks the mouth
Soft palate closes off the nose
Larynx (Adam’s Apple) rises so the Epiglottis (a flap of tissue) can close the opening of the trachea.
Слайд 12
Esophagus
A straight muscular tube that is about 10
inches (25 cm) long which connects the mouth with
the stomachFood takes about 4 to 8 seconds as it passes through to the stomach.
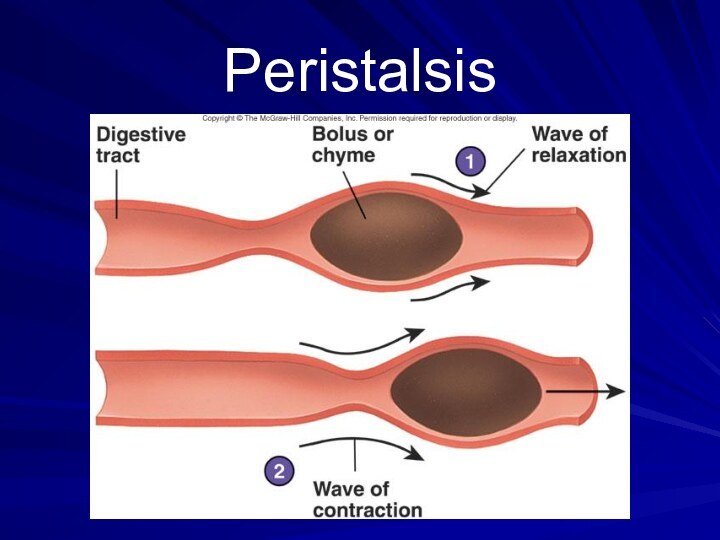
Its walls contain smooth muscles that contracts in wavy motion (Peristalsis).
Peristalsis propels food and liquid slowly down the esophagus into the stomach.
Cardiac Sphincter (ring-like valve) relaxes to allow food into the stomach.
Слайд 14
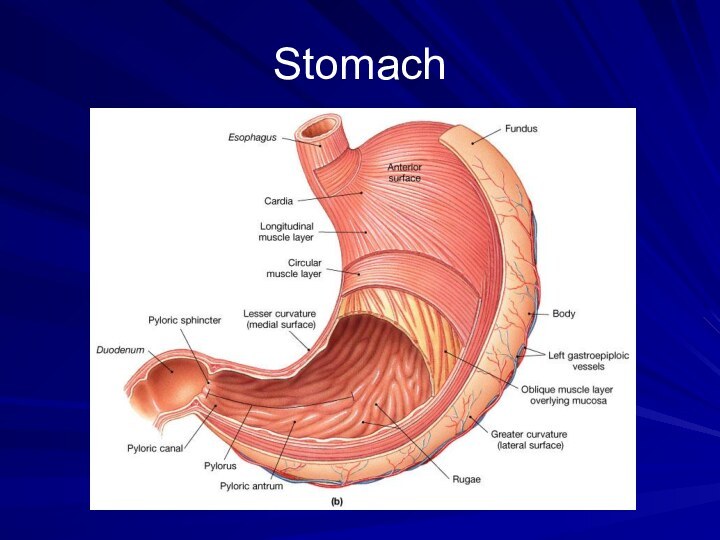
Stomach
J-shaped muscular sac
Has inner folds (rugae) that increases
the surface area of the stomach.
Churns and grinds together
the bolus into smaller pieces.Food is mixed with gastric juices (hydrochloric acid and enzymes) secreted by the stomach walls.
HCL helps break down food and kills bacteria that came along with the food.
Слайд 16
Stomach
Pepsin – major enzyme; converts proteins into peptides
in the presence of HCL.
Mucus – lubricates food and
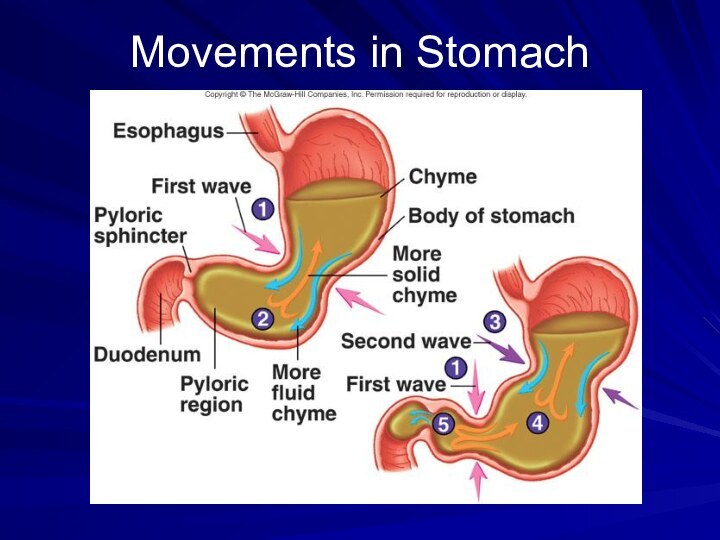
protects the gastric lining from strong digestive juices.Converts the bolus into a liquid (chyme) after 4 hrs of mechanical and chemical digestion
Chyme passes through the pyloric sphincter into the small intestine.
Слайд 18
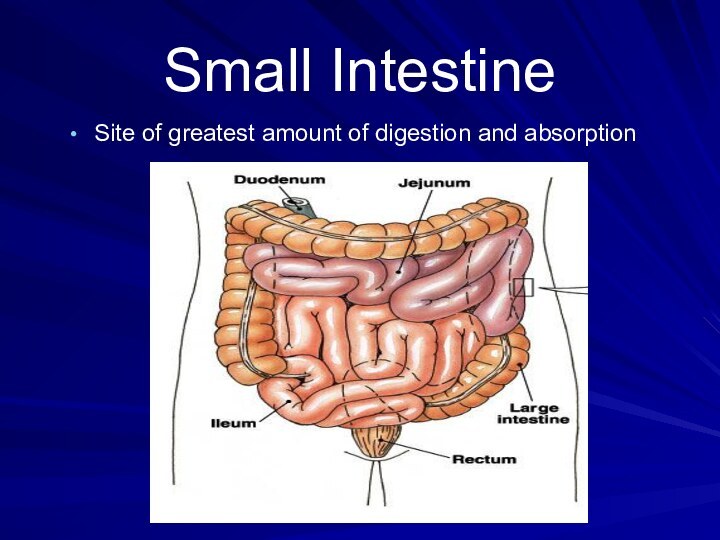
Small Intestine
Long (20 ft), coiled tube beneath the
stomach.
Has three parts:
Duodenum – upper part; about 10 in;
connected to the stomach.– where the digestive juices from the pancreas and the liver combine with chyme making it thin and watery.
Jejunum – about 8 ft
Ileum – about 12 ft
Слайд 20
Small Intestine
Takes about 4 – 8 hrs to
complete its journey.
Mucosa (inner wall) – secretes several enzymes
that acts on the food.Where the pancreatic enzymes are emptied into.
Digested nutrients are absorbed through intestinal walls.
Absorbed materials cross the mucosa into the blood then other parts of the body for storage or further chemical change.
Слайд 21
Small Intestine
Has folded inner walls covered with fingerlike
projections (villi; sing. – villus)
Each villus has tinier projections
called microvilli that absorbs digested food.Villi and microvilli increases the surface area of the small intestine for greater absorption.
Peristalsis moves the undigested food to the large intestine.
Слайд 22
Movement in small intestine:
Mixing: Segmental contraction that occurs
in small intestine
Secretion: Lubricate, liquefy, digest
Digestion: Mechanical and chemical
Absorption:
Movement from tract into circulation or lymphElimination: Waste products removed from body
Слайд 23
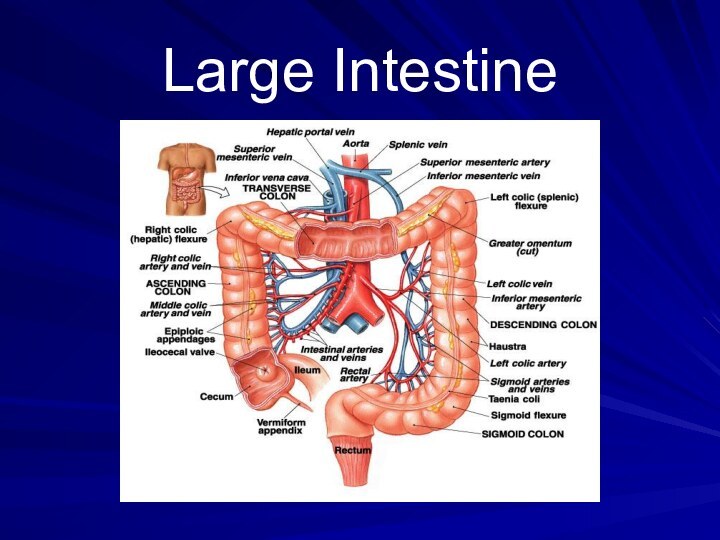
Large Intestine
a.k.a. Colon
larger diameter, but shorter (5 ft)
Water
is absorbed from the undigested food making the waste
harder until it becomes solid.Waste stays for 10 – 12 hours.
Слайд 25
Large Intestine
Waste is pushed into the expanded portion
(rectum) of the large intestine.
Solid waste stays in the
rectum until it is excreted through the anus as feces.Appendix hangs on the right side of the large intestine.
Слайд 26
Accessory Organs
Produce or store enzymes that helps in
digestion.
Liver
Largest gland of the body
Stores vitamins A,D,E,K
Stores sugar and glycogen
Produces bile (watery, greenish substance)
Secretes bile to the gall bladder via the hepatic duct and cystic duct.
Слайд 27
Accessory Organs
Gall bladder
Stores bile in between
meals
Secretes bile to the duodenum through the bile
duct during mealtime. Bile contains bile salts, pigments, cholesterol and phospholipids.
Bile is an emulsifier NOT an enzyme.
Emulsifier – dissolves fat into the watery contents of the intestine.
Слайд 28
Accessory Organs
Pancreas
Produces a juice that contains enzymes
(amylase and insulin) to break down carbohydrates, fats and
protein.Secretes the juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct.





























