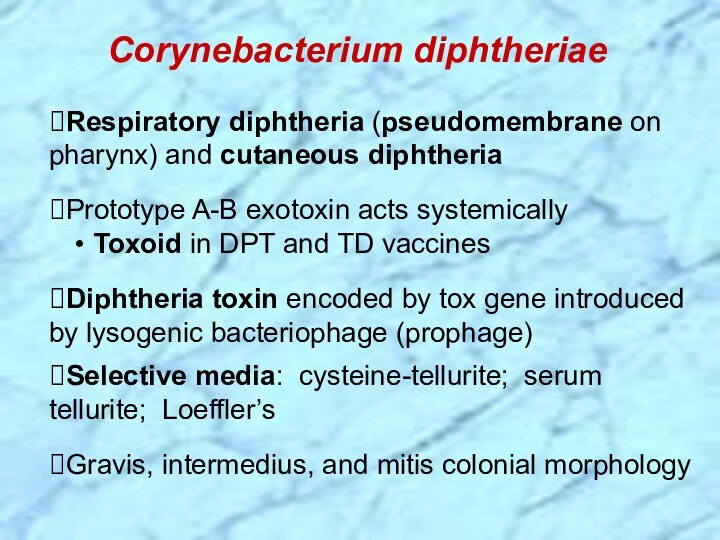
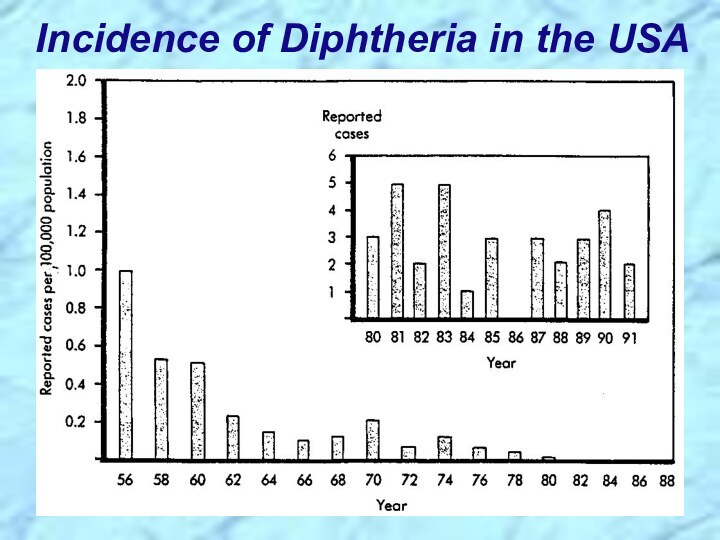
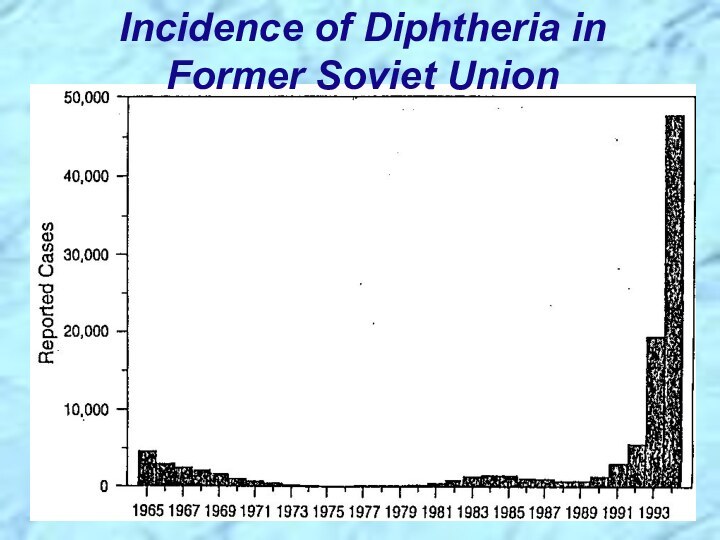
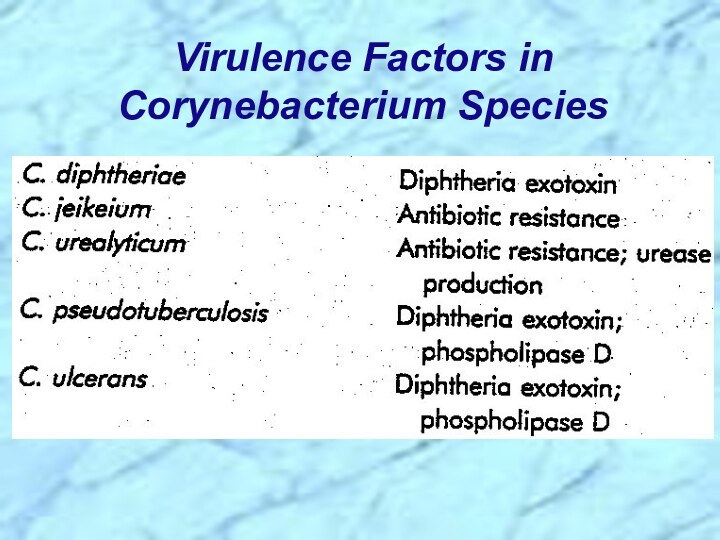
gram-positive bacilli that appear in short chains (“V” or
“Y” configurations) or in clumps resembling “Chinese letters”⮚Cells contain metachromatic granules (visualize with methylene blue stain)
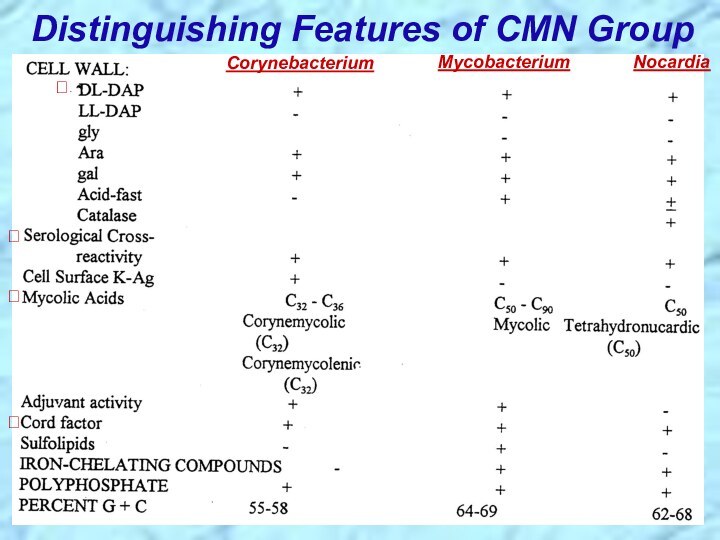
⮚Lipid-rich cell wall contains meso-diaminopimelic acid, arabino-galactan polymers, and short-chain mycolic acids
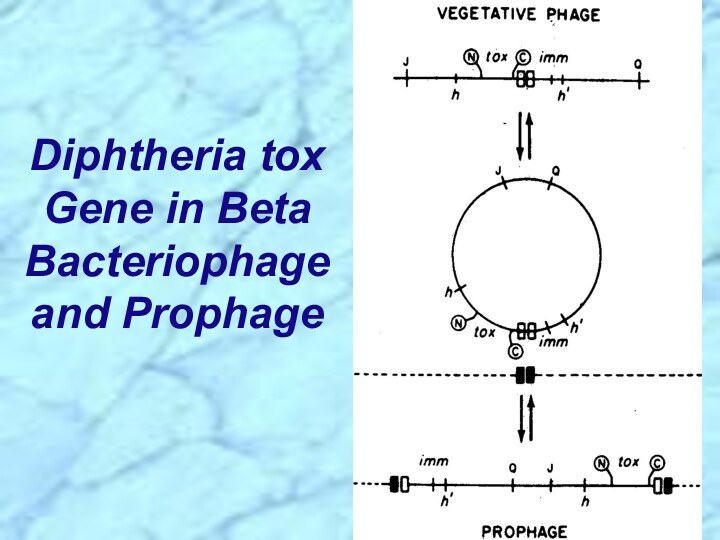
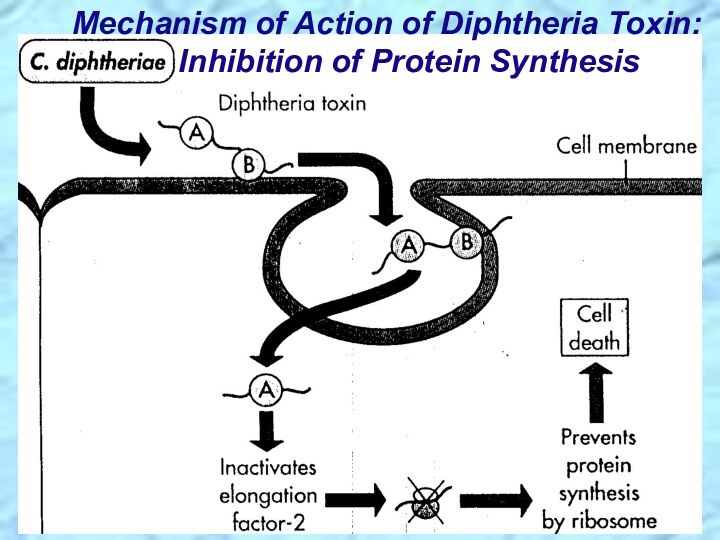
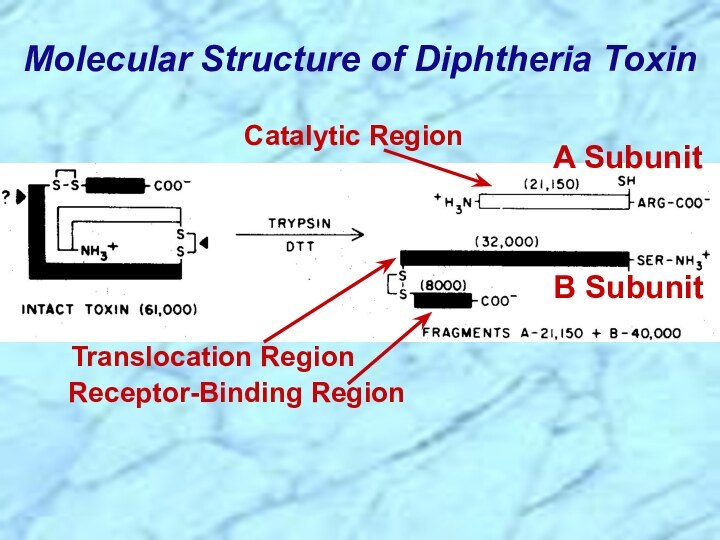
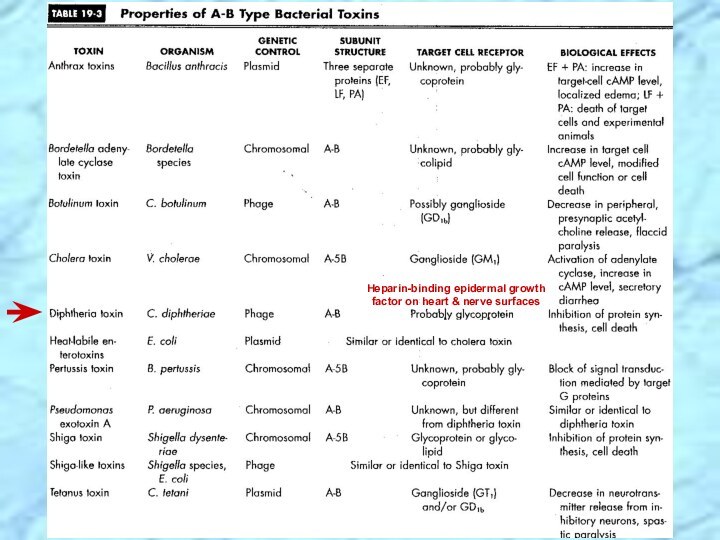
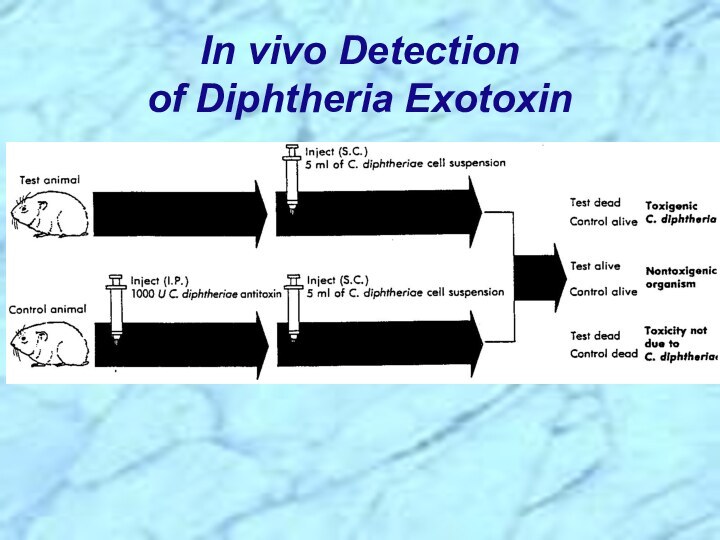
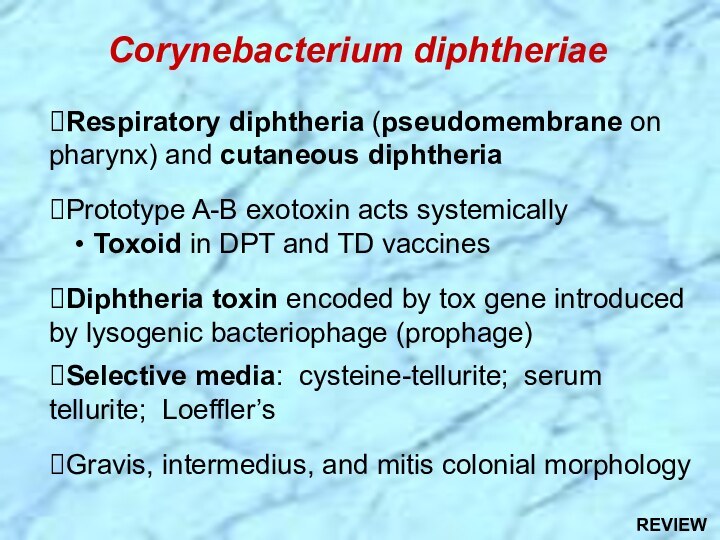
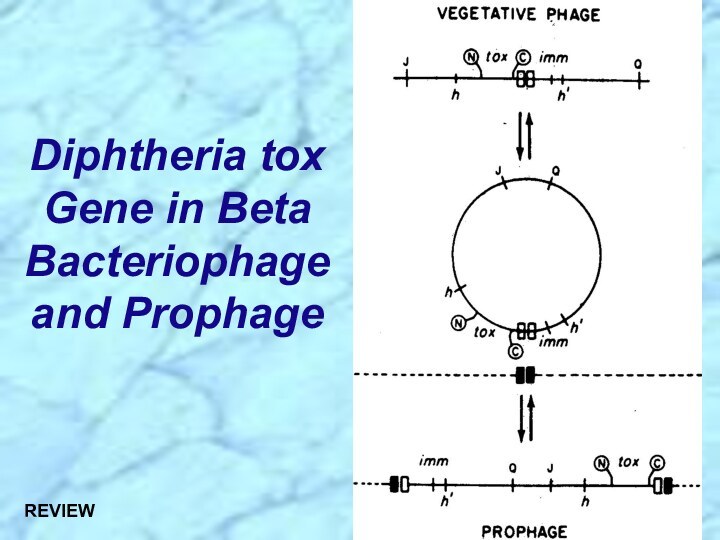
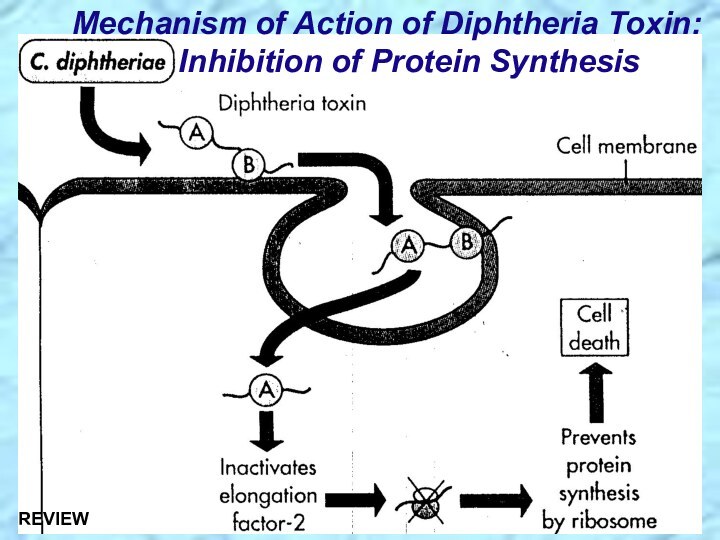
⮚Lysogenic bacteriophage encodes for potent exotoxin in virulent strains