How much do I pay?
Financing
How do I pay?
Integration
Implementation of acquisitionTactics
How do I make the offer?
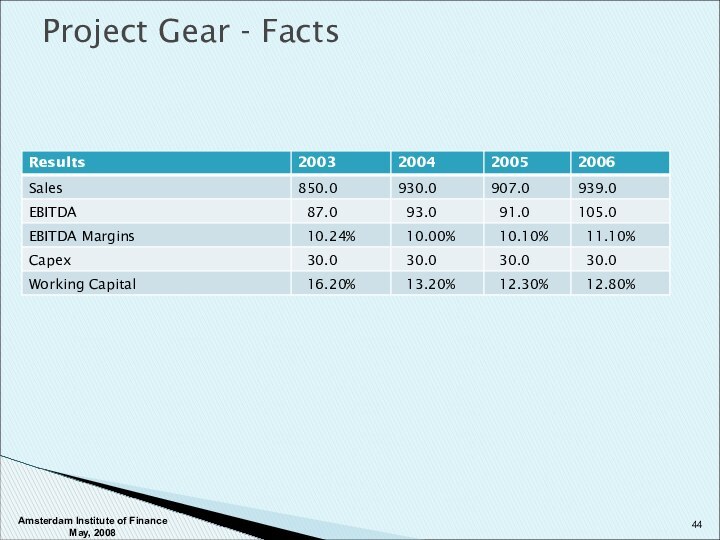
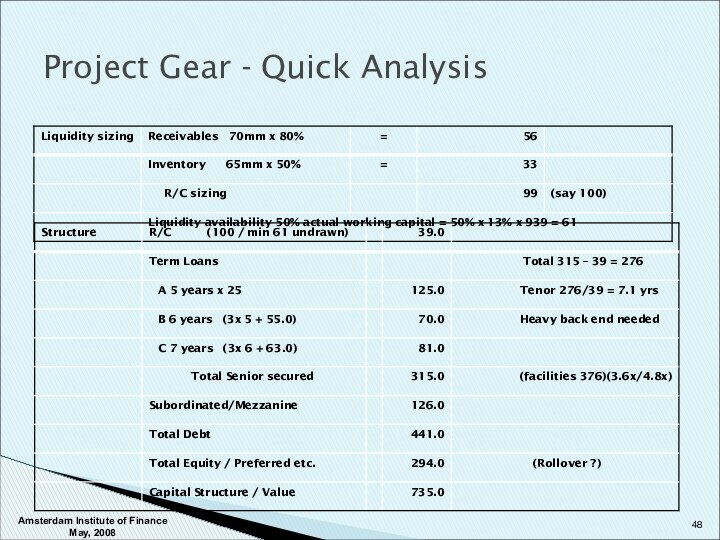
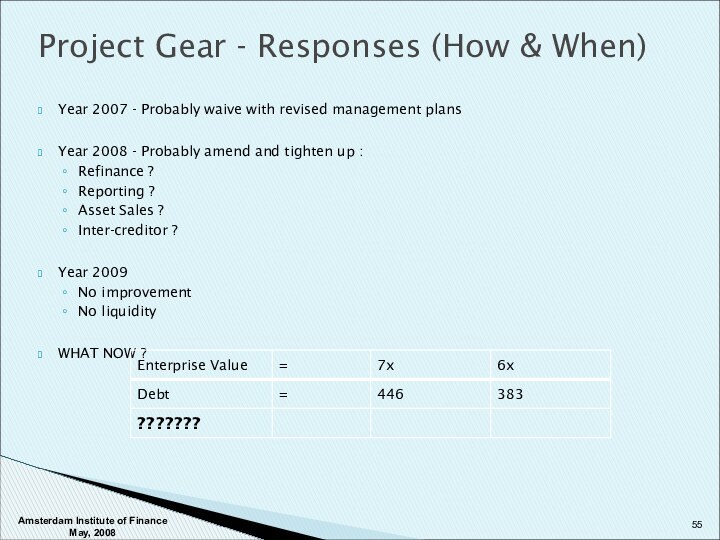
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть



























Tactics
How do I make the offer?
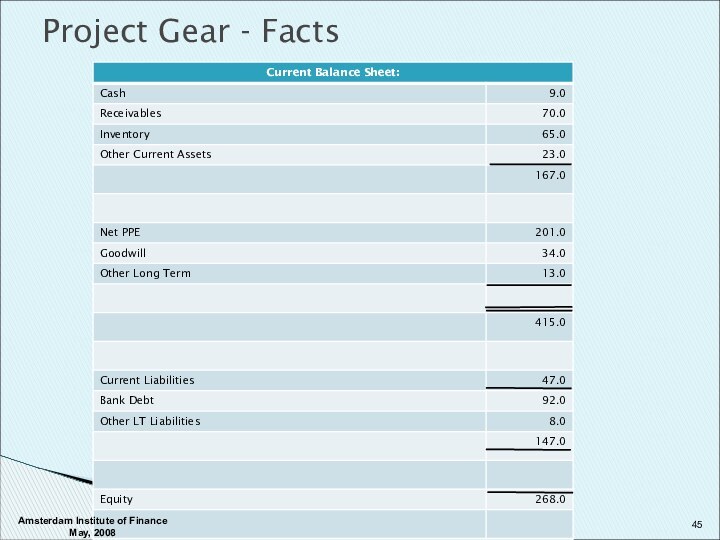
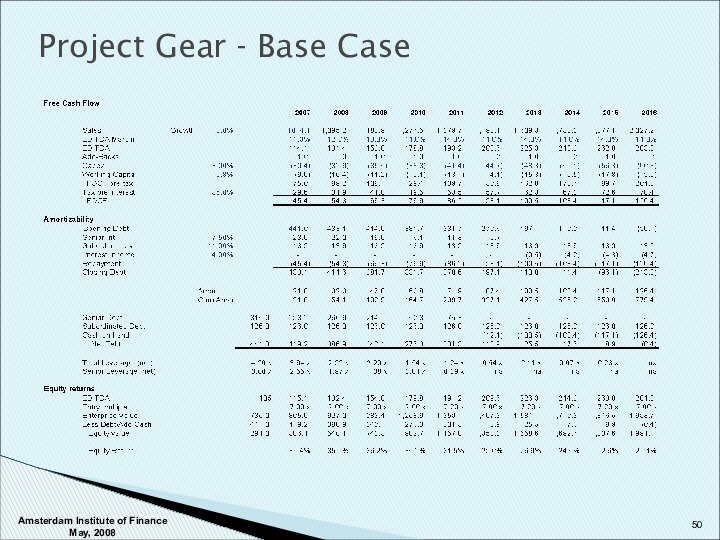
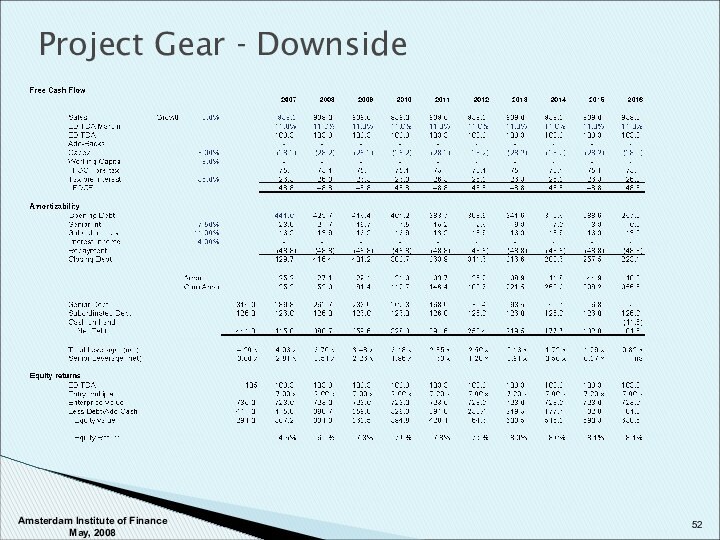
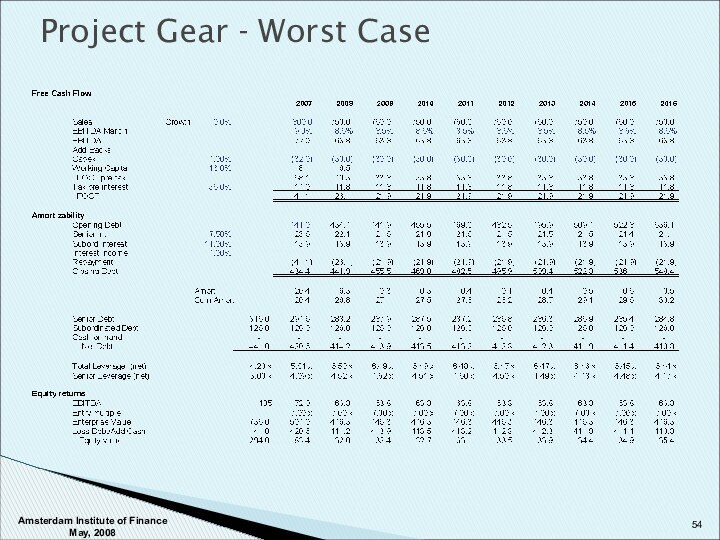
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
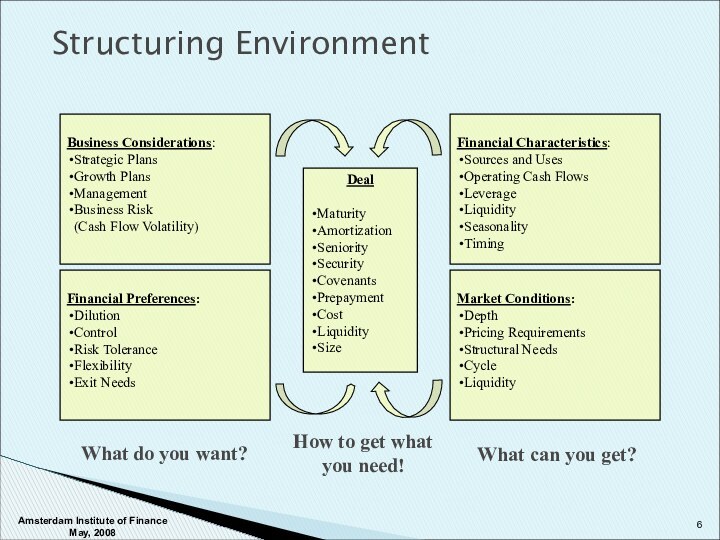
Deal
Maturity
Amortization
Seniority
Security
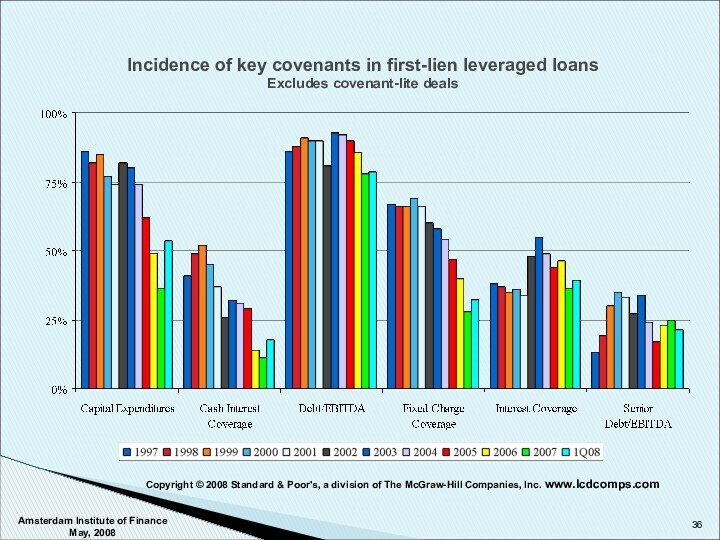
Covenants
Prepayment
Cost
Liquidity
Size
What do you want?
How to get what
you need!
What can you get?
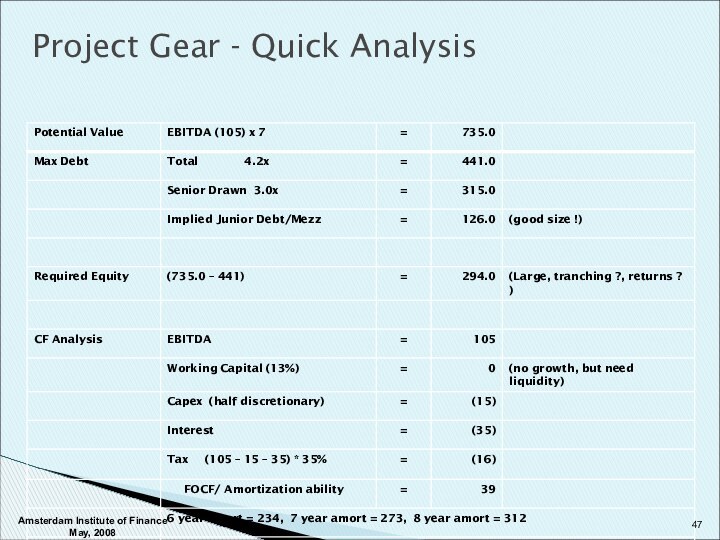
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
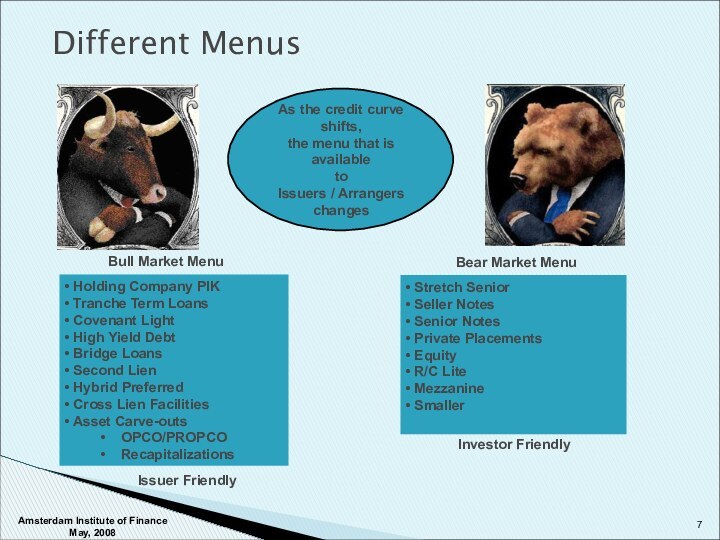
Holding Company PIK
Tranche Term Loans
Covenant Light
High Yield Debt
Bridge Loans
Second Lien
Hybrid Preferred
Cross Lien Facilities
Asset Carve-outs
OPCO/PROPCO
Recapitalizations
Stretch Senior
Seller Notes
Senior Notes
Private Placements
Equity
R/C Lite
Mezzanine
Smaller
Issuer Friendly
Investor Friendly
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Based on the cash flow of the entire company.
Some examples include:
Bank Debt
Public Bonds
Mezzanine
Preferred Stock
Common Stock
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
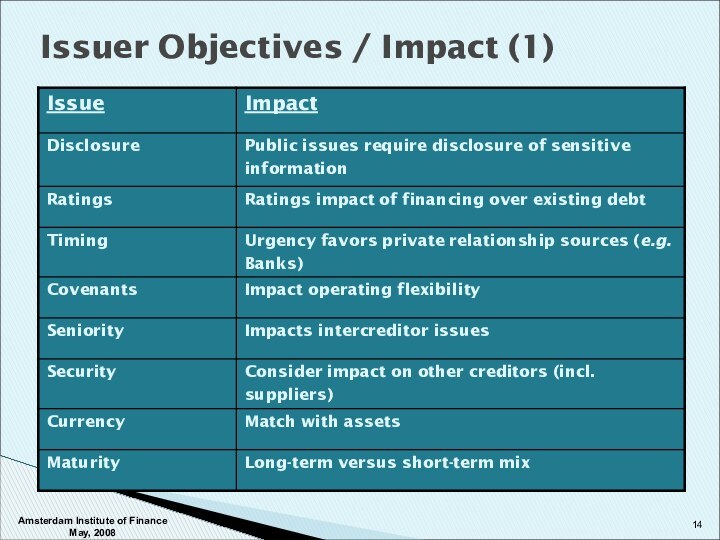
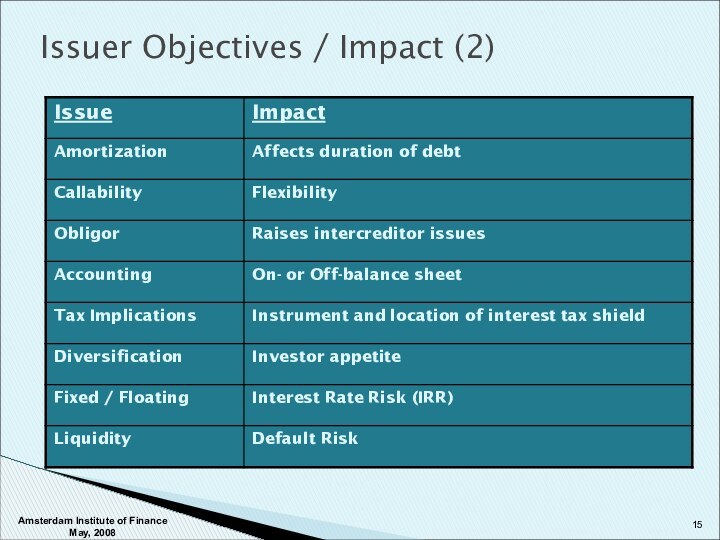
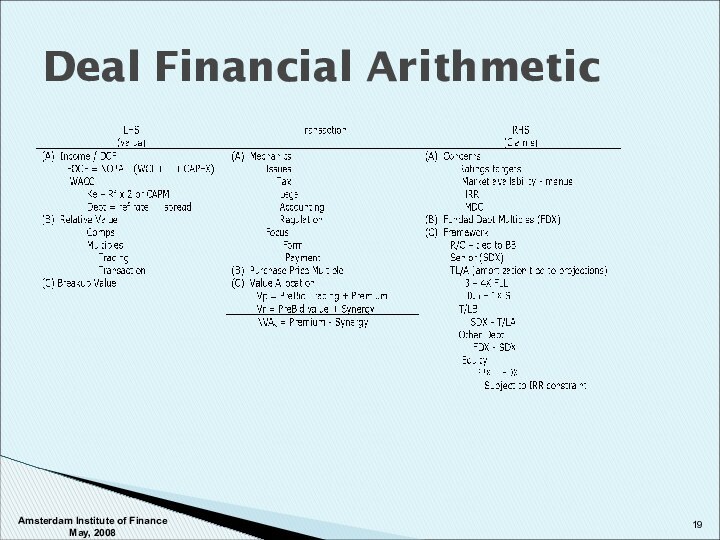
Structuring Issues
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
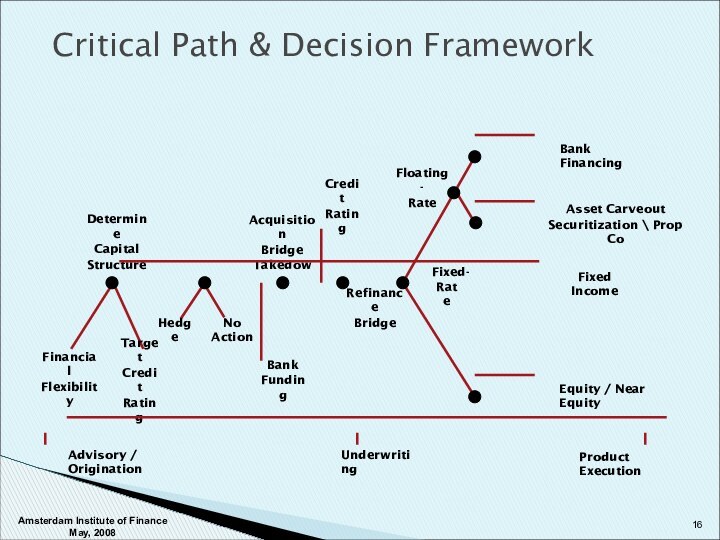
Underwriting
Product Execution
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Structuring Framework
Senior Secured
First Lien
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
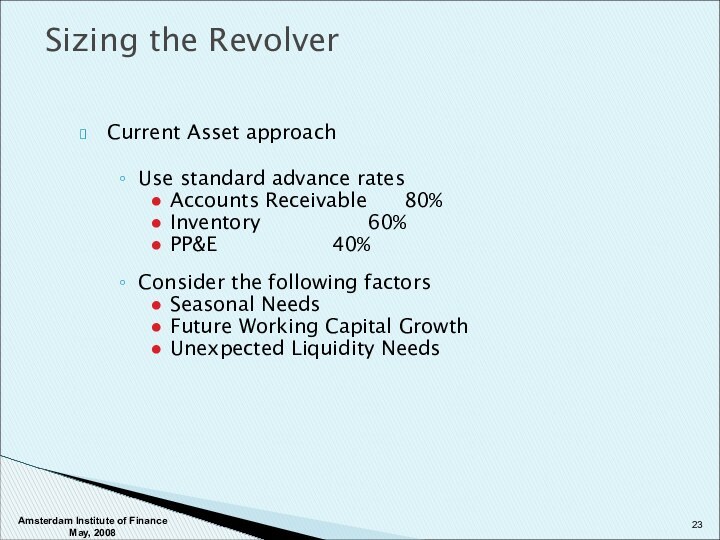
Sizing the Revolver
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Sizing the Term Loans
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Large unfunded revolvers are seldom used today due to the fact that it is capital unfriendly to banks and companies don’t like to pay for unused commitments.
In the interest of keeping flexibility for the long term, additional indebtedness baskets should be negotiated upfront. This allows companies to access either the bank or bond markets under their existing credit agreements and saves the costs of having to refinance.
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
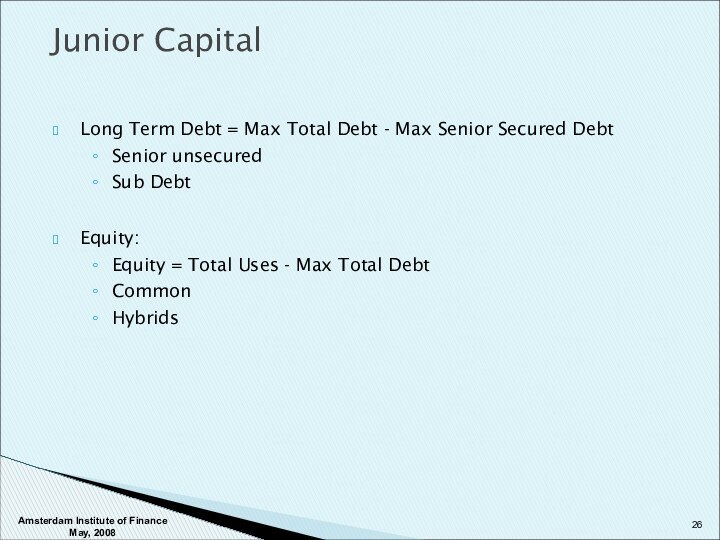
Junior Capital
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
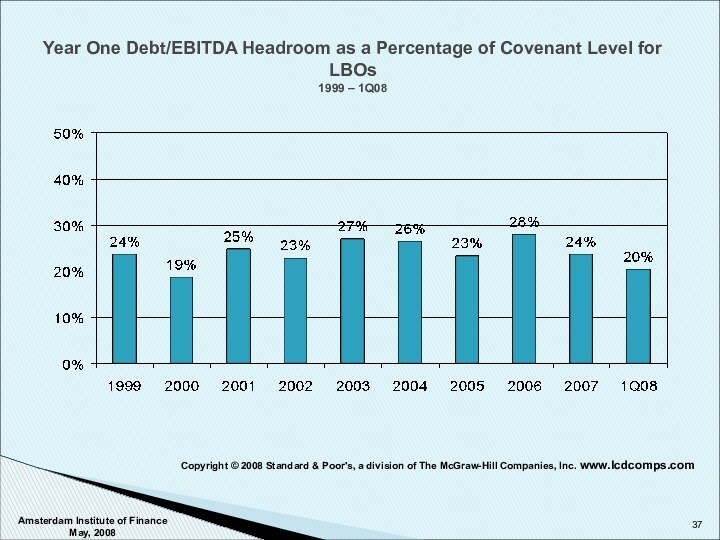
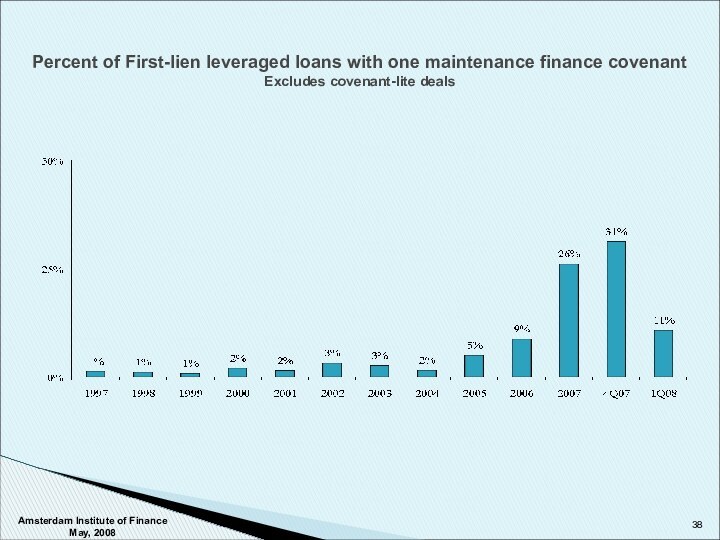
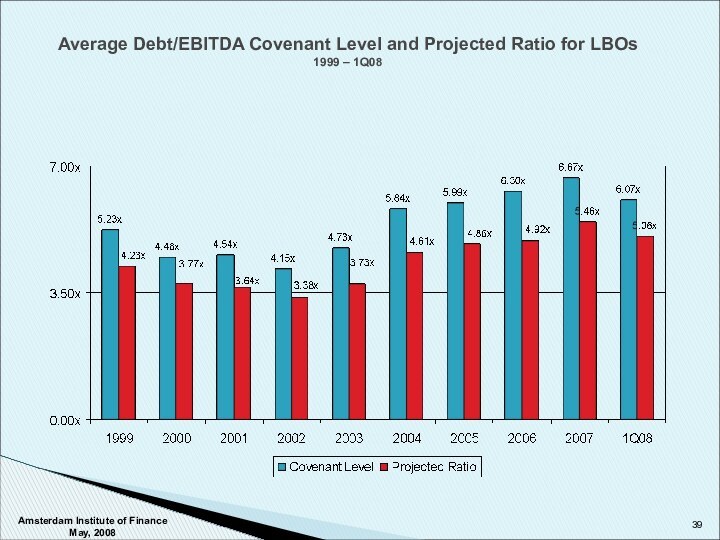
Covenants – Categories and Approach
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Structuring Covenants
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
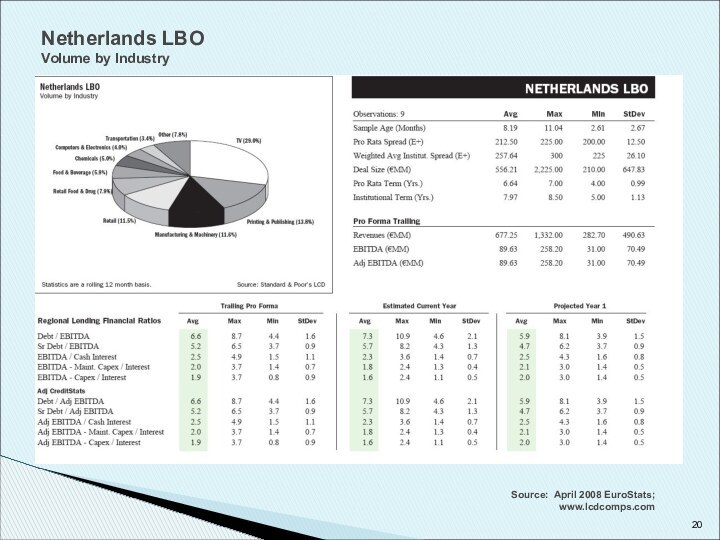
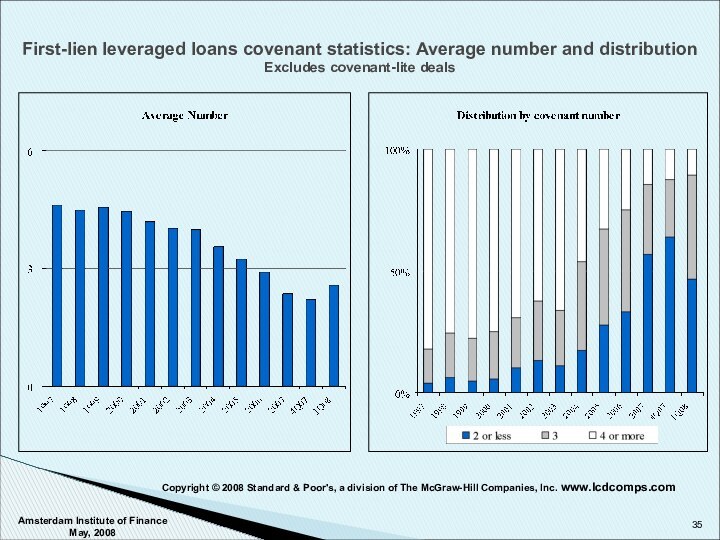
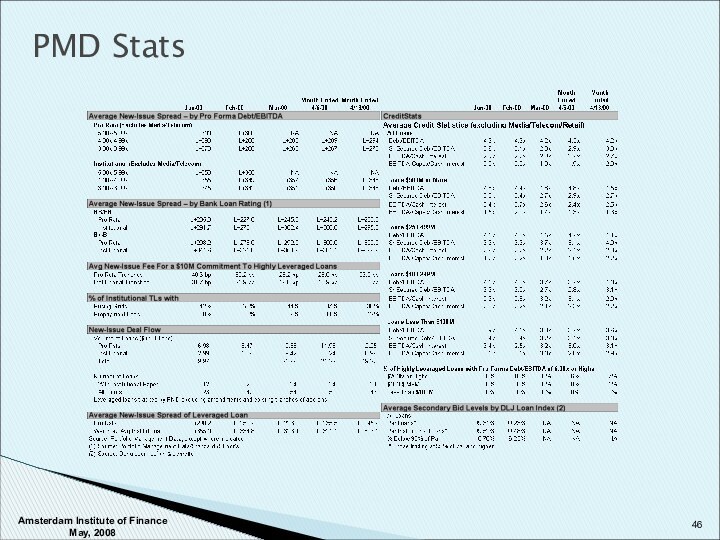
Copyright © 2008 Standard & Poor's, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. www.lcdcomps.com
Copyright © 2008 Standard & Poor's, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. www.lcdcomps.com
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008