Слайд 2
1.NATIONAL ECONOMY AS A SYSTEM
Слайд 3
Science section of the economy as a whole,
the problems of economic growth and employment, opportunities and
work of the economic mechanism of the functions of the state and economic policy called macroeconomics.
The objective is to analyze the interaction of macro economic operators and individual markets.
Under the national economy is considered to be the country's economy. This is a collection of all sectors and regions, connected in a single organism multilateral economic ties.
Слайд 5
2. SYSTEM OF NATIONAL ACCOUNTS
Слайд 6
A summary of the economic development of the
state is reflected in the national accounts
National Accounts -
a collection of various macroeconomic indicators.
Слайд 8
There are many kinds of indicators of economic
well-being of society. The primary measure in the preparation
of the SNA is the gross national product, or - briefly - GNP.
Gross national product (GNP) - is the total market value of the total final output of goods and services in the economy for the year.
Gross domestic product (GDP) - is monetary value of all final goods produced and services in the economy for the year in that country.
Net National Product (NNP) is the gross national product, net of depreciation.
GDP = NNP – D (net of depreciation)
Слайд 9
National Income (NI) - is a newly established
annual cost, which has added production in a given
year to the welfare of society. With his calculation does not include the amount of depreciation, indirect taxes and government subsidies. LP - a "Wages income" society (wages, income, profits).
NI = NNP – Te (indirect taxes)
Personal income (PI) is the total income received by the owners of economic resources.
PI = NI - contributions to system of social insurance - corporation profit taxes - retained earnings of corporation + transfer payments
Disposable income (DI) - the income, which is in the personal possession. It is smaller than the personal income tax on the value of the individual, who must pay the owners of economic resources in the form of the (primarily income) taxes.
Yd = PI – individual taxes
Слайд 12
THE CALCULATION OF GNP EXPENDITURE
GNP = C
+ I + G + Xn ,
where:
C -
personal consumption expenditures of households on durable consumer goods, goods for current consumption, and consumer spending on services.
I – gross private domestic investment, or "investment spending." They include three components: 1) the purchase of entrepreneurs machinery, equipment and tools, 2) all construction (commercial and residential construction), 3) investments in stocks.
G - government procurement, which include public consumption and public investment.
X – net exports. It represents the difference between income from exports and expenditure on imports of the country and meets the trade balance.
Слайд 13
CALCULATING GNP BY REVENUE
IN THIS CASE, GDP IS
CONSIDERED AS THE SUM OF REVENUE OF OWNERS OF
RESOURCES, I.E. AS THE SUM OF FACTOR INCOME
GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT = (C+S) + I + R + Π + D
Слайд 14
THE CALCULATION OF GNP "VALUE ADDED"
With this method,
the calculation of GNP must sum of value added
by all sectors and industries in the economy. An objective analysis of the economy is possible only with a stable (or comparable) price level. Analysis of the price level is necessary in order to:
- To know whether there have inflation or deflation,
- Reduced to a single base heterogeneous components of total production.
Слайд 15
THE CIRCULAR FLOW – SIMPLE VERSION
Factors of production
Factors
of production
Goods
Goods
GDP
GDP
GDP
GDP
Слайд 16
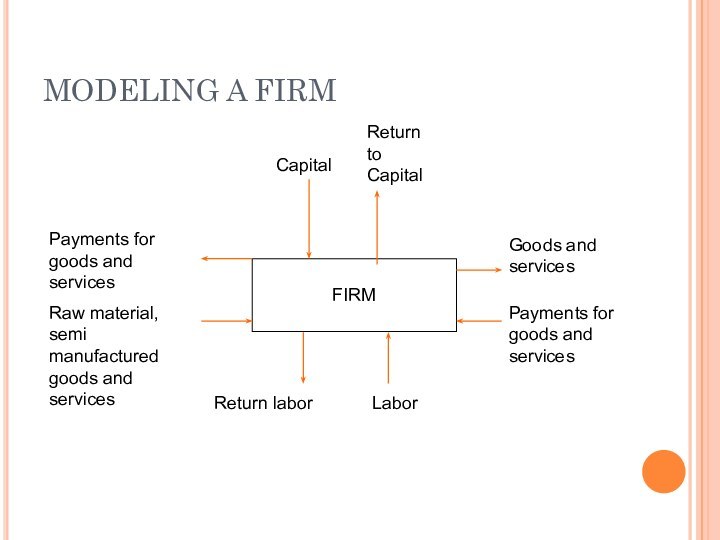
MODELING A FIRM
Before we look at the more
detailed version of the circular flow, we will illustrade
the model of the firm.
A firm in our model is a unit which adds value to products. These products may be raw material, semi-manufactured goods, final goods and services. By adding value, we mean that the firm acquires the good, adds value to it and then sells it. A supermarket adds value to a final good by making it more available to consumers and a bakery adds value to flour when it bakes bread.
From the diagram we see that the value added in a firm must be equal to the compensation to the factors of production. This must be the case since the net flow of money for a firm must be zero (remember that profits become return to capital – a compensation to the owners of the firm).
Слайд 17
MODELING A FIRM
FIRM
Capital
Return to Capital
Payments for goods and
services
Raw material, semi manufactured goods and services
Return labor
Labor
Goods
and services
Payments for goods and services
Слайд 18
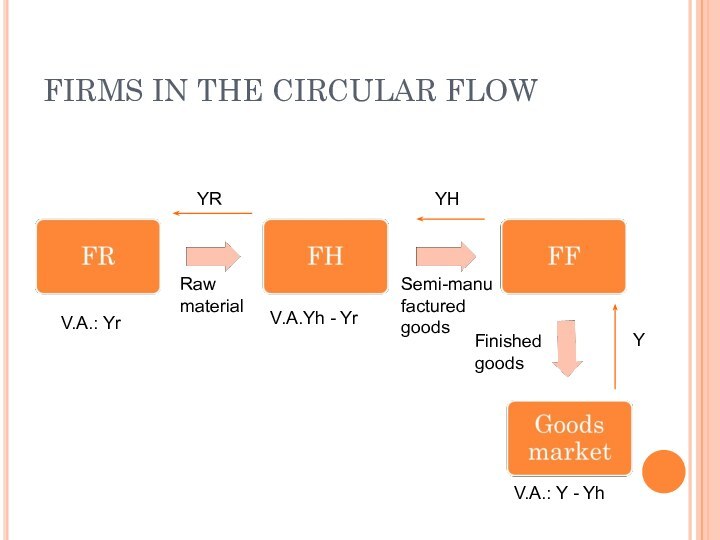
FIRMS IN THE CIRCULAR FLOW
We aivide all firms

into three categories: FR consists of all firms that
acquire raw material (iron ore, farm products and so on), FH all those that produce semi-manufactured goods (steel, pulp and so on) and FF all firms producing finished goods (software, cars and so on). We use the symbol Y for GDP. All of Y will go to the firms in the FF box. However, if we sum the value added from all firms, we will get exactly Y.
If YR is the total value of all goods going from FR to FH, then the total value added from all firms in the FR box is equal to YR (they do not purchase any goods to which they add value)
In the same way, if the total value of all goods going from FH to FF is given by YH, then the total value added from all firms in the FH box is YH – YR.
In the same way, the total value added for all firms in the FF box will be equal to Y – YH. If we sum all the value added from all firms, we get
YR +(YH – YR) + (Y – YH) = Y
The total return to the factor market = Sum of all value added = GDP
Слайд 19
FIRMS IN THE CIRCULAR FLOW
YR
YH
Y
Raw material
Semi-manufactured goods
V.A.: Yr
V.A.Yh
- Yr
Finished goods
V.A.: Y - Yh
Слайд 20
MONEY IN CIRCULAR FLOW
Firms
Finished goods and services
Exports
Imports
Government
spending
Private consumption
Investment
Factors of production
Factors of production
Factor of production
Слайд 21
CICULAR FLOW – CIRCULAR OF MONEY
FR
FH
FF
Goods market
Rest of
the world
Government
Household
Factor market
Financial markets
Yr
Yh
I
C
G
Y
NT
Sg
Y
Y
Sh
Sr
Im
X
I
Firms