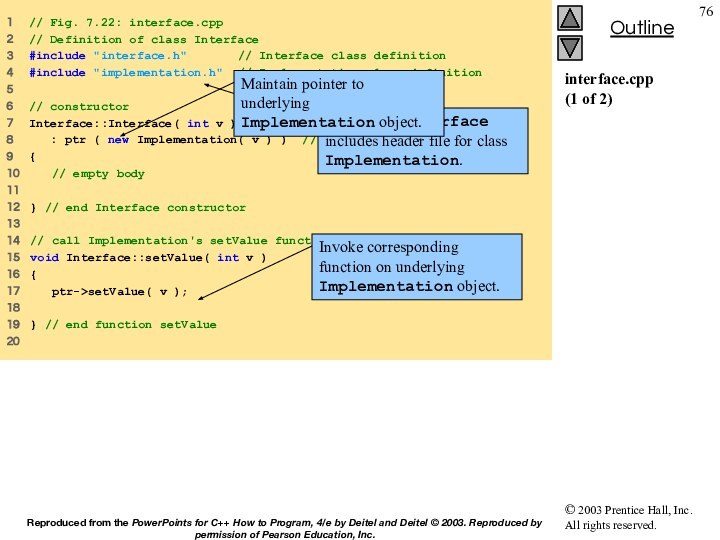
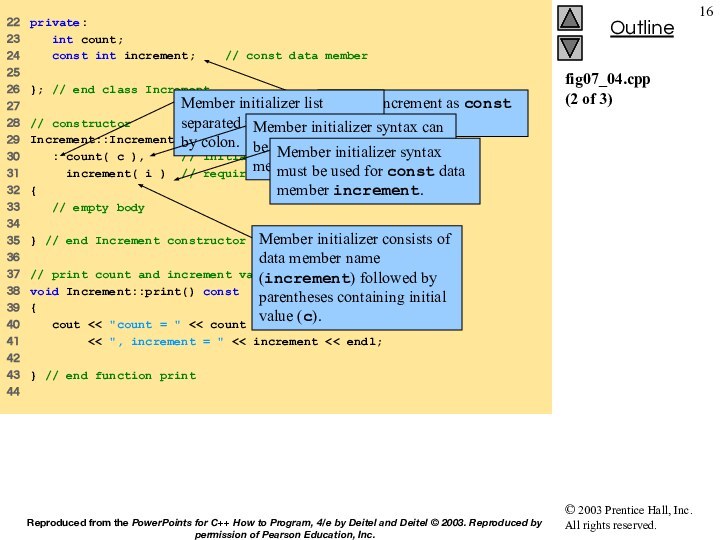
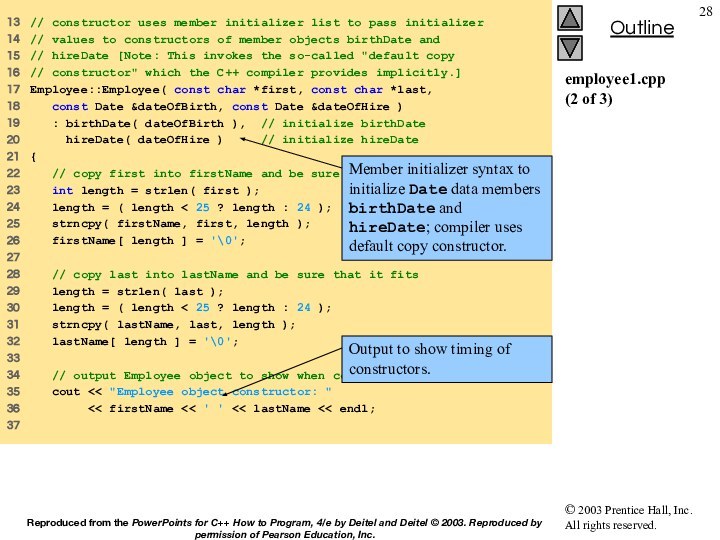
initializer list to pass initializer
14 // values to
constructors of member objects birthDate and
15 // hireDate [Note: This invokes the so-called "default copy
16 // constructor" which the C++ compiler provides implicitly.]
17 Employee::Employee( const char *first, const char *last,
18 const Date &dateOfBirth, const Date &dateOfHire )
19 : birthDate( dateOfBirth ), // initialize birthDate
20 hireDate( dateOfHire ) // initialize hireDate
21 {
22 // copy first into firstName and be sure that it fits
23 int length = strlen( first );
24 length = ( length < 25 ? length : 24 );
25 strncpy( firstName, first, length );
26 firstName[ length ] = '\0';
27
28 // copy last into lastName and be sure that it fits
29 length = strlen( last );
30 length = ( length < 25 ? length : 24 );
31 strncpy( lastName, last, length );
32 lastName[ length ] = '\0';
33
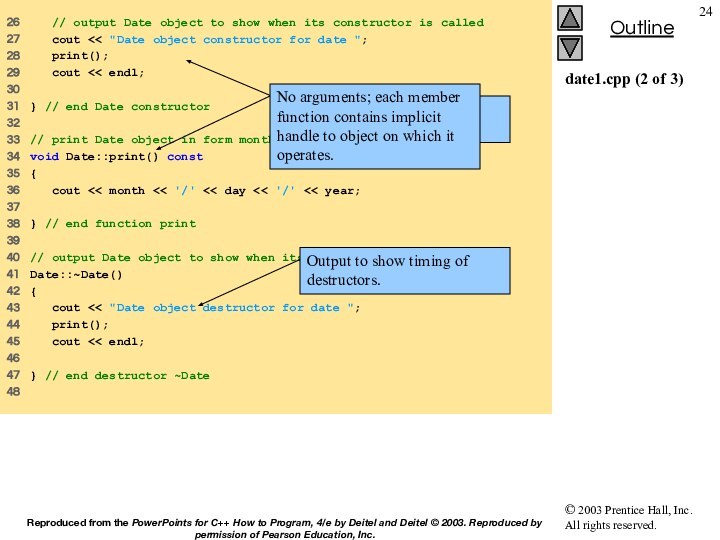
34 // output Employee object to show when constructor is called
35 cout << "Employee object constructor: "
36 << firstName << ' ' << lastName << endl;
37
Reproduced from the PowerPoints for C++ How to Program, 4/e by Deitel and Deitel © 2003. Reproduced by permission of Pearson Education, Inc.



























![Οντοκεντρικοσ προγραμματισμοσ ΙΙ (С++). Τάξεις και αφαίρεση δεδομένων employee2.cpp (3 of 3) 48 delete [] firstName;](/img/tmb/15/1423346/9d1b15dcb48c180d0ddd428a24dd9a13-720x.jpg)