Слайд 2
Preliminary Remark
Review Course Outline (posted on website)
Слайд 3
Course Syllabus
This course presents a variety of topics
on the design and use of modern digital computers,
including:
Digital representations, Digital (Boolean) Logic
Modular design concepts in digital circuits
Combinational circuits
Sequential circuits.
Instruction architecture, cycle, timing logic
Memory, CPU and Bus Organization.
Assemblers, assembly language
The detailed schedule and topics covered may be adjusted at the discretion of the instructor
Students will be advised in advance of lecture topics and assigned reading.
Слайд 4
Digital Design and Computer Architecture
Von Neumann Architecture
The 5
component design model
The Instruction Cycle
Basic
Exceptions
Instruction architecture
software design
hardware circuits
Слайд 5
Digital Design & Computer Architecture
Computer Science – Grade
11
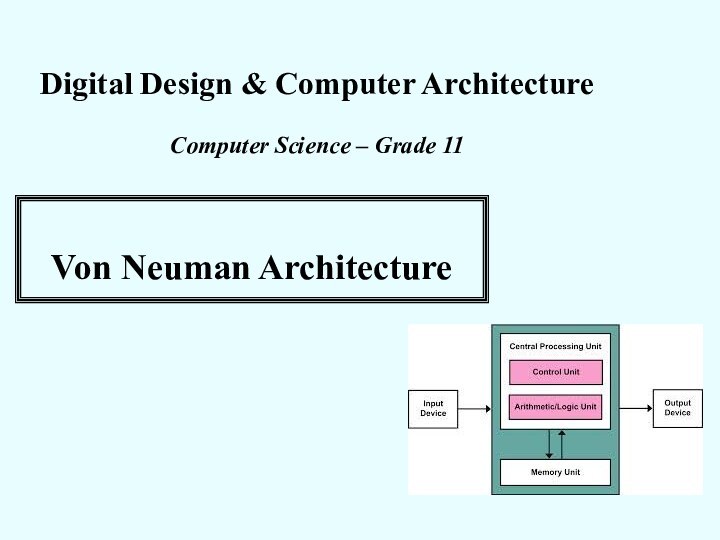
Von Neuman Architecture
Слайд 6
Objectives
Von Neumann Architecture
5 component design of the stored
program digital computer
the instruction cycle
Basic
Exceptions
instruction architecture
software design
hardware circuits
Digital Design
Boolean
logic and gates
Basic Combinational Circuits
Karnaugh maps
Advanced Combinational Circuits
Sequential Circuits
Слайд 7
von Neumann Architecture
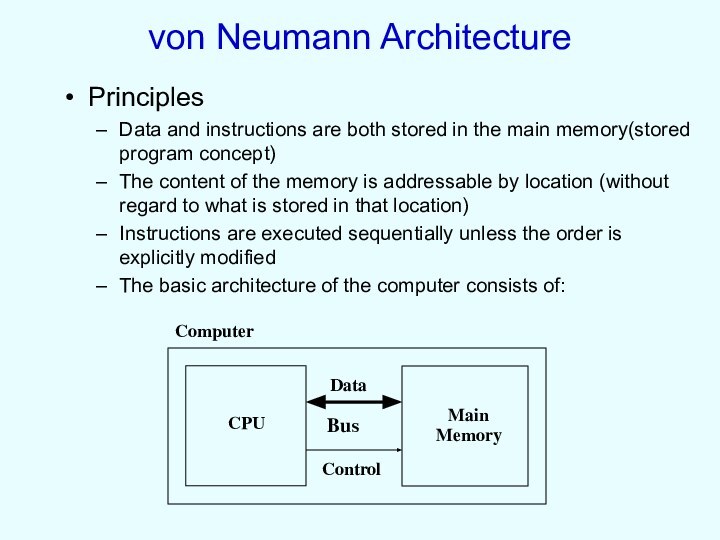
Principles
Data and instructions are both stored
in the main memory(stored program concept)
The content of the
memory is addressable by location (without regard to what is stored in that location)
Instructions are executed sequentially unless the order is explicitly modified
The basic architecture of the computer consists of:
Слайд 8
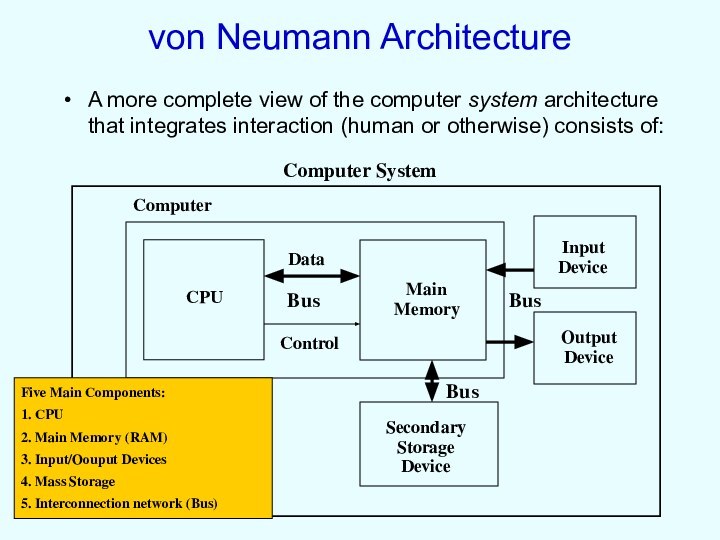
von Neumann Architecture
A more complete view of the
computer system architecture that integrates interaction (human or otherwise)
consists of:
Five Main Components:
1. CPU
2. Main Memory (RAM)
3. Input/Oouput Devices
4. Mass Storage
5. Interconnection network (Bus)
Слайд 9
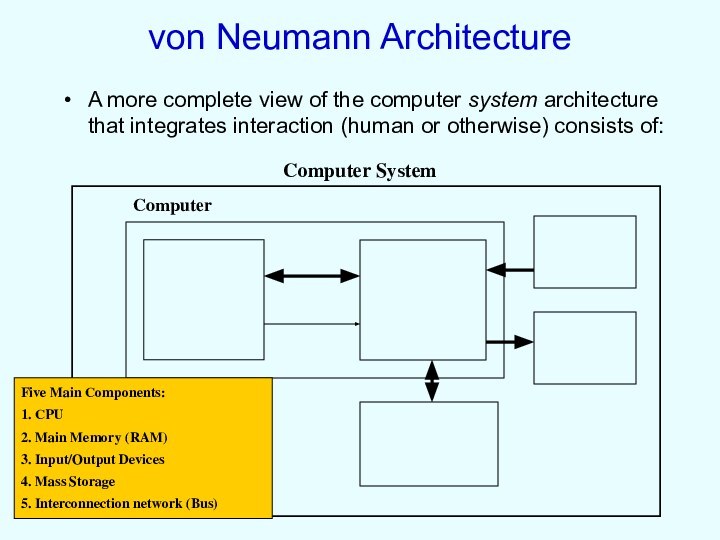
von Neumann Architecture
A more complete view of the
computer system architecture that integrates interaction (human or otherwise)
consists of:
Five Main Components:
1. CPU
2. Main Memory (RAM)
3. Input/Output Devices
4. Mass Storage
5. Interconnection network (Bus)
Слайд 10
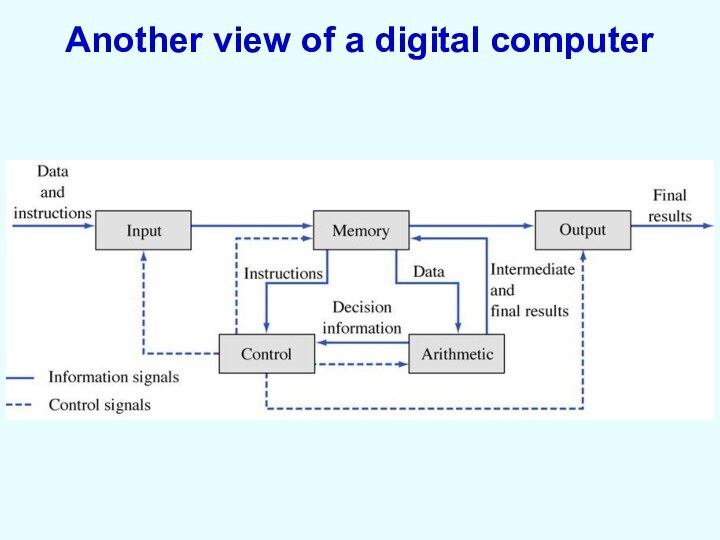
Another view of a digital computer
Слайд 11
The Instruction Cycle
The Instruction Cycle
Basic
Intermediate
Exceptions
Слайд 12
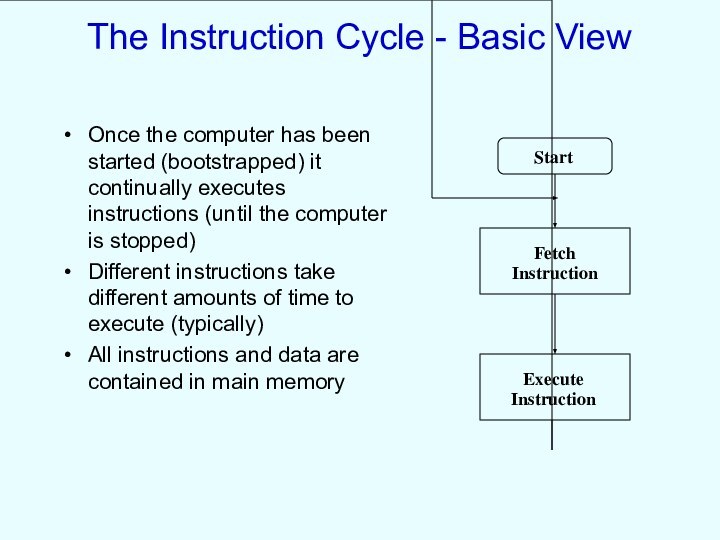
The Instruction Cycle - Basic View
Once the computer
has been started (bootstrapped) it continually executes instructions (until
the computer is stopped)
Different instructions take different amounts of time to execute (typically)
All instructions and data are contained in main memory
Слайд 13
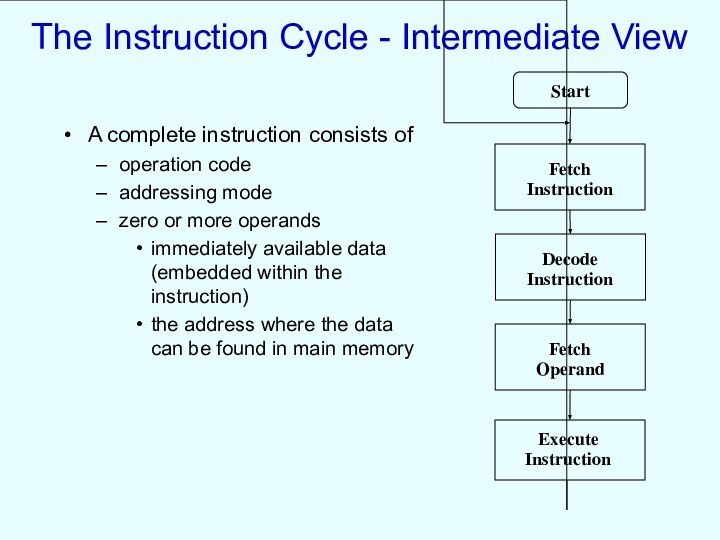
The Instruction Cycle - Intermediate View
A complete instruction
consists of
operation code
addressing mode
zero or more operands
immediately available
data (embedded within the instruction)
the address where the data can be found in main memory
Слайд 14
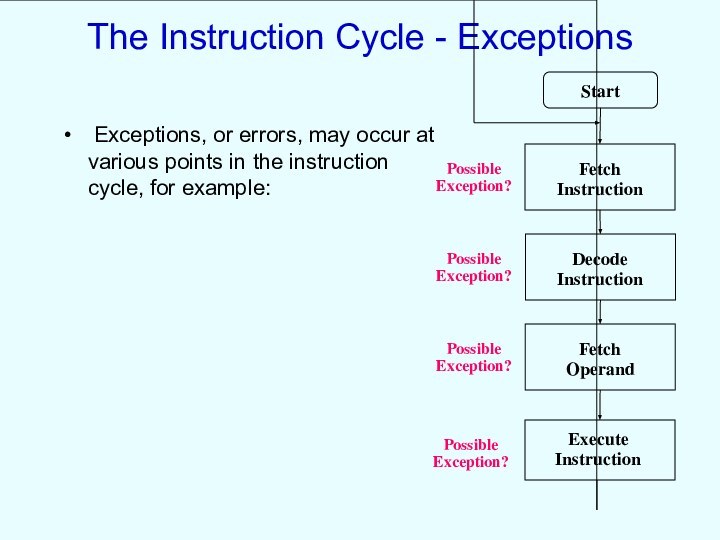
The Instruction Cycle - Exceptions
Exceptions, or errors,
may occur at various points in the instruction cycle,
for example:
Possible Exception?
Possible Exception?
Possible Exception?
Possible Exception?
Слайд 15
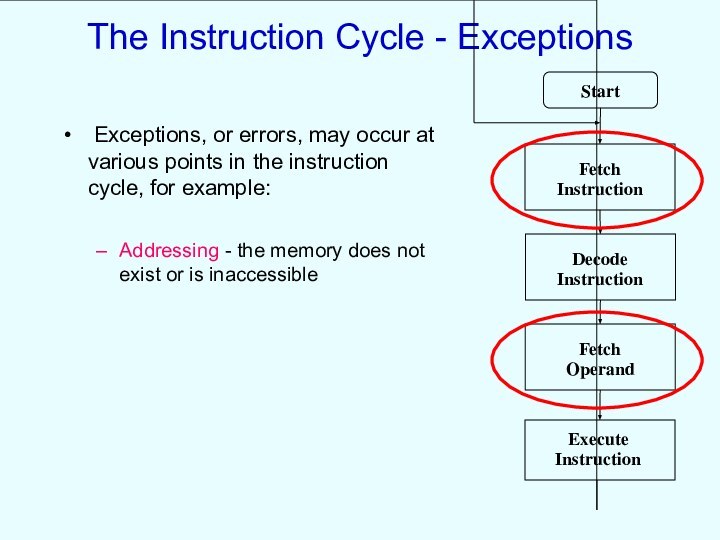
The Instruction Cycle - Exceptions
Exceptions, or errors,
may occur at various points in the instruction cycle,
for example:
Addressing - the memory does not exist or is inaccessible
Слайд 16
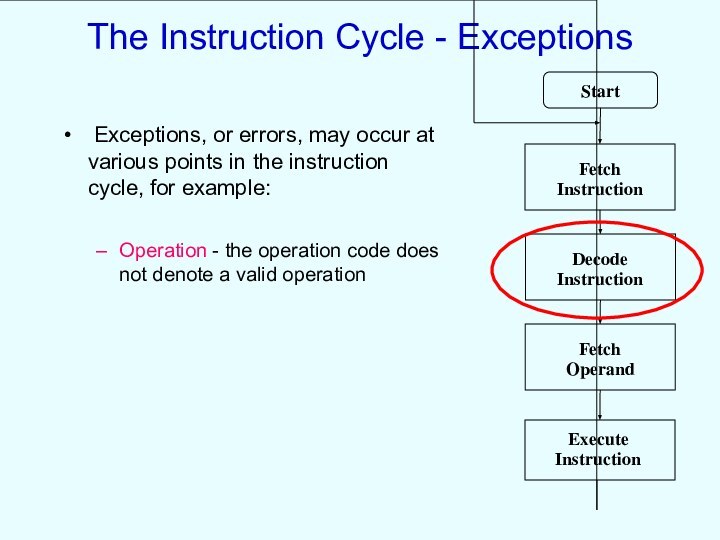
The Instruction Cycle - Exceptions
Exceptions, or errors,
may occur at various points in the instruction cycle,
for example:
Operation - the operation code does not denote a valid operation
Слайд 17
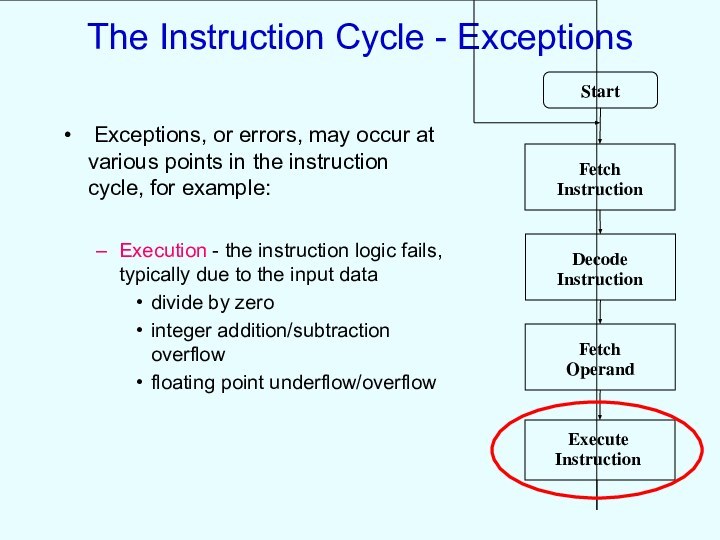
The Instruction Cycle - Exceptions
Exceptions, or errors,
may occur at various points in the instruction cycle,
for example:
Execution - the instruction logic fails, typically due to the input data
divide by zero
integer addition/subtraction overflow
floating point underflow/overflow
Слайд 18
Instruction Architecture
Software design
Hardware circuits
Слайд 19
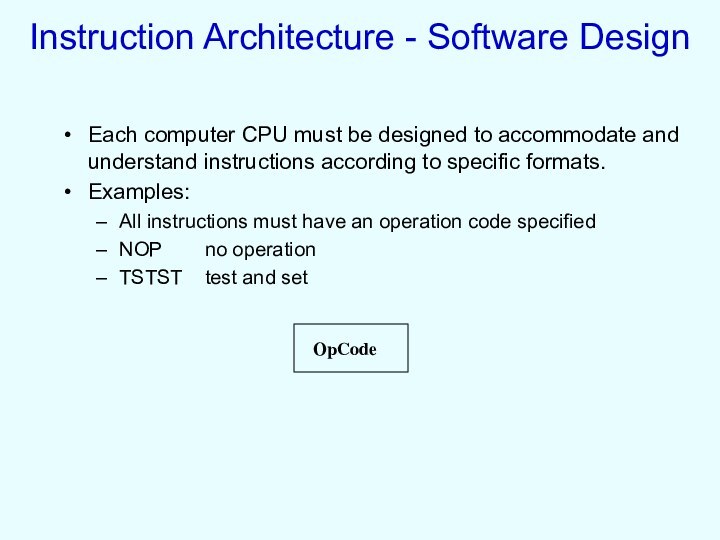
Instruction Architecture - Software Design
Each computer CPU must
be designed to accommodate and understand instructions according to
specific formats.
Examples:
All instructions must have an operation code specified
NOP no operation
TSTST test and set
Слайд 20
Instruction Architecture - Software Design
Each computer CPU must
be designed to accommodate and understand instructions according to
specific formats.
Examples:
Most instructions will require one, or more, operands
These may be (immediate) data to be used directly
or, addresses of memory locations where data will be found (including the address of yet another location)
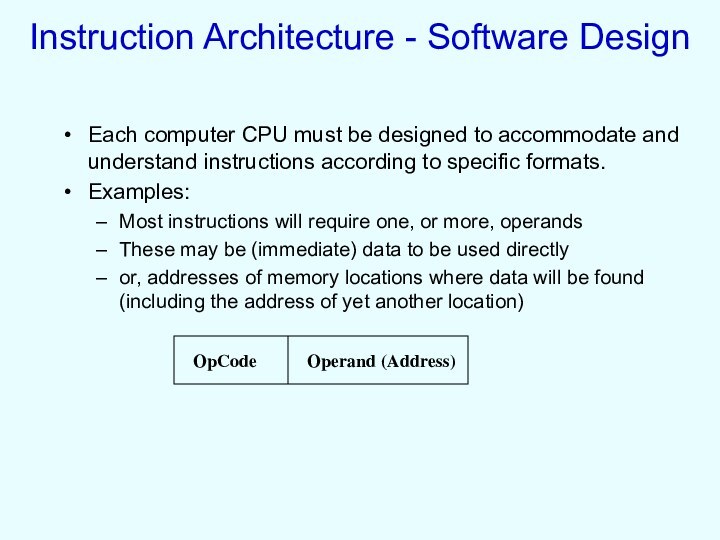
Слайд 21
Instruction Architecture - Software Design
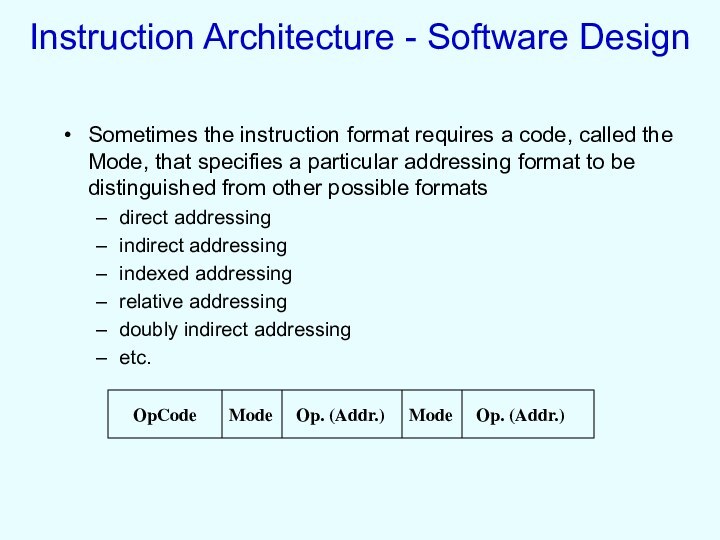
Sometimes the instruction format
requires a code, called the Mode, that specifies a
particular addressing format to be distinguished from other possible formats
direct addressing
indirect addressing
indexed addressing
relative addressing
doubly indirect addressing
etc.
Слайд 22
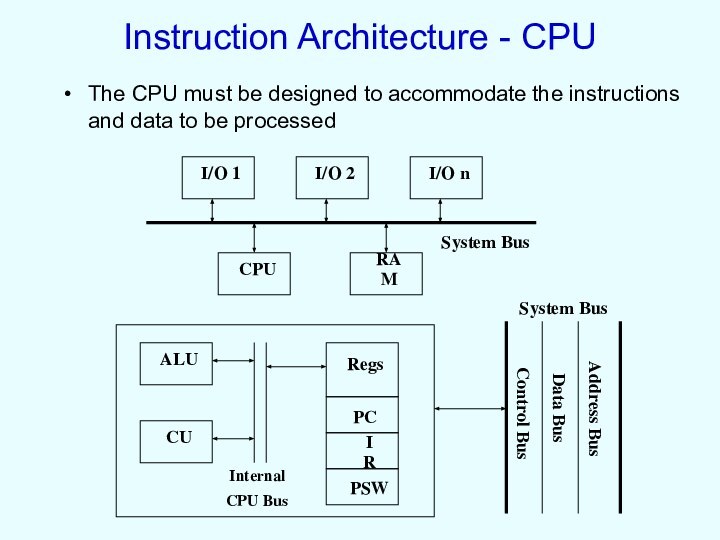
Instruction Architecture - CPU
The CPU must be designed
to accommodate the instructions and data to be processed
Слайд 23
Instruction Architecture - Hardware Circuits
Everything that the computer
can do is the result of designing and building
devices to carry out each function – no magic!
At the most elementary level the devices are called logic gates.
There are many possible gate types, each perform a specific Boolean operation (e.g. AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR)
ALL circuits, hence all functions, are defined in terms of the basic gates.
We apply Boolean Algebra and Boolean Calculus in order to design circuits and then optimize our designs.
Слайд 24
Instruction Architecture - Hardware Circuits
Data is represented by
various types of “signals”, including electrical, magnetic, optical and
so on. Data “moves” through the computer along wires that form the various bus networks (address, data, control) and which interconnect the gates.
Combinations of gates are called integrated circuits (IC).
All computer functions are defined and controlled by IC’s of varying complexity in design. The manufacture of these may be scaled according to size/complexity:
LSI large scale integration
VLSI very large scale integration
ULSI ultra large scale integration
Слайд 25
Instruction Architecture - CU
The control unit must decode
instructions, set up for communication with RAM addresses and
manage the data stored in register and accumulator storages.
Each such operation requires separate circuitry to perform the specialized tasks.
It is also necessary for computer experts to have knowledge of the various data representations to be used on the machine in order to design components that have the desired behaviours.
Слайд 26
Instruction Architecture - ALU
All instructions together are called
the instruction set
CISC complex instruction set
RISC reduced instruction set
Each ALU instruction
requires a separate circuit, although some instructions may incorporate the circuit logic of other instructions
Слайд 27
Our Goal – Design Circuits!
After all the conceptualization
we must now get down to the most fundamental
business – learning how to design circuits that can implement the logic we intend to impose and use
Circuit design arises out of a study of Boolean Set Theory and Boolean Algebra
We need to study and learn some new mathematics
We will need to understand design optimization
How to make the design as lean and efficient as possible
We will work towards higher level abstraction of device components, but start at an elementary level of concrete behaviours with predefined units called gates.