Слайд 2
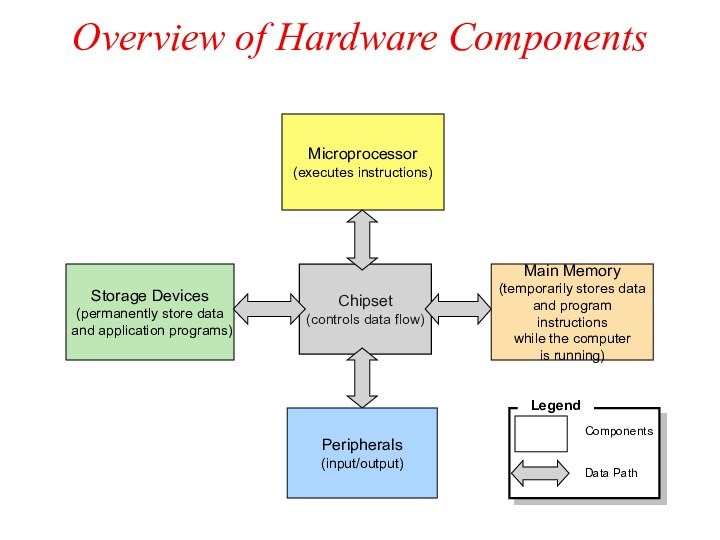
Overview of Hardware Components
Microprocessor
(executes instructions)
Chipset
(controls data flow)
Main
Memory
(temporarily stores data
and program instructions
while the
computer
is running)
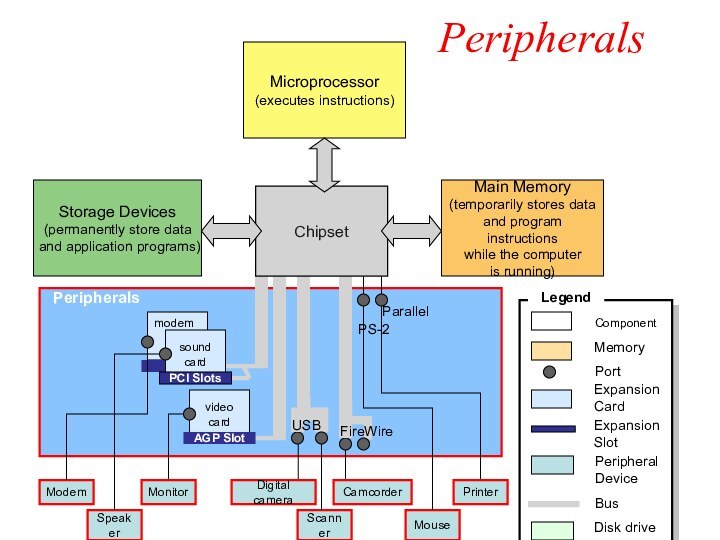
Peripherals
(input/output)
Data Path
Components
Legend
Storage Devices
(permanently store data
and application programs)
Слайд 3
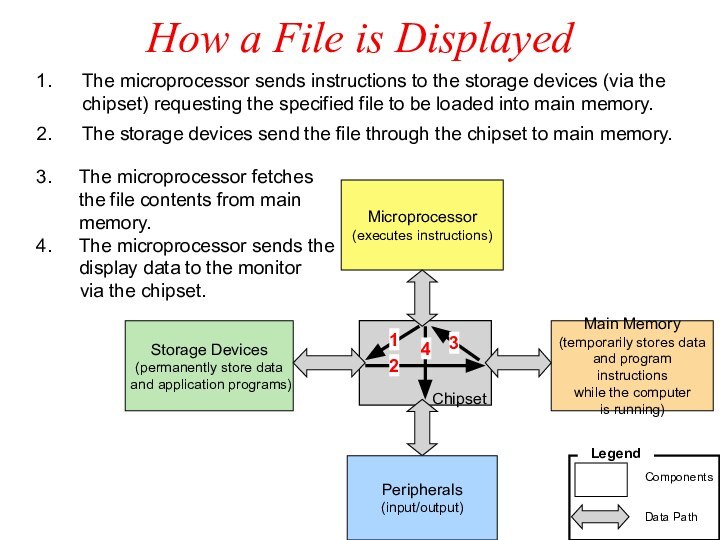
How a File is Displayed
The microprocessor sends instructions
to the storage devices (via the chipset) requesting the
specified file to be loaded into main memory.
The storage devices send the file through the chipset to main memory.
The microprocessor fetches
the file contents from main
memory.
The microprocessor sends the display data to the monitor
via the chipset.
Слайд 4
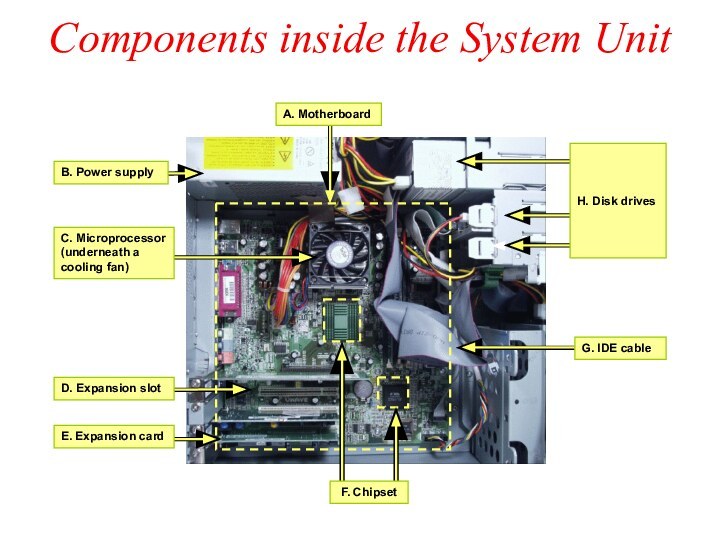
Components inside the System Unit
B. Power supply
E. Expansion
card
C. Microprocessor
(underneath a cooling fan)
D. Expansion
slot
G. IDE cable
F. Chipset
H. Disk drives
A. Motherboard
Слайд 5
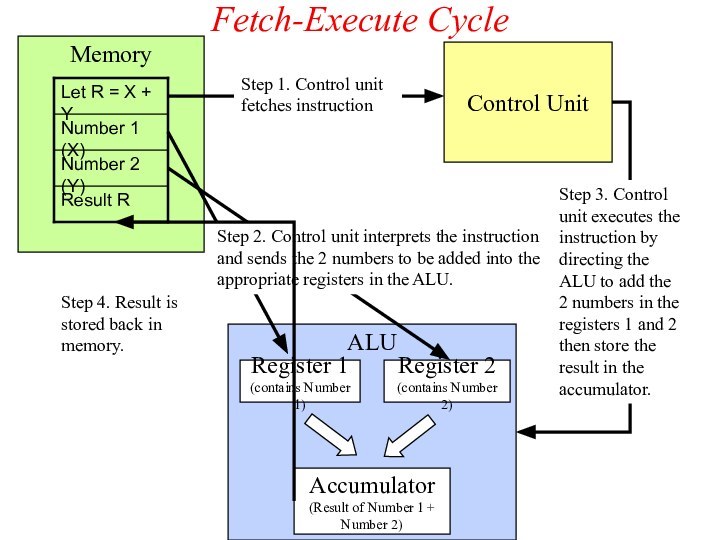
Fetch-Execute Cycle
ALU
Register 1
(contains Number 1)
Register 2
(contains Number 2)
Accumulator
(Result
of Number 1 + Number 2)
Step 1. Control unit
fetches instruction
Step 2. Control unit interprets the instruction and sends the 2 numbers to be added into the appropriate registers in the ALU.
Control Unit
Step 4. Result is stored back in memory.
Step 3. Control unit executes the instruction by directing the ALU to add the 2 numbers in the registers 1 and 2 then store the result in the accumulator.
Слайд 6
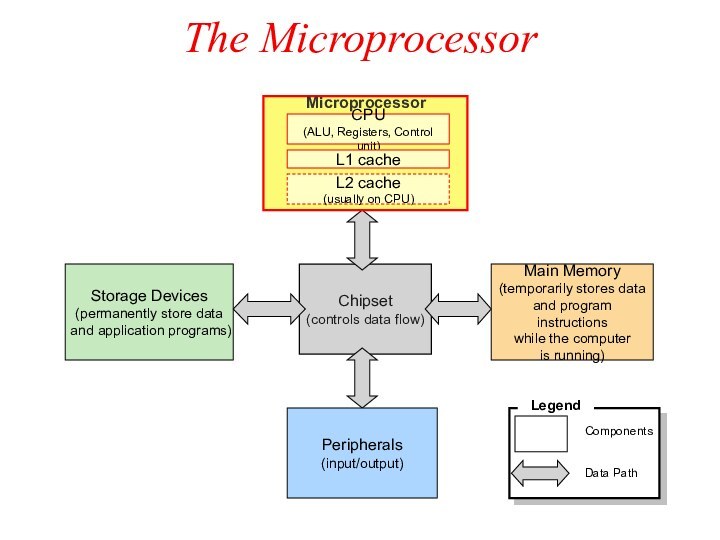
The Microprocessor
Chipset
(controls data flow)
Main Memory
(temporarily stores data
and program instructions
while the computer
is running)
Peripherals
(input/output)
Data Path
Components
Legend
Storage
Devices
(permanently store data
and application programs)
Microprocessor
Слайд 7
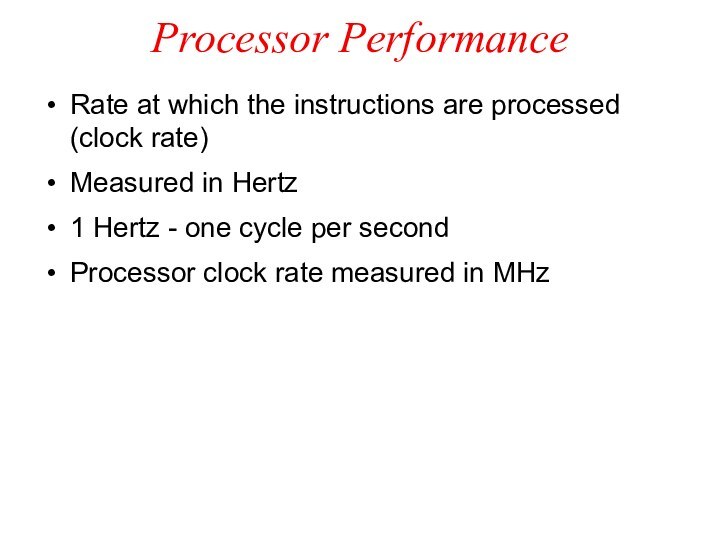
Processor Performance
Rate at which the instructions are processed
(clock rate)
Measured in Hertz
1 Hertz - one cycle per
second
Processor clock rate measured in MHz
Слайд 8
Processor Performance (continued)
Machines are compared based on their
clock speed or number of instructions per second (ISP).
This
measure depends on both the number of cycles per second and the mix of instructions executed.
Measure of processor performance is benchmarking.
Слайд 9
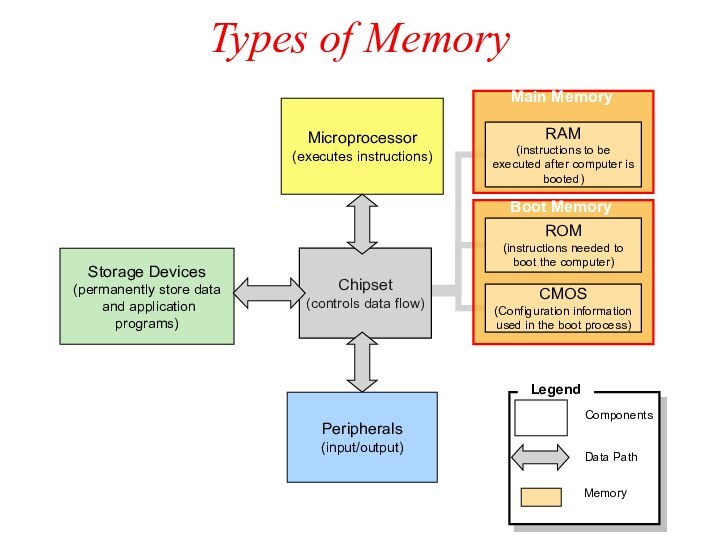
Types of Memory
Chipset
(controls data flow)
Microprocessor
(executes instructions)
Storage Devices
(permanently
store data
and application programs)
Peripherals
(input/output)
Data Path
Components
Legend
RAM
(instructions to be executed
after computer is booted)
ROM
(instructions needed to boot the computer)
CMOS
(Configuration information used in the boot process)
Main Memory
Boot Memory
Слайд 10
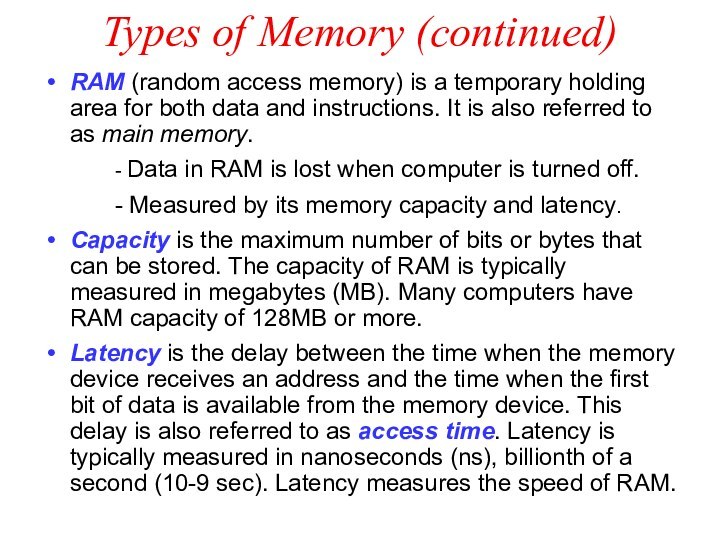
Types of Memory (continued)
RAM (random access memory) is
a temporary holding area for both data and instructions.
It is also referred to as main memory.
- Data in RAM is lost when computer is turned off.
- Measured by its memory capacity and latency.
Capacity is the maximum number of bits or bytes that can be stored. The capacity of RAM is typically measured in megabytes (MB). Many computers have RAM capacity of 128MB or more.
Latency is the delay between the time when the memory device receives an address and the time when the first bit of data is available from the memory device. This delay is also referred to as access time. Latency is typically measured in nanoseconds (ns), billionth of a second (10-9 sec). Latency measures the speed of RAM.
Слайд 11
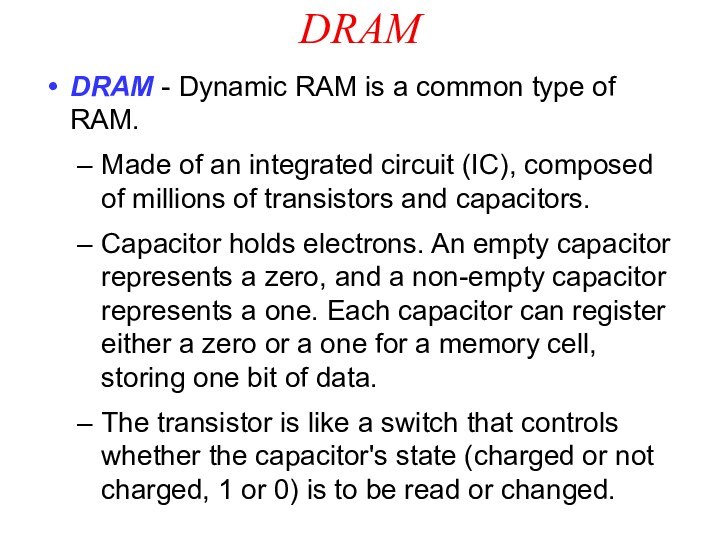
DRAM
DRAM - Dynamic RAM is a common type
of RAM.
Made of an integrated circuit (IC), composed
of millions of transistors and capacitors.
Capacitor holds electrons. An empty capacitor represents a zero, and a non-empty capacitor represents a one. Each capacitor can register either a zero or a one for a memory cell, storing one bit of data.
The transistor is like a switch that controls whether the capacitor's state (charged or not charged, 1 or 0) is to be read or changed.
Слайд 12
DRAM (continued)
However, a capacitor is like a cup
that leaks, in order to keep its charge, the
memory control needs to be recharged or refreshed periodically. Therefore, it is called the dynamic RAM because its state is not constant.
Refreshing capacitors also takes time and slows down memory.
Слайд 13
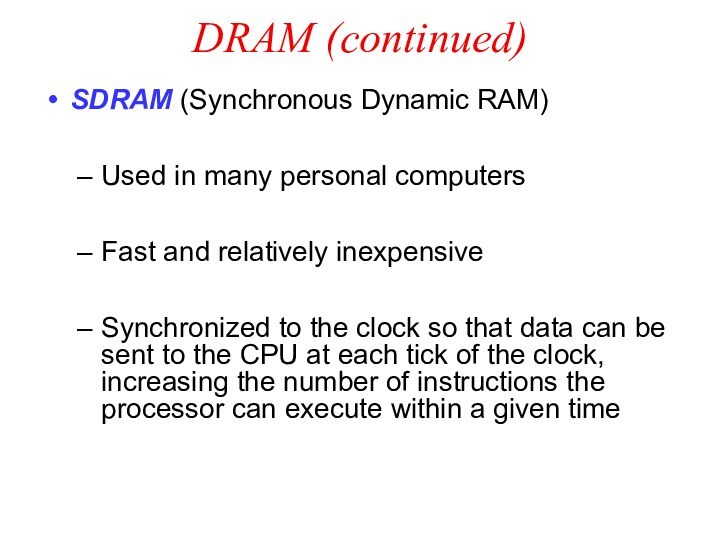
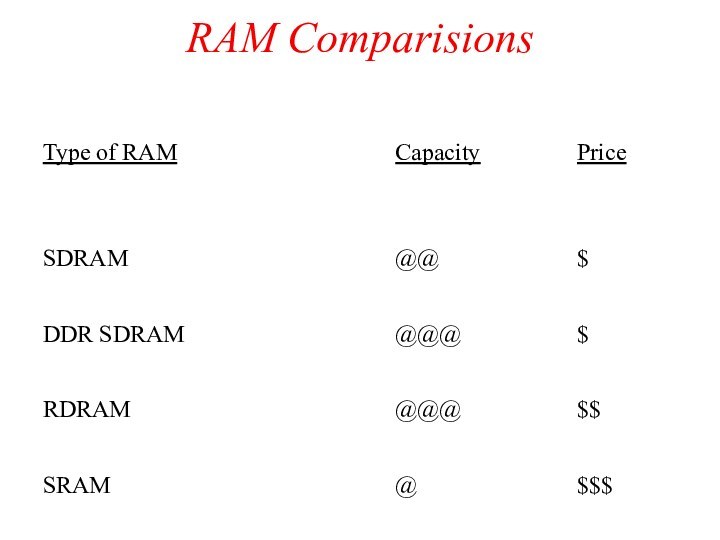
DRAM (continued)
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM)
Used in many
personal computers
Fast and relatively inexpensive
Synchronized to the clock so
that data can be sent to the CPU at each tick of the clock, increasing the number of instructions the processor can execute within a given time
Слайд 14
DRAM (continued)
DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM)
Transfers twice
the amount of data per clock cycle compared to
SDRAM
Capacity is up to 2 GB
Слайд 15
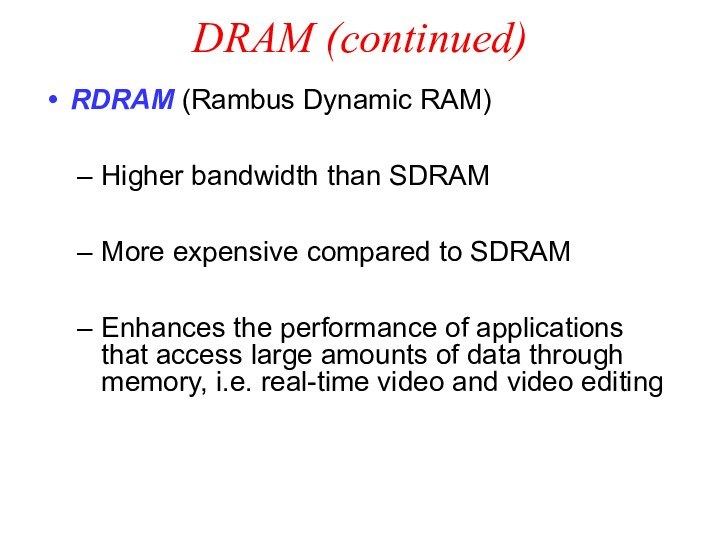
DRAM (continued)
RDRAM (Rambus Dynamic RAM)
Higher bandwidth than SDRAM
More
expensive compared to SDRAM
Enhances the performance of applications that
access large amounts of data through memory, i.e. real-time video and video editing
Слайд 16
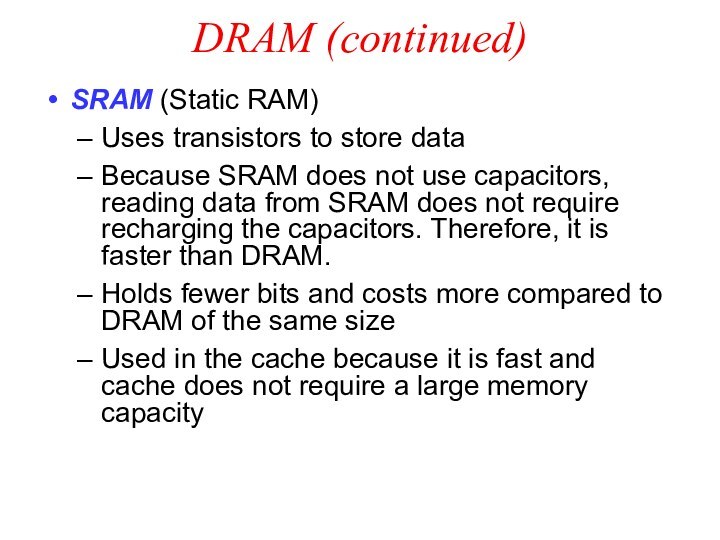
DRAM (continued)
SRAM (Static RAM)
Uses transistors to store data
Because
SRAM does not use capacitors, reading data from SRAM
does not require recharging the capacitors. Therefore, it is faster than DRAM.
Holds fewer bits and costs more compared to DRAM of the same size
Used in the cache because it is fast and cache does not require a large memory capacity
Слайд 18
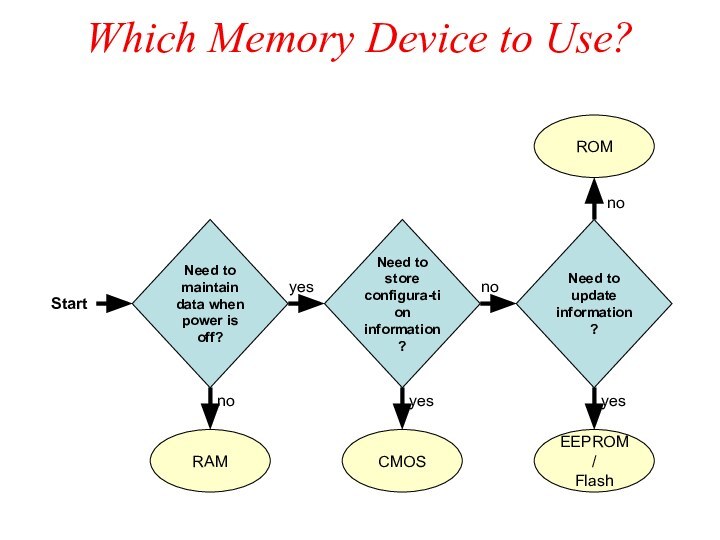
Which Memory Device to Use?
Start
Need to maintain data
when power is off?
Need to update information?
Need to store
configura-tion information?
yes
no
no
yes
no
yes
ROM
EEPROM/
Flash
RAM
CMOS
Слайд 19
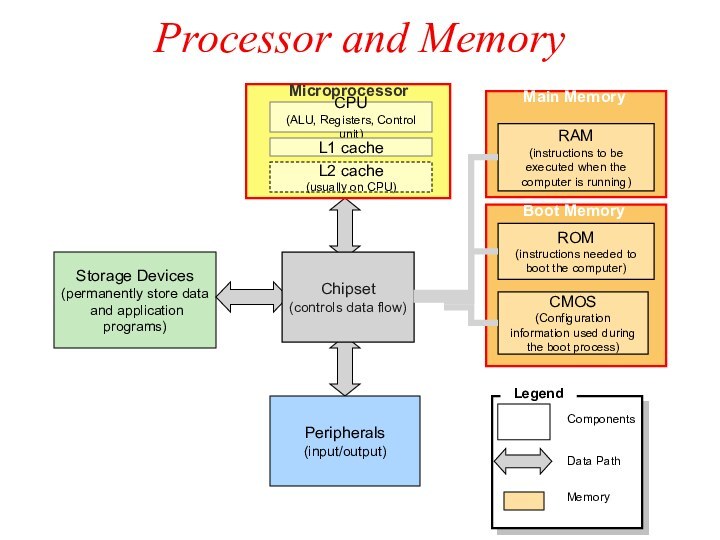
Processor and Memory
Storage Devices
(permanently store data
and application
programs)
Peripherals
(input/output)
Data Path
Components
Legend
Chipset
(controls data flow)
CPU
(ALU, Registers, Control unit)
L1 cache
L2
cache
(usually on CPU)
Microprocessor
RAM
(instructions to be executed when the computer is running)
ROM
(instructions needed to boot the computer)
CMOS
(Configuration information used during the boot process)
Main Memory
Boot Memory
Peripherals
Digital camera
Camcorder
Parallel
Mouse
PS-2
video
card
AGP Slot
Monitor
Speaker
sound
card
PCI Slots
FireWire
USB
modem
Modem
Scanner
Printer
Peripherals
Component
Legend
Port
Expansion Card
Expansion Slot
Peripheral
Device
Bus
Disk drive
Memory
Storage Devices
Chipset
Storage Devices
(permanently store data
and application programs)
Main Memory
(temporarily stores data
and program instructions
while the computer
is running)
Microprocessor
(executes instructions)
Слайд 21
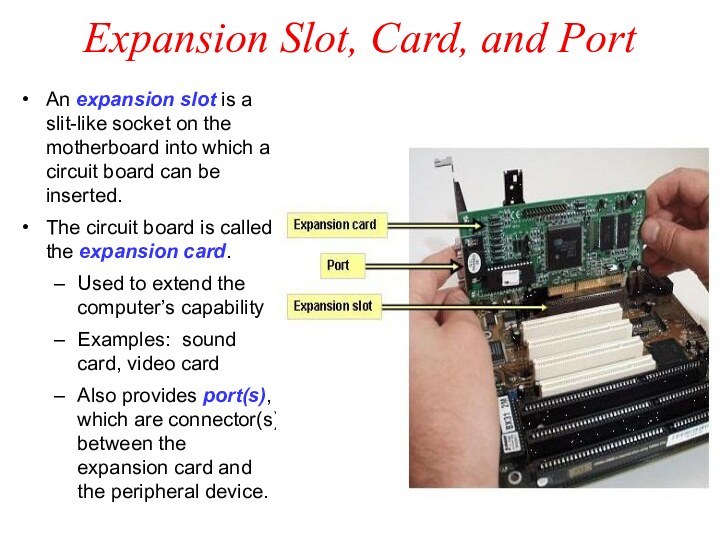
Expansion Slot, Card, and Port
An expansion slot is
a slit-like socket on the motherboard into which a
circuit board can be inserted.
The circuit board is called the expansion card.
Used to extend the computer’s capability
Examples: sound card, video card
Also provides port(s), which are connector(s) between the expansion card and the peripheral device.
Слайд 22
Expansion Slots
The two most common types of expansion
slots are Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) and Accelerated Graphics
Port (AGP).
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect ) slot
Can hold a variety of expansion cards such as a sound card or an Ethernet card
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) slot
Primarily used for graphics cards
PCMCIA (personal computer memory card international association) slot
Used for laptops in place of PCI slots
Relatively smaller than a PCI slot
Слайд 23
Expansion Cards
Small circuit boards that control the peripheral
devices
Graphics Cards
Takes signals from the processor and displays the
graphics, images in the monitor
Sound Cards
Converts analog sound signals to digital and vice versa
Modem
Transmits data over phone or cable lines
Слайд 24
Expansion Cards (continued)
Ethernet card
Serves as the interface to
a Local Area Network (LAN)
Transfers data at a rate
of 10 Mb/s
Newer versions of Ethernet called "Fast Ethernet" and "Gigabit Ethernet" support data rates of 100 Mb/s and 1 Gb/s (1000 Mb/s).
Слайд 25
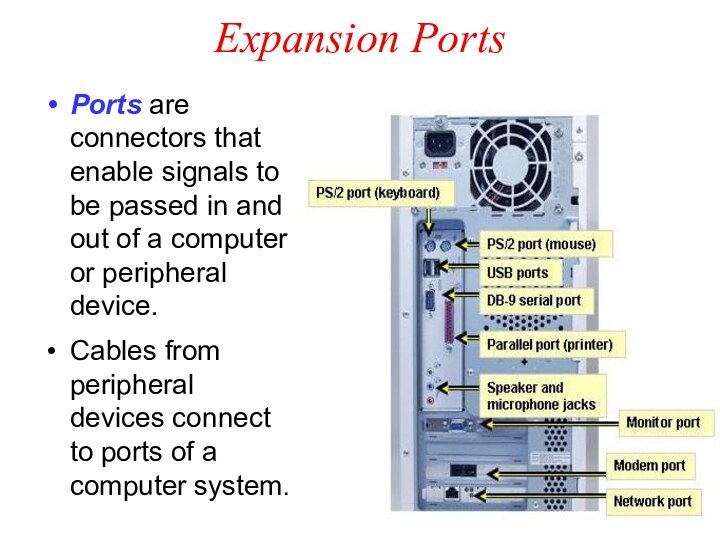
Expansion Ports
Ports are connectors that enable signals to
be passed in and out of a computer or
peripheral device.
Cables from peripheral devices connect to ports of a computer system.
Слайд 26
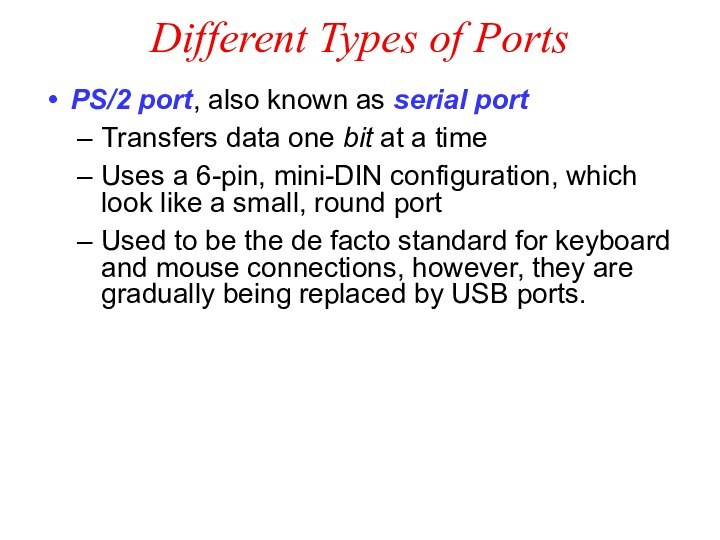
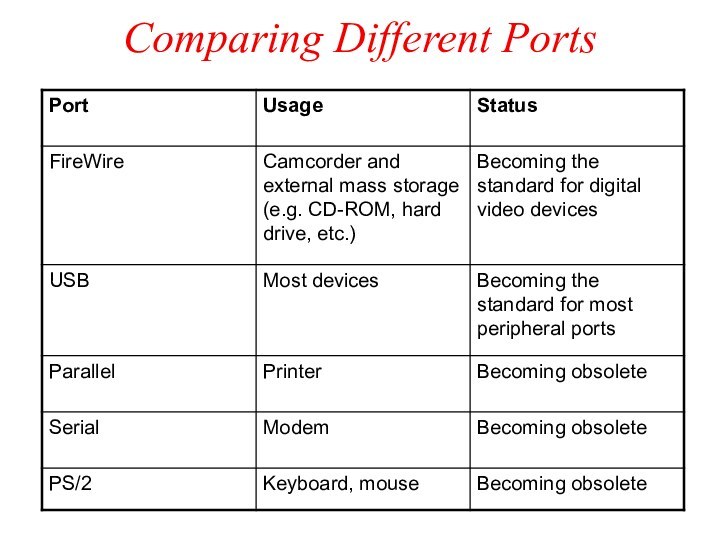
Different Types of Ports
PS/2 port, also known as
serial port
Transfers data one bit at a time
Uses
a 6-pin, mini-DIN configuration, which look like a small, round port
Used to be the de facto standard for keyboard and mouse connections, however, they are gradually being replaced by USB ports.
Слайд 27
Different Types of Ports (continued)
DB-9 port
Also becoming obsolete
Used
to connect PDA devices before the advent of USB
ports
Connects external modem, barcode scanner, and other older electronic devices
Слайд 28
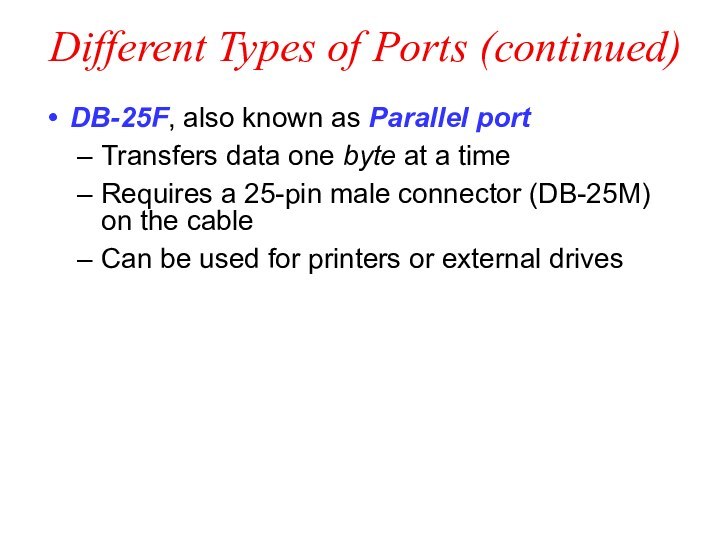
Different Types of Ports (continued)
DB-25F, also known as
Parallel port
Transfers data one byte at a time
Requires a
25-pin male connector (DB-25M) on the cable
Can be used for printers or external drives
Слайд 29
USB and FireWire
USB (Universal Serial Bus) port
Appears on
desktop systems and laptops
Can connect up to 127 devices
via a USB hub, which provides multiple USB ports (e.g. mouse, keyboard, scanner, printer, digital camera, and hard disk drive)
Supports "hot connectivity," which allows peripherals to be connected to the system, configured, and used without restarting the machine
Replacing serial and parallel ports
Слайд 30
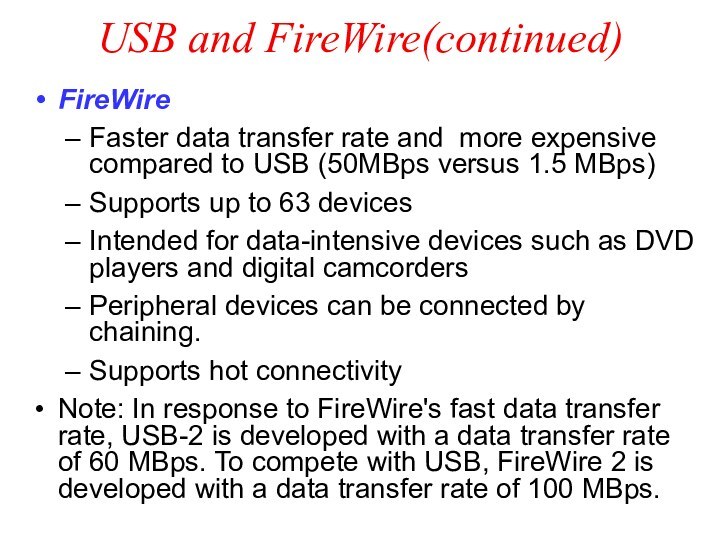
USB and FireWire(continued)
FireWire
Faster data transfer rate and more
expensive compared to USB (50MBps versus 1.5 MBps)
Supports up
to 63 devices
Intended for data-intensive devices such as DVD players and digital camcorders
Peripheral devices can be connected by chaining.
Supports hot connectivity
Note: In response to FireWire's fast data transfer rate, USB-2 is developed with a data transfer rate of 60 MBps. To compete with USB, FireWire 2 is developed with a data transfer rate of 100 MBps.
Слайд 32
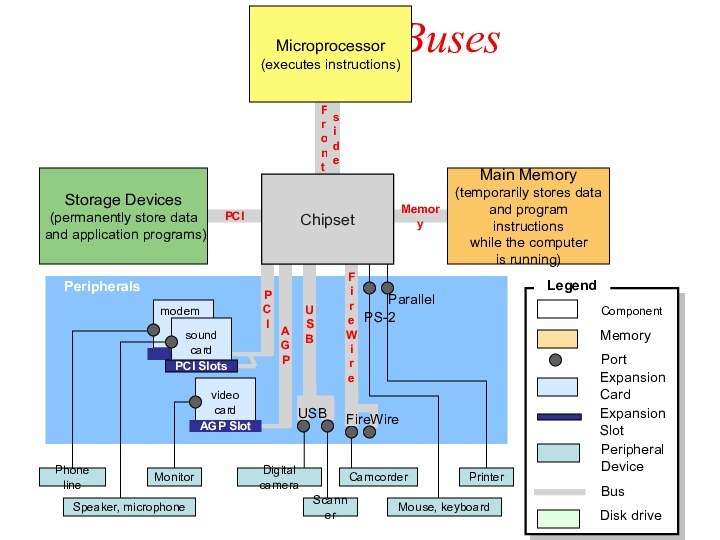
Buses
Digital camera
Camcorder
Parallel
PS-2
video
card
AGP Slot
Monitor
sound
card
PCI Slots
FireWire
USB
modem
Scanner
Printer
PCI
Peripherals
Component
Legend
Port
Expansion Card
Expansion Slot
Peripheral
Device
Bus
PC
I
AGP
USB
F
i
r
eWi
r
e
F
r
o
n
t
Disk
drive
Memory
Storage Devices
Memory
s
i
d
e
Chipset
Storage Devices
(permanently store data
and application programs)
Main
Memory
(temporarily stores data
and program instructions
while the computer
is running)
Microprocessor
(executes instructions)
Mouse, keyboard
Speaker, microphone
Phone line
Слайд 33
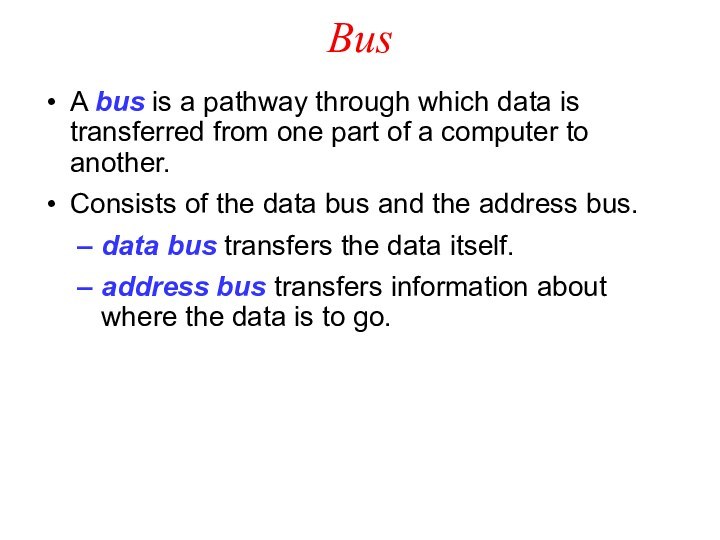
Bus
A bus is a pathway through which data
is transferred from one part of a computer to
another.
Consists of the data bus and the address bus.
data bus transfers the data itself.
address bus transfers information about where the data is to go.
Слайд 34
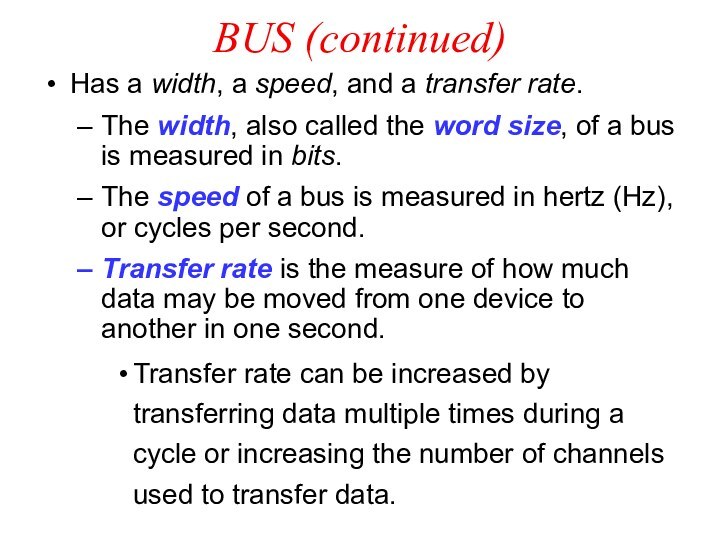
BUS (continued)
Has a width, a speed, and a
transfer rate.
The width, also called the word size,
of a bus is measured in bits.
The speed of a bus is measured in hertz (Hz), or cycles per second.
Transfer rate is the measure of how much data may be moved from one device to another in one second.
Transfer rate can be increased by transferring data multiple times during a cycle or increasing the number of channels used to transfer data.
Слайд 35
Different Types of Buses
Front Side bus
Bus on the
motherboard that transfers data between the CPU and the
chipset
Memory Buses: RAM bus and DRAM bus
Usually transfers data multiple times during a clock cycle or uses multiple channels to transmit data to increase data transfer rate to match that of the CPU.
Слайд 36
Different Types of Buses (continued)
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect)
Predominant
bus for newer systems
32 bits (standard), running at 33
MHz—giving PCI up to 133MBps of bandwidth
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
Bus architecture similar to that of PCI
Provides video cards with rapid access to the system memory
To date, only used for graphics cards, especially those that perform texture-mapping onto three-dimensional renderings
Very fast, running at 66 MHz with a 32-bit word size, and transferring 266 MBps
Слайд 37
Different Types of Buses (continued)
IDE bus
Transfers data
between storage devices and the chipset
USB (Universal Serial Bus)
and FireWire (IEEE 1394)
Transfer data one bit at a time at a variable pace
Not rated with a MHz speed; rated by peak transfer rate.
Слайд 38
Different Types of Buses (continued)
USB
Faster than standard
serial connections, with a peak transfer rate of 1.5
MBps.
Considered a low-speed bus and is designed to handle low to medium-speed peripherals
An extension to USB-1 is USB-2, which supports data rates up to 60 MBps versus the 1.5 MBps in USB-1; USB-2 is fully compatible with USB-1.
Слайд 39
Different Types of Buses (continued)
FireWire
High transfer rate designed
for high-speed external peripherals such as DVD-ROM and hard
disk drives
FireWire 2 (IEEE 1394b) emerged with data rates up to 100 MBps, double that of FireWire 1 (IEEE 1394).
Слайд 40
Input Devices
Cameras
Digital Camera
Enables photos taken to be
stored in digital form, which can uploaded onto a
computer.
Web Camera (webcam)
Captures live video and sends the compressed image stream to the computer or to other computers via the Internet
Scanners
Convert a 2-D physical image (for example, a photograph or a paper copy of an image) into a digital image that can be viewed and edited on your computer
Слайд 41
Input Devices (continued)
Digital Camcorders
Record video in digital form,
which can be uploaded onto a computer without further
loss in image quality
Recorded video can be edited using movie-editing software
Images are more clear than those captured by a webcam, but requires more bandwidth
Uses fireWire jack/interface to enable host computers to provide enough bandwidth for the camcorder
Слайд 42
Output Devices: Monitors and Projectors
CRT (cathode ray tube)
monitors
Used to be the most common type of computer
monitors until LCD monitors began to gain popularity
Use three electron beams to create colors, red, green, and blue.
To generate white, all three beams are fired simultaneously. To create black, all three beams are turned off.
Other colors are created using different mixtures of these three color beams.
Inexpensive and dependable. Also found in conventional TV sets.
Слайд 43
Output Devices: Monitors and Projectors (continued)
LCD (liquid crystal
display) monitors
Produce images by manipulating light within a layer
of liquid crystal cells
Also known as flat-panel screens
Compact, lightweight, easy-to-read, and emit less radiation compared to CRT monitors
Used in notebook computers and desktop computers
Слайд 44
Projectors
Enable images on the computer screen to be
magnified and projected onto a bigger screen
Use two types
of technologies
LCD (liquid crystal display) system
Images are projected as light shines through a layer of liquid crystal cells
DLP (digital light processing) system
Uses tiny mirrors that reside on a special microchip called the Digital Micromirror Device (DMD)
Images are smoother and have better contrast than those created using LCD
Слайд 45
Printers
Ink Printers
Works by spraying and dyeing the page
with color
Rated according to their resolution and color depth
Color
depth is the range of colors that any given drop may represent
Resolution is measured in dpi, the number of dots per inch (horizontally or vertically) that a printer can place on a page. Sometimes the dpi is the same both horizontally and vertically, such as 1200 dpi. Other times, the horizontal and vertical dpi differ—as in1440x720 dpi.
Use a four-color process, CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black), to produce various colors. Sometimes the color black is excluded because it can be produced by mixing the other three colors.
Multiple drops of colors can also be placed on a single dot to produce more colors.