- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Understanding JavaScript and Coding Essentials
Содержание
- 2. AgendaBasic InformationHow to include JS Code into
- 3. Basic informationJavaScript - dynamic computer programming language.It
- 4. 1. Inline JavaScript: 2. Internal tag :
- 5. CommentsComments - part of the program text
- 6. VariablesVariable – symbolic name associated with a
- 7. Declaration and initializationvar – special keyword for
- 8. Global and localJavaScript has two types of
- 9. Data typesJavaScript has 6 base data types:
- 10. Number, Boolean and Stringvar n = 10;
- 11. Null and Undefinedvar n = null; //null
- 12. Type castingvar a, b, c; a =
- 13. Type castingRules of typing casting:All scalar types
- 14. FunctionsIn mathematics:In classical programming[3]Function is a relation
- 15. Examplevar i, base, power, result;base = 2;
- 16. Function Declarationfunction name (a, b) {
- 17. Function callCall - operation for execution of
- 18. Examplevar out;out = pow(2, 2);console.log(out);out = pow(3,
- 19. Code processingvar a = 10;test();function test ()
- 20. Code processingvar a = 10;test();function test ()
- 21. Code processingvar a = 10;test();function test ()
- 22. Code processingvar a = 10;test();function test ()
- 23. Code processingvar a = 10;test();function test ()
- 24. Function Declaration and Expressionfunction name () {
- 25. Additional Facts About FunctionsFunctions in JavaScript are
- 26. Program flowOperators in a program processed in
- 27. Conditions: if-elseVery often we have to choose
- 28. Conditions: if-elseExample: function discount (type) {
- 29. Conditions: ?:Sometimes if-else too bulky. If we
- 30. Conditions: ?:function discount (type) { if
- 31. Loops: forLoops are used when algorithm requires
- 32. Loops: while and do-whileTwo others types of
- 33. Loops: examplesExample 1: for (var i =
- 34. Loops: break and continue There are two
- 35. SwitchSwitch statement allows to select one of
- 36. SwitchExample: This switch looks for the word
- 37. Practice Task
- 38. Скачать презентацию
- 39. Похожие презентации







![Understanding JavaScript and Coding Essentials FunctionsIn mathematics:In classical programming[3]Function is a relation between a set of inputs](/img/tmb/15/1437744/c8cf34807ef9926d494821b32f4aabc1-720x.jpg)
![Understanding JavaScript and Coding Essentials Function Declarationfunction name (a, b) { return a + b;} [1]*](/img/tmb/15/1437744/4403029b0ec7e6ec384ac0ef6fc7ca5a-720x.jpg)




![Understanding JavaScript and Coding Essentials Function Declaration and Expressionfunction name () { body;} [1]var name =](/img/tmb/15/1437744/489de26c827e85cd88ff98789454498a-720x.jpg)










Слайд 2
Agenda
Basic Information
How to include JS Code into HTML
Comments
Variables
Data
Types
and Expression
Слайд 3
Basic information
JavaScript - dynamic computer programming language.
It is
most commonly used as part of web browsers, whose
implementations allow client-side to interact with the user, control the browser and asynchronously communicate with server-side.JavaScript syntax was influenced by C.
JS supported object-oriented, imperative and functional programming styles.
Слайд 4
1. Inline JavaScript:
2. Internal tag :
alert('Hello!');
3. External file:
How to add JavaScript
to HTML?
Слайд 5
Comments
Comments - part of the program text which
will be ignored by language interpreter
The /* characters, followed by
any sequence of characters (including new lines), followed by the */ characters.The // characters, followed by any sequence of characters, but only in current line. Therefore, it is commonly called a "single-line comment."
[1]
[2]
[3]
Слайд 6
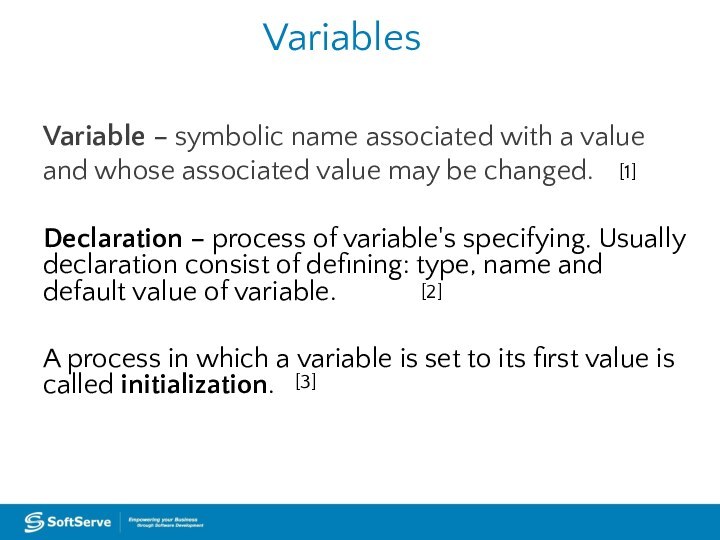
Variables
Variable – symbolic name associated with a value
and whose associated value may be changed.
Declaration – process
of variable's specifying. Usually declaration consist of defining: type, name and default value of variable. A process in which a variable is set to its first value is called initialization.
[1]
[2]
[3]
Слайд 7
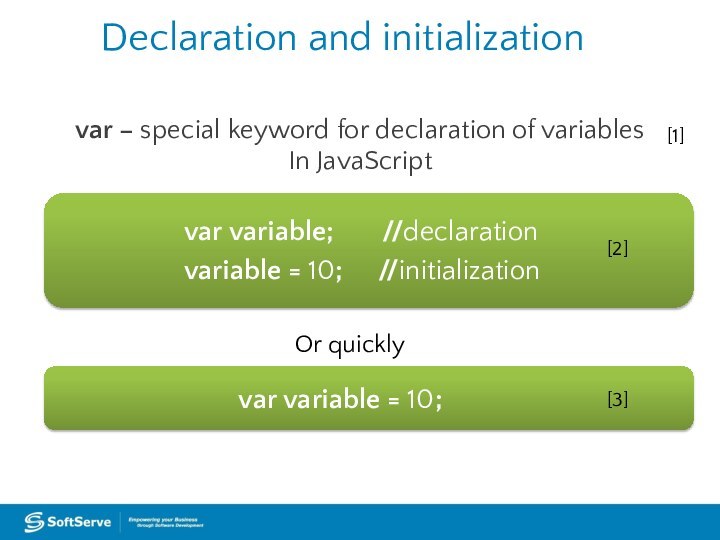
Declaration and initialization
var – special keyword for declaration
of variables
In JavaScript
var variable; //declaration
variable =
10; //initializationOr quickly
var variable = 10;
[1]
[2]
[3]
Слайд 8
Global and local
JavaScript has two types of variables:
global - exist in memory and is available at
all times of the program. In JS it's a variables of page.local - exist in memory and is available only in block when variable is defined. In JS it's defined in function variables.
[1]
[2]
Слайд 9
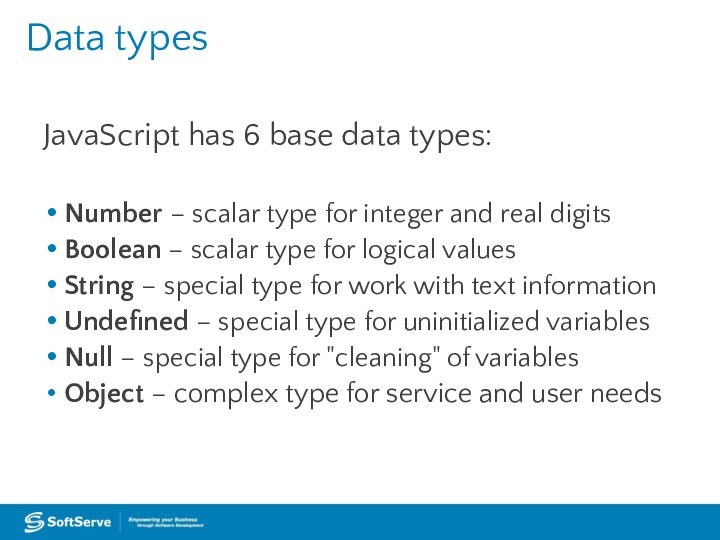
Data types
JavaScript has 6 base data types:
Number
– scalar type for integer and real digits
Boolean
– scalar type for logical valuesString – special type for work with text information
Undefined – special type for uninitialized variables
Null – special type for "cleaning" of variables
Object – complex type for service and user needs
Слайд 10
Number, Boolean and String
var n = 10; or
var n = Number(10);
//number values for example: -1,
10, 3.14, Nan, Infinityvar s = “text”; or var s = String(“text”);
//string values for example: “”, “text”, ‘text’
var b = true; or var b = Boolean(true);
//bollean values: true and false
[1]
[2]
[3]
Слайд 11
Null and Undefined
var n = null;
//null variables
can have only null value
var u;
// created and
uninitializedAnd Object type… but it will be reviewed in future :)
[1]
Слайд 12
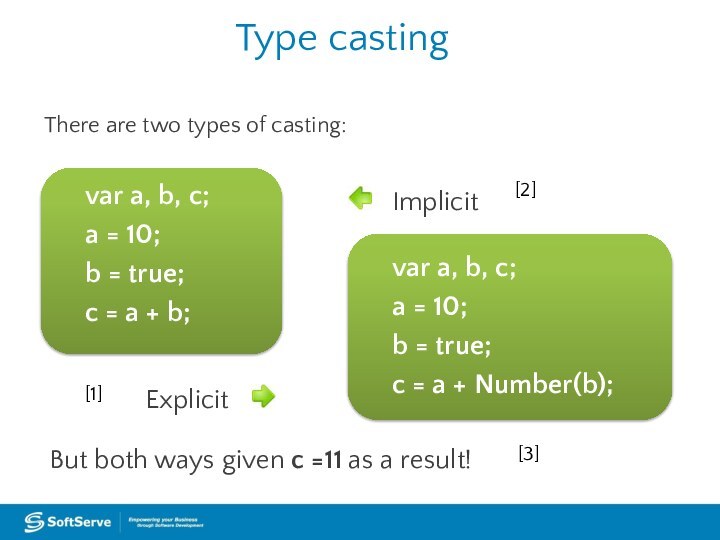
Type casting
var a, b, c;
a = 10;
b = true;
c = a + b;
var a,
b, c; a = 10;
b = true;
c = a + Number(b);
There are two types of casting:
Implicit
Explicit
But both ways given c =11 as a result!
[2]
[1]
[3]
Слайд 13
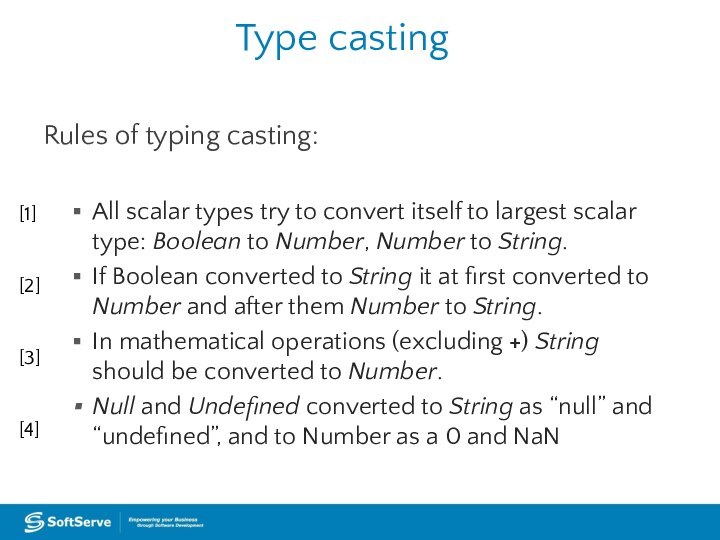
Type casting
Rules of typing casting:
All scalar types try
to convert itself to largest scalar type: Boolean to
Number, Number to String.If Boolean converted to String it at first converted to Number and after them Number to String.
In mathematical operations (excluding +) String should be converted to Number.
Null and Undefined converted to String as “null” and “undefined”, and to Number as a 0 and NaN
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
Слайд 14
Functions
In mathematics:
In classical programming
[3]
Function is a relation between
a set of inputs and a set of permissible
outputs.[1]
[2]
y = f(x)
Function is a named part of a code that performs a distinct service.
Слайд 15
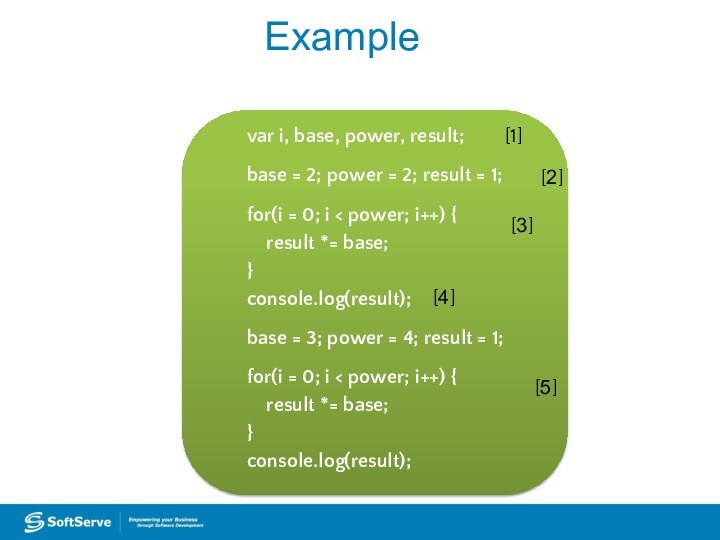
Example
var i, base, power, result;
base = 2; power
= 2; result = 1;
for(i = 0; i
< power; i++) {result *= base;
}
console.log(result);
base = 3; power = 4; result = 1;
for(i = 0; i < power; i++) {
result *= base;
}
console.log(result);
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
Слайд 16
Function Declaration
function name (a, b) {
return
a + b;
}
[1]
* you can return one value
only* return always interrupts the execution.
* place your return at the end of a function
[2]
[3]
[3]
Слайд 17
Function call
Call - operation for execution of function.
( ) – operator for this action.
Usually function
can be called by name. [1]
[2]
[3]
Слайд 18
Example
var out;
out = pow(2, 2);
console.log(out);
out = pow(3, 4);
console.log(out);
function
pow (base, power) {
var result = 1;
for(var i = 0; i < power; i++) {
result *= base;
}
return result;
}
Слайд 19
Code processing
var a = 10;
test();
function test () {
a = 30;
var b = 40;
}
var
b = 20;console.log(a, b);
Слайд 20
Code processing
var a = 10;
test();
function test () {
a = 30;
var b = 40;
}
var
b = 20;console.log(a, b);
1.
Слайд 21
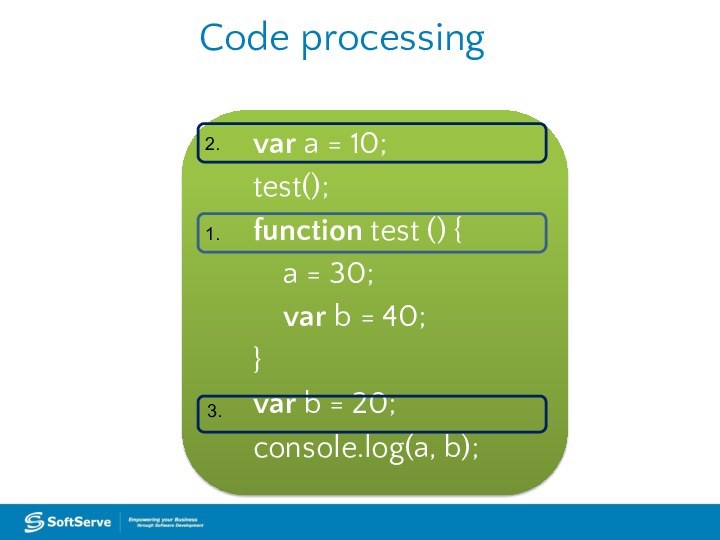
Code processing
var a = 10;
test();
function test () {
a = 30;
var b = 40;
}
var
b = 20;console.log(a, b);
1.
2.
3.
Слайд 22
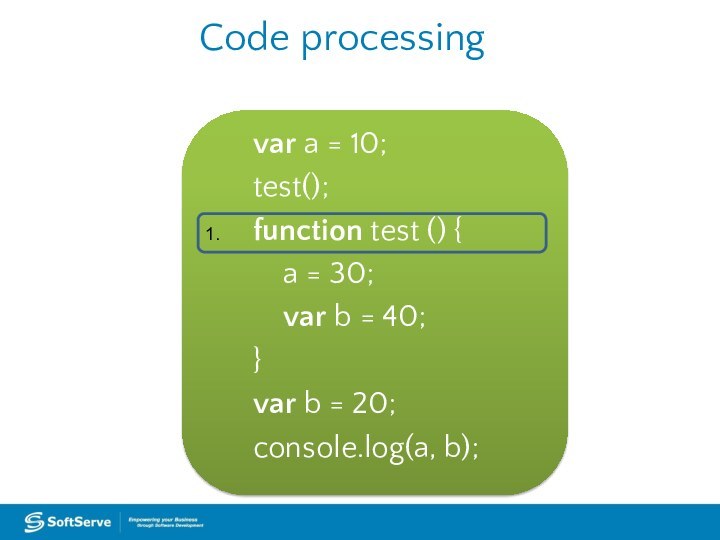
Code processing
var a = 10;
test();
function test () {
a = 30;
var b = 40;
}
var
b = 20;console.log(a, b);
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Слайд 23
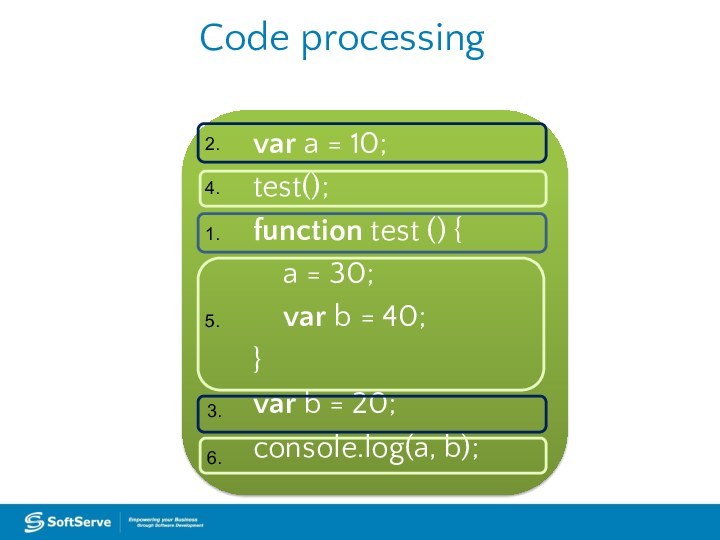
Code processing
var a = 10;
test();
function test () {
a = 30;
var b = 40;
}
var
b = 20;console.log(a, b);
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
5.1
5.2
Слайд 24
Function Declaration and Expression
function name () {
body;
}
[1]
var name = function () {
body;};
[2]
Слайд 25
Additional Facts About Functions
Functions in JavaScript are Objects.
As
a result, functions are accessible by reference.
Functions can be
used as a parameter in other function.References to functions can be saved in any other variable.
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
Слайд 26
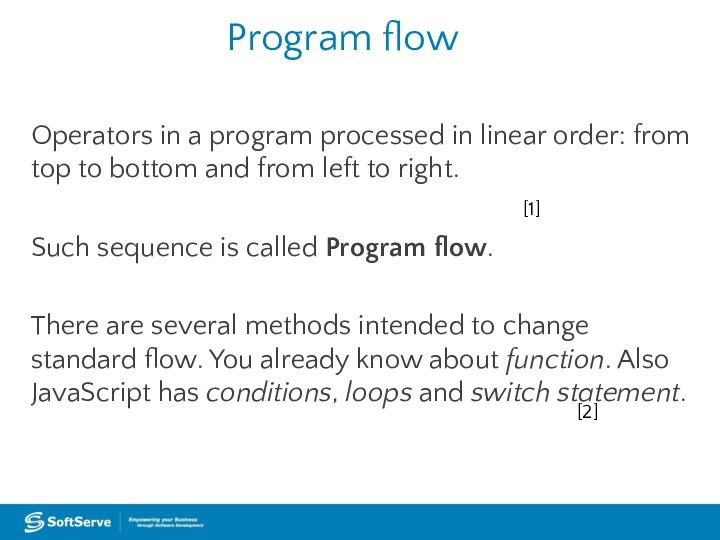
Program flow
Operators in a program processed in linear
order: from top to bottom and from left to
right.Such sequence is called Program flow.
There are several methods intended to change standard flow. You already know about function. Also JavaScript has conditions, loops and switch statement.
[1]
[2]
Слайд 27
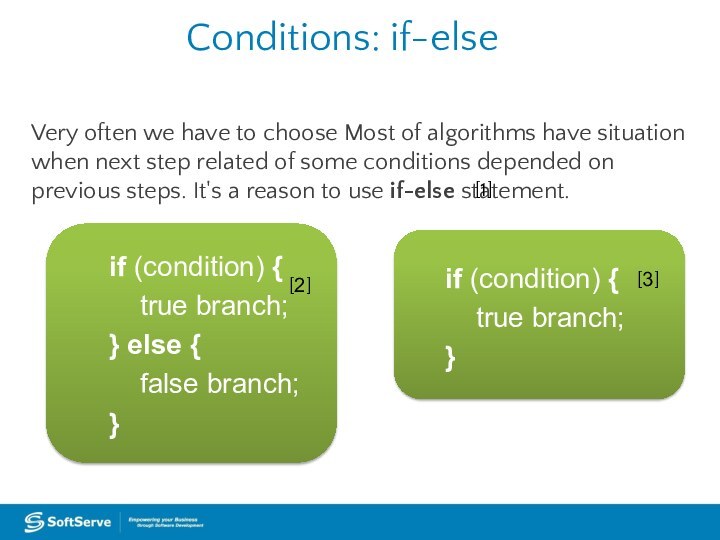
Conditions: if-else
Very often we have to choose Most
of algorithms have situation when next step related of
some conditions depended on previous steps. It's a reason to use if-else statement.if (condition) {
true branch;
} else {
false branch;
}
if (condition) {
true branch;
}
[1]
[2]
[3]
Слайд 28
Conditions: if-else
Example:
function discount (type) {
if
(type === “silver”) {
price *=
0.9;}
if (type === “gold”) {
price *= 0.85;
}
return price;
}
Function get a parameter with a information about discount. And if discount is "silver" or "gold“, function modifies global variable price.
In this example a shortened form of operator was used.
Слайд 29
Conditions: ?:
Sometimes if-else too bulky. If we need
to initialize a variable modifying it by simple conditions;
or we need to return a value from function and this value is dependent on something, we can use ternaryTernary operator like ?:.
result = (condition)? true action: false action;
Let’s rewrite the last example using ternary operator.
[1]
Слайд 30
Conditions: ?:
function discount (type) {
if (type
=== “silver”) {
price *= 0.9;
}if (type === “gold”) {
price *= 0.85;
}
return price;
}
function discount (type) {
price *= (type === “silver”)? 0.9: 1;
price *= (type === “gold”)? 0.85: 1;
return price;
}
We get a more compact but a less readable code. So be careful!
Слайд 31
Loops: for
Loops are used when algorithm requires repeating
of statements.
First of them: for - loop with counter
for
(start position; repeat condition; step) {body of loop; // will be repeated
}
One processing of loop’s body is called iteration.
[1]
[2]
[3]
Слайд 32
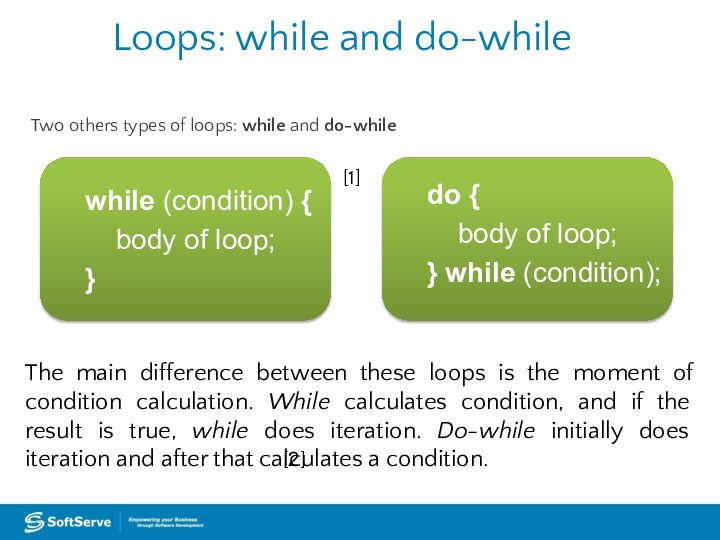
Loops: while and do-while
Two others types of loops:
while and do-while
while (condition) {
body of
loop;}
do {
body of loop;
} while (condition);
The main difference between these loops is the moment of condition calculation. While calculates condition, and if the result is true, while does iteration. Do-while initially does iteration and after that calculates a condition.
[1]
[2]
Слайд 33
Loops: examples
Example 1:
for (var i = 0;
i < 5; i++) {
console.log(“Iteration # %d”,
i + 1);}
Text with number of current iteration will be print 5 times
Example 2:
while (accumulation < 100) {
accumulation += doSomething();
}
This loop will be repeated until accumulation reaches 100 or gets grater value.
[1]
[2]
Слайд 34
Loops: break and continue
There are two keywords
for loops control :
break – aborts loop and moves
control to next statement after the loop;continue – aborts current iteration and immediately starts next iteration.
Try not to use this keywords. A good loop have one entering point, one condition and one exit.
Слайд 35
Switch
Switch statement allows to select one of many
blocks of code to be executed. If all options
don’t fit, default statements will be processedswitch (statement) {
case value1: some body;
break;
case value2: some body;
break;
. . .
default: some body;
}
Слайд 36
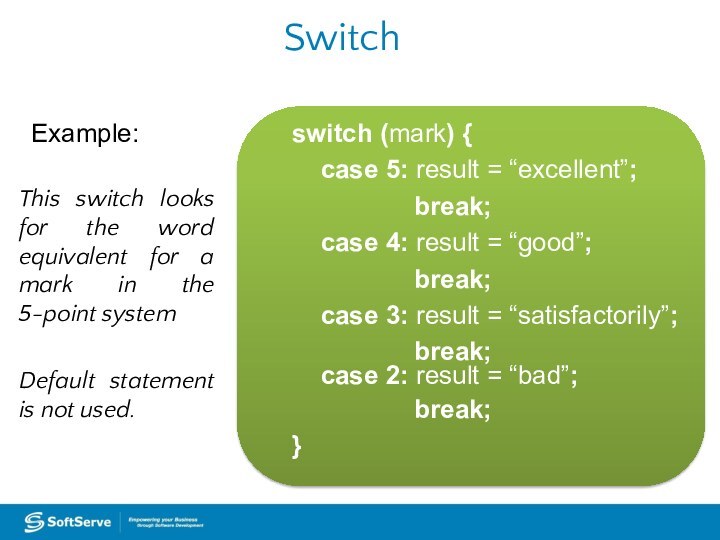
Switch
Example:
This switch looks for the word equivalent
for a mark in the 5-point system
Default statement is
not used.switch (mark) {
case 5: result = “excellent”;
break;
case 4: result = “good”;
break;
case 3: result = “satisfactorily”;
break;
case 2: result = “bad”;
break;
}