Слайд 2
Psychostimulants
(Psychomotor Stimulants)
1. Methylxanthines:
Caffeine (Coffeinum-natrii
benzoas )
tab. 0.1 g; amp. 10% and 20%
- 1 ml)
2. Phenylalkyl amines:
Phenamine (Amphetamine)
3. Phenylalkyl sydnonimines:
Sydnocarb (tab. 0.005 and 0.01 g)
4. Piperidine compounds:
Meridil (tab. 10 mg)
Слайд 3
Mechanisms of Action of Caffeine
1). Blockade of Phosphodiesterase
=> ⇑ cAMP and ⇑cGMP
2) Blockade of Adenosine
Receptors
Adenosine –
⮚ an Inhibitory Transmitter of the CNS
⮚ inhibits Adenyl Cyclase activity, causing Contraction of Airway Smooth Muscle
Слайд 4
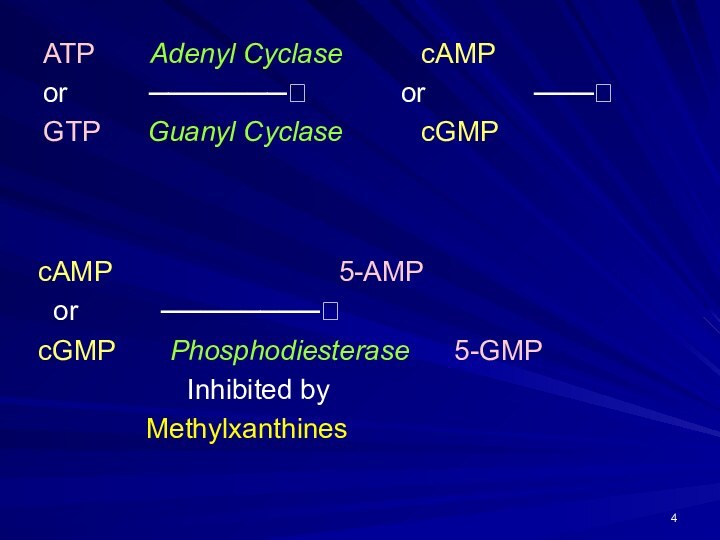
ATP Adenyl Cyclase
cAMP
or ───────?
or ───?
GTP Guanyl Cyclase cGMP
cAMP 5-AMP
or ────────?
cGMP Phosphodiesterase 5-GMP
Inhibited by
Methylxanthines
Слайд 5
Pharmacological Effects of Caffeine :
Stimulation of Medullary,
Vagal,
Respiratory and Vasomotor centers
?Cardiac Output
and ?Cardiac Work
(+) Inotropic and (+) Chronotropic Effects
Improvement of :
● Coronary, Cerebral and Renal Circulation,
● Eye Ground Blood Circulation
● Acuity of Vision and Color Vision
Smooth muscles relaxation, most prominent effect –
on Bronchi, esp. in asthmatics
Clinical Uses: CNS depression,
Neonatal Apnea, Hypotension.
Слайд 6
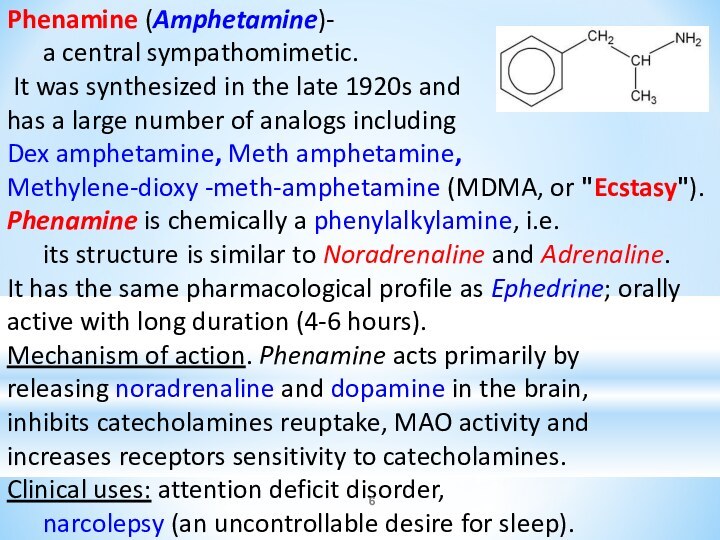
Phenamine (Amphetamine)-
a central sympathomimetic.
It was synthesized in
the late 1920s and
has a large number of
analogs including
Dex amphetamine, Meth amphetamine,
Methylene-dioxy -meth-amphetamine (MDMA, or "Ecstasy").
Phenamine is chemically a phenylalkylamine, i.e.
its structure is similar to Noradrenaline and Adrenaline.
It has the same pharmacological profile as Ephedrine; orally active with long duration (4-6 hours).
Mechanism of action. Phenamine acts primarily by
releasing noradrenaline and dopamine in the brain,
inhibits catecholamines reuptake, MAO activity and
increases receptors sensitivity to catecholamines.
Clinical uses: attention deficit disorder,
narcolepsy (an uncontrollable desire for sleep).
Слайд 7
Sydnocarb (Mesocarb) –
chemically and
pharmacologically similar to
phenamine but does not cause drug dependence,
hypnosis,
less influences on peripheral adrenoreceptors.
Sympathomimetic and cardiovascular actions are insignificant.
Mechanism of action:
?Catecholamines Reuptake
? MAO activity
? Receptors Sensitivity to Catecholamines
Clinical uses: Neurotic disorders, Narcolepsy, Asthenia, Apathy, Attention deficit hyperkinetic disorder, Excessive day time sleepiness, Decreased working capacity.
Adverse effects: anorexia, insomnia, abdominal discomfort and bowel upset, AP increase.
Слайд 8
ADAPTOGENS
1. Plant origin –
Powders, T-res and
Extracts from roots or fruit of:
Ginseng, Eleutherococcus,
Rhodiola, Schizandra,
Aralia
2. Animal origin – Extracts from
the young Siberian male deer’s antlers: Pantocrin, Rantatrin
Mechanism of Action:
1). Activation of RNA and Protein synthesis
2). ?Biochemical Disorders in Stress Reactions
3). Normalization of Pituitary-Adrenal and Immune System functions
Слайд 9
Pharmacodynamics of Adaptogens:
? Physical and Mental Capacity
? Fatigue, ? Appetite Disorders
? Tolerance to Harmful
Influences,
High to, Cooling, Intoxications;
Ionizing Radiation
? Specific and Non- Specific Immunity
Improvement: Blood Circulation,
Breathing, Vision and Hearing,
Cardio-Protector and Hepato-Protector effect
Ginseng
Eleutherococcus
Слайд 10
Clinical Uses:
Physical Overwork
Physical and Mental
Overfatigue
Asthenic Syndrome
State after Infection and Somatic Diseases
Ionizing Radiation Influence
Adverse effect:
Overexcitement of Nervous and
Cardio-Vascular Systems,
Arterial Hypertension,
Hyperglycemia
Rhodiola
Слайд 11
Classification of ANALEPTICS
1. With prevalent action upon the
BRAIN CORTEX Caffeine
Caffeine-Natrium Benzoate
2. With prevalent action upon the MEDULLA OBLONGATA:
Bemegride– amp. 0.5%-10 ml
Etimizol – amp. 1.5%-3 ml
Cordiamin – amp. 1 ml, vial 15 and 30 ml
Sulfocamphocaine – amp. 10%-2 ml
3. With prevalent action on the SPINAL CORD:
Strychnine Nitrate
Strength According to Analeptic Activity:
Bemegride – Cordiamin - Sulfocamphocaine - Etimizol
Слайд 12
Clinical Uses of Analeptics
Acute Respiratory Failure:
Aggravation
of COPD [Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases] with sleepiness,
inability to cough out
Respiratory depression during Infectious Diseases,
Shock, Syncopal conditions
Asphyxia (Respiratory Arrest) of Newborns and
during surgical operations
Poisons with Hypnotic drugs, Opioid Analgesics,
General Anesthetics
Слайд 13
Etimizol amp. 1.5% - 3 ml, tab. 0.1
g –
an analeptic of direct action
1. Direct
excitement of the Respiratory Center
2. ? ACTH production => Glucocorticoids’ level in blood
- is used as Anti-inflammatory and Antiallergic agent
to treat Arthritis, Polyarthritis, Asthma
3. Acceleration and Deepening of Respiration
4. ? HR, ? BP.
Clinical uses:
Respiratory failure in Shock; Collapse, Asphyxia; Respiratory Depression in Infectious Diseases; Prophylaxis of Lung Atelectasis and Pneumonia,
Arthritis, Polyarthritis, Asthma
Слайд 14
Cordiamin (Niketamide) –
amp. 1
ml, vial 30 ml –
an analeptic of mixed
action
? direct exciting influence on Respiratory Center
? Stimulates N-Receptors of Carotid Sinus
Acceleration and Deepening of Respiration
↑HR, ↑BP
Clinical uses:
Respiratory failure in Shock, Collapse, Asphyxia; Respiratory depression in Infectious diseases; Prophylaxis of lung atelectasis and pneumonia
Adverse effects:
clonic seizures, face hyperemia
Слайд 17
MAO A – NORADRENALINE and SEROTONIN,
MAO B
– DOPAMINE, PHENYLETHYLAMINE, TYRAMINE
MAO A – NORADRENALINE and SEROTONIN,
MAO B – DOPAMINE, PHENYLETHYLAMINE, TYRAMINE
Слайд 18
Amitriptyline (tab. 0.01 and 0.025 g) –
a Tricyclic
Antidepressant.
Inhibits reuptake of
Noradrenaline and Serotonin
in
Nerve Terminals (Presynaptic Neurons) =>
=> ? their Level in the synaptic cleft.
More actively inhibits reuptake of
Serotonin than Noradrenaline => SEDATION.
Anxiolytic, Sedative and
Psychomotor Dampening effects.
Clinical uses:
Depression, Anorexia, Bulimia.
Слайд 19
Adverse Effects of Tricyclic Antidepressants
Antagonism at M-cholinoceptors
?
Atropine-like effects:
Tachycardia
Inhibition of Exocrine Glands
Xerostomia (dry
mouth)
Urinary retention
Constipation
Blurred vision
Aggravation of Glaucoma and Epilepsy
Слайд 20
Fluoxetine (Prozak – tab. 0.02 g)
- a Selective
Serotonin-Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI) –
specifically inhibits SEROTONIN reuptake
Advantages include:
Absence
of cardiotoxicity
Free of Anti-Cholinergic Effects, orthostatic hypotension
Loss of appetite and Weight Reduction
the ease of once-a-day dosing
Clinical Uses:
Depression, Bulimia nervosa, Obsessive-Compulsive disorder,
Anorexia nervosa, Panic disorder, Premenstrual Syndrome
Adverse Effects: Over arousal, Insomnia, Tremor, Anxiety,
Akathisia (a state of Agitation, Distress, Restlessness and
the Inability to sit still), sexual dysfunction, hot flashes, cough, flu-like syndrome
Слайд 21
MAO Inhibitors: Nialamide, Moclobemide and
SSRI : Fluoxetine
et al.
should not be co-administered due to the risk
of Life Threatening "Serotonin Syndrome"
as a result of excess SEROTONIN (5-HT):
?to, Muscle Rigidity, Myoclonus,
Rapid Changes in Mental Status and Vital Signs
Cardiovascular collapse
Drugs require WASHOUT PERIODS of 6 weeks before administering the other.
Слайд 22
Nootrop Drugs – activate learning,
improve memory and
intellectual activity
I. ACTOPROTECTORS:
1. Activators of Brain Metabolism:
∙ Methyl
Xanthines:
Instenon
Caffeine
Aminophylline (Euphylline)
∙ Protein Hydrolyzates:
Actovegin
Cerebrolysin
Solcoseryl
2. Cerebral Vasodilators:
Nicergoline (Sermion)
Vinpocetine
Слайд 23
3. Ca2+- Antagonists: Nimodipine, Cinnarizine
4. Antioxidants: Tocopherole acetatate
(Vitamin E)
5. GABA and its derivatives:
Aminalon (GABA)
Oxybutyrate Sodium
(GOBA)
Pantogam, Phenibut, Picamilon
II. Affecting Advantageously MEMORY:
1. Racetams - cyclic GABA derivatives:
Piracetam (Nootropil)
Aniracetam Oxiracetam
2. Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) derivatives:
Encephabol
Слайд 24
Actovegin - amp. 4% 2 and 5 ml,
vial 20%-250 ml, Dr. 0.2 g,
is proved to
be the Most Effective Nootrop.
contains Deproteinized Hemoderivate from plasma of
the Calf blood with Low-molecular Peptides, Amino Acids, Nucleosides, Lipids, Electrolytes and Microelements.
After 60-90 min IV infusion of 20% 250 ml:
? Cardiac Index by 25%
? Stroke Index by 30%
? O2 Content in Arterial Blood by 13%
HR does not change
?? Intensity and Efficiency of Aerobic Processes
?? Energy and Contractibility of Muscles
? Prevents accumulation of LACTATE
Слайд 25
Instenon – 1 ampoule 2 ml contains:
Methylxantine
Ethophylline - 100 mg
Analeptic Etamivan - 50 mg
Vasodilator
Hexobendin- 10 mg
? ?Cardiac Output ?
? ?Perfusion Pressure in the Vessels of
the Edge Zone of Ischemia
STIMULATES:
the Respiratory and Vasomotor centers
Centers of vegetative regulation
Nuclei of the cranial nerves.
Clinical uses:
brain diseases of vascular and age-dependent nature, stroke, sequences of cerebrovascular insufficiency.
Слайд 26
Cerebrolysin amp. 21.5% 1, 5 and 10 ml
a peptidergic nootrop with neurotrophic action.
1 ml
Є 215 mg of NEUROPEPTIDES
from the Swine’s Cerebrum.
Pharmacological action: nootrop,
Metabolic regulation
Neuroprotection
Functional Neuromodulation
Neurotrophic activity - analogous to natural Neuron Growth Factors
Слайд 29
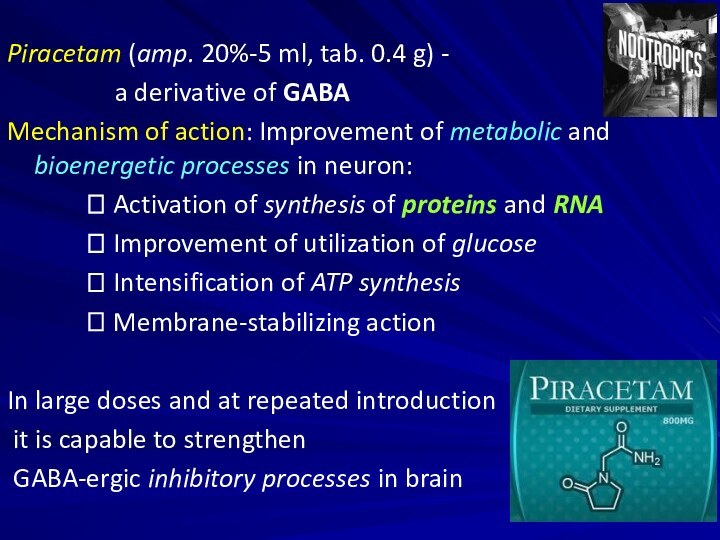
Piracetam (amp. 20%-5 ml, tab. 0.4 g) -
a derivative of GABA
Mechanism of action: Improvement of
metabolic and bioenergetic processes in neuron:
? Activation of synthesis of proteins and RNA
? Improvement of utilization of glucose
? Intensification of ATP synthesis
? Membrane-stabilizing action
In large doses and at repeated introduction
it is capable to strengthen
GABA-ergic inhibitory processes in brain