Слайд 2
Roadmap
How are processes represented and controlled by the
OS.
Process states which characterize the behaviour of processes.
Data structures used to manage processes.
Ways in which the OS uses these data structures to control process execution.
Discuss process management in UNIX SVR4.
Слайд 3
Requirements of an
Operating System
Fundamental Task: Process Management
The Operating
System must
Interleave the execution of multiple processes
Allocate resources to
processes, and protect the resources of each process from other processes,
Enable processes to share and exchange information,
Enable synchronization among processes.
Слайд 4
Concepts
From earlier chapters we saw:
Computer platforms consists of
a collection of hardware resources
Computer applications are developed to
perform some task
It is inefficient for applications to be written directly for a given hardware platform
Слайд 5
Concepts cont…
OS provides an interface for applications to
use
OS provides a representation of resources that can be
requested and accessed by application
Слайд 6
The OS Manages
Execution of Applications
Resources are made
available to multiple applications
The processor is switched among multiple
application
The processor and I/O devices can be used efficiently
Слайд 7
What is a “process”?
A program in execution
An instance
of a program running on a computer
The entity that
can be assigned to and executed on a processor
A unit of activity characterized by the execution of a sequence of instructions, a current state, and an associated set of system instructions
Слайд 8
Process Elements
A process is comprised of:
Program code (possibly
shared)
A set of data
A number of attributes describing the
state of the process
Слайд 9
Process Elements
While the process is running it has
a number of elements including
Identifier
State
Priority
Program counter
Memory pointers
Context data
I/O status
information
Accounting information
Слайд 10
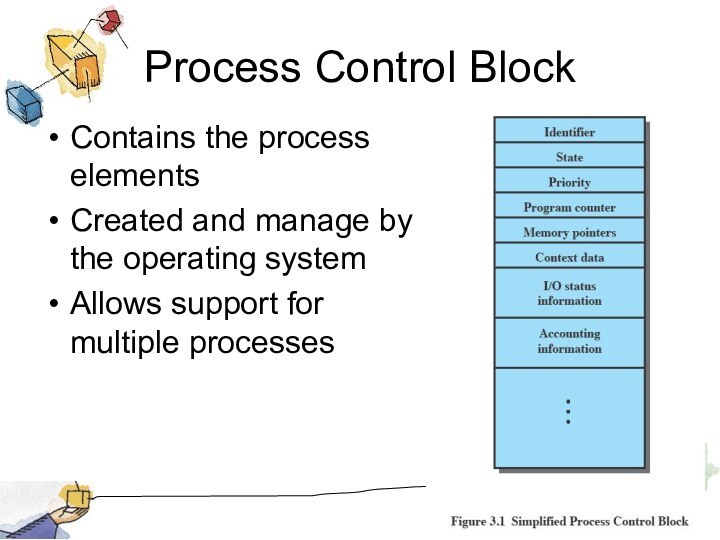
Process Control Block
Contains the process elements
Created and manage
by the operating system
Allows support for multiple processes
Слайд 11
Trace of the Process
The behavior of an individual
process is shown by listing the sequence of instructions
that are executed
This list is called a Trace
Dispatcher is a small program which switches the processor from one process to another
Слайд 12
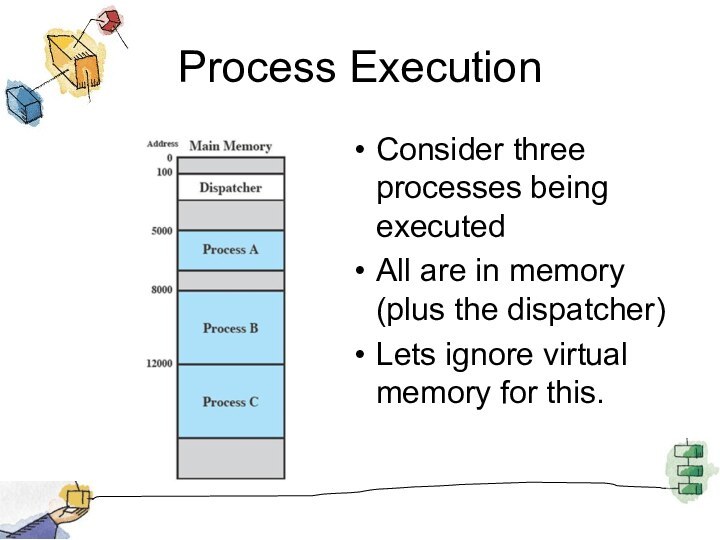
Process Execution
Consider three processes being executed
All are in
memory (plus the dispatcher)
Lets ignore virtual memory for this.
Слайд 13
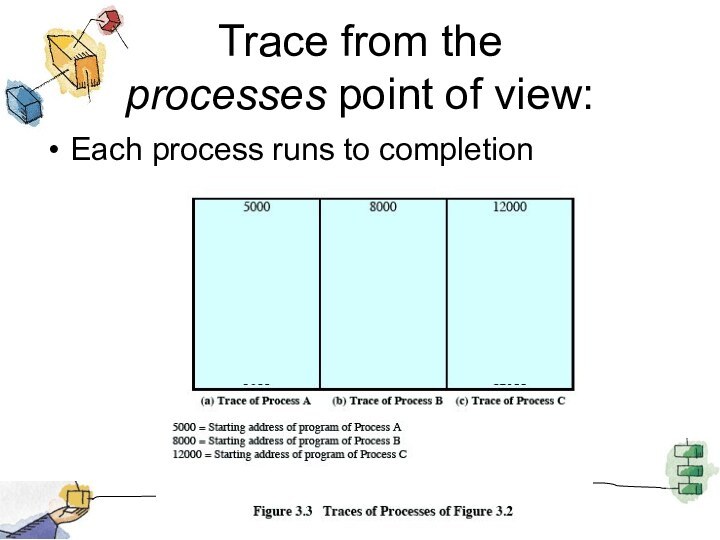
Trace from the
processes point of view:
Each process
runs to completion
Слайд 14
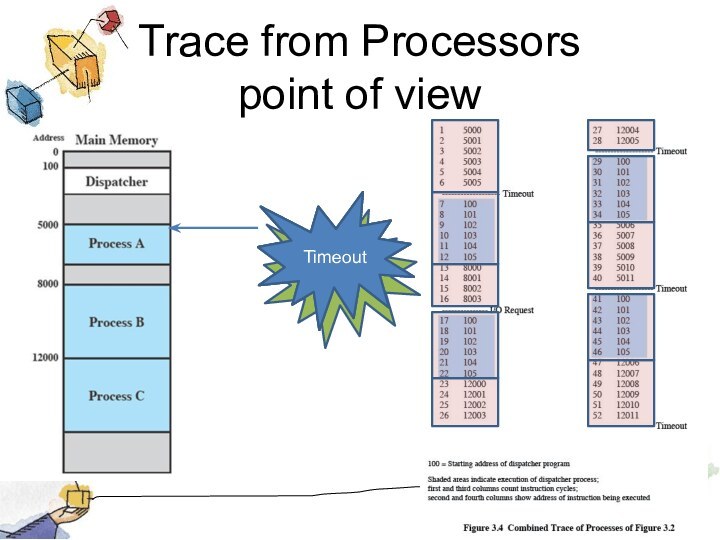
Trace from Processors
point of view
Timeout
I/O
Timeout
Timeout
Слайд 15
Roadmap
How are processes represented and controlled by the
OS.
Process states which characterize the behaviour of processes.
Data structures used to manage processes.
Ways in which the OS uses these data structures to control process execution.
Discuss process management in UNIX SVR4.
Слайд 16
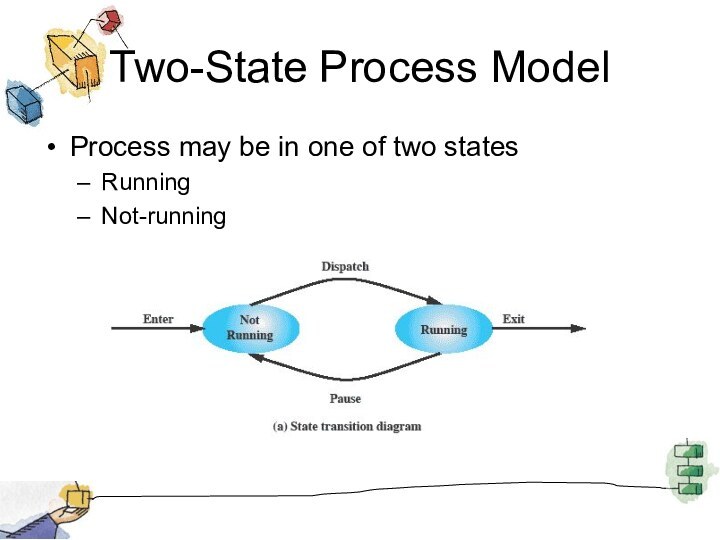
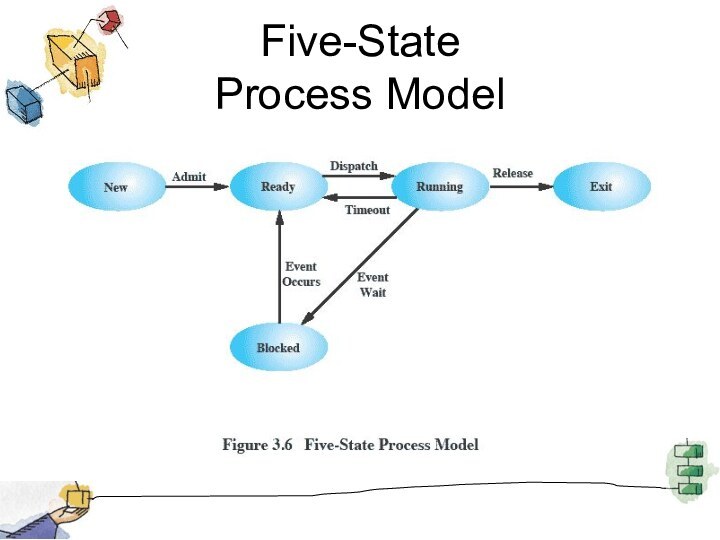
Two-State Process Model
Process may be in one of
two states
Running
Not-running
Слайд 17
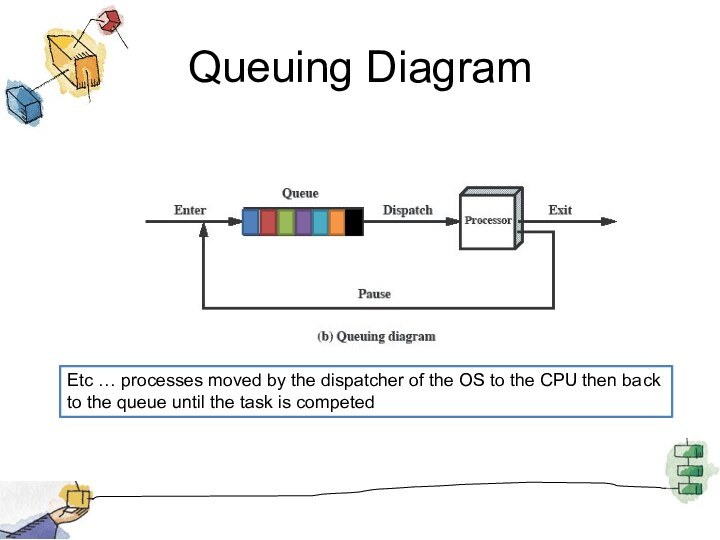
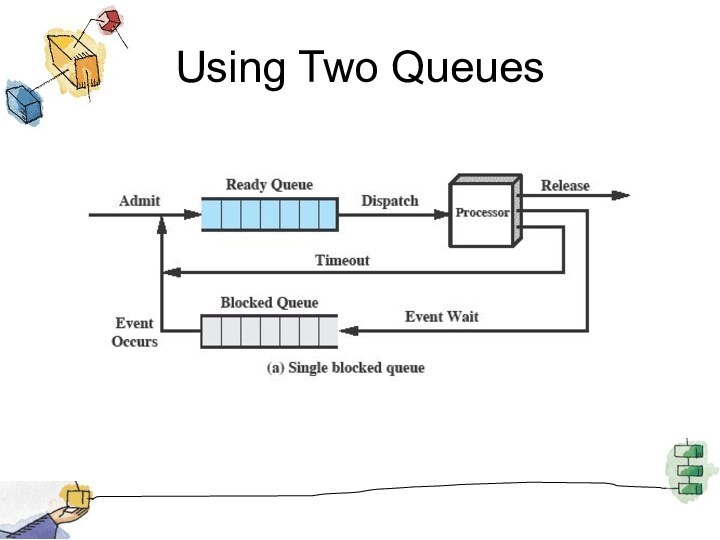
Queuing Diagram
Etc … processes moved by the dispatcher
of the OS to the CPU then back to
the queue until the task is competed
Слайд 18
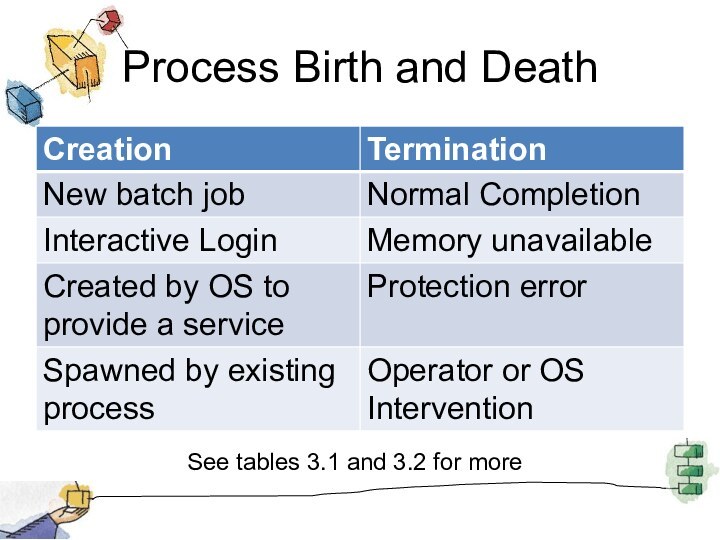
Process Birth and Death
See tables 3.1 and 3.2
for more
Слайд 19
Process Creation
The OS builds a data structure to
manage the process
Traditionally, the OS created all processes
But it
can be useful to let a running process create another
This action is called process spawning
Parent Process is the original, creating, process
Child Process is the new process
Слайд 20
Process Termination
There must be some way that a
process can indicate completion.
This indication may be:
A HALT instruction
generating an interrupt alert to the OS.
A user action (e.g. log off, quitting an application)
A fault or error
Parent process terminating
Слайд 24
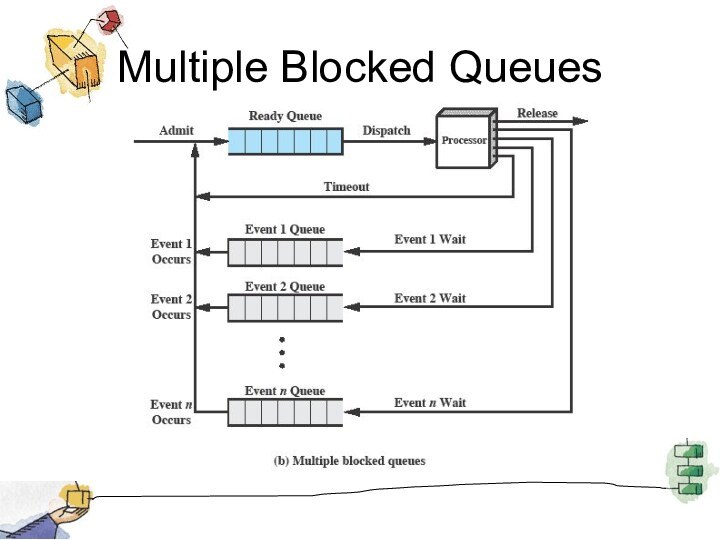
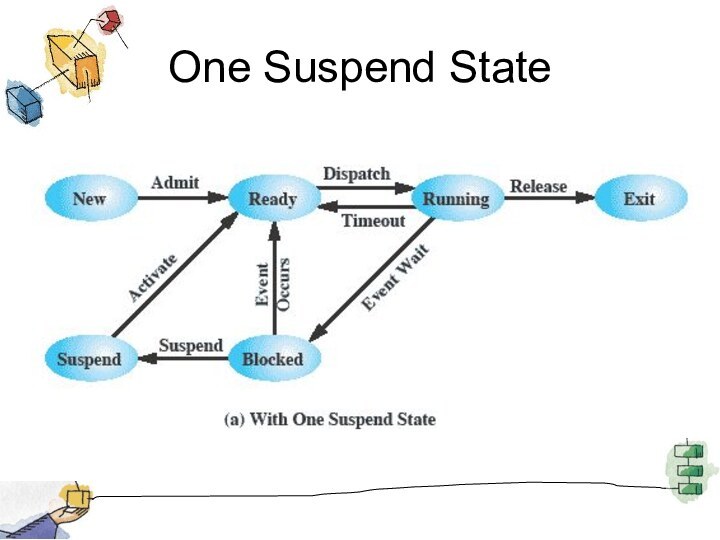
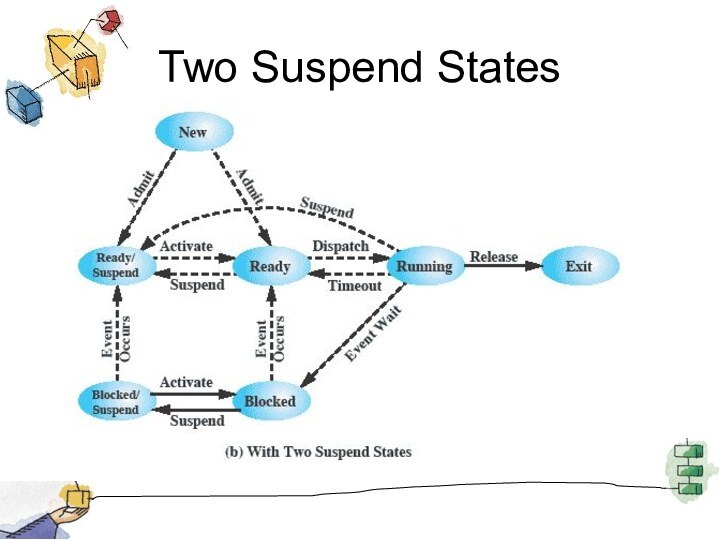
Suspended Processes
Processor is faster than I/O so all
processes could be waiting for I/O
Swap these processes to
disk to free up more memory and use processor on more processes
Blocked state becomes suspend state when swapped to disk
Two new states
Blocked/Suspend
Ready/Suspend
Слайд 27
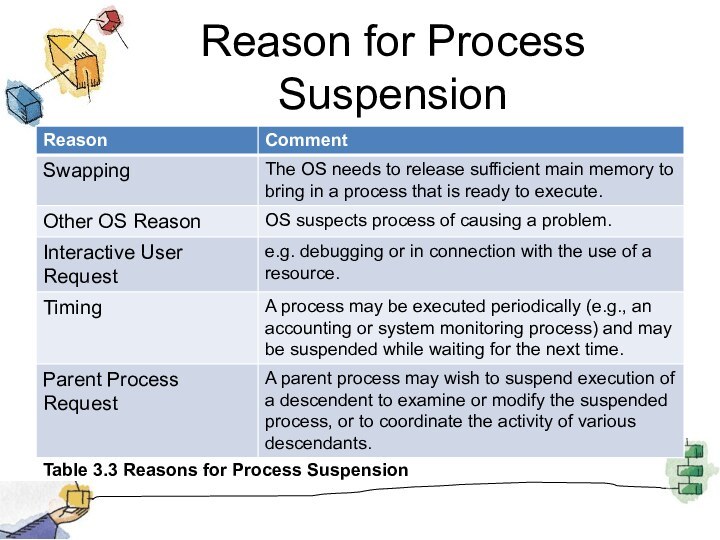
Reason for Process Suspension
Table 3.3 Reasons for Process
Suspension
Слайд 28
Roadmap
How are processes represented and controlled by the
OS.
Process states which characterize the behaviour of processes.
Data structures used to manage processes.
Ways in which the OS uses these data structures to control process execution.
Discuss process management in UNIX SVR4.
Слайд 30
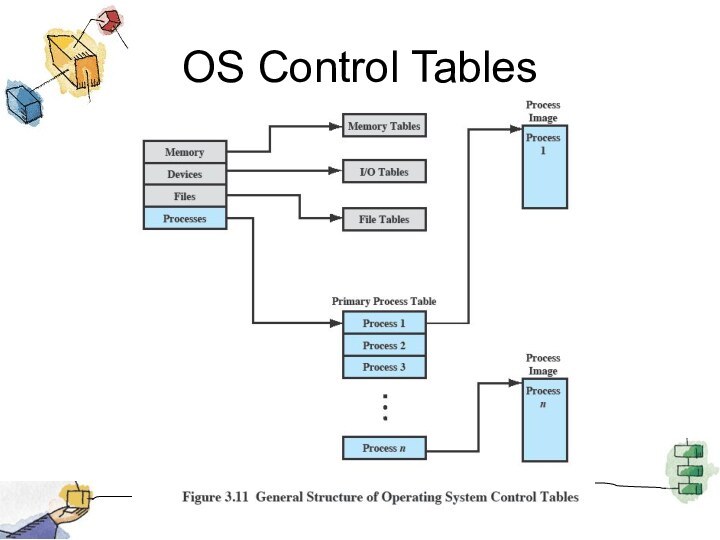
Operating System
Control Structures
For the OS is to
manage processes and resources, it must have information about
the current status of each process and resource.
Tables are constructed for each entity the operating system manages
Слайд 32
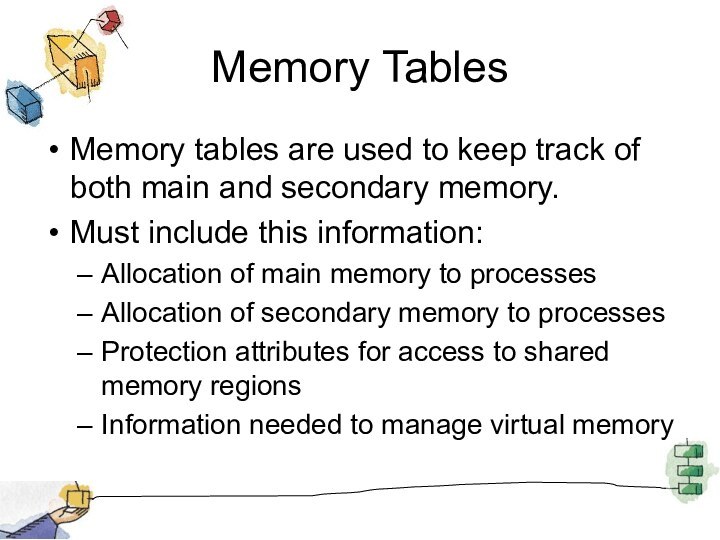
Memory Tables
Memory tables are used to keep track
of both main and secondary memory.
Must include this
information:
Allocation of main memory to processes
Allocation of secondary memory to processes
Protection attributes for access to shared memory regions
Information needed to manage virtual memory
Слайд 33
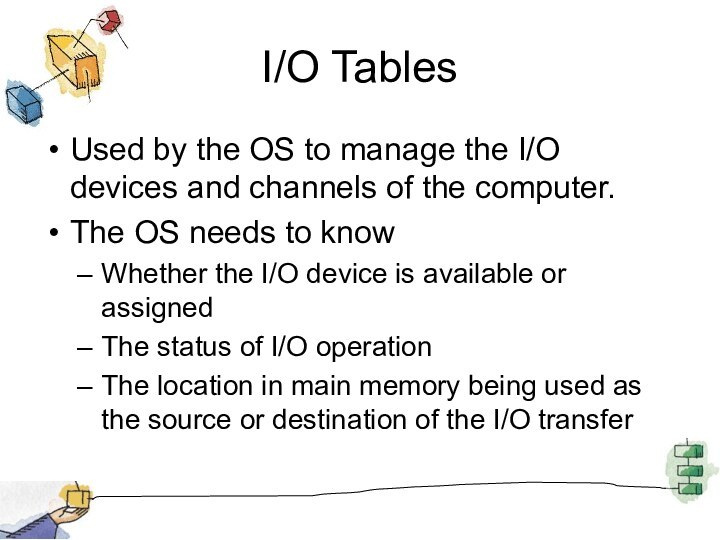
I/O Tables
Used by the OS to manage the
I/O devices and channels of the computer.
The OS needs
to know
Whether the I/O device is available or assigned
The status of I/O operation
The location in main memory being used as the source or destination of the I/O transfer
Слайд 34
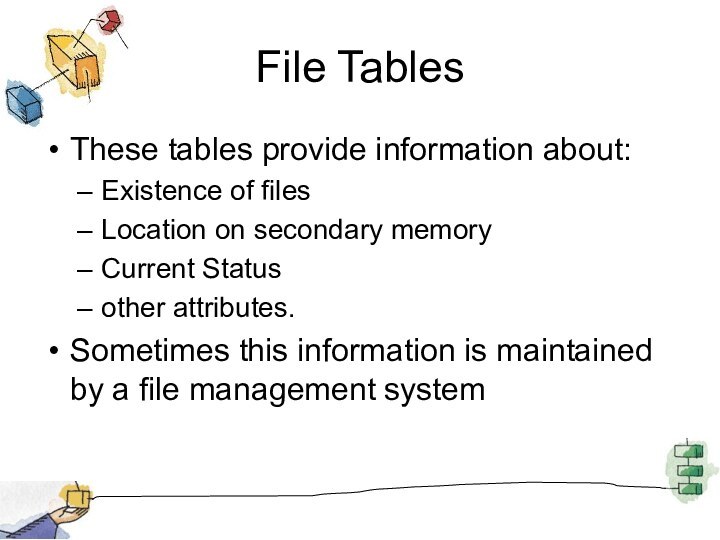
File Tables
These tables provide information about:
Existence of files
Location
on secondary memory
Current Status
other attributes.
Sometimes this information is maintained
by a file management system
Слайд 35
Process Tables
To manage processes the OS needs to
know details of the processes
Current state
Process ID
Location in
memory
etc
Process control block
Process image is the collection of program. Data, stack, and attributes
Слайд 36
Process Attributes
We can group the process control block
information into three general categories:
Process identification
Processor state information
Process control
information
Слайд 37
Process Identification
Each process is assigned a unique numeric
identifier.
Many of the other tables controlled by the OS
may use process identifiers to cross-reference process tables
Слайд 38
Processor State
Information
This consists of the contents of
processor registers.
User-visible registers
Control and status registers
Stack pointers
Program status
word (PSW)
contains status information
Example: the EFLAGS register on Pentium processors
Слайд 39
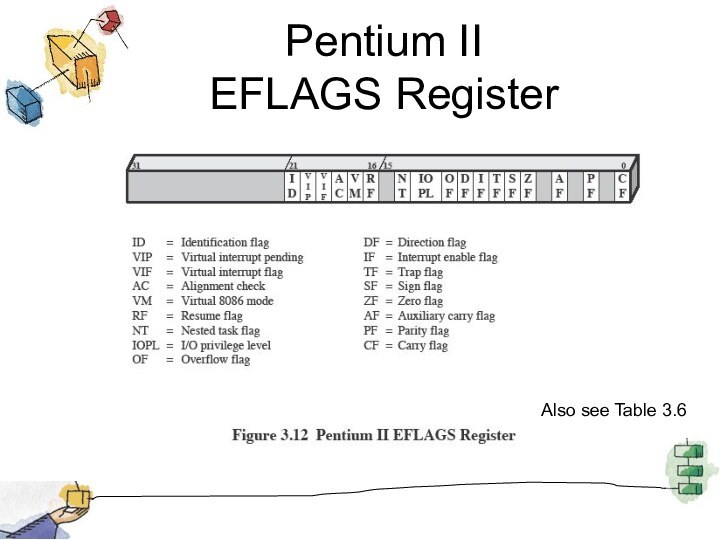
Pentium II
EFLAGS Register
Also see Table 3.6
Слайд 40
Process Control
Information
This is the additional information needed by
the OS to control and coordinate the various active
processes.
See table 3.5 for scope of information
Слайд 41
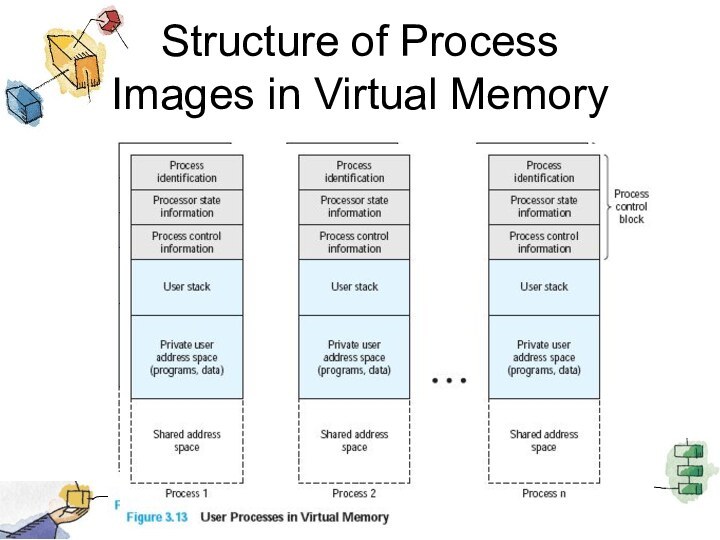
Structure of Process
Images in Virtual Memory
Слайд 42
Role of the
Process Control Block
The most important
data structure in an OS
It defines the state
of the OS
Process Control Block requires protection
A faulty routine could cause damage to the block destroying the OS’s ability to manage the process
Any design change to the block could affect many modules of the OS
Слайд 43
Roadmap
How are processes represented and controlled by the
OS.
Process states which characterize the behaviour of processes.
Data structures used to manage processes.
Ways in which the OS uses these data structures to control process execution.
Discuss process management in UNIX SVR4.
Слайд 44
Modes of Execution
Most processors support at least two
modes of execution
User mode
Less-privileged mode
User programs typically execute in
this mode
System mode
More-privileged mode
Kernel of the operating system
Слайд 45
Process Creation
Once the OS decides to create a
new process it:
Assigns a unique process identifier
Allocates space for
the process
Initializes process control block
Sets up appropriate linkages
Creates or expand other data structures
Слайд 46
Switching Processes
Several design issues are raised regarding process
switching
What events trigger a process switch?
We must distinguish
between mode switching and process switching.
What must the OS do to the various data structures under its control to achieve a process switch?
Слайд 47
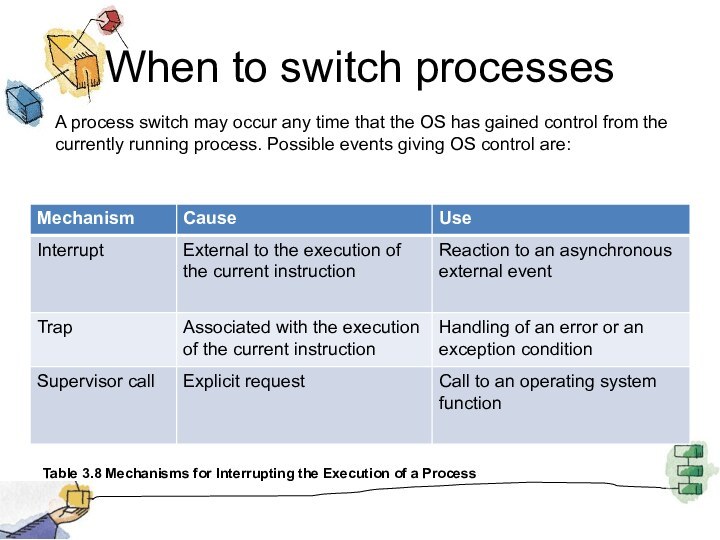
When to switch processes
Table 3.8 Mechanisms for Interrupting
the Execution of a Process
A process switch may occur
any time that the OS has gained control from the currently running process. Possible events giving OS control are:
Слайд 48
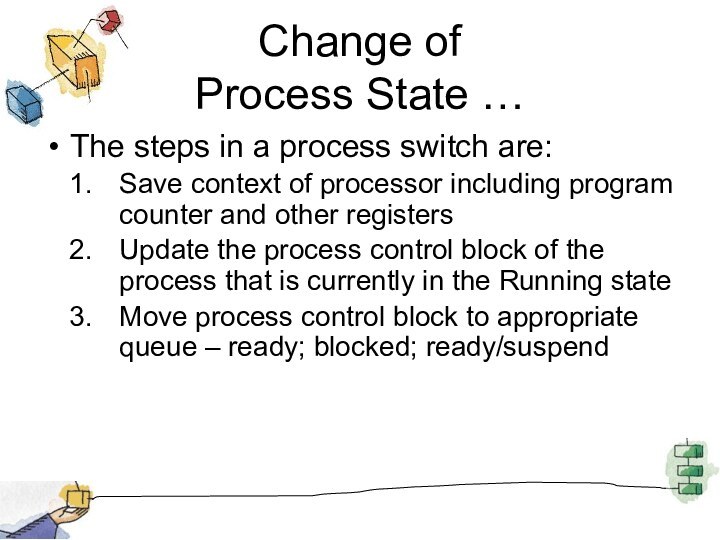
Change of
Process State …
The steps in a
process switch are:
Save context of processor including program counter
and other registers
Update the process control block of the process that is currently in the Running state
Move process control block to appropriate queue – ready; blocked; ready/suspend
Слайд 49
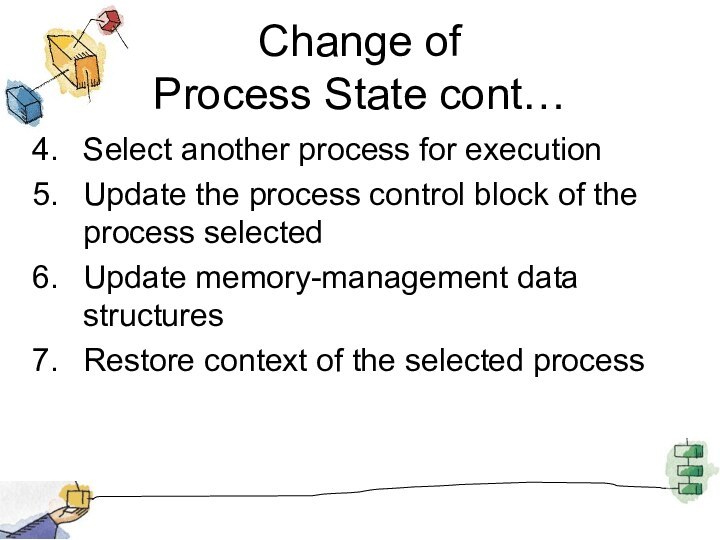
Change of
Process State cont…
Select another process for
execution
Update the process control block of the process selected
Update
memory-management data structures
Restore context of the selected process
Слайд 50
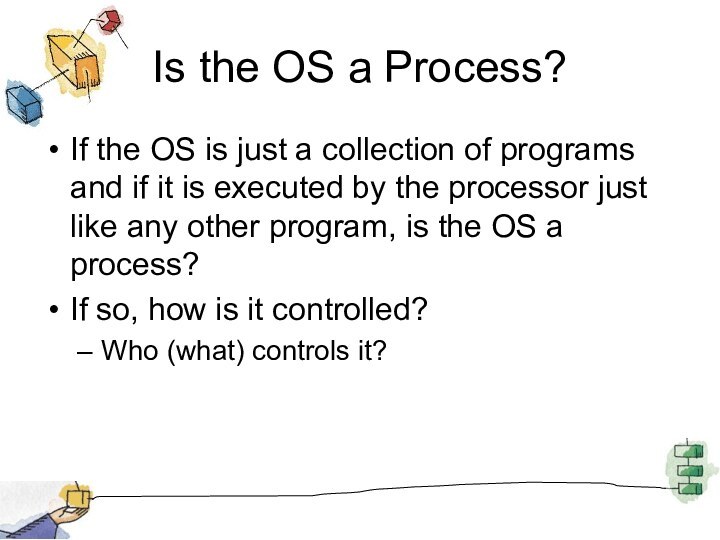
Is the OS a Process?
If the OS is
just a collection of programs and if it is
executed by the processor just like any other program, is the OS a process?
If so, how is it controlled?
Who (what) controls it?
Слайд 51
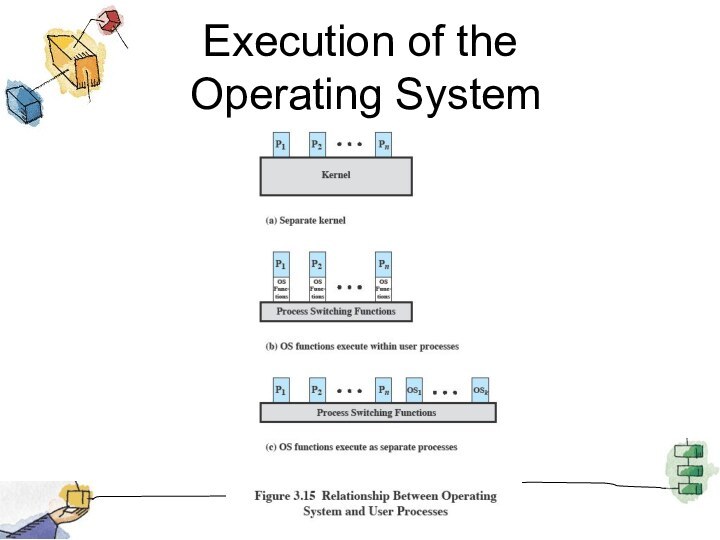
Execution of the
Operating System
Слайд 52
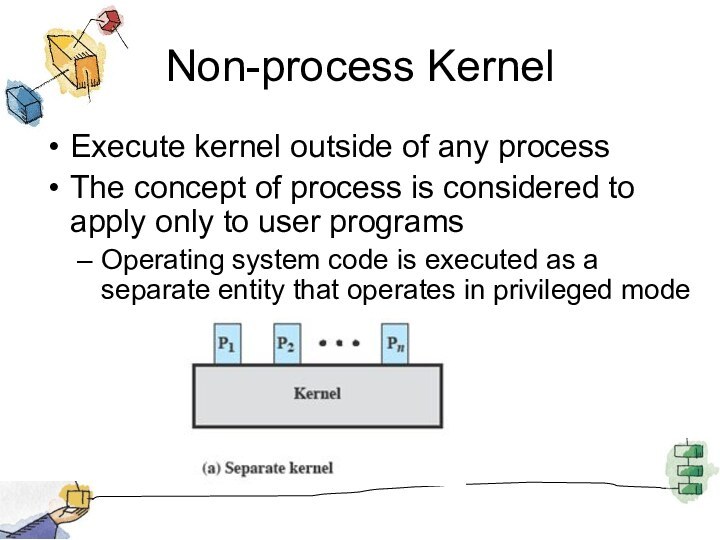
Non-process Kernel
Execute kernel outside of any process
The concept
of process is considered to apply only to user
programs
Operating system code is executed as a separate entity that operates in privileged mode
Слайд 53
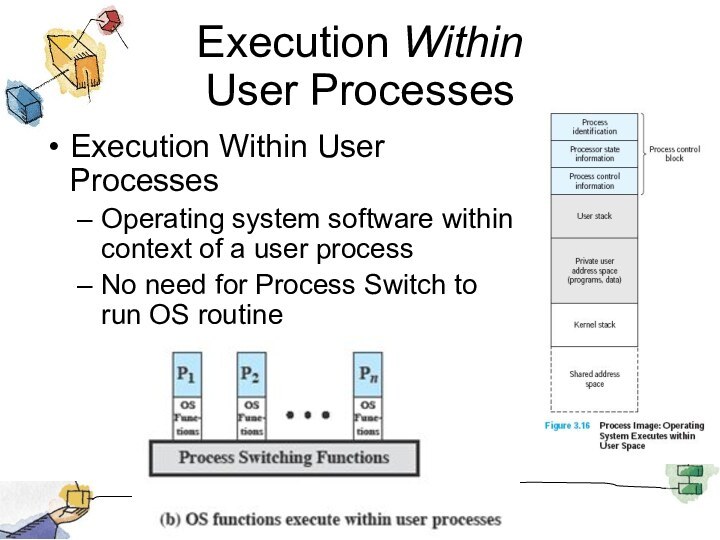
Execution Within
User Processes
Execution Within User Processes
Operating system
software within context of a user process
No need for
Process Switch to run OS routine
Слайд 54
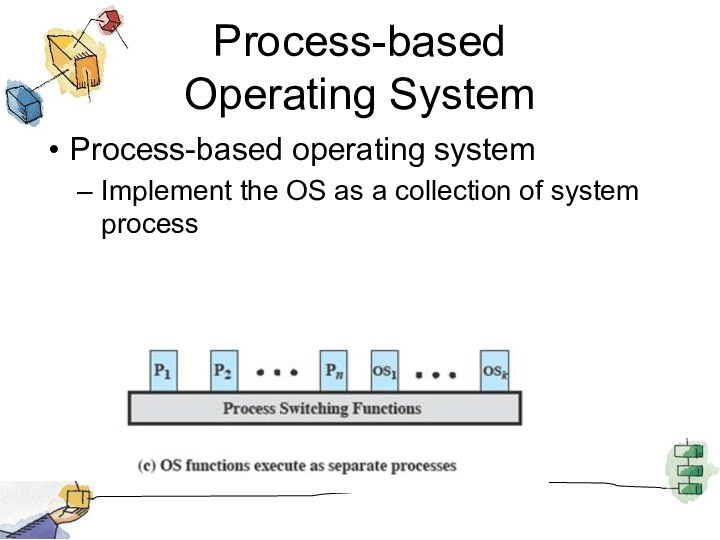
Process-based
Operating System
Process-based operating system
Implement the OS as
a collection of system process
Слайд 55
Security Issues
An OS associates a set of privileges
with each process.
Highest level being administrator, supervisor, or root,
access.
A key security issue in the design of any OS is to prevent anything (user or process) from gaining unauthorized privileges on the system
Especially - from gaining root access.
Слайд 56
System access threats
Intruders
Masquerader (outsider)
Misfeasor (insider)
Clandestine user (outside or
insider)
Malicious software (malware)
Слайд 57
Countermeasures:
Intrusion Detection
Intrusion detection systems are typically designed
to detect human intruder and malicious software behaviour.
May be
host or network based
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) typically comprise
Sensors
Analyzers
User Interface
Слайд 58
Countermeasures:
Authentication
Two Stages:
Identification
Verification
Four Factors:
Something the individual knows
Something the
individual possesses
Something the individual is (static biometrics)
Something the individual
does (dynamic biometrics)
Слайд 59
Countermeasures:
Access Control
A policy governing access to resources
A
security administrator maintains an authorization database
The access control function
consults this to determine whether to grant access.
An auditing function monitors and keeps a record of user accesses to system resources.
Слайд 60
Countermeasures:
Firewalls
Traditionally, a firewall is a dedicated computer
that:
interfaces with computers outside a network
has special security
precautions built into it to protect sensitive files on computers within the network.
Слайд 61
Roadmap
How are processes represented and controlled by the
OS.
Process states which characterize the behaviour of processes.
Data structures used to manage processes.
Ways in which the OS uses these data structures to control process execution.
Discuss process management in UNIX SVR4.
Слайд 62
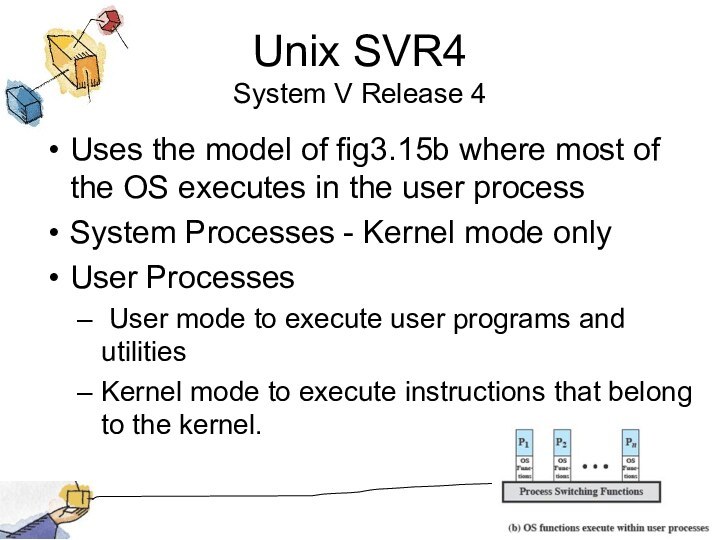
Unix SVR4
System V Release 4
Uses the model of
fig3.15b where most of the OS executes in the
user process
System Processes - Kernel mode only
User Processes
User mode to execute user programs and utilities
Kernel mode to execute instructions that belong to the kernel.
Слайд 63
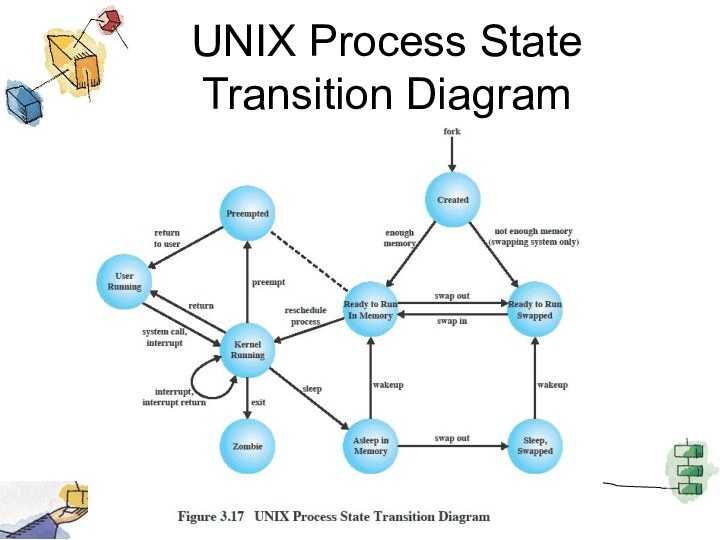
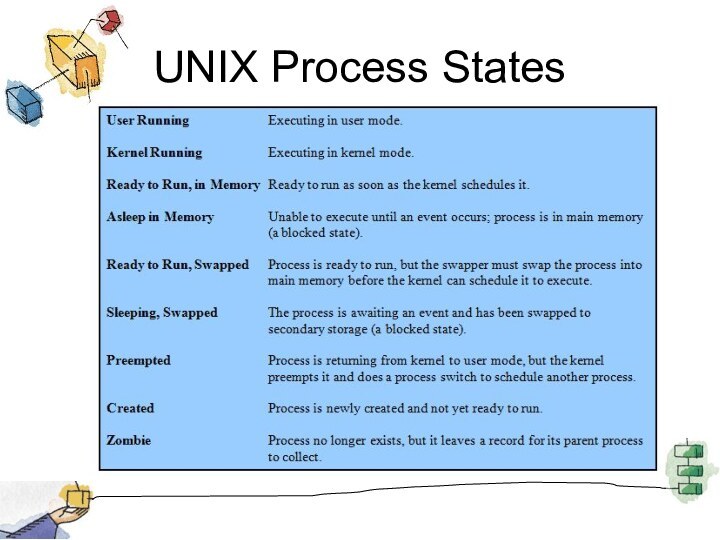
UNIX Process State Transition Diagram
Слайд 65
A Unix Process
A process in UNIX is a
set of data structures that provide the OS with
all of the information necessary to manage and dispatch processes.
See Table 3.10 which organizes the elements into three parts:
user-level context,
register context, and
system-level context.
Слайд 66
Process Creation
Process creation is by means of the
kernel system call,fork( ).
This causes the OS, in Kernel
Mode, to:
Allocate a slot in the process table for the new process.
Assign a unique process ID to the child process.
Copy of process image of the parent, with the exception of any shared memory.
Слайд 67
Process Creation
cont…
Increment the counters for any files
owned by the parent, to reflect that an additional
process now also owns those files.
Assign the child process to the Ready to Run state.
Returns the ID number of the child to the parent process, and a 0 value to the child process.