- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Process equipment for medical textile industry
Содержание
- 2. Brief History of X-Ray Discovered in 1895
- 4. FluoroscopyIt is used for viewing organs or passage of substances through organs
- 5. Computed tomography Computed tomography (CT scanning)
- 6. RadiographBones contain much calcium , which due
- 7. Adverse effectsDiagnostic X-rays (primarily from CT scans
- 8. Radiation Safety and DoseReducing patient exposure-Advances in
- 9. Words can be like X-rays if you
- 10. Скачать презентацию
- 11. Похожие презентации
Brief History of X-Ray Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Konrad RoentgenElectromagnetic waveTravels 186,000 miles/secShort wavelengthPenetrates solid objectsReacts with photographic film
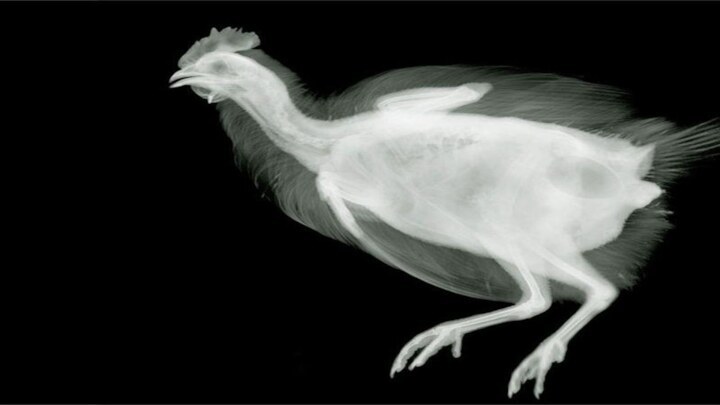









Слайд 5
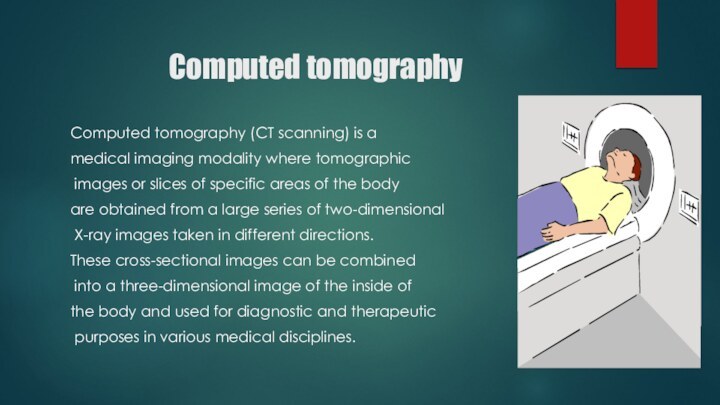
Computed tomography
Computed tomography (CT scanning) is a
medical imaging modality where tomographic
images or slices of
specific areas of the body are obtained from a large series of two-dimensional
X-ray images taken in different directions.
These cross-sectional images can be combined
into a three-dimensional image of the inside of
the body and used for diagnostic and therapeutic
purposes in various medical disciplines.
Слайд 6
Radiograph
Bones contain much calcium , which due to
its relatively high atomic number absorbs x-rays efficiently. This
reduces the amount of X-rays reaching the detector in the shadow of the bones, making them clearly visible on the radiograph.
Слайд 7
Adverse effects
Diagnostic X-rays (primarily from CT scans due
to the large dose used) increase the risk of
developmental problems and cancer in those exposed. X rays are classified as carcinogenic ones.
Слайд 8
Radiation Safety and Dose
Reducing patient exposure
-Advances in technology
-Assessment
of benefit-to-risk ratio
-Prevent serious damage from radiation by limiting
radiation dose levels-Individual dose limits set
Слайд 9 Words can be like X-rays if you use
them properly--they'll go
through anything. You read and you're
pierced.” ~ Aldous Huxley





























