- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Psychology of management
Содержание
- 2. Module 1. Subject and history of psychology of Management
- 3. Topic 1. Psychology of Management as a
- 4. Management is a process of affecting particular
- 5. Management in all business and organizational activities
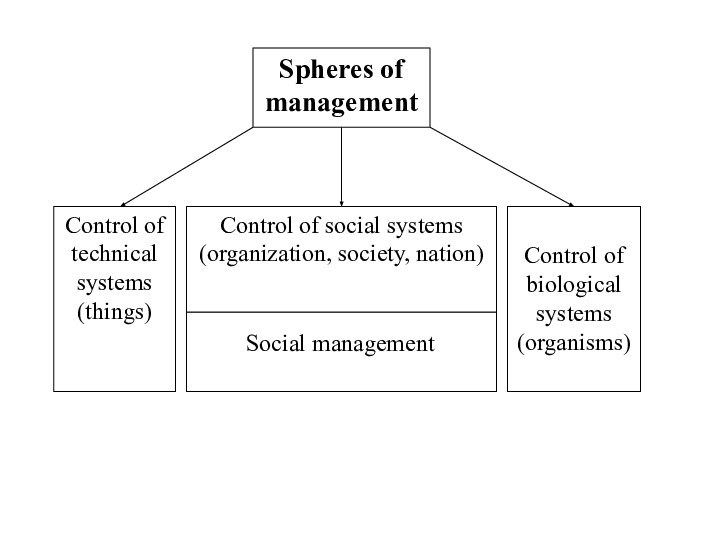
- 6. Social managementControl of biological systems (organisms)
- 7. What does social management mean?What are objectives of social management?
- 8. Objectives of social management:The stateParticular regionsCommercial and non-profit organizationsUnits of organizationCertain groups of people
- 9. What does organization mean?
- 10. ORGANIZATION is a group of people whose
- 11. Any organization is an open system.To receive
- 12. People are the most valuable what any organization has
- 13. Psychology of management is a branch of
- 14. Subject of management psychology is a psychology
- 15. Main task of managerial psychology is analyzing
- 16. Objects of management include: Innovations Manufacturing Market
- 17. Major problem of managerial psychology is:How to motivate people to achieve goals of organization?
- 18. Two main subsystems of management systemSubsystem which manageThe headManagerEmploerDirectorExecutersWorkersEmploeesStaffSubsystem which are managedSubject of managementObject of management
- 19. Management structuresubject of management is one who manages.object of management is one (thing) being managed.
- 20. 1. Subject of management is a manager
- 21. Can management be successful? When?
- 22. Management can be successful if:Subject of management
- 23. Management is a certain type of interaction
- 24. change in objectchange in object behaviorcollection, transmission
- 25. Feedback mechanism is ability moving information about
- 26. Systems of managementOpen-loop control systems(no feedback)Closed-loop control systems(with feedback )
- 27. Management is influence of managing system (subject
- 28. Levels of managementLevel of management is a
- 30. Management functions
- 31. Two groups of management functions:General management functions
- 32. General
- 33. Topic 2. THE history of Psychology of
- 34. SCHOOLS in management1. Classical school of managementSchool
- 35. Classical school of managementAdministrative managementemphasis on organization
- 36. Three main moments of scientific management school
- 37. The contribution of scientific management school to
- 38. Administrative management schoolHenri Fayol (1841-1925)the first who
- 39. The purpose of administrative management school is
- 40. The contribution of administrative management school to
- 41. School of human relations Mary Parker Follett
- 42. managerworkercaresatisfactionProductivity and efficiency
- 43. The purpose of human relation school
- 44. The school ofhuman relationsfocused on an employee
- 45. The basic purpose of behavioral science school:Increase
- 46. Main representatives of behavioral science school Chester
- 47. The basic ideas of human relations schoolManagement
- 48. Contribution of human relations school to theory
- 49. Quantitative school of management orschool of management
- 51. Processing approachManagement is considered as a process
- 52. Systematic approachOrganization is considered as complex, open,
- 53. Systematic approachOrganization is a system:ComplexOpenSocial and technicalinputprocessfeedbackoutput
- 54. Situational approachFocused on situationSituation is particular conditions
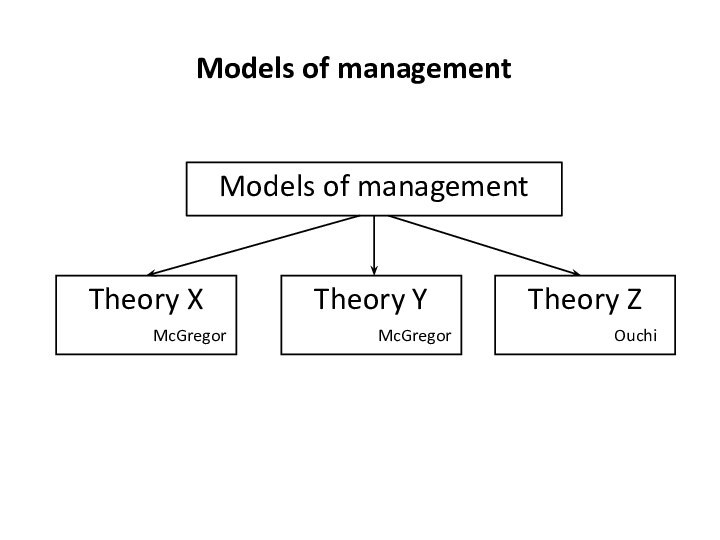
- 55. Models of management Models of management Theory XTheory YTheory ZMcGregorOuchiMcGregor
- 57. Скачать презентацию
- 58. Похожие презентации









































Слайд 4 Management is a process of affecting particular system
in order to achieve certain goals.
Any system can be
an object of managementSYSTEM is a group of interconnected elements forming single whole and cooperating for achieving goals.
Слайд 5 Management in all business and organizational activities is
the act of getting people together to accomplish desired
goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively.
Слайд 8
Objectives of social management:
The state
Particular regions
Commercial and non-profit
organizations
Units of organization
Certain groups of people
Слайд 10 ORGANIZATION is a group of people whose activity
is coordinated consciously for achieving certain goals.
Requirements:
two or more
people consider themselves as a part of a group; all members of a group accept a goal or more purposes as common;
members of a group work together consciously to achieve an important goal for everyone.
Слайд 11
Any organization is an open system.
To receive resources
from external surrounding (input)
To produce products
To return products into
external surrounding (output) Open system deals with external surrounding.
There are 3 processes in any organization:
All these processes are realized by people.
Слайд 13
Psychology of management is a branch of psychology.
Behavior
Communication
Activity
Individuality
Mind
and etc.
Person and his psyche is a subject
of psychology:Psychology of management studies psychological aspects of management.
Слайд 14 Subject of management psychology is a psychology phenomena
in management systems and in processes of human relationships
and communications.Psychology of management studies following:
Psychological features of the heads and executors - their qualities and psychological characteristic of a commanding activity.
Various favorable or negative factors influencing a mental condition of a person.
Relationships between the head and executors, relationships between members of supervised collective.
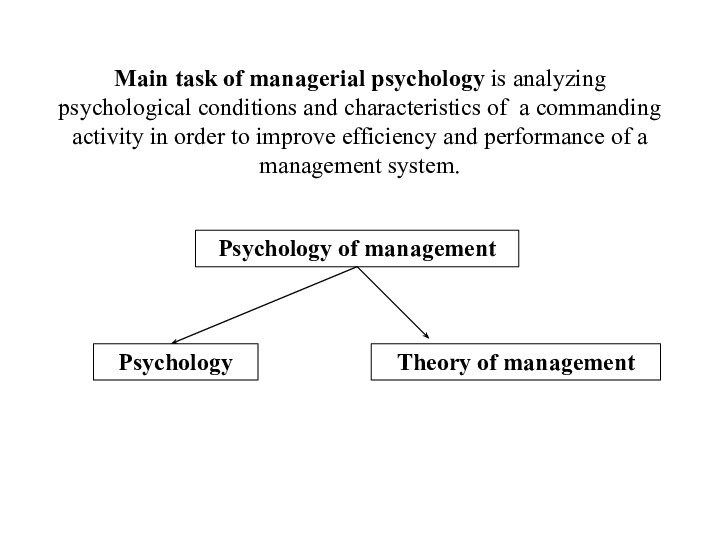
Слайд 15 Main task of managerial psychology is analyzing psychological
conditions and characteristics of a commanding activity in order
to improve efficiency and performance of a management system.Psychology of management
Psychology
Theory of management
Слайд 16
Objects of management include:
Innovations
Manufacturing
Market
Finance
Information
Supplies
Personnel
Control of these processes is connected
with management of people behavior
Слайд 17
Major problem of managerial psychology is:
How to motivate
people to achieve goals of organization?
Слайд 18
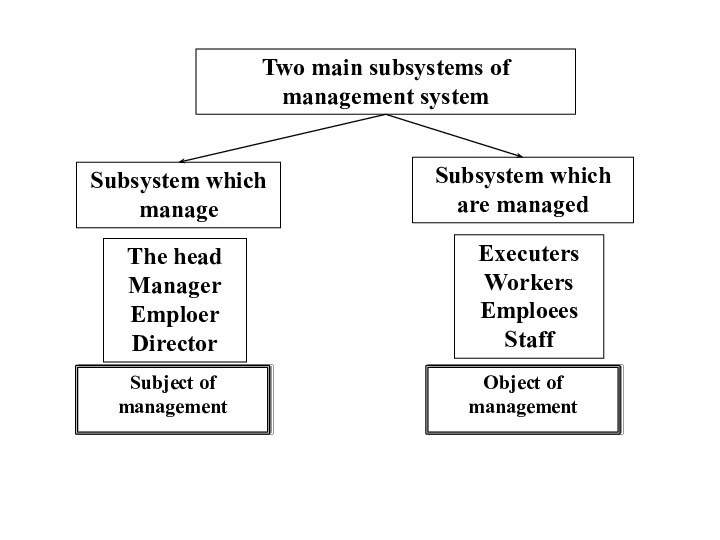
Two main subsystems of management system
Subsystem which manage
The
head
Manager
Emploer
Director
Executers
Workers
Emploees
Staff
Subsystem which are managed
Subject of management
Object of management
Слайд 19
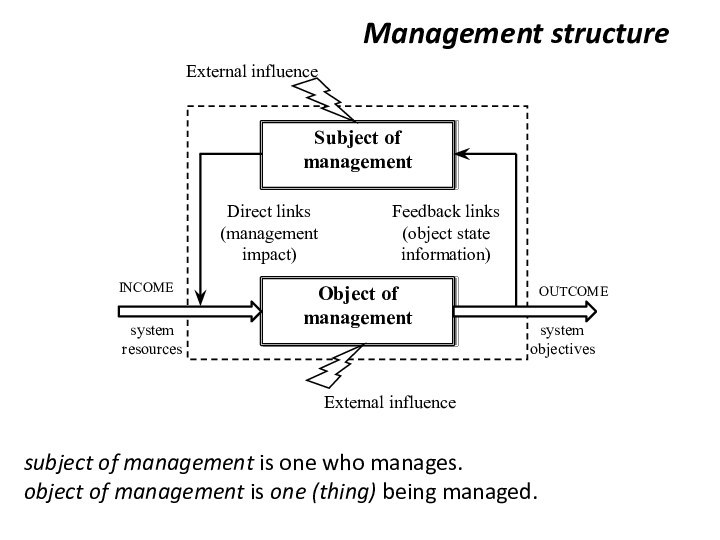
Management structure
subject of management is one who manages.
object
of management is one (thing) being managed.
Слайд 20 1. Subject of management is a manager (head)
who has administrative responsibilities and performs administrative activity.
2. Object
of management is workers or groups of workers who are managed by the head. Subject of management influences object of management using certain management impacts.3. Management impacts (or management methods) means system of actions used by subject of management to influence object of management.
4. System objectives are desired future state of management object. They are formulated by subject of management.
Слайд 22
Management can be successful if:
Subject of management sets
objectives of activity and it has motivation and possibility
to manage.Object can achieve these objectives and it has motivation and possibility to work.
Слайд 23 Management is a certain type of interaction existing
between management subject and object.
In this case:
Subject of management
performs specific activities aimed at achieving a goal of management towards object of management.Activity of managing subject includes:
knowledge of capabilities of managed object
exploring external conditions sustaining or preventing achievement of a goal by object of management
making decisions by subject of management for achieving a goal of management
Objects of management have built-in mechanism.
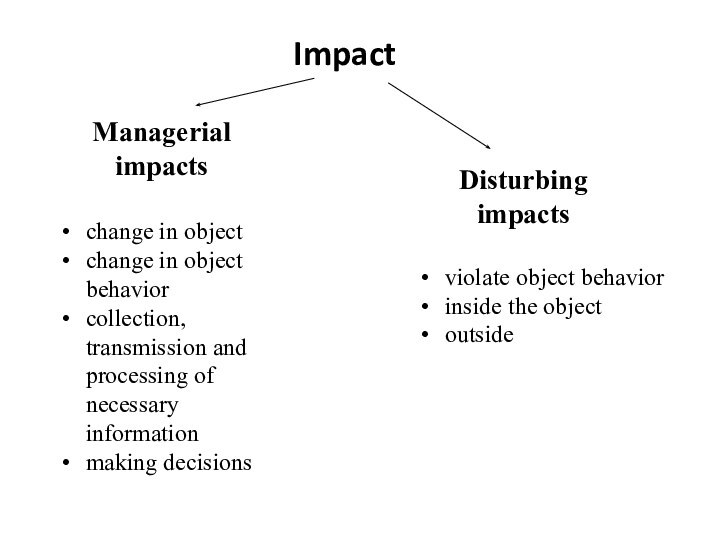
Слайд 24
change in object
change in object behavior
collection, transmission and
processing of necessary information
making decisions
violate object behavior
inside the
objectoutside
Impact
Managerial impacts
Disturbing impacts
Слайд 25 Feedback mechanism is ability moving information about state
of management object to management subject as result of
management impacts.Direct link means move of management impacts from subject to object of management.
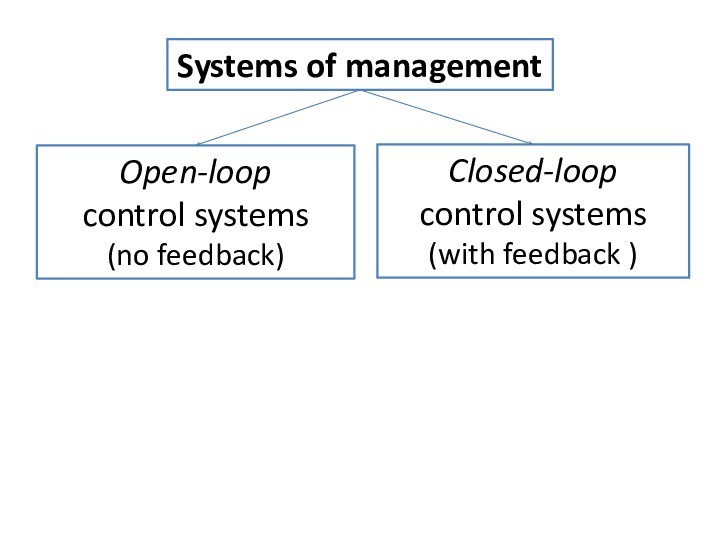
Слайд 26
Systems of management
Open-loop
control systems
(no feedback)
Closed-loop
control systems
(with
feedback )
Слайд 27 Management is influence of managing system (subject of
management) on managed system (object of management) for the
purpose to move managed system in required condition.
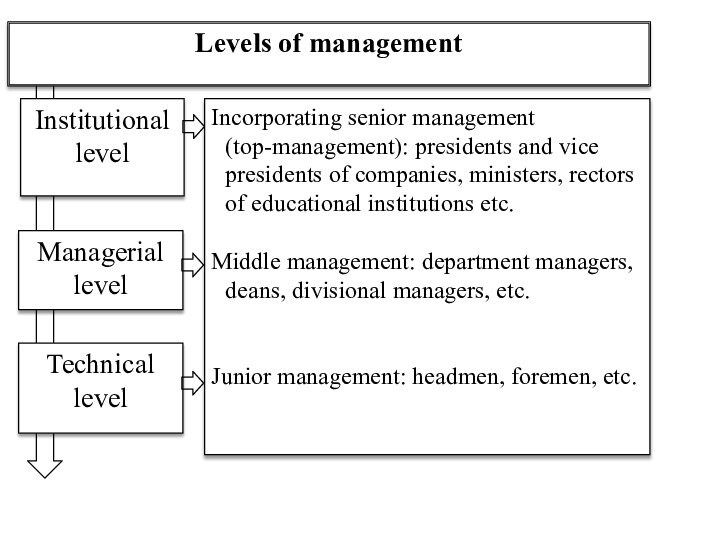
Слайд 28
Levels of management
Level of management is a part
of organization where independent decisions can be made without
permission of higher or subordinate parts.
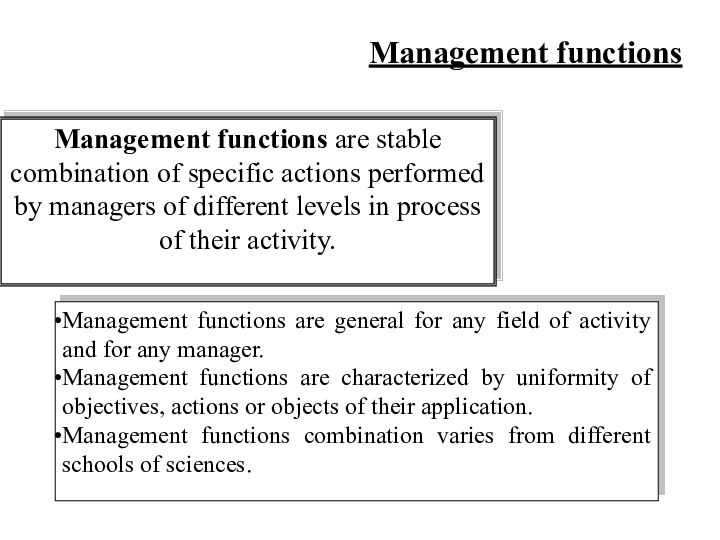
Слайд 31
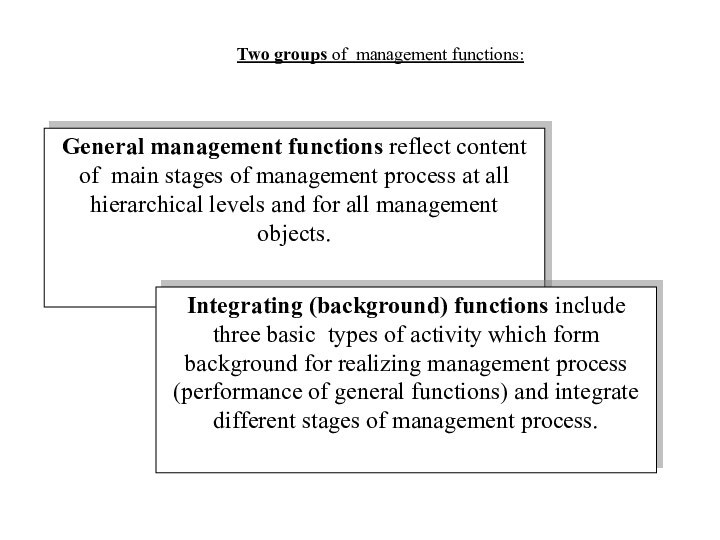
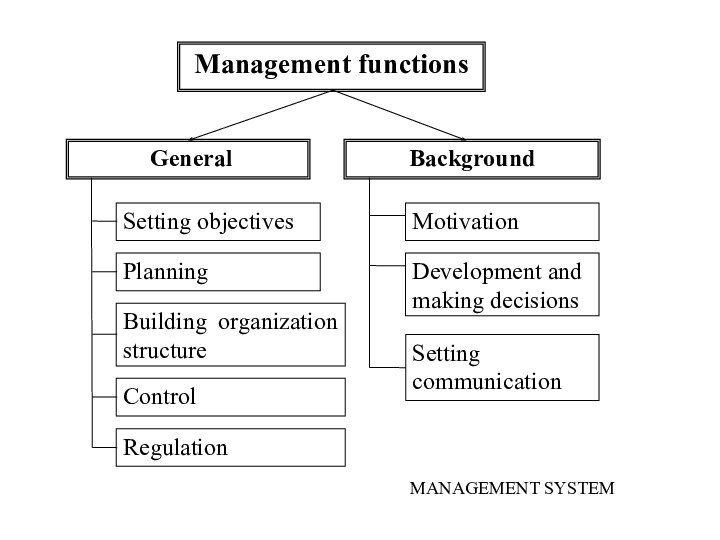
Two groups of management functions:
General management functions reflect
content of main stages of management process at all
hierarchical levels and for all management objects.Integrating (background) functions include three basic types of activity which form background for realizing management process (performance of general functions) and integrate different stages of management process.
Слайд 33 Topic 2. THE history of Psychology of Management
building and main models of management
The beginning of management
is considered the beginning and development of industrial manufacture
Слайд 34
SCHOOLS in management
1. Classical school of management
School of
scientific management
Administrative school of management
2. School of human relations
3.
Quantitative school of management
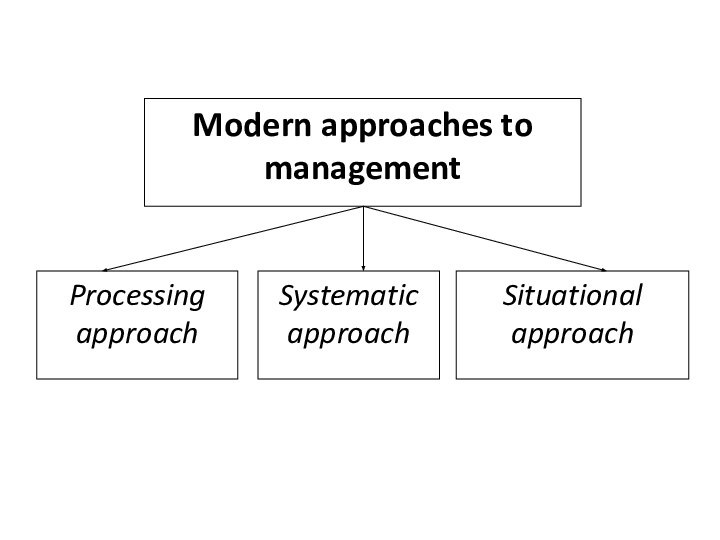
or school of management science Processing approach
Systematic approach
Situational approach
Слайд 35
Classical school of management
Administrative management
emphasis on organization as
a whole
Main representatives:
Henri Fayol (1841-1925)
Max Weber (1864-1920)
Frederick Taylor is
the founder of the school of scientific management.His main contribution in management science is creation of management as a scientific approach.
Scientific management
emphasis on organization of manufacture, management was considered as industrial
Main representatives:
Frederick Winslow Taylor (1856-1915)
Henry L. Gantt
Frank and Lillian Gilbreth
Слайд 36
Three main moments of scientific management school creation
Rational
organization of work:
replacement of traditional methods of work with
rules based on analysis of workappropriate organization of labor
organization of training for employees
Development of formal structure of enterprise
Differentiation of executive and administrative functions
Слайд 37 The contribution of scientific management school to the
theory of management
Use of the scientific analysis for defining
the best ways of object performance;Purposeful selection of workers suitable to object performance and training of these workers;
Supply of workers with resources;
Use of material stimulation for increasing labor productivity ;
Appropriate distribution of responsibility between workers and managers
Слайд 38
Administrative management school
Henri Fayol (1841-1925)
the first who classified
studying management according to its functions – forecasting, planning,
organizing, commanding, coordinating and controllingHarrington Emerson (1853-1931)
Researches of a staff principle in management
Concept of productivity and efficiency
Max Weber (1864-1920)
Rational bureaucracy
Слайд 39
The purpose of administrative management school is
creation
of universal principles of management
leading to success
Слайд 40 The contribution of administrative management school to the
theory of management
Creation of universal principles of management;
The description
of management functions;The systematized approach to management of enterprise.
Слайд 41
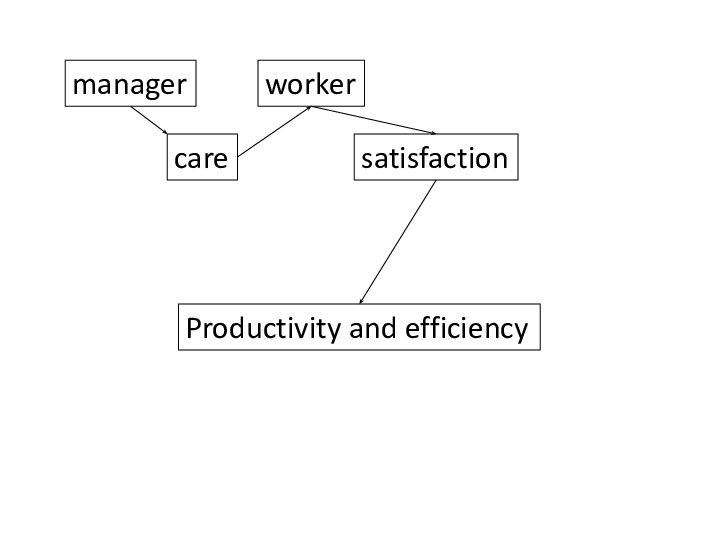
School of human relations
Mary Parker Follett (1868-1933)
proved necessity of scientific research of psychological aspects of
management. She defined management as "the art of getting things done through people“.Elton Mayo (1880-1949) – the founder of school
Hawthorne experiments (1927-1933)
Proved value of social and psychological factors for increasing production efficiency
Слайд 43 The purpose of human relation school is
managing enterprise influencing system of social and psychological factors.
Human
relations school is an effort of management to consider each organization as a social system.
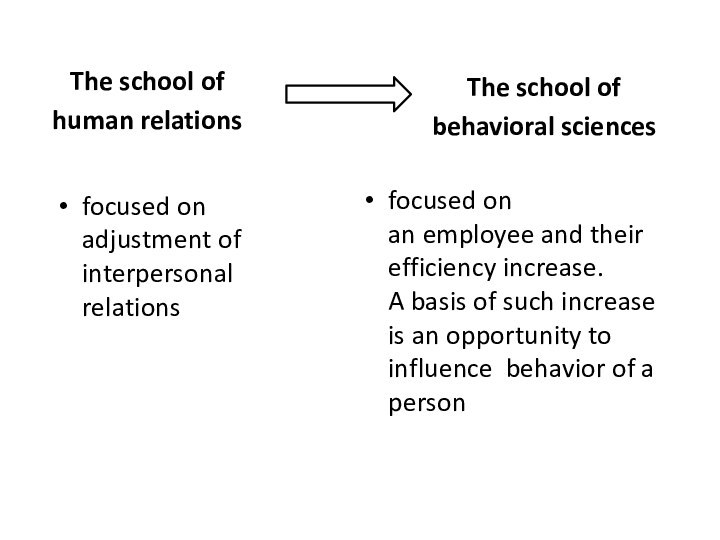
Слайд 44
The school of
human relations
focused on
an employee and their
efficiency increase. A basis of such increase is an opportunity
to influence behavior of a personThe school of
behavioral sciences
focused on
adjustment of interpersonal relations
Слайд 45
The basic purpose of behavioral science school:
Increase of
activity of the organization efficiency by increasing efficiency of
human resources;Creation of all necessary conditions for realization of each employee’s creative abilities for the purpose of awareness of own importance in management of organization.
Researchers of this school showed a role of a person’s motives and needs for their labor activity.
Motives are a main parameter of the human attitude to work.
Positive motivation is a main factor of successful work.
Слайд 46
Main representatives of behavioral science school
Chester Barnard
(1886-1961) - the founder of school
problems of cooperation of
human activityformal and informal structures of organization
Abraham Maslow (1908-1970). The main work is «Motivation and the person»
McGregor (1906-1964)
Слайд 47
The basic ideas of human relations school
Management is
a social and psychological process rather than economic process;
In
a basis of management there is a person. Person is a unique individual with his(her) interests, needs and motives;The person is social essence submitting to laws of collective;
The hard hierarchy of subordination and formalization of organizational processes is incompatible with human nature. Therefore it is necessary to create such methods of management which would control people’s behavior in groups and in organizations and which could use worker’s psychological and emotional features;
Labor productivity is influenced by psychological and social factors rather than material factors;
Managers should establish and develop loyal relations with informal working groups and their leaders.
Слайд 48 Contribution of human relations school to theory of
management
Using methods of interpersonal relation management
Studying informal relations
Using knowledge
about human behavior
Слайд 49
Quantitative school of management or
school of management science
contribution:
Development and using models for making decision;
Development and using
quantitative methods at making decision in complex and crisis situations;Using methods of exact sciences in research of administrative activity.
Purpose is increasing rationality of made decisions
Слайд 51
Processing approach
Management is considered as a process of
continuous interconnected actions (functions);
All kinds of activity are integrated
into uniform chain.
Слайд 52
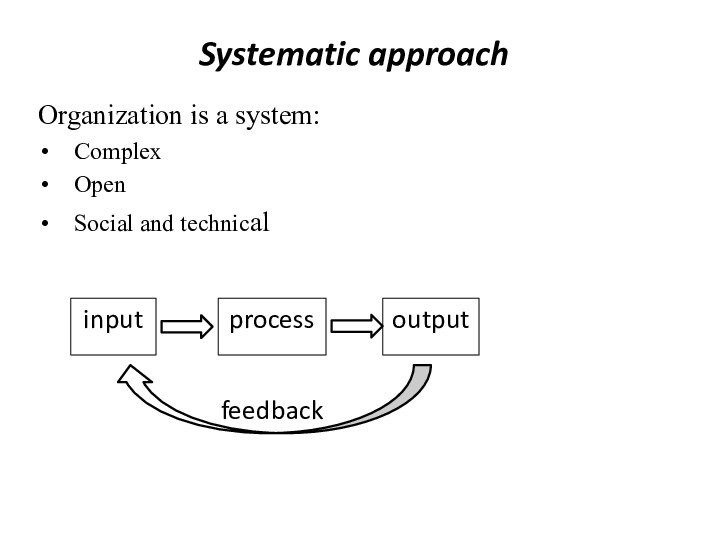
Systematic approach
Organization is considered as complex, open, social
and technical system having input, output and feedback. In
system input transforms to outputAll elements of system are interconnected





























