Principles of Government
SECTION 1 Government and the State
SECTION 2 Forms of
GovernmentSECTION 3 Basic Concepts of Democracy
Chapter 1
2
3
1
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
















Chapter 1
2
3
1
2
3
Chapter 1, Section 1
2
3
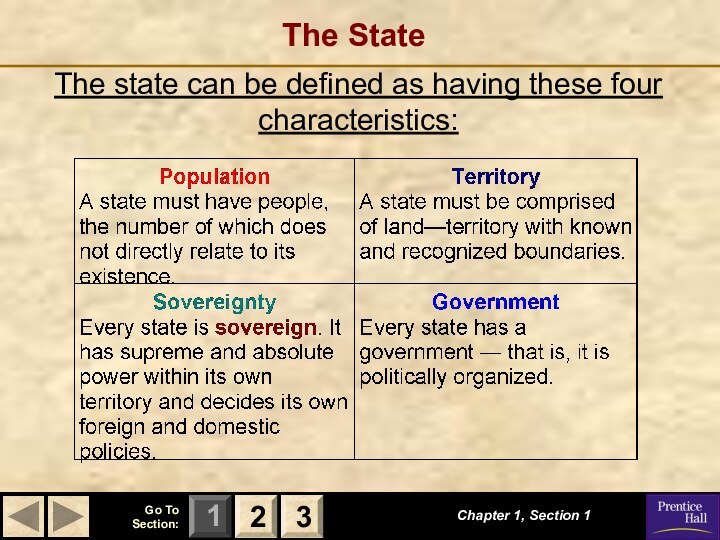
“We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America.”
Chapter 1, Section 1
2
3
Chapter 1, Section 1
Want to connect to the Magruder’s link for this chapter? Click Here!
2
3
Chapter 1, Section 2
3
1
Dictatorship
A dictatorship exists where those who rule cannot be held responsible to the will of the people.
An autocracy is a government in which a single person holds unlimited political power.
An oligarchy is a government in which the power to rule is held by a small, usually self-appointed elite.
Chapter 1, Section 2
3
1
Confederate Government
A confederation is an alliance of independent states.
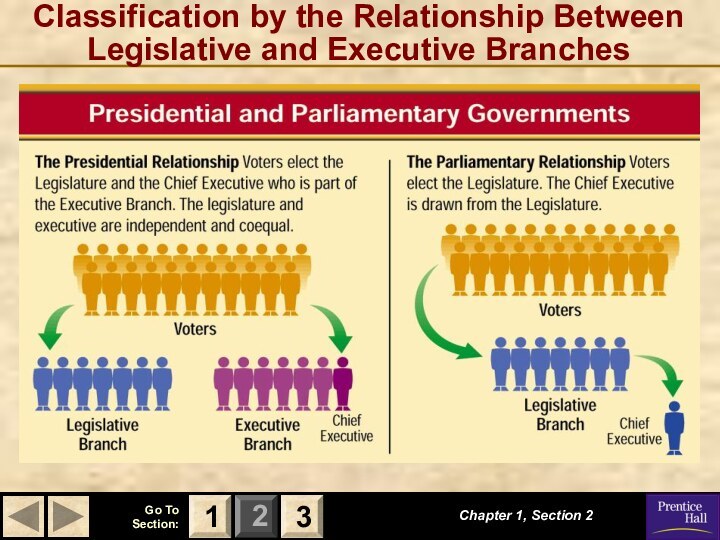
Federal Government
A federal government is one in which the powers of government are divided between a central government and several local governments.
An authority superior to both the central and local governments makes this division of power on a geographic basis.
Chapter 1, Section 2
Want to connect to the Magruder’s link for this section? Click Here!
3
1
2
1