- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему The classification of the tooth
Содержание
- 2. Teeth of humans are small, calcified, whitish
- 3. Teeth are among the most distinctive (and
- 4. The anatomic crown of a tooth is
- 5. Canines and most premolars, except for maxillary
- 6. Teeth are classified as incisors, canines, premolars,
- 7. Если глагол в главном предложении стоит в
- 10. В подобных случаях возможны три основных варианта:
- 11. 2. Действие придаточного предложения
- 12. . Действие придаточного предложения относится к будущему
- 13. Скачать презентацию
- 14. Похожие презентации
Teeth of humans are small, calcified, whitish structures found in the mouth that are used to break down food. The roots of teeth are embedded in the maxilla (upper jaw) or the mandible (lower jaw) and

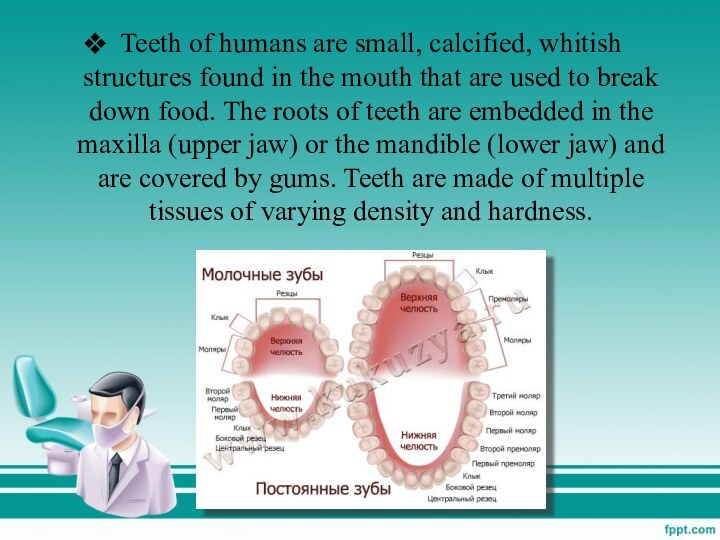








Слайд 3 Teeth are among the most distinctive (and long-lasting)
features of mammal species. Humans, like other mammals, are
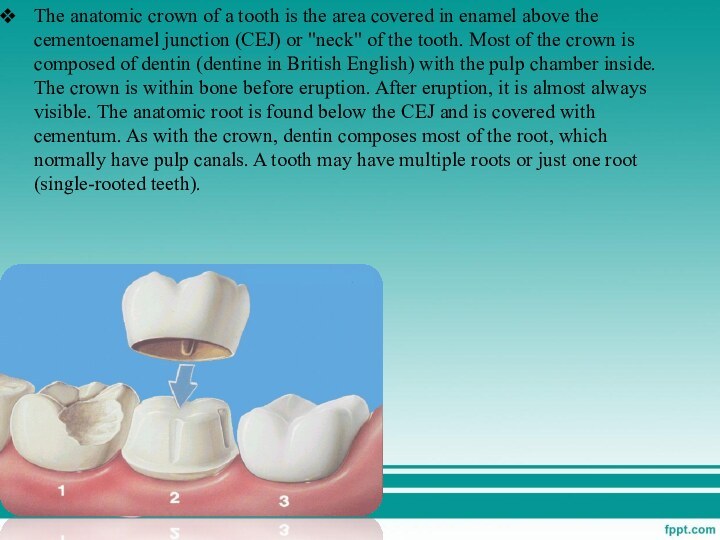
diphyodont, meaning that they develop two sets of teeth. The first set (also called the "baby", "milk", "primary", and "deciduous" set) normally starts to appear at about six months of age, although some babies are born with one or more visible teeth, known as neonatal teeth. Normal tooth eruption at about six months is known as teething and can be painful.Слайд 4 The anatomic crown of a tooth is the
area covered in enamel above the cementoenamel junction (CEJ)
or "neck" of the tooth. Most of the crown is composed of dentin (dentine in British English) with the pulp chamber inside. The crown is within bone before eruption. After eruption, it is almost always visible. The anatomic root is found below the CEJ and is covered with cementum. As with the crown, dentin composes most of the root, which normally have pulp canals. A tooth may have multiple roots or just one root (single-rooted teeth).Слайд 5 Canines and most premolars, except for maxillary first
premolars, usually have one root. Maxillary first premolars and
mandibular molars usually have two roots. Maxillary molars usually have three roots. Additional roots are referred to as supernumerary roots. Humans usually have 20 primary (deciduous or "baby") teeth and 32 permanent (adult) teeth.Слайд 6 Teeth are classified as incisors, canines, premolars, and
molars. Incisors are primarily used for biting pieces from
foods such as raw carrots or apples and peeled but uncut bananas, while molars are used primarily for grinding foods after they are already in bite size pieces inside the mouth. Most teeth have identifiable features that distinguish them from others. There are several different notation systems to refer to a specific tooth. The three most common systems are the FDI World Dental Federation notation, the universal numbering system, and Palmer notation method. The FDI system is used worldwide, and the universal is used widely in the United States.
Слайд 7
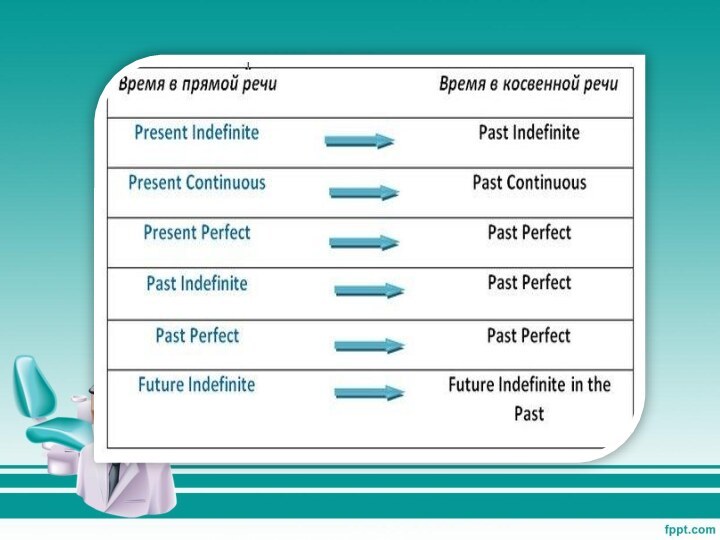
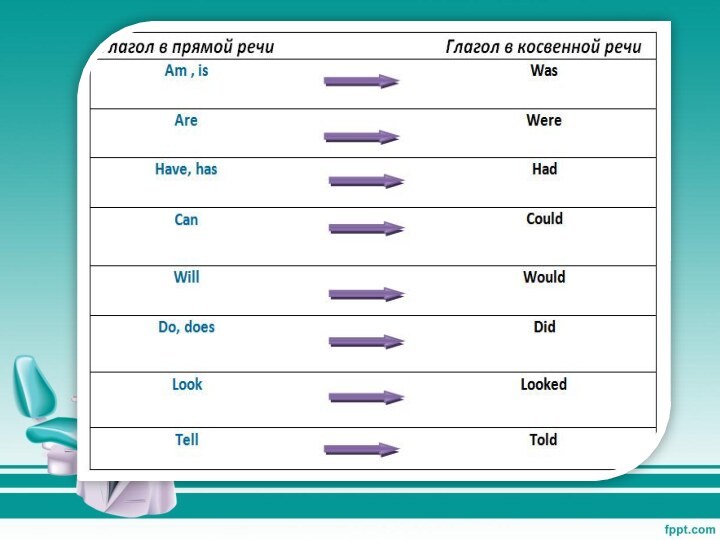
Если глагол в главном предложении стоит в одном
из прошедших времен, то и глагол придаточного предложения должен
стоять в одном из прошедших времен. Пользуйтесь следующей схемой:
Слайд 10
В подобных случаях возможны три основных варианта:
1 . Действие придаточного предложения происходит одновременно
с действием главного предложения: в этих случаях глагол придаточного предложения стоит в Simple Past либо в Past Continuous. (одновременность)Я знал, что он каждый год ходит к стоматологу. I knew (that) he went to dentist every year.





























