Слайд 2
AGENDA: FOREX RISK
Sources of foreign exchange risk and
FX trading activities;
FX risk and hedging: futures, forwards, swaps
Estimation
of Basis risk
Interest rate Parity Theorem
Слайд 3
Sources of FX Risk
Spot positions denominated in foreign
currency
Forward positions denominated in foreign currency
Net exposure = (FX
assets - FX liabilities) + (FX bought - FX sold)
Net long position in currency = FI bought more currency than it has sold or have more FX assets than liabilities.
Net short position in currency = FI has sold more foreign currency that it has purchased or have more FX liabilities than assets.
Слайд 4
Problem 1
Bank has Euro 14 million in assets
and Euro 23 million in liabilities and has sold
Euro 8 million in foreign currency trading.
a) What is the net exposure for the Bank?
b) For what type of exchange rate movement does this exposure put the bank at risk?
Слайд 5
FX Risk Exposure
Greater exposure to a foreign currency
combined with greater volatility of the foreign currency implies
greater DEAR.
Dollar loss/gain in currency i
= [Net $ exposure in foreign currency i] × Shock (Volatility) to the $/Foreign currency i exchange rate
Слайд 6
Trading Activities
Basically 4 trading activities:
Purchase and sale of
currencies to complete international transactions.
Facilitating positions in foreign real
and financial investments.
Accommodating hedging activities.
Speculation.
Слайд 7
Foreign Assets & Liabilities
Mismatches between foreign asset
and liability portfolios.
Ability to raise funds from internationally diverse
sources presents opportunities as well as risks:
Greater competition in well-developed (lower risk) markets.
Слайд 8
Return and Risk of
Foreign Investments
Returns are affected
by:
Spread between costs and revenues
Changes in FX rates
Changes in
FX rates are not under the control of the FI
Слайд 9
EXAMPLE: FI issued $200 mill one-year CDs at
8% and invested proceeds in one-year US dollar loan
(50%) at 9% and one-year sterling loan (50%) at 15%. Spot exchange rate is 1.6$/£
$100mill/1.6 = £62.5 mill
Invest £62.5 mill in loans at 15%
The revenue by the end of the year = £62.5 mill x 1.15% = £71.875 mill
Suppose that the spot exchange rate has fallen in value from $1.6/£ to $1.45/£ next year, hence
£71.875 mill x $1.45/£ = $104.22 mill.
Return on the investments is 4.22%
The weighted return on the FI’s asset portfolio =
0.5x0.09 +0.5 x 0.0422 = 0.0661 or 6.61% that is less than the cost of funds 8%
Слайд 10
Risk and Hedging
Hedge can be constructed on balance
sheet or off balance sheet.
On - balance-sheet hedge requires
duration matching and currency matching.
Off-balance-sheet hedge involves forwards, futures, options or swaps.
No balance sheet rebalancing;
No immediate cash flow only future contingent cash flow;
Lower costs and administration.
BUT, we have a default risk of counterparty.
Слайд 11
On balance sheet hedging
We match maturities and currency
foreign asset-liability book: $100 mill UK loans are financed
by UK CDs at 11%, 100 mill US loans are financed by US CDs at 8%. Spot rate is 1.6$/£.
£ Depreciation to $1.45/£
£ Cost of liabilities: $100mill/1.6 = £62.5 mill
£62.5 mill x 1.11 = £69.375
The repayment in Dollars: £69.375 x $1.45/£ = $100.59 mill
Cost of funds = 0.59%
Net return = (0.5 x 0.09 + 0.5 x 0.0422) – (0.5 x 0.08 + 0.5 x
0.0059) = 6.61% - 4.295% = 2.315%
Слайд 12
£ appreciation to $1.70/£, the return on
British loan is equal to 22.188%
£ Cost of liabilities:
$100mill/1.6 = £62.5 mill
£62.5 mill x 1.11 = £69.375
The repayment in Dollars: £69.375 x $1.70/£ = $117.94 mill
Cost of funds = 17.94%
Net return = (0.5 x 0.09 +0.5 x 0. 22188) – (0.5 x 0.08 + 0.5 x 0.1794) = 15.59% - 12.969% = 2.625%
By directly matching its foreign asset and liability book, FI lock in an positive return or profit spread whichever direction the exchange rates change over investment period.
On balance sheet hedging
Слайд 13
Off balance sheet hedge with forward contracts
$100mill/$1.6/£ =
£62.5 mill Invested £62.5 mill in loans at 15%
FI sells the expected principal and interest on a loan forward at the current forward rate $155/£
The forward buyer of £ promises to pay £62.5 mill x 1.15% = £71.875 mill x $155/£ = $111.406 mill in one year
FI has a guaranteed return on a British loan =
(111.46 – 100)/100 = 11.406%
The overall expected return on the FI’s asset portfolio =
0.5x0.09 +0.5 x 0.11406 = 0.10203 or 10.203%
Слайд 14
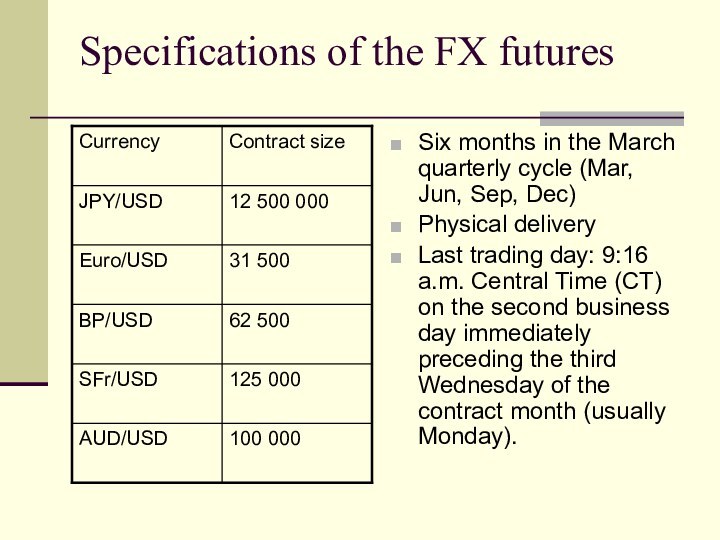
Specifications of the FX futures
Six months in the
March quarterly cycle (Mar, Jun, Sep, Dec)
Physical delivery
Last
trading day: 9:16 a.m. Central Time (CT) on the second business day immediately preceding the third Wednesday of the contract month (usually Monday).
Слайд 15
Hedging with futures.
What is your risk if you
have a long position in FX futures?
Foreign currency
appreciation
Foreign currency depreciation
Слайд 16
Hedging with futures
Should you take long or short
position in FX futures contracts if:
you are planning
to sell Foreign currency in the future;
You want to hedge the portfolio of foreign stocks against the foreign exchange risk;
You are planning to borrow a syndicated loan from a foreign bank;
You are planning to buy foreign bonds in 2 months.
Liabilities in foreign currency exceed the assets in foreign currency.
Слайд 17
Hedging with futures
Futures market does not allow to
institute a long-term one-year hedge usually due to defined
maturity (4 times per year). So we need to rollover the futures positions into new futures contracts.
EXAMPLE: Suppose that FI made a £100 mill loan at 15% and wished to hedge fully the risk of £ depreciation. The spot exchange rate is $1.47/£ and forward exchange rate is $1.46/£
The size of each £ futures contract is £62500, therefore, the number of contracts needed:
Nf = £115 mill / £62500 = 1840 contracts to be sold.
Слайд 18
Example (continued)
Suppose that by the end of the
year the £ depreciates against the $ from $1.47/£
to $1.42/£ at the spot market and from $1.46/£ to $1.41/£ at the forward market.
Loss on the £ loan:
£115 mill x ($1.47/£ - $1.42/£) = $5.75mill
Gain on futures contracts:
1840 x £62500 x ($1.46/£ - $1.41/£) = $5.75 mill
In this example we ignore the marking to market effect and the basis risk:
If spot and futures prices are not perfectly correlated, then basis risk remains.
Tailing the hedge
Interest income effects of marking to market allows hedger to reduce number of futures contracts that must be sold to hedge
Слайд 19
Basis Risk
Suppose we have a basis risk: ΔS
= - 5 c and ΔF = -3 c
Loss
on the £ loan:
£115 mill x ($1.47/£ - $1.42/£) = $5.75mill
Gain on futures contracts:
1840 x £62500 x ($1.46/£ - $1.43/£) = $3.45 mill
Net Loss = 5.75 - 3.45 = 2.3 mill
In order to adjust for basis risk we apply the hedge ratio: h = ΔS t/Δft
Nf = (Long asset position × h)/(size of one contract).
Слайд 20
Example (continued)
H = 0.5/0.3 = 1.66
Nf =
(£115mill x 1.66) / £62500 = 3054.4 contracts
Gain
on futures position:
3054 x £62500 x ($1.46/£ - $1.43/£) = $5.73 mill
Net loss = 0.02 mill
Слайд 21
Estimating the Hedge Ratio
Look at recent past behavior
of ΔSt relative to ΔFt.
The h may be estimated
using ordinary least squares regression:
ΔSt = α + βΔft + ut
The hedge ratio, h, will be equal to the coefficient β. The R2 from the regression reveals the effectiveness of the hedge.
R2 = p2 = [Cov(ΔSt, ΔFt)]/ [δΔStδ ΔFt]
Слайд 22
Fixed-for-fixed currency swap:
Exchange of principal and interest
payments in one currency for principal and interest payments
in another currency.
The principal should be specified for each of two currencies;
The principal is usually exchanged at the beginning and at the end of the life of the swap (note, in an interest rate swap the principal is not exchanged)
Слайд 23
Currency Swaps
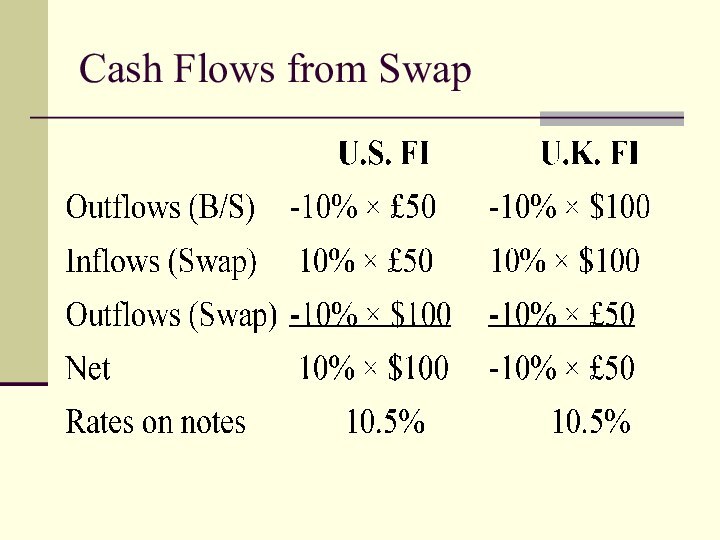
Fixed-Fixed
Example: U.S. bank with fixed-rate assets
denominated in dollars, partly financed with £50 million in
4-year 10 percent (fixed) notes. By comparison, U.K. bank has assets partly funded by $100 million 4-year 10 percent notes.
US FI has the risk of dollar depreciation
UK FI has the risk of dollar appreciation
Solution: Enter into currency swap.
Слайд 24
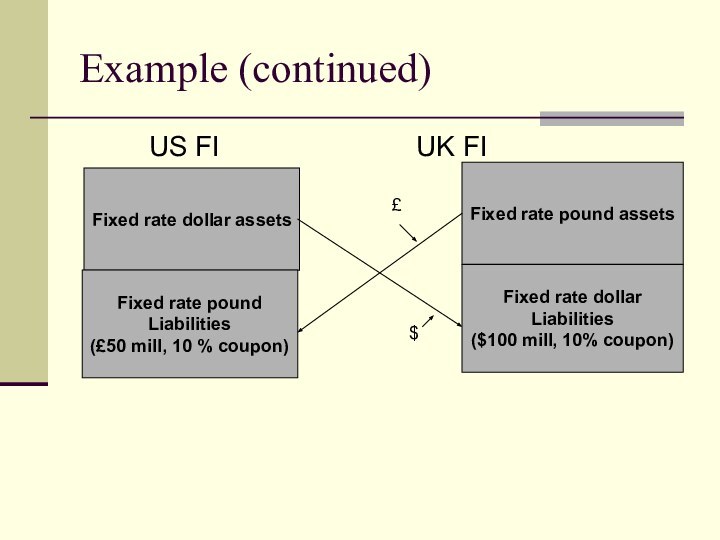
Example (continued)
US
FI UK FI
Fixed rate
dollar assets
Fixed rate pound
Liabilities
(£50 mill, 10 % coupon)
Fixed rate pound assets
Fixed rate dollar
Liabilities
($100 mill, 10% coupon)
£
$
Слайд 26
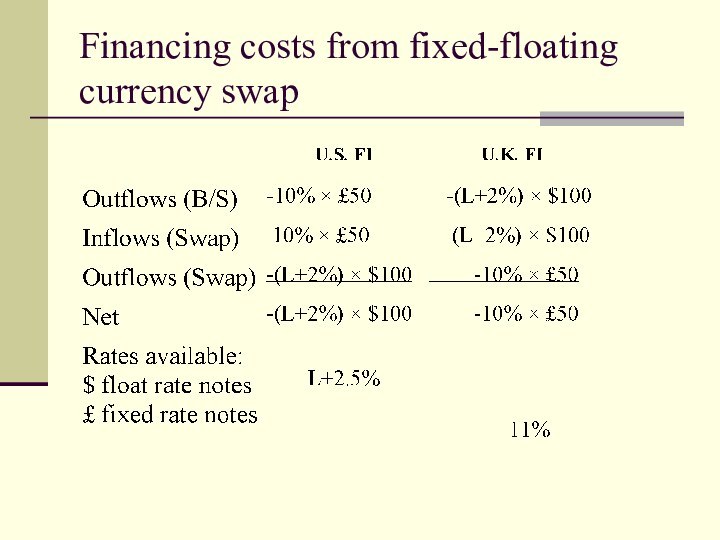
Fixed-Floating + Currency
Fixed-Floating currency swaps.
Allows hedging of interest
rate and currency exposures simultaneously
Example:
FIs make payments
at some prearrange $/£ exchange rate ($2/£)
Слайд 27
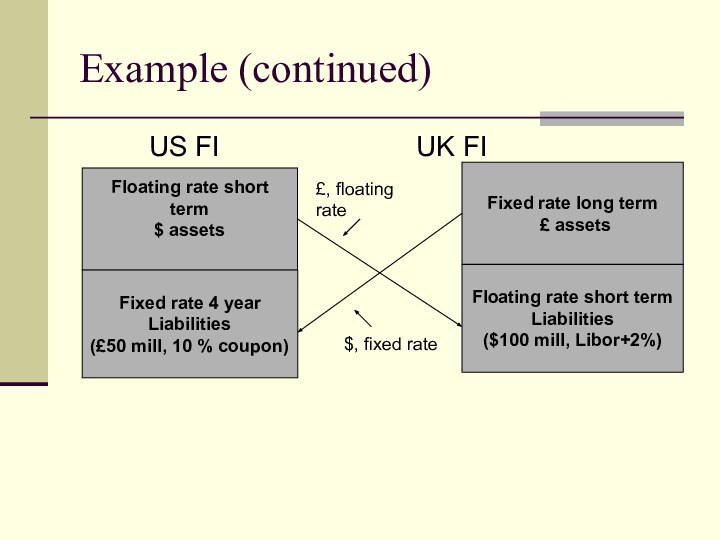
Example (continued)
US
FI UK FI
Floating rate
short term
$ assets
Fixed rate 4 year
Liabilities
(£50 mill, 10 % coupon)
Fixed rate long term
£ assets
Floating rate short term
Liabilities
($100 mill, Libor+2%)
£, floating rate
$, fixed rate