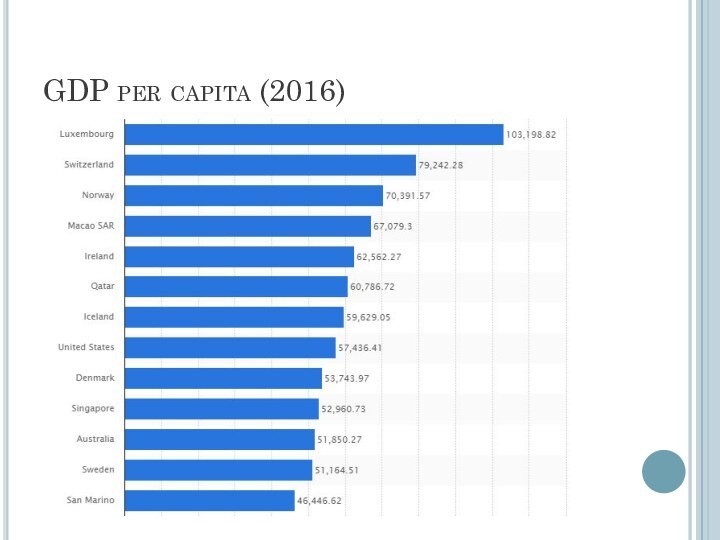
Слайд 3
“It isn’t a case of more globalization or
less, but of a different and less predictable path,
as some countries turned protectionist while others went in the other direction and deregulated their markets.”
Pier Carlo Padoan, Italy’s Finance Minister
Слайд 4
What Is Globalization
Globalization is defined as a process
that, based on international strategies, aims to expand business
operations on a worldwide level, and was precipitated by the facilitation of global communications due to technological advancements, and socioeconomic, political and environmental developments.
economic globalization
cultural globalization
political globalization
Слайд 5
basic aspects of globalization
In 2000, the International Monetary
Fund (IMF) identified four basic aspects of globalization:
trade
and transactions,
capital and investment movements,
migration and movement of people,
the dissemination of knowledge.
Environmental challenges (global warming, cross-boundary water and air pollution, and overfishing of the ocean)
Слайд 6
Globalization Encompasses
Internationalization (trade & investment)
Liberalization (freeing markets)
Universalization (cultural
interchange)…or…
Westernization (Western cultural dominance)
“Deterritorialization” (the severance of social, political,
or cultural practices from their native places and populations)
Слайд 7
Impact
Economic impact
Improvement in standard of living
Increased competition among
nations
Widening income gap between the rich and poor
Social impact
Increased
awareness of foreign cultures
Loss of local culture
Environmental impact
Environmental degradation
Environmental management
Слайд 8
Focus on: Measuring globalisation
STATISTICAL INDICATORS
OECD Economic Globalization Indicators
helps identify the economic activities of member countries that
are under foreign control, and more particularly the contribution of multinational enterprises to growth, employment, productivity, labour compensation, research and development, technology diffusion and international trade. These indicators shed new light on financial, technological and trade interdepe
World Development Indicators (WDI). The WDI affords readers more than 900 indicators organized in six sections: World View, People, Environment, Economy, States and Markets, and Global Links. In each section a plethora of information is presented. ndencies within OECD countries.
Слайд 9
Focus on: Measuring globalisation
STATISTICAL INDICATORS
UNCTAD Development and
Globalization: Facts and Figures. This publication covers subjects tackled
by UNCTAD such as trade, investment, external finance, commodities and manufactures, together with relevant facts about population.
Global Policy Forum (GPF) gathers a large number of tables and graphs providing the main features of globalization, asking what is new, what drives the process, how it changes politics, and how it affects global institutions like UN. In addition to indicators of social and economic policy, trade and capital flows, global poverty and development etc.
Слайд 10
Focus on: Measuring globalisation
COMPOSITE INDEXES
The A. T Kearney/FOREIGN
POLICY Globalization Index (2016 – the last data, in
free access up to 2006)
Centre for the Study of Globalisation and Regionalisation (CSGR) Globalisation Index (2004 – the last data)
Konjunkturforschungsstelle (KOF) Swiss Economic Institute Index of Globalization (2017 – the last data)
Слайд 11
The A. T Kearney/FOREIGN POLICY Globalization Index (Ukraine
Слайд 13
KOF Globalization Index - 100 most globalized countries
2017
Слайд 16
Methodology
POLITICAL GLOBALIZATION [27%]
Embassies in Country (25%)
Membership in International Organizations (27%)
Participation in
U.N. Security Council Missions (22%)
International Treaties (26%)
Слайд 17
“Arguably no other place on earth has so
engineered itself to prosper from globalization - and succeeded
at it. The small island nation of 5 million people boasts the world's second-busiest seaport, a far higher per capita income than its former British overlord and a raft of No. 1 rankings on lists ranging from least-corrupt to most business-friendly countries.”
Singapore a 'canary in the gold mine of globalization’
Straits Times, May 24 2014
Слайд 18
Economic dimension
Growing economic interdependence of countries worldwide through
increasing volume and variety of cross-border transactions in goods
and services, free international capital flows, and more rapid and widespread diffusion of technology
Слайд 20
Measuring globalization (economic aspects)
Statistics related to trade.
Total
exports, total trade (imports + exports), Trade as a
% of GDP
Statistics related to FDI.
Foreign Direct Investment. Money invested in a country by a foreign company. FDI inflows and outlflows.
Слайд 21
Factors which help the spread of globalisation
Low transport
costs, containerization
Telecommunications
Internet
Low trade barriers
Political stability
Increasing role of TNCs
Слайд 22
Increased competition among nations
For example, many companies have
shifted their production facilities to emerging markets such as
China and India to enjoy lower costs of production.
Benefiting from the increased revenue, these countries are able to rapidly develop their infrastructure such as road networks and industrial parks, which further increased their attractiveness to foreign investors.
This poses a strong challenge for developed economies like Singapore and Taiwan and more so for less developed countries with poor infrastructure and political stability such as Cambodia and East Timor
Слайд 23
Increased competition among nations
“They (economists) predict that increased
competition from low-wage countries will destroy jobs in richer
nations and there will be a “race to the bottom” as countries reduce wages, taxes, welfare and environmental controls so as to be more competitive, at enormous social cost. Pressure to compete will erode the ability of governments to set their own economic policies and the move towards deregulation will reduce their power to protect and promote the interests of their people.”
World Health Organization
Слайд 24
Widening income gap
For example, with improved communications and
transportation, business owners in developed countries are able to
outsource their operations to other countries to enjoy lower costs of production.
This inevitably leads to higher retrenchment rates and loss of income among the average workers, which translates into the rich getting richer and the poor becoming poorer
Слайд 25
Pros and Cons of Globalization
Free trade is supposed

to reduce barriers such as tariffs, value added taxes,
subsidies, and other barriers between nations. This is not true. There are still many barriers to free trade. The Washington Post story says “the problem is that the big G20 countries added more than 1,200 restrictive export and import measures since 2008
The proponents say globalization represents free trade which promotes global economic growth; creates jobs, makes companies more competitive, and lowers prices for consumers.
Competition between countries is supposed to drive prices down. In many cases this is not working because countries manipulate their currency to get a price advantage.
It also provides poor countries, through infusions of foreign capital and technology, with the chance to develop economically and by spreading prosperity, creates the conditions in which democracy and respect for human rights may flourish. This is an ethereal goal which hasn’t been achieved in most countries
Слайд 26
Pros & Cons
According to supporters globalization and democracy
should go hand in hand. It should be pure
business with no colonialist designs.
There is now a worldwide market for companies and consumers who have access to products of different countries.
Gradually there is a world power that is being created instead of compartmentalized power sectors. Politics is merging and decisions that are being taken are actually beneficial for people all over the world. This is simply a romanticized view of what is actually happening.
There is more influx of information between two countries, which do not have anything in common between them.
There is cultural intermingling and each country is learning more about other cultures.
Since we share financial interests, corporations and governments are trying to sort out ecological problems for each other.
Слайд 27
Pros & Cons
Socially we have become more open
and tolerant towards each other and people who live
in the other part of the world are not considered aliens.
Most people see speedy travel, mass communications and quick dissemination of information through the Internet as benefits of globalization.
Labor can move from country to country to market their skills. (but this can cause problems with the existing labor and downward pressure on wages).
Sharing technology with developing nations will help them progress (true for small countries but stealing technologies and IP have become a big problem with larger competitors like China).
Transnational companies investing in installing plants in other countries provide employment for the people in those countries often getting them out of poverty.
Globalization has given countries the ability to agree to free trade agreements like NAFTA, South Korea Korus, and The TPP.
Слайд 28
Pros & Cons
The general complaint about globalization is
that it has made the rich richer while making
the non-rich poorer. “It is wonderful for managers, owners and investors, but hell on workers and nature.”
Globalization is supposed to be about free trade where all barriers are eliminated but there are still many barriers. For instance161 countries have value added taxes (VATs) on imports which are as high as 21.6% in Europe. The U.S. does not have VAT.
The biggest problem for developed countries is that jobs are lost and transferred to lower cost countries.” According to conservative estimates by Robert Scott of the Economic Policy Institute, granting China most favored nation status drained away 3.2 million jobs, including 2.4 million manufacturing jobs. He pegs the net losses due to our trade deficit with Japan ($78.3 billion in 2013) at 896,000 jobs, as well as an additional 682,900 jobs from the Mexico –U.S. trade-deficit run-up from 1994 through 2010.”
Слайд 29
Pros & Cons
Workers in developed countries like the
US face pay-cut demands from employers who threaten to
export jobs. This has created a culture of fear for many middle class workers who have little leverage in this global game
Large multi-national corporations have the ability to exploit tax havens in other countries to avoid paying taxes.
Multinational corporations are accused of social injustice, unfair working conditions (including slave labor wages, living and working conditions), as well as lack of concern for environment, mismanagement of natural resources, and ecological damage.
Multinational corporations, which were previously restricted to commercial activities, are increasingly influencing political decisions. Many think there is a threat of corporations ruling the world because they are gaining power, due to globalization.
Building products overseas in countries like China puts our technologies at risk of being copied or stolen, which is in fact happening rapidly
Слайд 30
Pros & Cons
The anti-globalists also claim that globalization

is not working for the majority of the world.
“During the most recent period of rapid growth in global trade and investment, 1960 to 1998, inequality worsened both internationally and within countries. The UN Development Program reports that the richest 20 percent of the world's population consume 86 percent of the world's resources while the poorest 80 percent consume just 14 percent. “
Some experts think that globalization is also leading to the incursion of communicable diseases. Deadly diseases like HIV/AIDS are being spread by travelers to the remotest corners of the globe.
Globalization has led to exploitation of labor. Prisoners and child workers are used to work in inhumane conditions. Safety standards are ignored to produce cheap goods. There is also an increase in human trafficking.
Social welfare schemes or “safety nets” are under great pressure in developed countries because of deficits, job losses, and other economic ramifications of globalization.















![Macroeconomics The Measurement and Structure of the National Economy. (Lecture 4) MethodologyPOLITICAL GLOBALIZATION [27%] Embassies in Country (25%) Membership in International Organizations (27%) Participation in U.N. Security Council Missions (22%) International Treaties (26%)](/img/tmb/15/1470528/40b2722e9699e0a6f29c1ae278c782d7-720x.jpg)