- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Database. Database management system MySQL
Содержание
- 2. Learning objectives describe relational databases and their
- 3. Success criteriaknows and understands the purpose of
- 4. A database is a collection of information that is
- 5. Hierarchical model This model presents data to
- 6. Network model: In the network model of
- 7. Relational model: The most recent and
- 8. Main database objectsTables – Data collection objectsQueries
- 9. Main objectsField (attribute): a single piece of
- 10. MySQL is an open source relational database
- 11. SQL Commands: SQL commands are instructions, coded
- 12. Data Definition Language (DDL) - These SQL commands
- 13. Transaction Control Language (TCL) - These SQL commands
- 14. SQL Create DataBaseCREATE DATABASE database_nameSQL Alter DataBaseThe
- 15. SQL CREATE TABLECREATE TABLE table_name (column_name1 datatype,
- 16. SQL ALTER TABLE StatementThe SQL ALTER TABLE
- 17. Local server XAMPPXAMPP is a free and
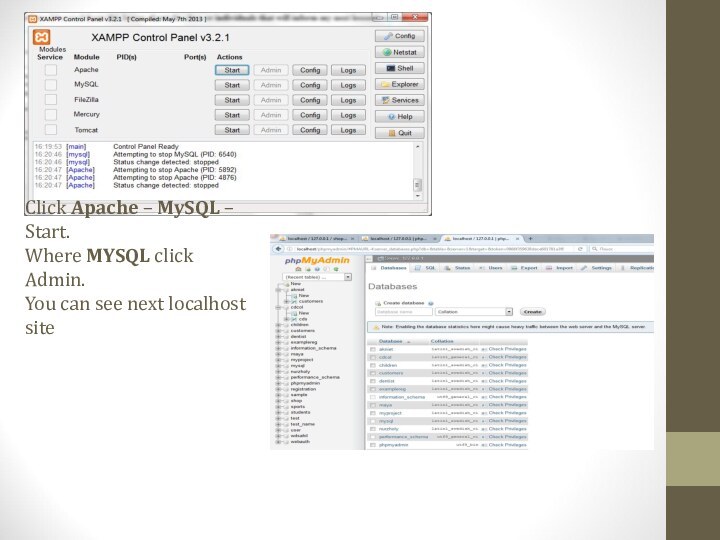
- 18. Click Apache – MySQL – Start. Where
- 19. Скачать презентацию
- 20. Похожие презентации
Learning objectives describe relational databases and their useuse the terms attribute, entity, index record, table and tuple to describe databases













Слайд 3
Success criteria
knows and understands the purpose of using
the database
can provide examples of the database
knows the types
of the databasecan describe a relational, network, and hierarchical database
knows the main elements of the database
knows and understands the purpose of using MySQL
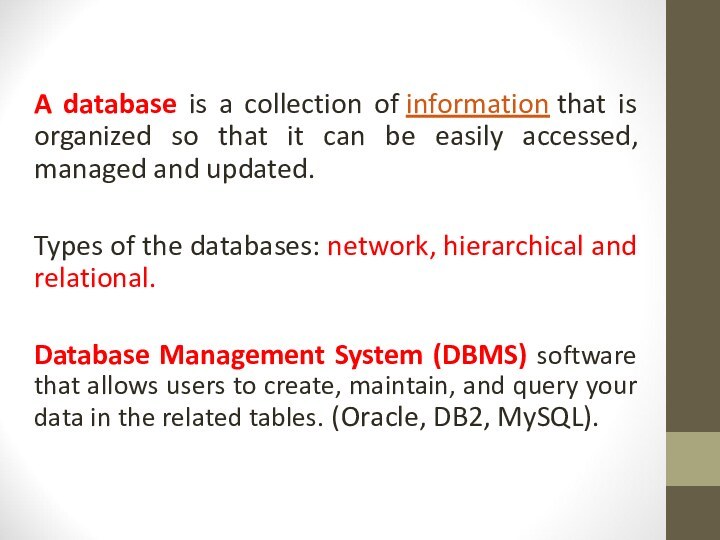
Слайд 4 A database is a collection of information that is organized
so that it can be easily accessed, managed and
updated.Types of the databases: network, hierarchical and relational.
Database Management System (DBMS) software that allows users to create, maintain, and query your data in the related tables. (Oracle, DB2, MySQL).
Слайд 5
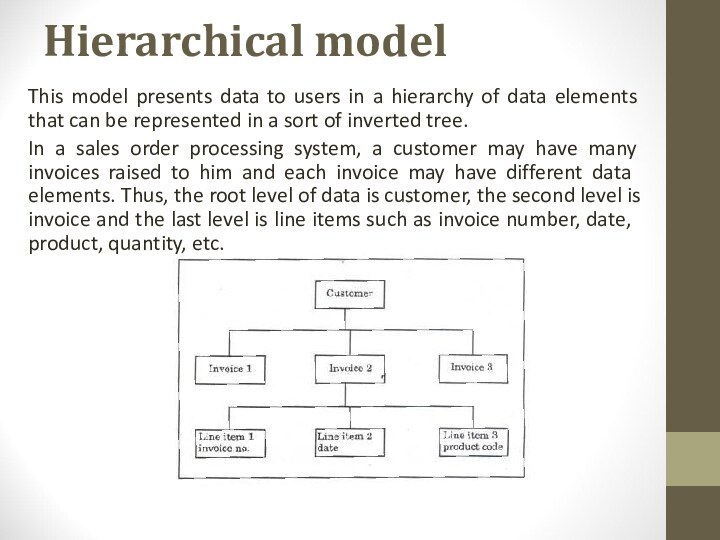
Hierarchical model
This model presents data to users in
a hierarchy of data elements that can be represented
in a sort of inverted tree.In a sales order processing system, a customer may have many invoices raised to him and each invoice may have different data elements. Thus, the root level of data is customer, the second level is invoice and the last level is line items such as invoice number, date, product, quantity, etc.
Слайд 6
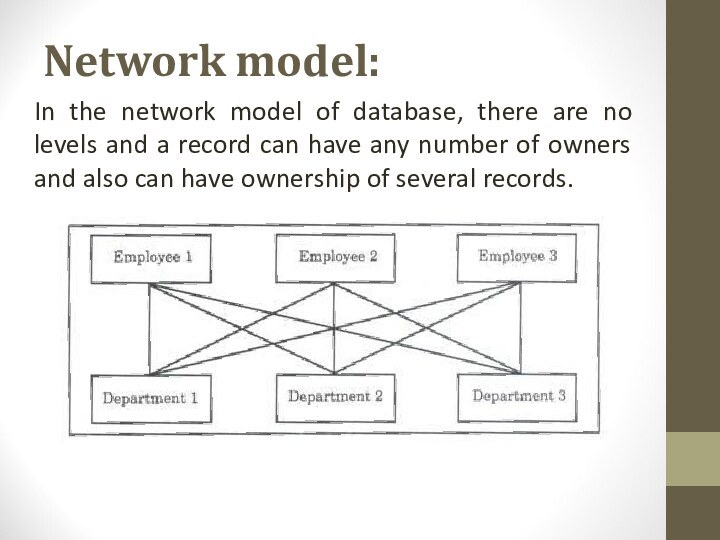
Network model:
In the network model of database, there
are no levels and a record can have any
number of owners and also can have ownership of several records.
Слайд 7
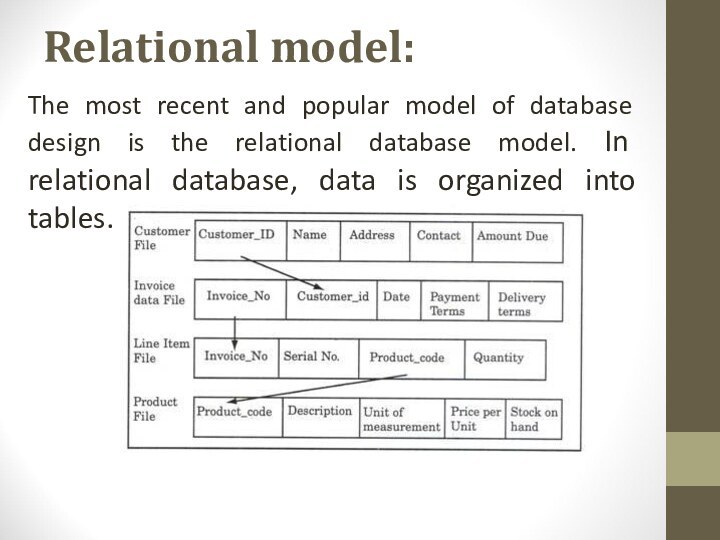
Relational model:
The most recent and popular model of
database design is the relational database model. In relational
database, data is organized into tables.
Слайд 8
Main database objects
Tables – Data collection objects
Queries –
Questions of your data
Forms – Predefined format to display
or enter dataReports – Printable version of database information
Слайд 9
Main objects
Field (attribute): a single piece of information.
Could be a name, or a number.
Record (Row):
a collection of related fields. A number of pieces of information that relate to the same object. Records on an employee, their name, address, social security number, phone number, etc. This would be the employee’s record.
Table (entity): a collection of related records. If you put all the employee records together, you have a table of employees.
Слайд 10 MySQL is an open source relational database management
system (RDBMS) based on Structured Query Language (SQL).
Basic MySQL
OperationsCreate table
Insert records
Load data
Update records
Delete records
Modify table
Join table
Optimize table
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a standardized programming language used for managing relational databases and performing various operations on the data in them.
Слайд 11
SQL Commands:
SQL commands are instructions, coded into SQL statements,
which are used to communicate with the database to
perform specific tasks, work, functions and queries with data.SQL commands are grouped into four major categories depending on their functionality:
Data Definition Language (DDL)
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
Data Control Language (DCL)
Слайд 12 Data Definition Language (DDL) - These SQL commands are
used for creating, modifying, and dropping the structure of
database objects. The commands are CREATE, ALTER, DROP, RENAME, and TRUNCATE.Data Manipulation Language (DML) - These SQL commands are used for storing, retrieving, modifying, and deleting data. These Data Manipulation Language commands are: SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
Слайд 13 Transaction Control Language (TCL) - These SQL commands are
used for managing changes affecting the data. These commands
are COMMIT, ROLLBACK, and SAVEPOINT.Data Control Language (DCL) - These SQL commands are used for providing security to database objects. These commands are GRANT and REVOKE.
Слайд 14
SQL Create DataBase
CREATE DATABASE database_name
SQL Alter DataBase
The ALTER
DATABASE Statement is used to change characteristics of a
database.ALTER DATABASE database_name [COLLATE collation_name ]
SQL Drop DataBase
The DROP DATABASE Statement is used to drop or delete a database. Dropping of the database will drop all database objects (tables, views, procedures etc.) inside it.
DROP DATABASE database_name;
Слайд 15
SQL CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE table_name
(column_name1 datatype,
column_name2 datatype,
... column_nameN
datatype
);
CREATE TABLE employee
( id number(5),
name char(20),
dept char(10),
age number(2),
salary number(10),
location
char(10)
);
Слайд 16
SQL ALTER TABLE Statement
The SQL ALTER TABLE command
is used to modify the definition (structure) of a
table by modifying the definition of its columns. The ALTER command is used to perform the following functions.1) Add, drop, modify table columns 2) Add and drop constraints 3) Enable and Disable constraints
Syntax to add a column
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name datatype;
Syntax to drop a column
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP column_name;
Syntax to modify a column
ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY column_name datatype;
Syntax to rename a table
RENAME old_table_name To new_table_name;
Слайд 17
Local server XAMPP
XAMPP is a free and open
source cross-platform web server solution stack package developed by
Apache Friends, consisting mainly of the Apache HTTP Server, MySQL(M), database, and interpreters for scripts written in the PHP and Perl programming languages.XAMPP stands for Cross-Platform, XMP (X), Apache (A), MySQL(M), PHP (P) and Perl (P).





























