Слайд 2
Dealing with Errors
User input errors: In addition to
the inevitable typos, some users like to blaze their
own trail instead of following directions. Suppose, for example, that a user asks to connect to a URL that is syntactically wrong. Your code should check the syntax, but suppose it does not. Then the network package will complain.
Device errors: Hardware does not always do what you want it to. The printer may be turned off. A web page may be temporarily unavailable. Devices will often fail in the middle of a task. For example, a printer may run out of paper in the middle of a printout.
Physical limitations: Disks can fill up; you can run out of available memory.
Code errors: A method may not perform correctly. For example, it could deliver wrong answers or use other methods incorrectly. Computing an invalid array index, trying to find a nonexistent entry in a hash table, and trying to pop an empty stack are all examples of a code error.
Слайд 3
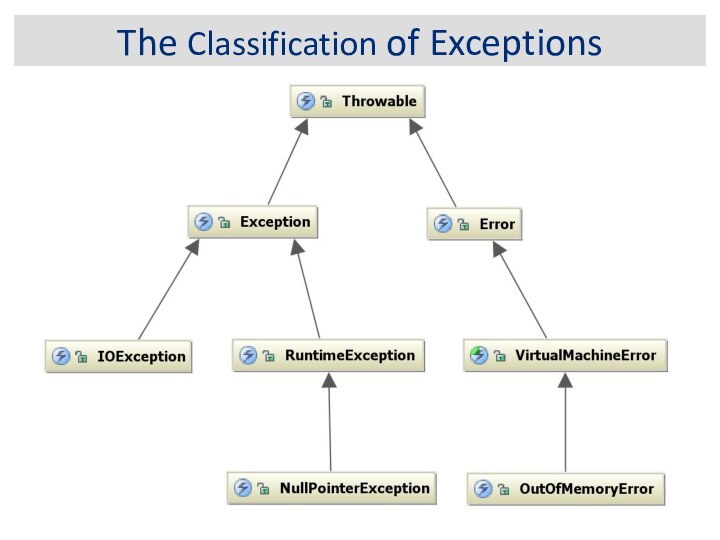
The Classification of Exceptions
Слайд 4
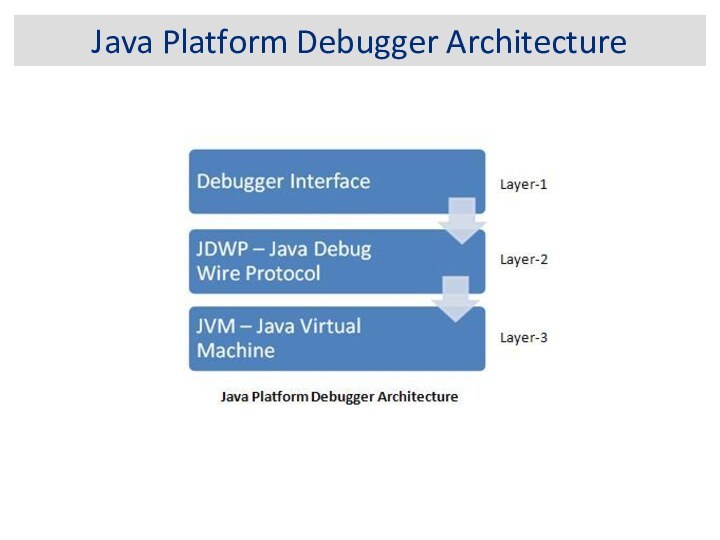
Java Platform Debugger Architecture
Слайд 5
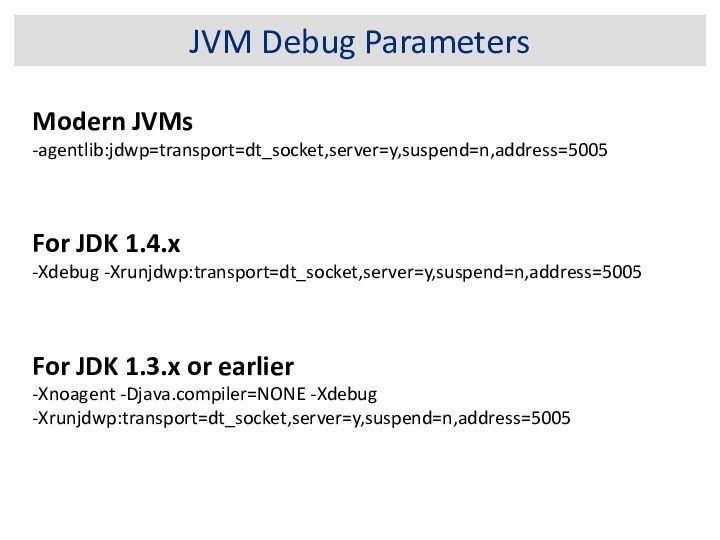
JVM Debug Parameters
Modern JVMs
-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005
For JDK 1.4.x
-Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005
For
JDK 1.3.x or earlier
-Xnoagent -Djava.compiler=NONE -Xdebug
-Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005
Слайд 6
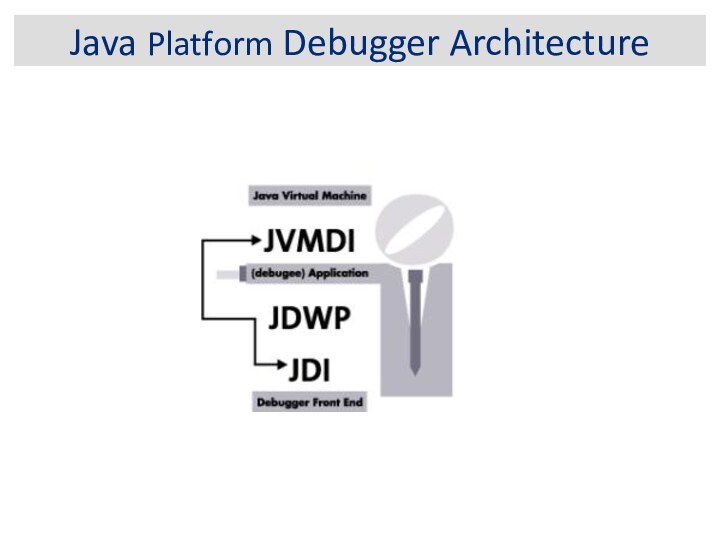
Java Platform Debugger Architecture
Слайд 7
Exceptions and Performance
15
millisecond
3000
millisecond
Слайд 9
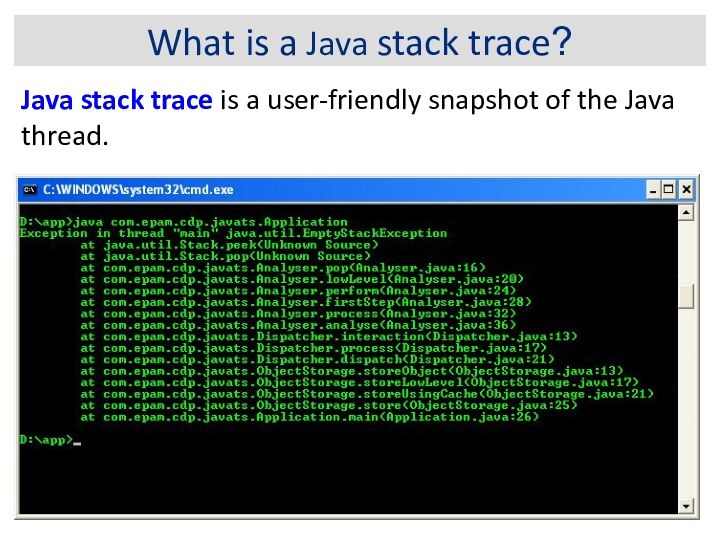
What is a Java stack trace?
Java stack trace
is a user-friendly snapshot of the Java thread.
Слайд 10
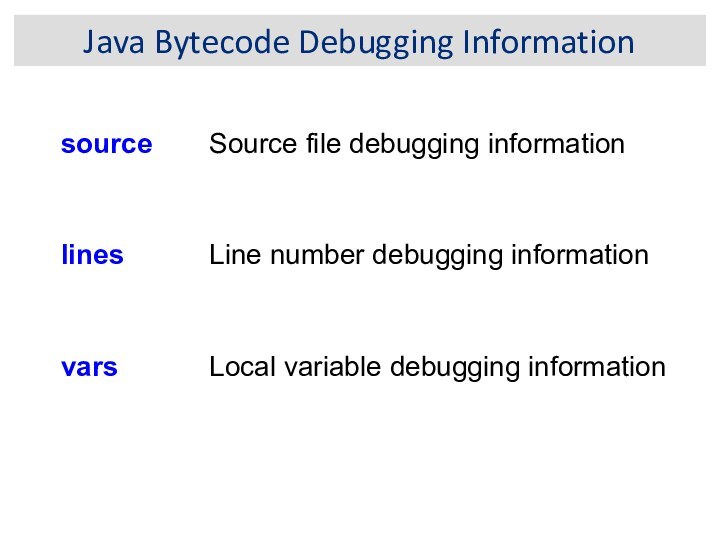
Java Bytecode Debugging Information
Слайд 11
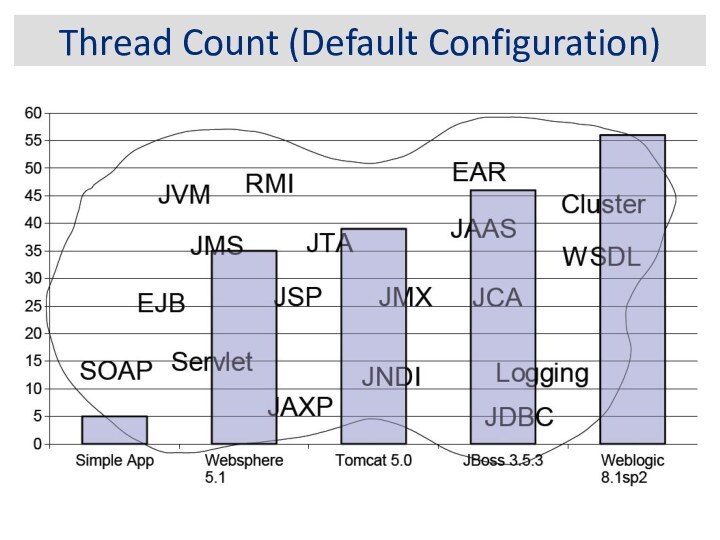
Thread Count (Default Configuration)
Слайд 13
Expert’s Checklist
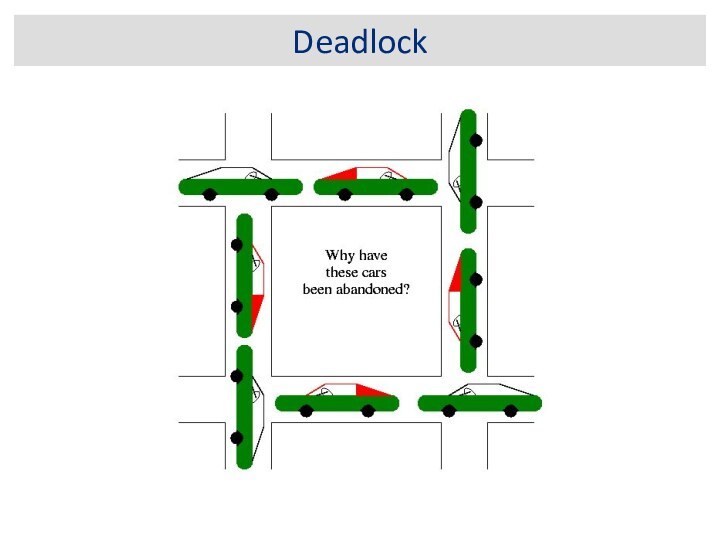
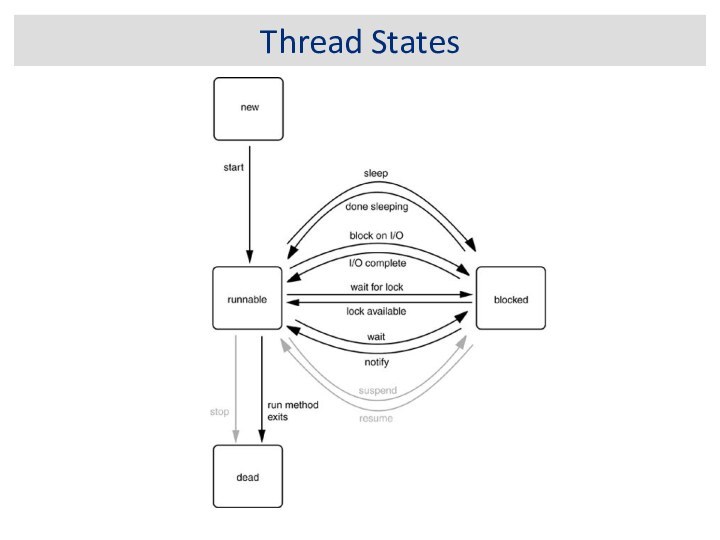
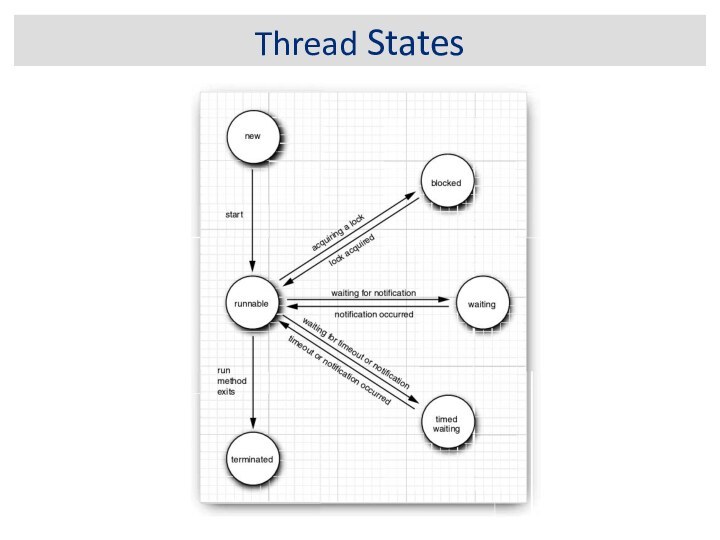
For hanging, deadlocked or frozen programs: If
you think your program is hanging, generate a stack
trace and examine the threads in states MW or CW. If the program is deadlocked then some of the system threads will probably show up as the current threads, because there is nothing else for the JVM to do.
For crashed, aborted programs: On UNIX look for a core file. You can analyze this file in a native debugging tool such as gdb or dbx. Look for threads that have called native methods. Because Java technology uses a safe memory model, any corruption probably occurred in the native code. Remember that the JVM also uses native code, so it may not necessarily be a bug in your application.
For busy programs: The best course of action you can take for busy programs is to generate frequent stack traces. This will narrow down the code path that is causing the errors, and you can then start your investigation from there.
Слайд 15
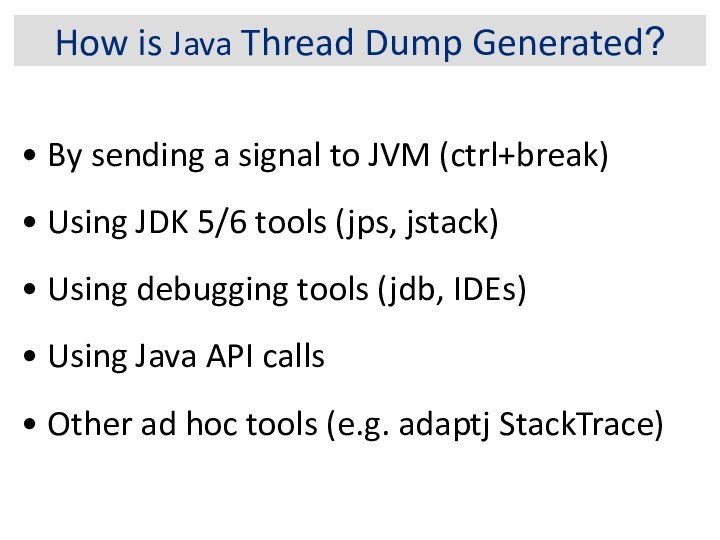
How is Java Thread Dump Generated?
By sending
a signal to JVM (ctrl+break)
Using JDK 5/6 tools
(jps, jstack)
Using debugging tools (jdb, IDEs)
Using Java API calls
Other ad hoc tools (e.g. adaptj StackTrace)
Слайд 16
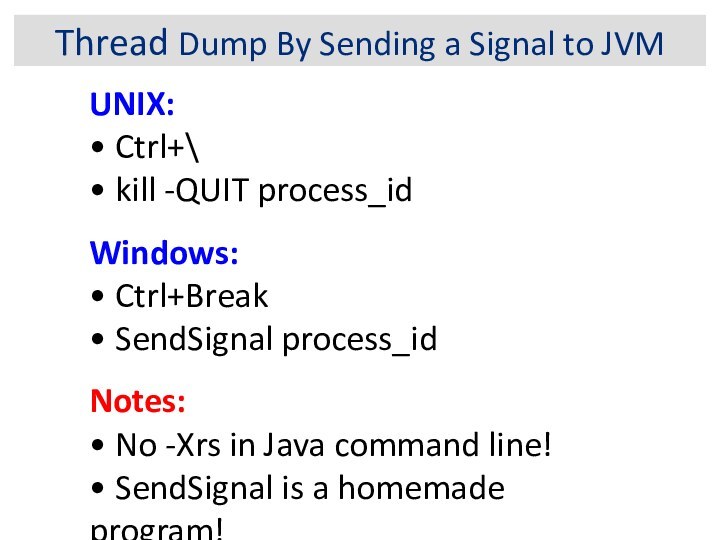
Thread Dump By Sending a Signal to JVM
UNIX:
Ctrl+\
kill -QUIT process_id
Windows:
Ctrl+Break
SendSignal process_id
Notes:
No -Xrs in Java command line!
SendSignal is a homemade program!
Слайд 17
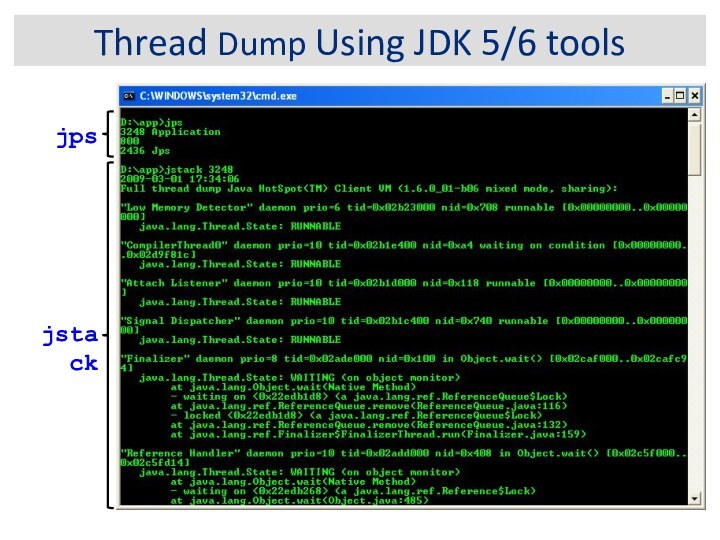
Thread Dump Using JDK 5/6 tools
jstack
jps
Слайд 18
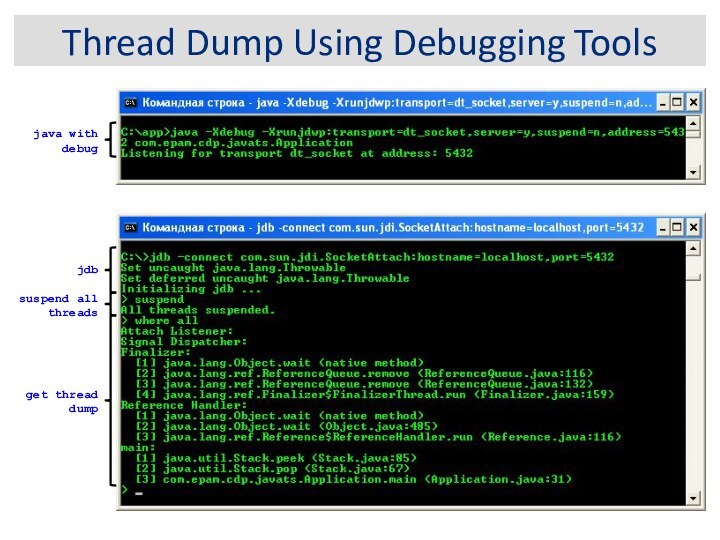
Thread Dump Using Debugging Tools
suspend all threads
jdb
get thread
dump
java with debug
Слайд 20
Using Java API calls
Throwable.printStackTrace()
Thread.dumpStack()
Since Java
1.5: Thread.getState()
Since Java 1.5: Thread.getStackTrace()
Since Java 1.5:
Thread.getAllStackTraces()
Слайд 22
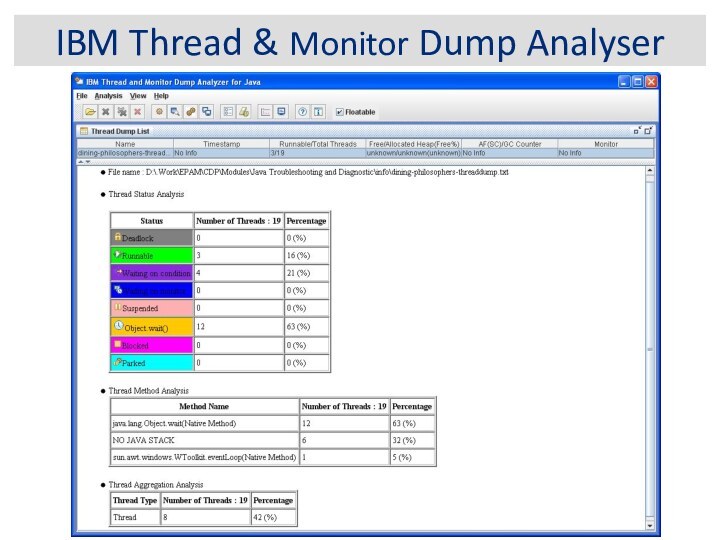
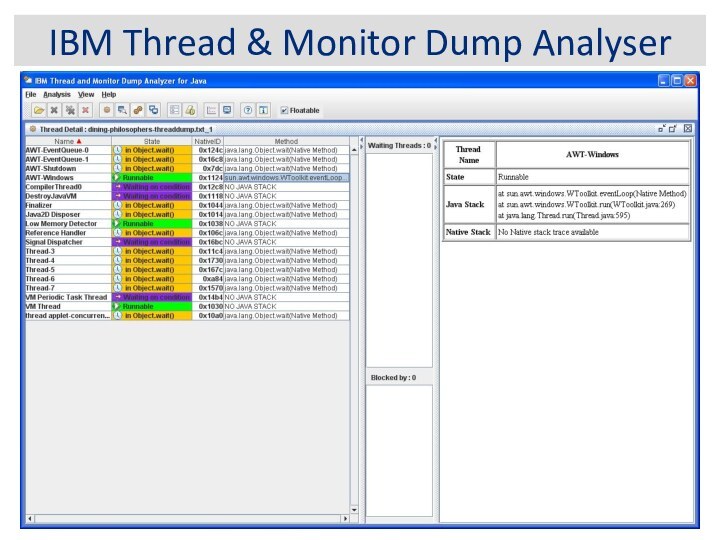
IBM Thread & Monitor Dump Analyser
Слайд 23
IBM Thread & Monitor Dump Analyser
Слайд 30
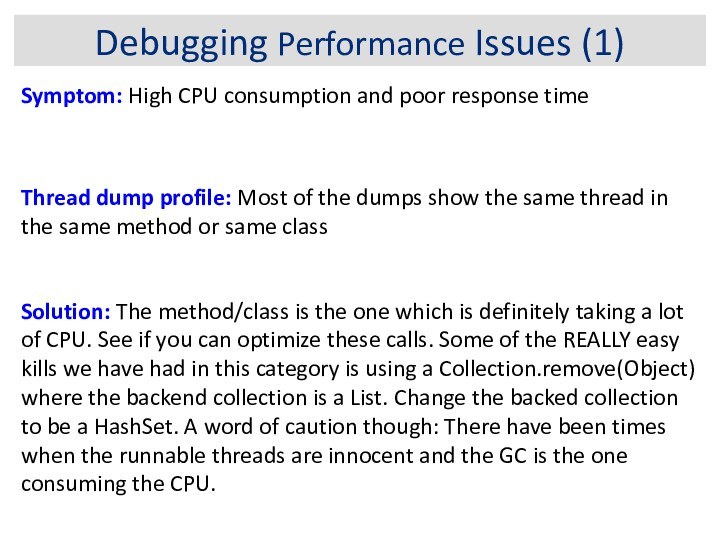
Debugging Performance Issues (1)
Symptom: High CPU consumption and
poor response time
Thread dump profile: Most of the dumps
show the same thread in the same method or same class
Solution: The method/class is the one which is definitely taking a lot of CPU. See if you can optimize these calls. Some of the REALLY easy kills we have had in this category is using a Collection.remove(Object) where the backend collection is a List. Change the backed collection to be a HashSet. A word of caution though: There have been times when the runnable threads are innocent and the GC is the one consuming the CPU.
Слайд 31
Debugging Performance Issues (2)
Symptom: Low CPU consumption most
of which is kernel time and poor response time
Thread
dump profile: Most thread dumps have the runnable threads performing some IO operations
Solution: Most likely your application is IO bound. If you are reading a lot of files from the disc, see if you can implement Producer-Consumer pattern. The Producer can perform the IO operations and Consumers do the processing on the data which has been read by the producer. If you notice that most IO operations are from the data base driver, see if you can reduce the number of queries to the database or see if you can cache the results of the query locally.
Слайд 32
Debugging Performance Issues (3)
Symptom: Medium/Low CPU consumption in
a highly multithreaded application
Thread dump profile: Most threads in
most thread dumps are waiting for a monitor on same object
Solution: The thread dump profile says it all. See if you can: eliminate the need for synchronization [using ThreadLocal/Session-scopeobjects] or reduce the amount of code being executed within the synchronized block.
Слайд 33
Debugging Performance Issues (4)
Symptom: Medium/Low CPU consumption in
a highly multithreaded application
Thread dump profile: Most threads in
most thread dumps are waiting for a resource
Solution: If all the threads are choked for resources, say waiting on the pool to create EJB-bean objects/DB Connection objects, see if you can increase the pool size.
Слайд 34
Example 1: Deadlock
org.apache.log4j.Category.callAppenders():
Слайд 35
Example 2: Performance Issue
...
at org.apache.tools.ant.DirectoryScanner.scandir(DirectoryScanner.java:1019)
at org.apache.tools.ant.DirectoryScanner.scandir(DirectoryScanner.java:1065)
at org.apache.tools.ant.DirectoryScanner.scandir(DirectoryScanner.java:1065)
at org.apache.tools.ant.DirectoryScanner.scandir(DirectoryScanner.java:1065)
at
org.apache.tools.ant.DirectoryScanner.scandir(DirectoryScanner.java:1065)
at org.apache.tools.ant.DirectoryScanner.scandir(DirectoryScanner.java:1065)
at org.apache.tools.ant.DirectoryScanner.scandir(DirectoryScanner.java:1065)
at org.apache.tools.ant.DirectoryScanner.checkIncludePatterns(DirectoryScanner.java:836)
at org.apache.tools.ant.DirectoryScanner.scan(DirectoryScanner.java:808)
...
Слайд 36
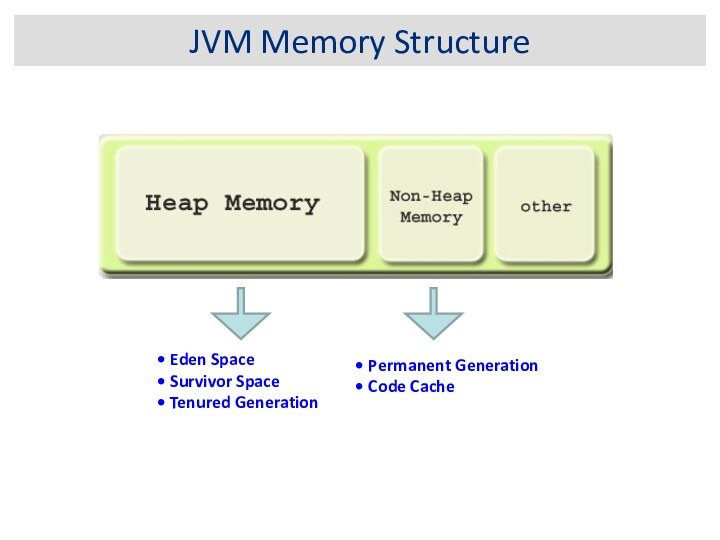
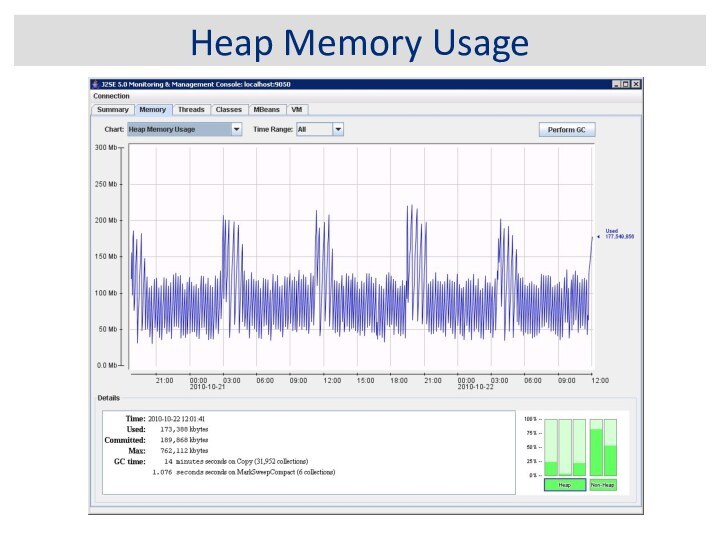
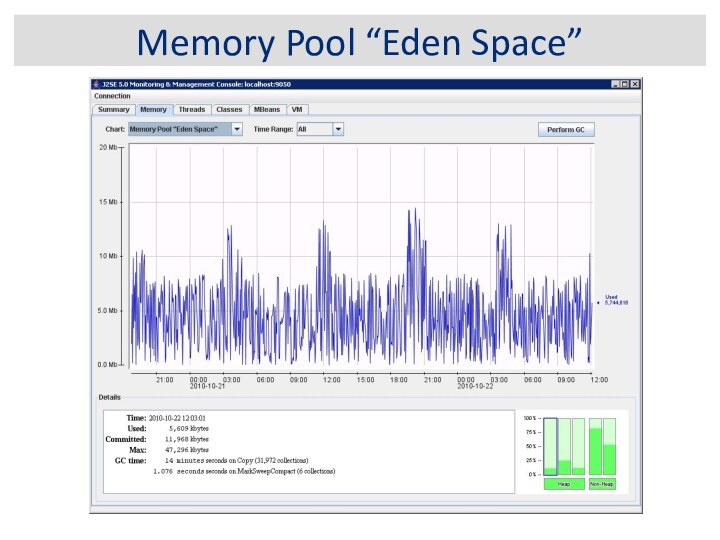
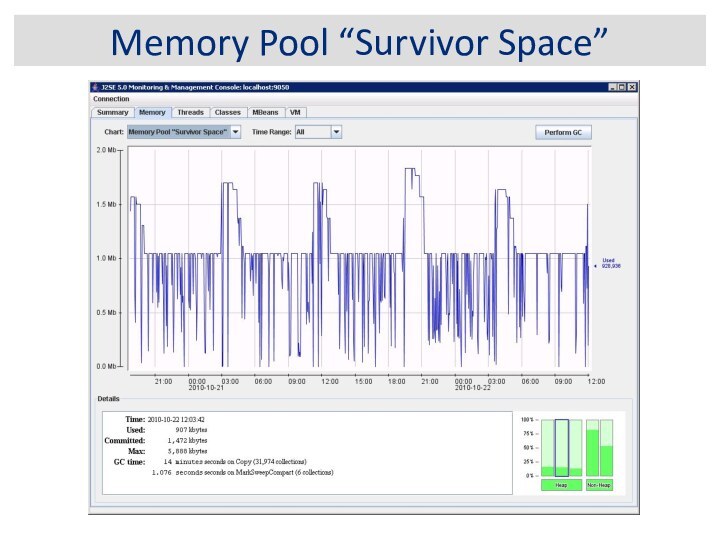
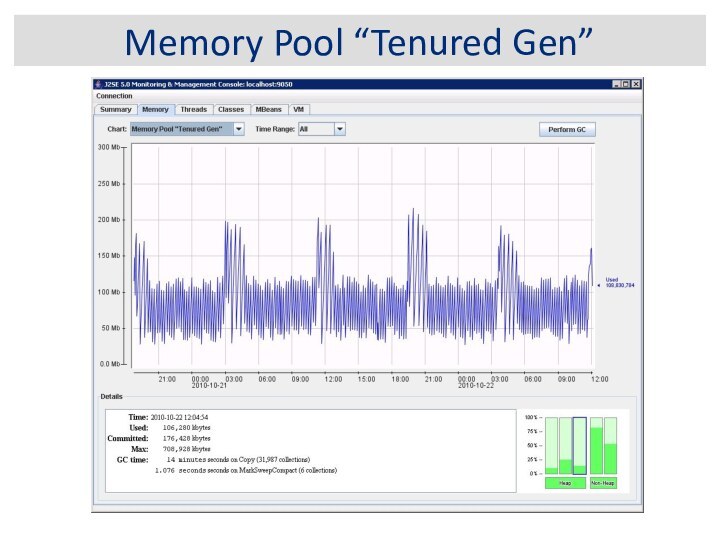
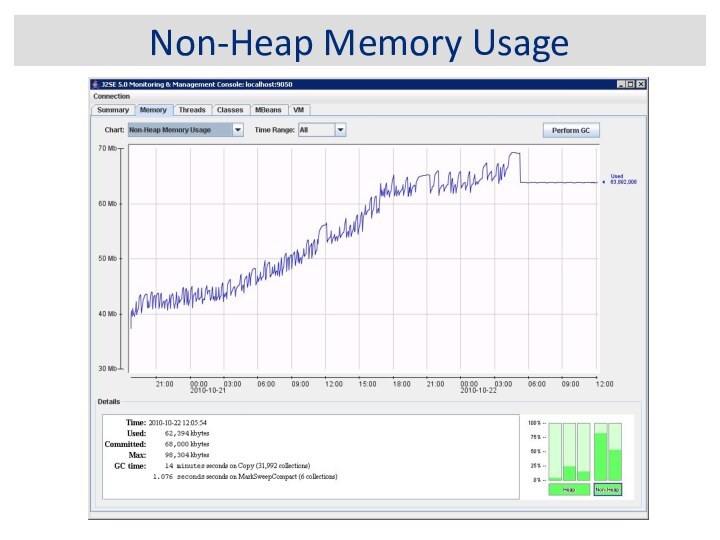
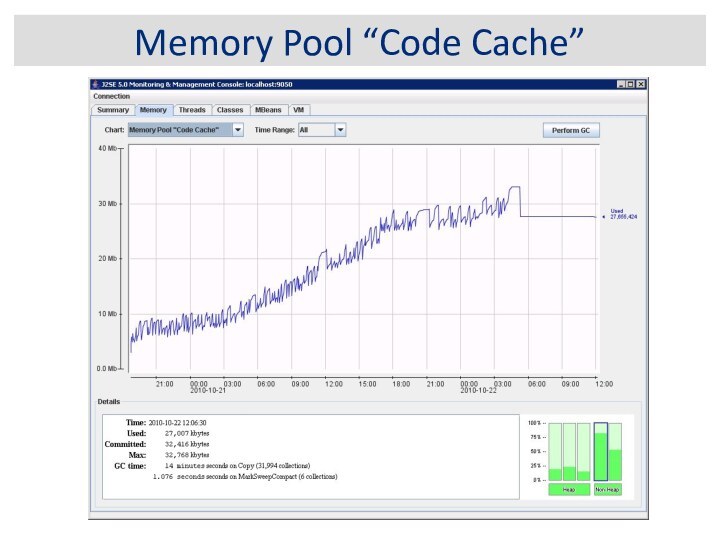
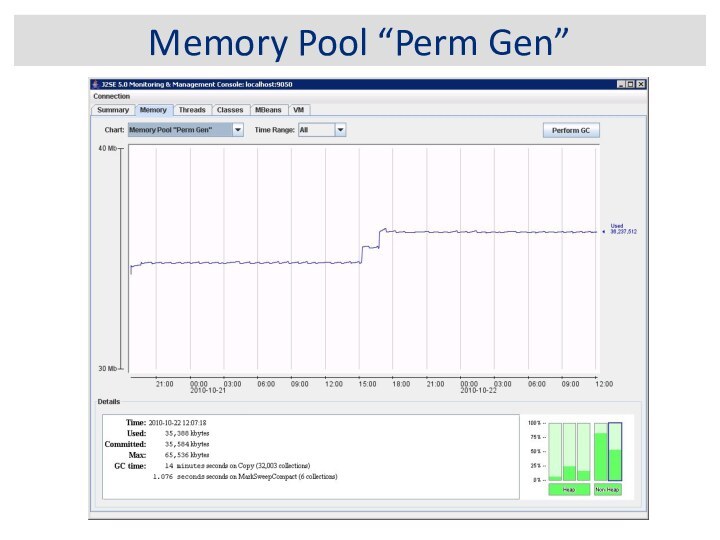
JVM Memory Structure
Eden Space
Survivor Space
Tenured
Generation
Permanent Generation
Code Cache
Слайд 38
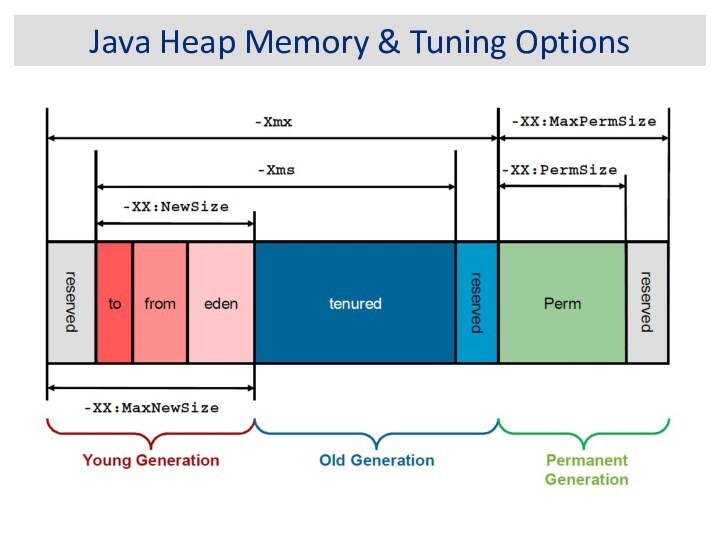
Java Heap Memory & Tuning Options
Слайд 39
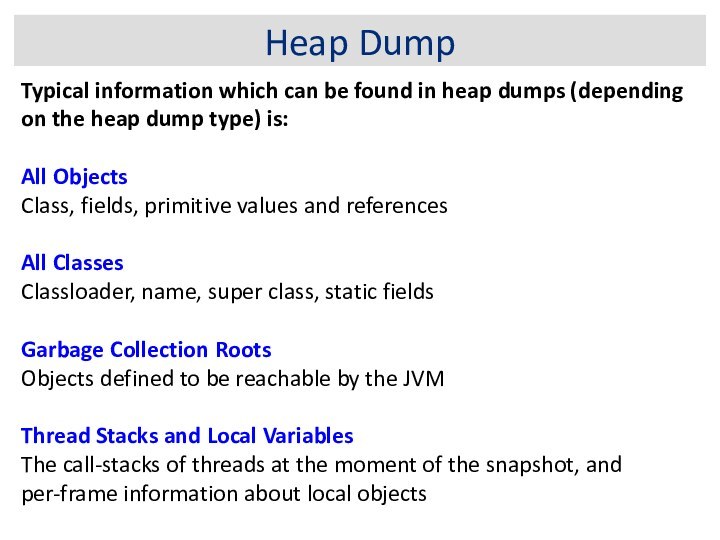
Heap Dump
Typical information which can be found in
heap dumps (depending on the heap dump type) is:
All Objects
Class, fields, primitive values and references
All Classes
Classloader, name, super class, static fields
Garbage Collection Roots
Objects defined to be reachable by the JVM
Thread Stacks and Local Variables
The call-stacks of threads at the moment of the snapshot, and per-frame information about local objects
Слайд 40
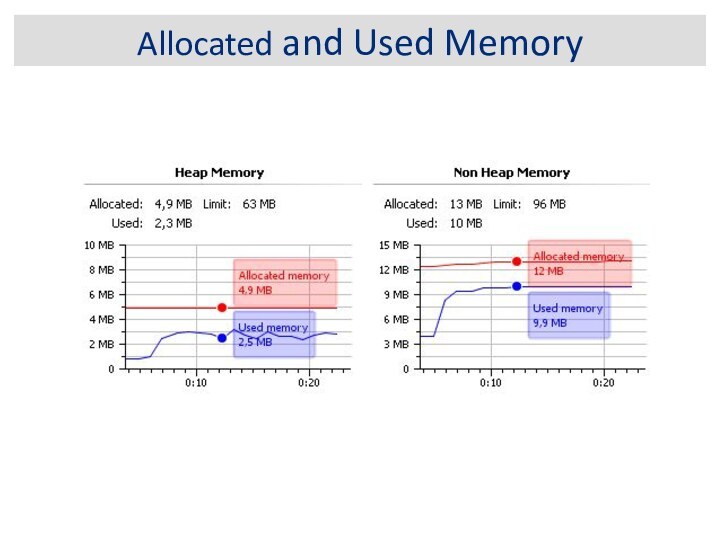
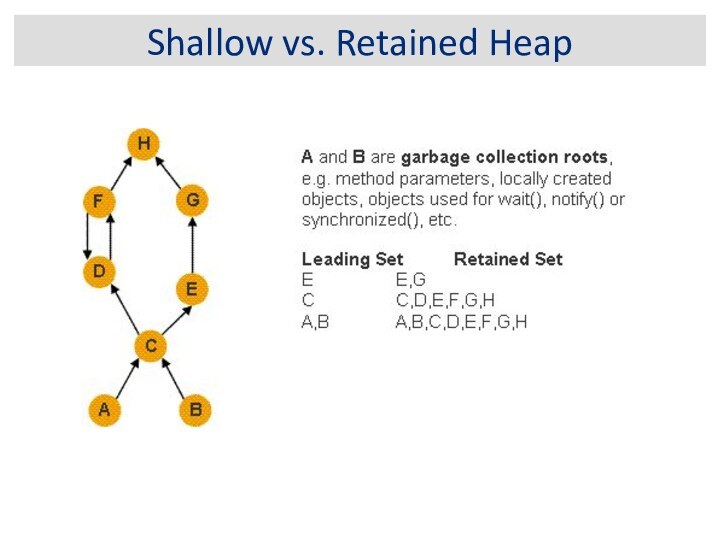
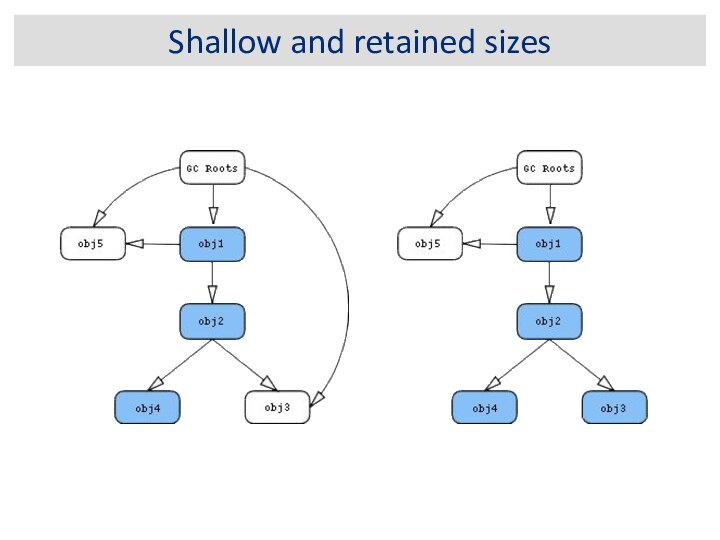
Shallow vs. Retained Heap
Shallow heap is the memory
consumed by one object. An object needs 32 or
64 bits (depending on the OS architecture) per reference, 4 bytes per Integer, 8 bytes per Long, etc. Depending on the heap dump format the size may be adjusted (e.g. aligned to 8, etc...) to model better the real consumption of the VM.
Retained set of X is the set of objects which would be removed by GC when X is garbage collected.
Retained heap of X is the sum of shallow sizes of all objects in the retained set of X, i.e. memory kept alive by X.
Слайд 43
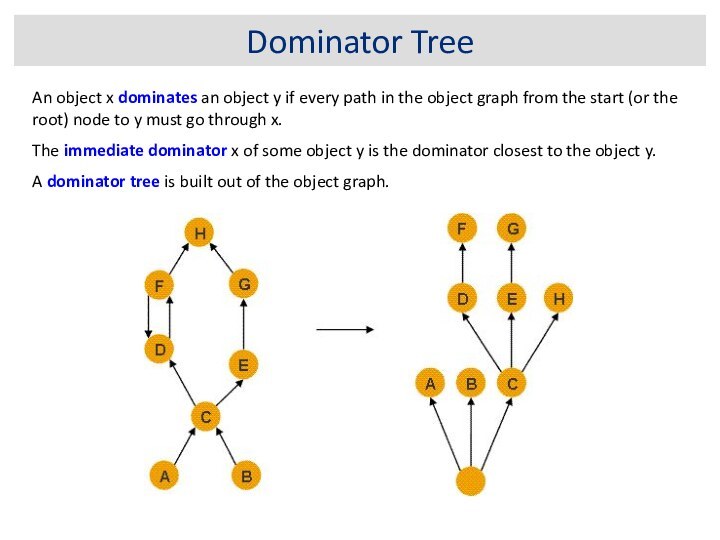
Dominator Tree
An object x dominates an object y
if every path in the object graph from the
start (or the root) node to y must go through x.
The immediate dominator x of some object y is the dominator closest to the object y.
A dominator tree is built out of the object graph.
Слайд 45
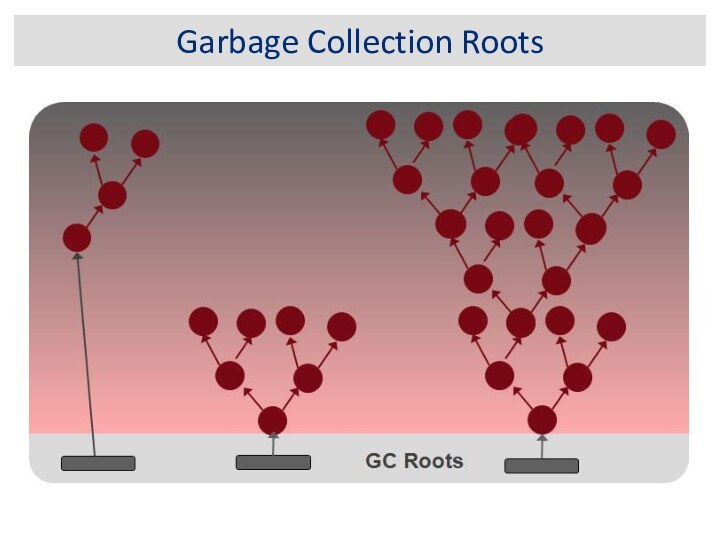
Garbage Collection Roots
System Class
JNI Local
JNI Global
Thread Block
Thread
Busy Monitor
Java Local
Native Stack
Finalizer
Unfinalized
Unreachable
Unknown
Слайд 46
Garbage Collection Roots
Class
Thread
Stack Local
JNI Local
JNI Global
Monitor Used
Held by JVM
Слайд 47
How is Java Heap Dump Generated?
By sending
a signal to JVM (ctrl+break)
Using JDK 5/6 tools
(jps, jmap)
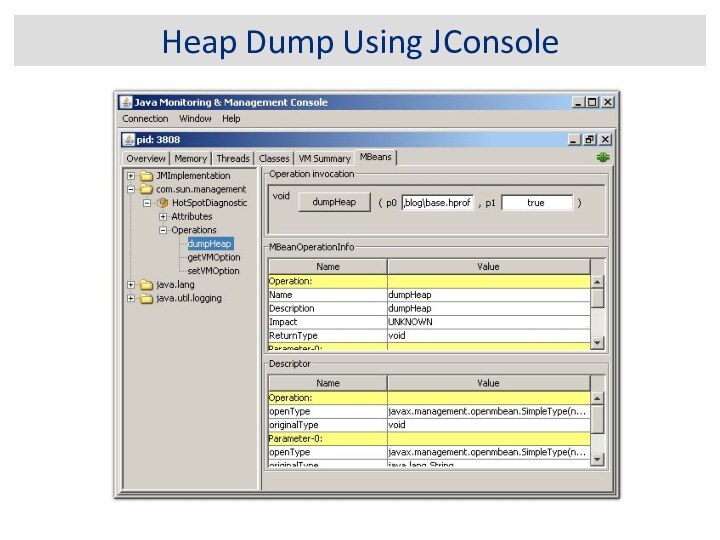
Using JConsole
Other ad hoc tools (e.g. Eclipse MAT)
1. Get Heap Dump on an OutOfMemoryError
2. Interactively Trigger a Heap Dump:
Слайд 48
Heap Dump on an OutOfMemoryError
java -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError MainClass
Слайд 49
Heap Dump By Sending a Signal to JVM
java
-XX:+HeapDumpOnCtrlBreak MainClass
+
See Thread Dump By Sending a Signal to
JVM
Слайд 50
Heap Dump Using JDK 5/6 tools
jmap -dump:format=b,file=
Слайд 61
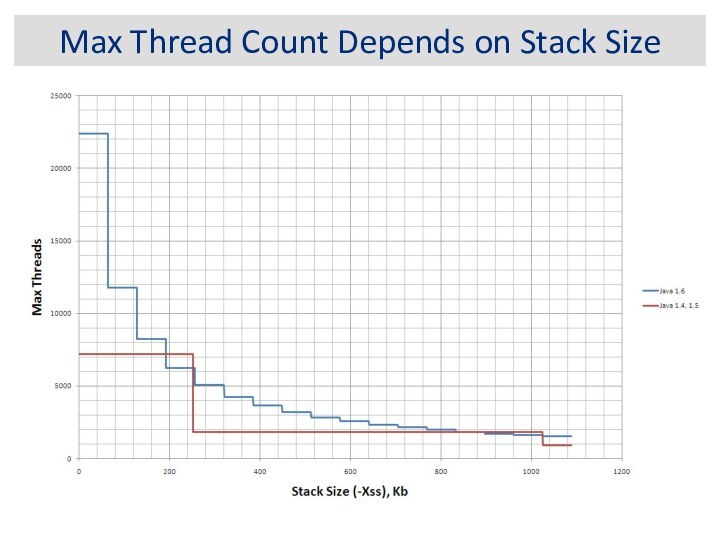
Max Thread Count Depends on Stack Size
Слайд 62
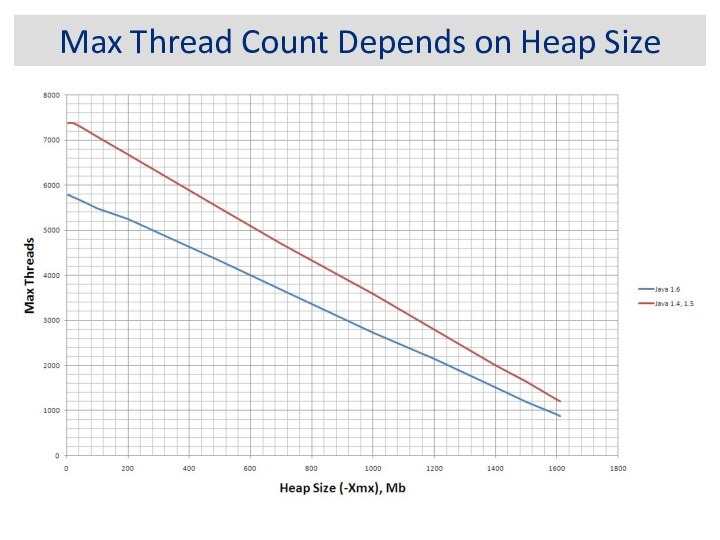
Max Thread Count Depends on Heap Size
Слайд 63
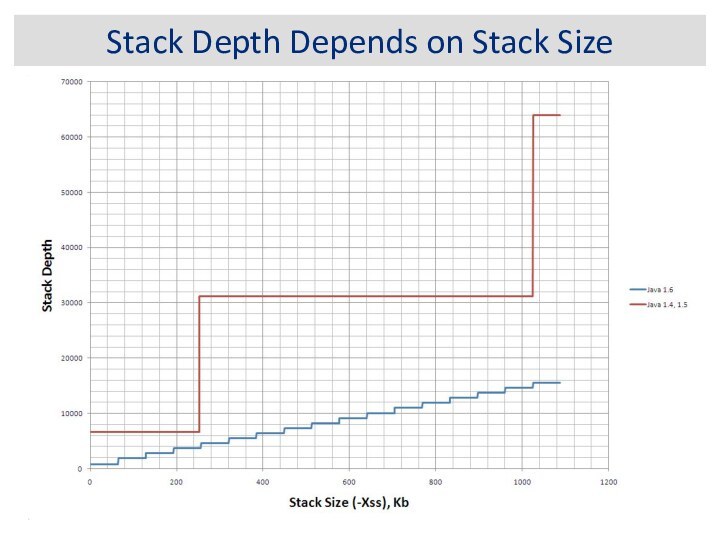
Stack Depth Depends on Stack Size
Слайд 65
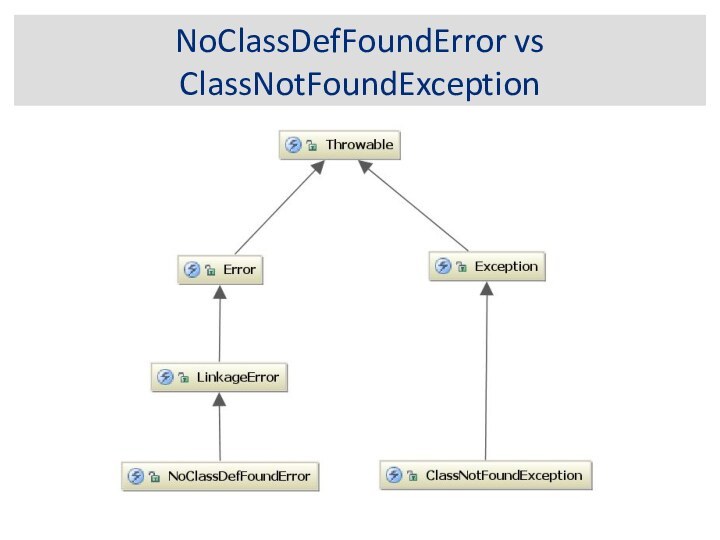
NoClassDefFoundError vs
ClassNotFoundException