Слайд 3
Chapter 11
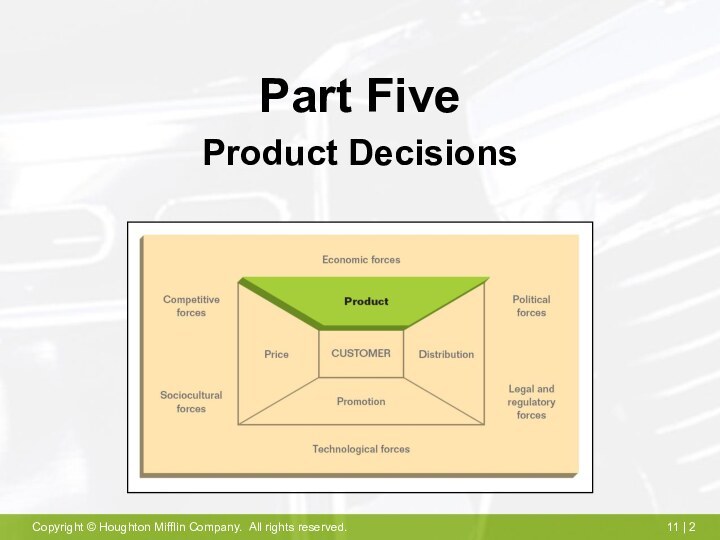
Product Concepts
Слайд 4
Objectives
Understand the concept of a product
Explain how to
classify products
Examine concepts of product: item, line, and mix
and how they are connected
Understand product life cycle and impact on marketing strategies
Describe product adoption process
Understand why products fail/succeed
Слайд 5
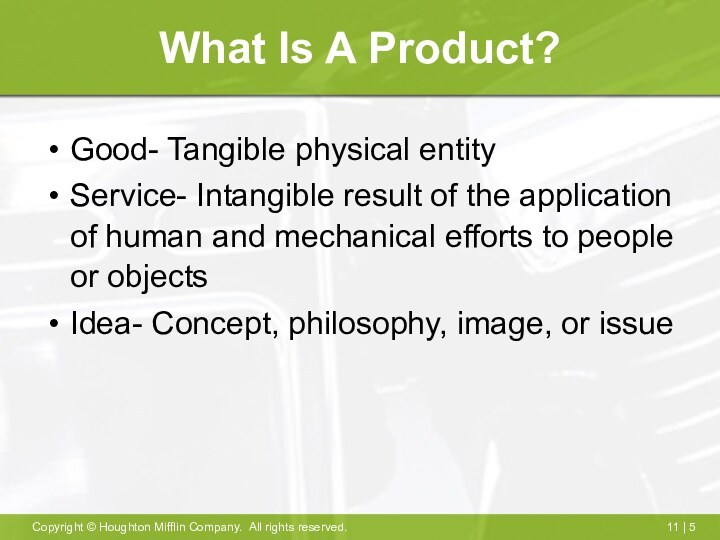
What Is A Product?
Good- Tangible physical entity
Service- Intangible
result of the application of human and mechanical efforts
to people or objects
Idea- Concept, philosophy, image, or issue
Слайд 7
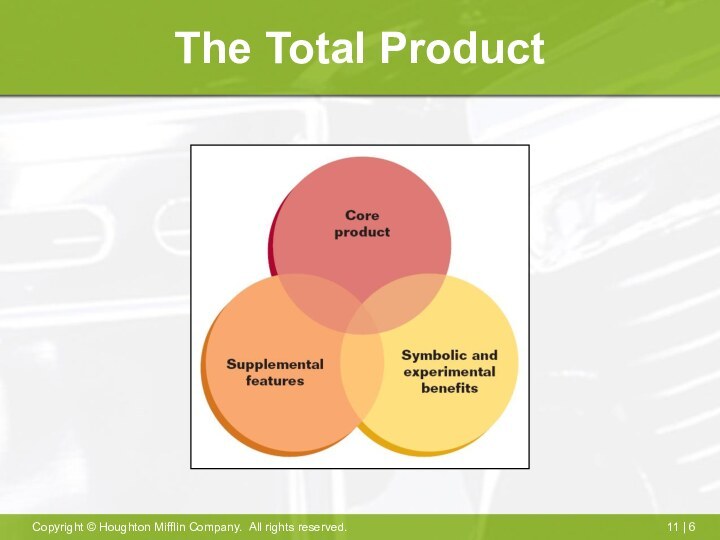
Product Characteristics
Fundamental utility
Supplemental features
Installation
Delivery
Training
Financing
Symbolic meaning
Слайд 8
Classifying Products
Consumer- products purchased to satisfy personal and
family needs
Business- products brought to use in an organization’s
operations, to resell, or to make other products
Слайд 9
Convenience Products
Relatively inexpensive, frequently purchased items for which
buyers exert only minimal purchasing effort
Слайд 10
Convenience Product
Strategy Implications
Retail outlets
Low per-unit gross margins
Little promotion
effort
Packaging important
Слайд 11
Shopping Products
Items for which buyers are willing to
expend considerable effort in planning and making purchases
Слайд 12
Shopping Product
Marketing Implications
No brand loyalty
Fewer retail outlets than
convenience
Lower inventory turnover
Higher gross margins
Personal selling
Channel member cooperation
Слайд 13
Specialty Products
Items with unique characteristics that buyers are
willing to expend considerable effort to obtain.
Слайд 14
Specialty Product
Marketing Implications
Limited retail outlets
Lower inventory turnover
High gross
margins
Слайд 15
Unsought Products
Products purchased to solve a sudden problem,
products of which customers are unaware, and products that
people do no necessarily think of buying.
Слайд 16
Unsought Products
Marketing Implications
Build trust with consumer by:
Recognizable brand
Superior
performance
Слайд 17
Business Products
Installations- facilities & nonportable equipment
Accessory equipment- not
part of final product
Raw materials- natural materials part of
product
Component parts- finished items ready for assembly or need little processing
Process materials-used in production but not identifiable
MRO supplies-maintenance, repair, and operating items not part of final product
Services-intangible products in operations
Слайд 18
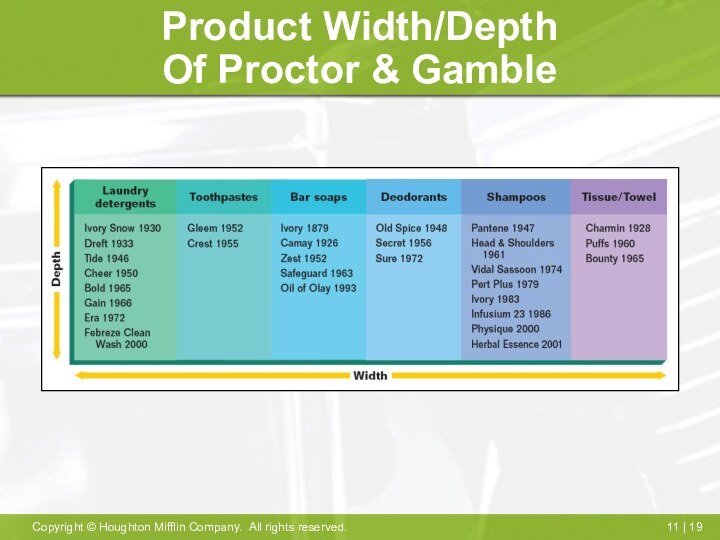
Product Line And Product Mix
Item- specific version of
product
Line- closely related items viewed as a unit
Mix- total
group of products
Width of mix- number to lines
Depth of mix- number of different products in line
Слайд 19
Product Width/Depth
Of Proctor & Gamble
Слайд 20
Product Life Cycle
The progression of a product through
four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
Windows Product Life
Cycle Policy
Слайд 21
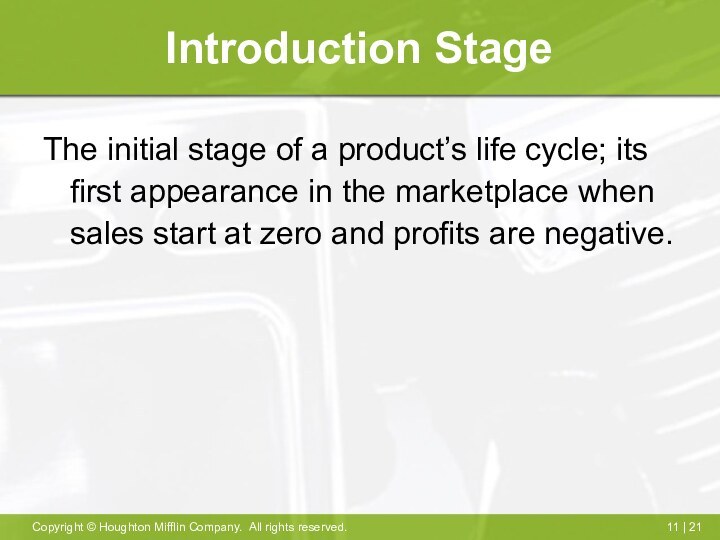
Introduction Stage
The initial stage of a product’s life
cycle; its first appearance in the marketplace when sales
start at zero and profits are negative.
Слайд 22
Introductory Stage
Risk of failure high
Buyers must be made
aware of:
Features
Uses
Advantages
Sellers lack
Resources
Technological knowledge
Marketing know-how
Слайд 23
Growth Stage
The product life cycle stage when sales
rise rapidly and profits reach a peak, then start
to decline.
Слайд 24
Growth Stage
Sales rise rapidly
Profits peak
Starts to decline
Competitors react
Слайд 25
Growth Stage
Marketing Strategy
Encourage brand loyalty- stress brand benefits
Strengthen
market share
Emphasize product’s benefits
Aggressive pricing
Analyze production position
Efficient distribution system
Promotion
costs drop as % of sales
Слайд 26
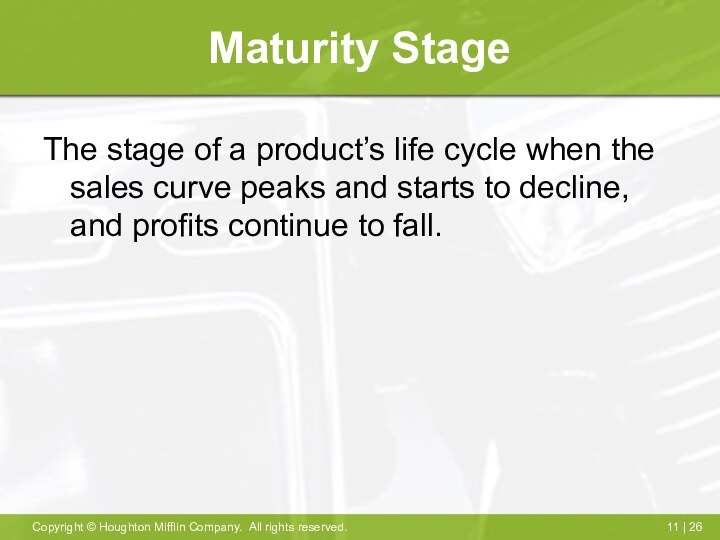
Maturity Stage
The stage of a product’s life cycle
when the sales curve peaks and starts to decline,
and profits continue to fall.
Слайд 27
Maturity Stage
Marketing Strategy
Intense competition
Emphasize improvements and differences
Advertising and
dealer-oriented promotion
Global expansion
Слайд 28
Maturity Stage Objectives
Generate Cash Flow
Maintain Share of Market
Increase
Share of Customer
Слайд 29
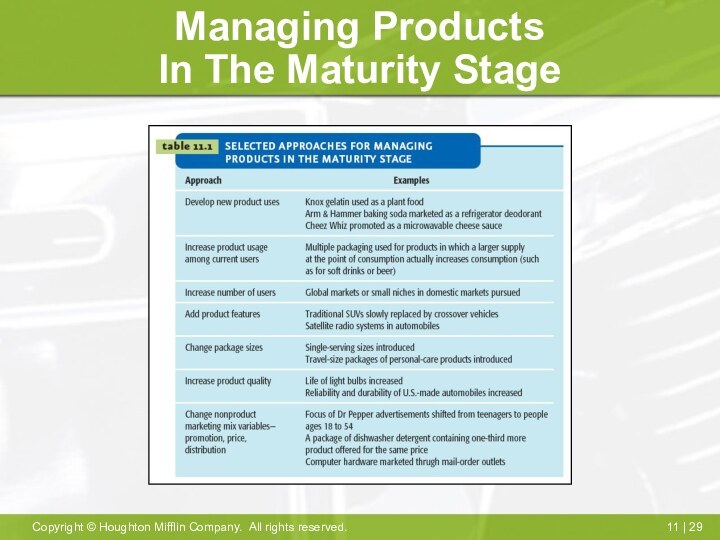
Managing Products
In The Maturity Stage
Слайд 30
Decline Stage
The stage of a product’s life cycle
when sales fall rapidly.
Слайд 31
Decline Stage
Marketing Strategy
Eliminate/reposition items
Cut promotion
Eliminate marginal distributors
Plan for
phase out
Approaches
Harvesting
Divesting
Nike Product Life Cycle
Слайд 32
Product Adoption Process
The five-stage process of buyer acceptance
of a product: awareness, interest, evaluation, trial, and adoption.
Слайд 33
Stages Of
Product Adoption Process
Awareness
Interest
Evaluation
Trial
Adoption
Diffusion
Слайд 34
Most New Ideas
Have Their Skeptics
Слайд 35
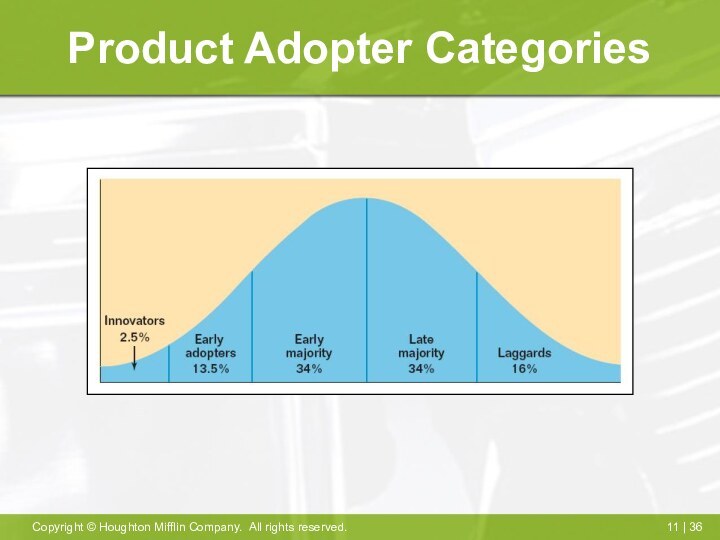
Adopter Categories
Innovators- first adopters
Early Adopters- careful choosers
Early Majority-
deliberate and cautious
Late Majority- skeptics who only adopt when
necessary
Laggards- distrust new products
Слайд 37
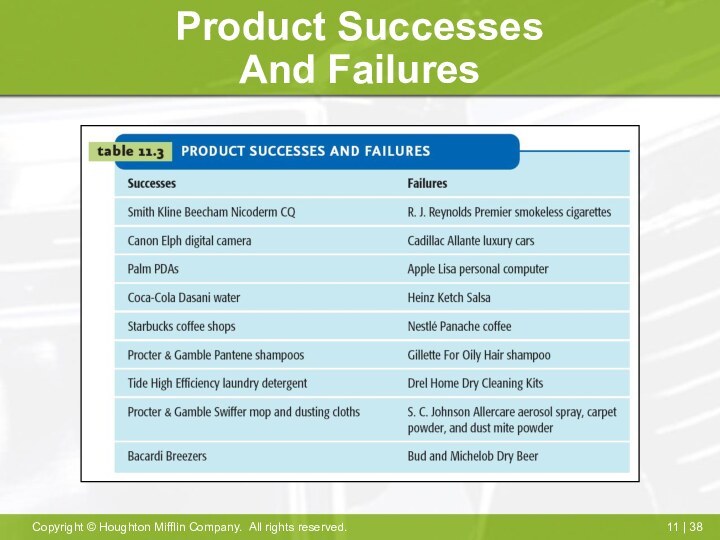
Why Some
Products Fail/Succeed
Failure to match product to needs
Failure
to send right message
Technical/design problems
Poor timing
Overestimate market
Ineffective promotion
Insufficient distribution