- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Acute and chronic glomerulonephritis
Содержание
- 2. Glomerulonephritis (GN), also known as glomerular
- 3. EtiologyInfectious- Streptococcal -Nonstreptococcal postinfectious glomerulonephritis
- 4. Pathogenesis of GlomerulonephritisCausative agent activates in organism
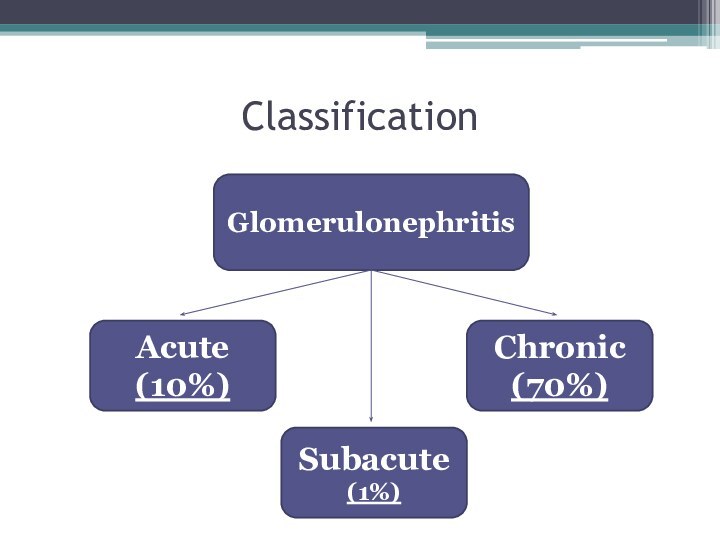
- 5. SclerotherapyProliferation and activation of mesangial cellsChanges in
- 6. ClassificationGlomerulonephritisAcute (10%)Chronic (70%) Subacute (1%)
- 7. Acute glomerulonephritisIt is an acute immunoinflammatory disease
- 9. SyndromsNephrotic syndrome Hypertonic syndromeMixed syndrome
- 12. Acute glomerulonephritis
- 13. Diagnostics of AGFull blood countClinical urine analysisDetermination
- 14. Treatment of AGDiet №7Antibiotics: -
- 15. Antiaggregants - dipyridamole tablets of 25 mg, film-coated, 75 mg/day, tab; pentoxifylline 100 mg/day amp.
- 16. With antihypertensive and nephroprotectivepurpose, angiotensin-converting enzymeinhibitors:- fozinopril
- 17. Chronic glomerulonephritisIt is the same as an
- 18. Diagnostics of CG1. General blood test: HB,
- 19. Treatment of CGGlucocorticoids: - Prednisolone
- 20. Antiaggregants and anticoagulants: - Dipyridamole 400-600 mg/day - Clopidogrel 0,2-0,3 g/day
- 21. Antihypertensive therapy: ACE inhibitor
- 22. Скачать презентацию
- 23. Похожие презентации
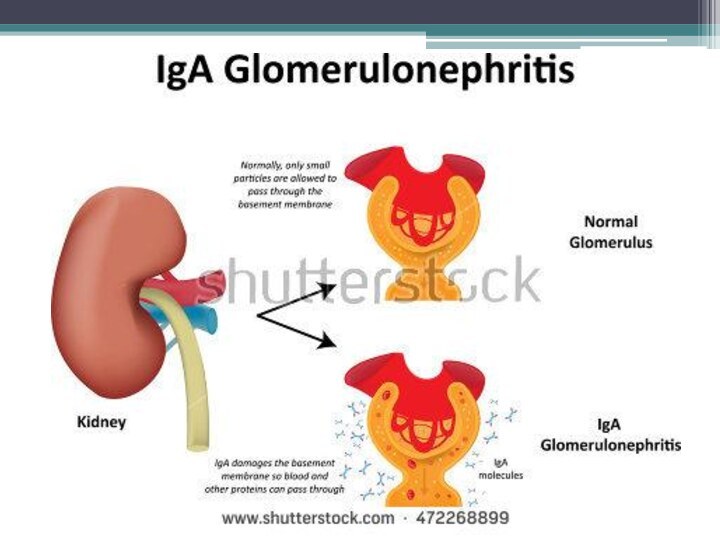
Glomerulonephritis (GN), also known as glomerular nephritis, is a term used to refer to several kidney diseases (usually affecting both kidneys). Many of the diseases are characterised by inflammation either of the glomeruli or of the small blood vessels in the















Слайд 3
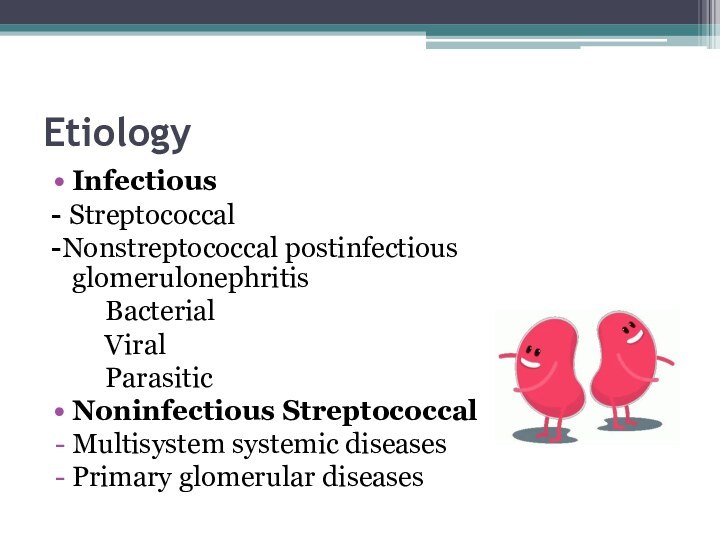
Etiology
Infectious
- Streptococcal
-Nonstreptococcal postinfectious glomerulonephritis
Bacterial
Viral
Parasitic
Noninfectious
StreptococcalMultisystem systemic diseases
Primary glomerular diseases
Слайд 4
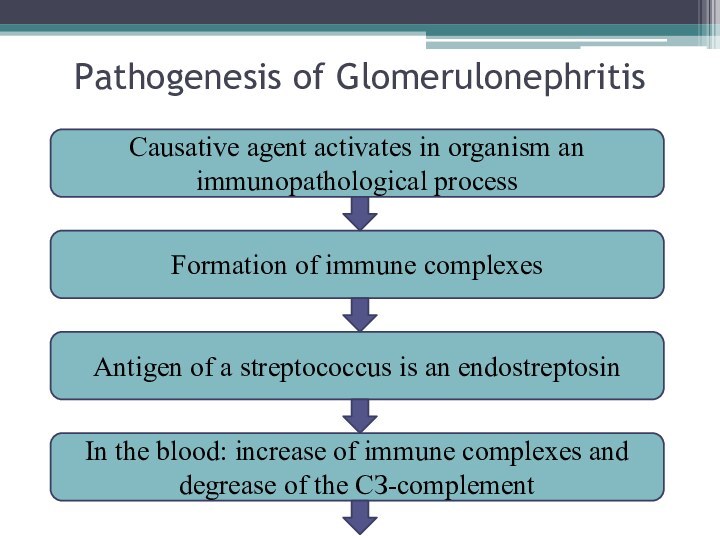
Pathogenesis of Glomerulonephritis
Causative agent activates in organism an
immunopathological process
Formation of immune complexes
In the blood: increase of
immune complexes and degrease of the СЗ-complementAntigen of a streptococcus is an endostreptosin
Слайд 5
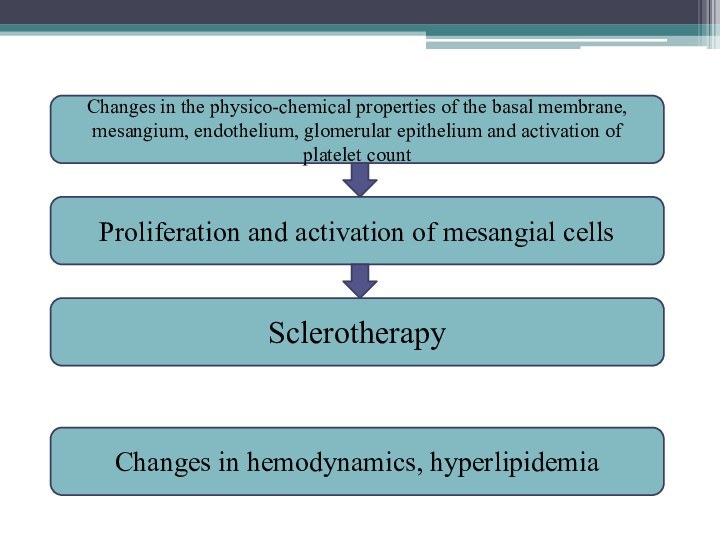
Sclerotherapy
Proliferation and activation of mesangial cells
Changes in the
physico-chemical properties of the basal membrane, mesangium, endothelium, glomerular
epithelium and activation of platelet countChanges in hemodynamics, hyperlipidemia
Слайд 7
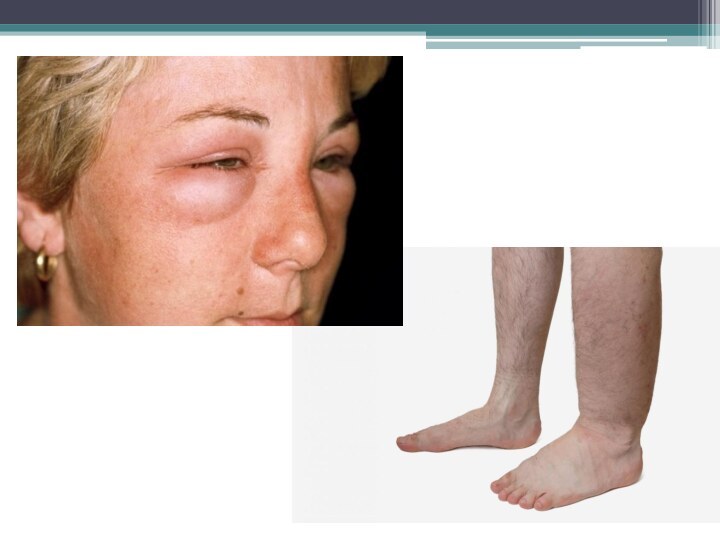
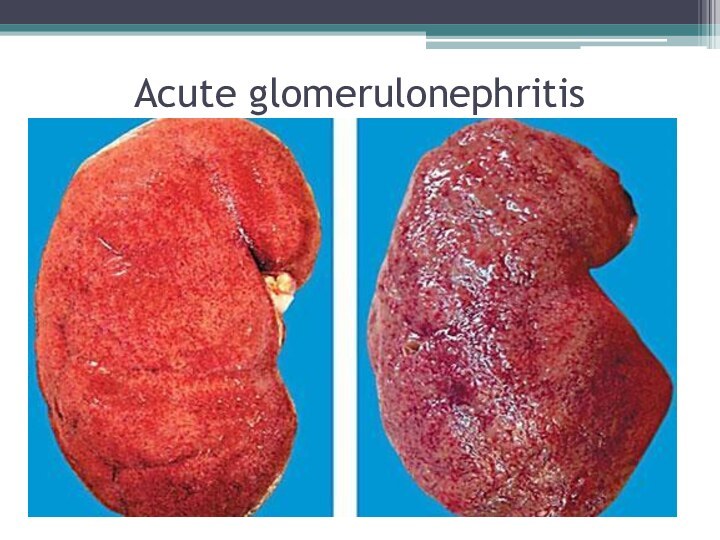
Acute glomerulonephritis
It is an acute immunoinflammatory disease of
the kidneys with the initial lesion of the glomeruli
and involvement in the pathological process of all renal structures, clinically manifested by renal and adrenal symptoms
Слайд 13
Diagnostics of AG
Full blood count
Clinical urine analysis
Determination of
creatinine, urea, uric acid
Calculation of the glomerular filtration
rateDetermination of total protein count, protein fractions
Determination of ALT, AST, cholesterol, bilirubin, total lipids
Determination of potassium, sodium, chlorides, iron, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus
Слайд 14
Treatment of AG
Diet №7
Antibiotics:
- Benzylpenicillin
1 000 000-2 000 000 UA/day, 7-10 days.
Glucocorticoids:
- Prednisolone 50-60 mg/day 1-1,5 monthsСлайд 15 Antiaggregants - dipyridamole tablets of 25 mg, film-coated,
75 mg/day, tab; pentoxifylline 100 mg/day amp.
Слайд 16
With antihypertensive and nephroprotective
purpose, angiotensin-converting enzyme
inhibitors:
- fozinopril 20
mg/day,
- enalapril 20 mg/day,
- ramipril 10 mg/day,
tab;
Слайд 17
Chronic glomerulonephritis
It is the same as an acute
form. It can be
difficult to detect it because of
the absence ofobvious symptoms (latent leakage), in contrast
to acute. The patient can feel quite normal, not
have puffiness, his urine is without blood.
Increased protein in the blood,
an increase in the number of
red blood cells can mean the
presence of the disease. If it
is not treated for a long time,
nephratonia develops.
Слайд 18
Diagnostics of CG
1. General blood test: HB, Erythrocytes,
Leukocytes, Platelets, ESR before and after kidney biopsy
2. Test
strips for hematuria, proteinuria, leukocyturia3. Protein / creatinine ratio
4. Creatinine, blood serum urea
5. Determination of clotting time
6. A biopsy of a kidney under the control of US
7. The account of the accepted and allocated liquid, daily measurement of weight
8. Determination of the concentration of Cyclosporine, Tacrolimus in serum
Слайд 19
Treatment of CG
Glucocorticoids:
- Prednisolone 1
mg/kg 2 months endovenous
Cytostatics:
- Cyclophosphamide 2-3
mg/kg/day- Chlorambucil 0,1-0,2 mg/kg/day
- Ciclosporin 2,5-3,5 mg/kg/day
Слайд 20
Antiaggregants and anticoagulants:
- Dipyridamole 400-600
mg/day
- Clopidogrel 0,2-0,3 g/day
Слайд 21
Antihypertensive therapy:
ACE inhibitor
- Captopril 50-100 mg/day
-
Enalapril 10-20 mg/dayСalcium channel blockers
- Nifedipine 20-40 mg/day
Antioxidants:
- Tocopherol