Слайд 2
Three level model of
Electronic Health Records
(EHR)
Co-operation
and healthcare processes
Data Exchange and enduser software
Infrastructure, standards and
legislation
HEDA
EHR
Слайд 3
Three level model of EHR - Infrastructure:
Infrastructure –
common secure environment for the data Exchange (interoperability of
technical systems)
Legislation – what kind of data when and how is allowed to use
Standards – data standards (interoperability of healthcare processes - understanding each other „language“, machine readable data)
Security – reliability of the system (technically, legally)
Слайд 4
Three level model of EHR – data exchange:
Data
exchagne standards (HL7, …)
Enduser software – EHR system
Usability aspects
(system speed, UI, UC)
Connection with other systems (prescription, x-ray, financial, insurance, statistics, medical staff databases)
Слайд 5
Three level model of EHR - cooperation:
Association of
medical processes with EHR technical solution (process standards and
compability)
Cooperation model – build up common system (sharing data with patient and other medical professionals)
Mutual understanding and reliability – interoperability on the level of processes
Слайд 8
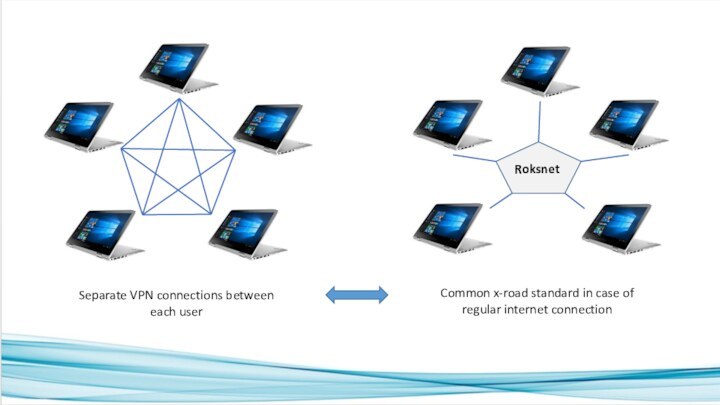
Advantages using Roksnet and x-road standard
Roksnet(using X-road standard)

is a secure data Exchange environment.
For the secure
data Exchange is necessary to establish separate secure channels (VPN) between service providers and consumers. Roksnet is like a secure two-side translation solution (on the base of adapter server). With help of Roksnet services will be translated to the x-road standard on the side of the service provider. On the side of consumer services will be (re)translated to the „language“ of consumer. Therefore it is not important what kind of information system or database are using different service providers or consumers. Each has it’s „own translator“ (as adapter server).
Thanks for the x-road standard it is possible to use for the secure data exchange a regular internet connection instead of number of separate VPN connections.
It is possible to build up Roksnet services one by one which makes the solution flexible and economically eficient. Roksnet can be used as a infrastructe base for healthcare data exchange between hospitals and regions.
Слайд 11
GenNet Laboratories and HEDA
Market size – HEDA previous
version is covering 58% of Estonian health software market,
including West and East Estonian Regional Hospitals.
Long experience - the software is used since 1997. GenNet Laboratories has 26 years experience of software developing.
Large scale of functionalities – HEDA offers all necessary functionalities for ambylatory and stationary care. Therefore all modules can be easily interfaced and there is no technical conflicts between different modules.
Support - HEDA modules and applications including data architecture and models are developed inhouse. All client specific developments will be completed fast and flexible and large scale support (including infrastructure technical support and data modelling suport) will be provided.
Слайд 13
HEDA is a next generatsion version of EHR
software which went to the production in Estonia in
1997.
Currently HEDA and it’s previous version covers 58% of Estonian healthcare market
High usability level - HEDA has designed on the base of long term healthcare user experience for supporting healthcare processes on the best way
Wide range of support for implementing EHR - HEDA is offered with support for all three levels of the EHR model – support for infrastructure (Roksnet), usability and processes (modelling software for supporting healthcare processes as tailor made solution)
Wide range of modules covers most of hospital processes - HEDA modules covers almost all enduser needs, including solutions for the X-ray, ePrescription, PatientPortal, Telemedicine, Laboratory, Blood bank and Booking system. There are also modules for stock, staff, accounting and connecting external databases. Therefore necessity to use different softwares is very low.
Background and main advantages of HEDA
Слайд 15
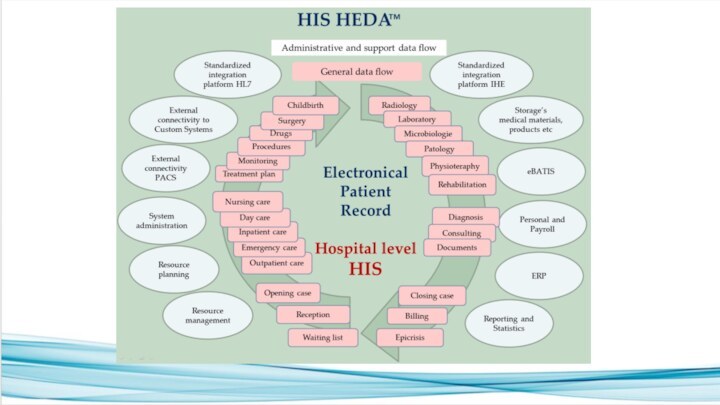
HEDA contains of seven bigger modules which have
75 different submodules:
Resources management (8 submodules)
Medical functionalities (40 submodules)
Reporting
and data management (8 submodules)
External interfaces (8 submodules)
System administration (8 submodules)
Specialized subsystems (2 submodules)
Telemedicine and communication (1 submodule)
Architecture and functionalities of the HEDA
Слайд 16
HEDA modules and submodules main functionalities:
Resources management (8

submodules) – including management of classificators, staff, hospital structure,
service, settlements, pricelists, helth insurance contracts and parameters.
Medical functionalities (40 submodules) – handling of all medical documents and data including procedures, medical examinations, labtests, pathology, nursing,rehabilitation,drugstore, etc. - data management of different specialties and departments
Reporting and data management (8 submodules) – statistics, financing, contracts
External interfaces (8 submodules) – external databases like Public Rgister, Healt Insurance Fund, National Health Information System, X-ray database, external laboratories, medical devices, ePrescription and Code center etc.
System administration (8 submodules) – managemnt of users, accounts, online services, user manuals, user interfaces, translation.
Specialized subsystems (2 submodules) – patient portal and interface for GP’s
Telemedicine and communication (1 submodule) – data, Document and screen sharing, text, voice and video Chat, group calls. Adressbooks of doctors (for doctor to doctor communication). Information management during conversation.
Слайд 20
HEDA can reduce healthcare cost up to 25%:
Common

treatment information management system offers possibility to handle easily
treatment information. All members of the treatment team (including external members) can complement common treatment information flow instead of creating many separate documents with repeated information.
Information can be automatically combined for the doctor as a summary of the treatment data. Therefore doctors do not need open all documents one by one.
Due to connectedness with healthcare process HEDA also makes available real time informaton for the management – treatment cost, treatment quality, length of treatment etc. – what makes service providing more cost effective and increase treatment quality.
Integrated telehealth communication tool can save patient and doctors time related with consultation process.
HEDA modules are suitable both for large hospitals, regional healthcare networks and also for smaller GP practices. Common technical solution between healthcare service providers and common information flow makes healthcare service providing more cost effective.
HEDA is build up to manage machine readable data (not PDF documents) that makes possible to use automatic informatsion management for saving medical staff time.
Patient Portal makes possible for patients (also abroad) to give remote accept for medical professionals to look patient treatment data (important in countries where is used Opt In system) .
Via Patient Portal is possible more efficiently involve patients to the treatment process through: teleconsultations; automatic feedback to patient health problems and monitoring data; making treatment data available also to patient.
Слайд 21
Security
HEDA™ conforms to level K2 T2 S2
of ISKE security standard. ISKE is a 3-layer baseline
security
system, which specifies different levels of requirements to data availability, integrity and confidentiality.
Conforming to K2 T2 S2 level means the following:
K2 - system is available at least 99% of time per year. Maximum allowed one-time downtime
time does not exceed 4 hours.
T2 - events that create, delete and modify data have to be detected and traced. Data is periodically
checked for integrity and being up-to-date.
S2 - data is confidential. Access is allowed only for certain user groups with verified needs.
Слайд 22
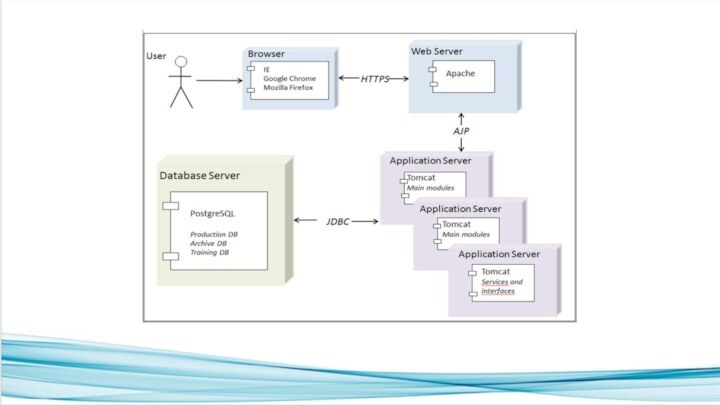
Technical requirements
HEDA™ has the following requirements for
server-side software:
Software platform (Linux 6.x suggested, MS Windows 2012
R2 possible)
Database server (Postgre SQL >= 9.x suggested, MS SQL or Sybase possible)
Application server (Apache Tomcat >= 7.x )
Web server (Apache 2.x)
Most of proposed system software is open-source and does not require purchasing any licenses. In addition to free possibilities, MS Windows Server and MS SQL Servers are supported.
Слайд 25
Decision point – create common electronic data exchange
system for hospitals / region;
Legislation – obligation to share
data. Opt Out/Opt In;
Standardization and data quality – common data standards. Process standards;
Reliability – security and transparency of all actions related to EHR;
Usability – machine-readable data. Fast and simple system;
Technical base – common infrastructure (X-road / Roksnet);
Interfacing – connecting (technically) healthcare providers;
Inclusion – all healthcare partners are involved to the process;
Involving clients – solutions for patients (patient portal, ePrescription);
Interoperability – benefits for all partners in healthcare via technical solutions;
Слайд 26
1. Decision point:
Does there exist necessity for the
secure healthcare data Exchange system for the:
Better public health
outcomes (through better prevention and treatment decisions)
Lower healthcare expenditures (transparency of the system, better control of the expenditures, avoiding duplication of healthcare procedures)
Higher employment avalability (better treatment results, better public health, saving patient time related to healthcare, less incapacity benefiits, less days of incapacity)
Слайд 27
All healthcare service providers (HSP) and treatment data
are connected on the base of common standards (technical,
data and process standards)
Treatment data are available for all HSPs.
Patient does not need to operate with any paper documents.
Patient´s treatment history will be available also for patients via Patient Portal.
Слайд 28
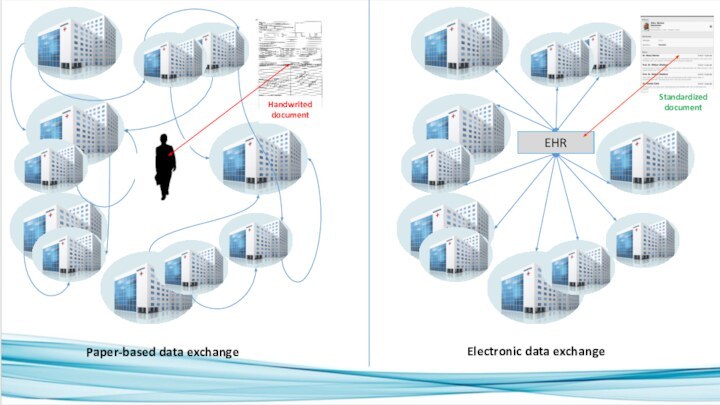
EHR
Paper-based data exchange
Electronic data exchange
Handwrited document
Standardized document
Слайд 29
Advantages of the EHR:
Saving patient time (not necessarily
saving physicians time)
Availability of the medical information and treatment
history
Avoiding mistakes
Better prevention
Better rehabilitation
Transparency of the health services
Avoiding duplication of tests and procedures
Discussion points:
EHR implementing and management costs
Measuring value of the EHR
Interfacing costs and interests of partners
Слайд 30
2. Legislation – what is mandatory for achieving
the goal
Data exchange is supported by law
Possibility to share
medical data with other medical professionals
Data standards are indicatively supported by law.
Secure standards and accepted/supported infrastructure.
Слайд 31
Availability of the medical data
Standards
Set of medical data
Слайд 32
3. Standardization – what data and how will
be exchanged
Data Exchange will be organized in a standardized
format:
Data have to be machine readable (not PDF);
Queries can be made in a detailed way (not whole document) - field by field (for example: diagnose, lab tests etc.);
Healthcare standards are managed in a centralized way (by connected healthcare providers).
Слайд 33
Advantages of the standardizaton:
All participants can change information
with each other
Exchangeable information is understandable for all participants
Data
are comparable
Data can be handled automatically
Слайд 34
4. Reliability – for use it you need
to trust it
People have to trust the system
All actions
in EHR are traceable (who and when have looked data)
EHR is in accordance with higher security requirements
Слайд 35
5. Usability – people like to use clear
and beautiful things/solutions
Users need fast and simple system
Entering data
to the EHR (include as much as possible existing data from different sources – for example personal data of the patient from the population register)
Integrating data from different sources (saving time, effectiveness)
Graphical solutions for better overview and effectiveness
Слайд 36
6. Technical base – appropriate infrastructure is a
premise for successful technical solution
Common infrastructure for the data
Exchange – x-road / Roksnet
Common secure environment and standards for data Exchange and e-services instead of multiple separate VPN connections
Possibility to use regular internet connection (VPN is not needed)
Слайд 37
7. Interconnecting – system has value in case
of all parties are using it
All HSP of the
region (state) are connected with each other
HSP’s have accepted the cooperation model and make data available for healthcare partners between medical professionals
Split expenses of infrastructure and software
Слайд 38
8. Inclusion – all partiess have to accept
new system
All healthcare parties are involved to the decision
process
All HSP’s understand benefit of the EHR
Endusers accept EHR and will use it
There is a consensus between partners what kind of problems should EHR to solve
Слайд 39
9. Solutions for patients – clients have to
use the system
EHR is for HSP’s and for patients
ePrescription
and Patient Portal are important applications of the EHR
Patients as users make the system needed and widely accepted
Слайд 40
10. Interoperability – what kind of benefit we
are expecting
Interoperability – system will be successful if all
parties have interests to run the system and get benefit
Data and process standards
Management of the healthcare processes
Слайд 41
Conclusion:
When measuring the effect of the investments to
the EHR we need to remember that the benefit
in healthcare will appear on the other location than EHR investments. Investments are made to the IT systems with the purpose of developing healthcare processes and reaching to the better public health. It has a positive impact for the healthcare expenditures, general employment and indirectly also to the GDP.
Only technical solution does not quarantee expected results. Technical solutions have to be implemented together with changes in healthcare processes and have to be supported by respective legislation.
All parties have to understand the benefit of the created system for being motivated to use it.
Слайд 42
Thank you!
Raul Mill
CEO of the GenNet Laboratories
raul@gennet.ee
+
372 52 22 150
Слайд 43
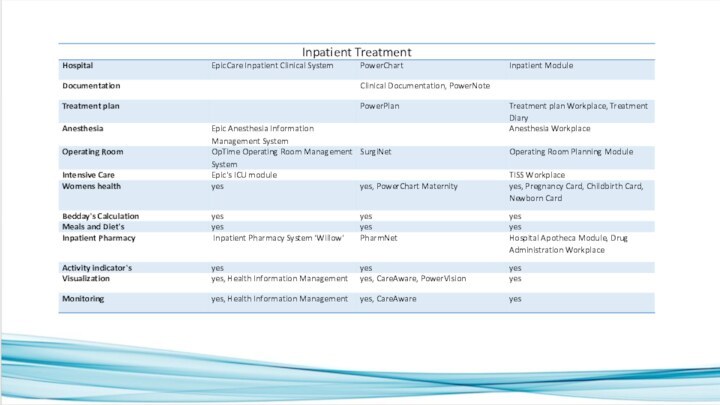
Annex 1: Comparison of healthcare information systems (3)