Слайд 2
Computer Science and Programming
Computer Science is more than
programming
The discipline is called informatics in many countries
Elements of
both science and engineering
Scientists build to learn, engineers learn to build
Fred Brooks
Elements of mathematics, physics, cognitive science, music, art, and many other fields
Computer Science is a young discipline
Fiftieth anniversary in 1997, but closer to forty years of research and development
First graduate program at CMU (then Carnegie Tech) in 1965
To some programming is an art, to others a science
Слайд 3
What is Computer Science?
What is it that distinguishes
it from the separate subjects with which it is
related? What is the linking thread which gathers these disparate branches into a single discipline? My answer to these questions is simple --- it is the art of programming a computer. It is the art of designing efficient and elegant methods of getting a computer to solve problems, theoretical or practical, small or large, simple or complex.
C.A.R. (Tony)Hoare
Слайд 4
Computer Science
Artificial Intelligence thinking machines
Scientific Computing weather, hearts
Theoretical CS analyze algorithms,
models
Computational Geometry theory of animation, 3-D models
Architecture hardware-software interface
Software Engineering peopleware
Operating Systems run
the machine
Graphics from Windows to Hollywood
Many other subdisciplines
Слайд 5
Algorithms as Cornerstone of CS
Step-by-step process that solves
a problem
more precise than a recipe
eventually stops with an
answer
general process rather than specific to a computer or to a programming language
Searching: for phone number of G. Samsa, whose number is 929-9338, or for the person whose number is 489-6569
Sorting: zip codes, hand of cards, exams
Why do we sort? What are good algorithms for sorting?
It depends
Number of items sorted, kind of items, number of processors, ??
Do we need a detailed sorting algorithm to play cards?
Слайд 6
Sorting Experiment
Groups of four people are given a
bag containing strips of paper
on each piece of paper
is an 8-15 letter English word
create a sorted list of all the words in the bag
there are 100 words in a bag
What issues arise in developing an algorithm for this sort?
Can you write a description of an algorithm for others to follow?
Do you need a 1-800 support line for your algorithm?
Are you confident your algorithm works?
Слайд 7
Themes and Concepts of CS
Theory
properties of algorithms, how
fast, how much memory
average case, worst case: sorting cards,
words, exams
provable properties, in a mathematical sense
Language
programming languages: C++, Java, C, Perl, Fortran, Lisp, Scheme, Visual BASIC, ...
Assembly language, machine language,
Natural language such as English
Architecture
Main memory, cache memory, disk, USB, SCSI, ...
pipeline, multi-processor
Слайд 8
Theory, Language, Architecture
We can prove that in the
worst case quicksort is bad
doesn’t matter what machine
it’s executed on
doesn’t matter what language it’s coded in
unlikely in practice, but worst case always possible
Solutions? Develop an algorithm that works as fast as quicksort in the average case, but has good worst case performance
quicksort invented in 1960
introsort (for introspective sort) invented in 1996
Sometimes live with worst case being bad
bad for sorting isn’t bad for other algorithms, needs to be quantified using notation studied as part of the theory of algorithms
Слайд 9
Abstraction, Complexity, Models
What is an integer?
In mathematics we
can define integers easily, infinite set of numbers and
operations on the numbers (e.g.,+, -, *, /)
{…-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …}
In programming, finite memory of computer imposes a limit on the magnitude of integers.
Possible to program with effectively infinite integers (as large as computation and memory permit) at the expense of efficiency
At some point addition is implemented with hardware, but that’s not a concern to those writing software (or is it?)
C++ doesn’t require specific size for integers, Java does
Floating-point numbers have an IEEE standard, required because it’s more expensive to do arithmetic with 3.14159 than with 2
Слайд 10
Alan Turing (1912--1954)
Instrumental in breaking codes during WW
II
Developed mathematical model of a computer called a Turing
Machine (before computers)
solves same problems as a Pentium III (more slowly)
Church-Turing thesis
All “computers” can solve the same problems
Showed there are problems that cannot be solved by a computer
Both a hero and a scientist/ mathematician, but lived in an era hard for gay people
Слайд 11
Search, Efficiency, Complexity
Think of a number between 1
and 1,000
respond high, low, correct, how many guesses needed?
Look
up a word in a dictionary
Finding the page, the word, how many words do you look at?
Looking up a phone number in the Manhattan, NY directory
How many names are examined?
How many times can 1,024 be cut in half?
210 = 1,024, 220 = 1,048,576
Слайд 12
Complexity: Travelling Salesperson
Some problems are hard to solve,
others seem hard to solve but we can’t prove
that they’re hard (hard means computationally expensive)
Visit every city exactly once
Minimize cost of travel or distance
Is there a tour for under $2,000 ? less than 6,000 miles?
Must phrase question as yes/no, but we can minimize with binary search.
Is close good enough?
Try all paths, from
every starting point --
how long does this take?
a, b, c, d, e, f, g
b, a, c, d, e, f, g ...
Слайд 13
Complexity Classifications
Given a route and a claim: This
route hits all cities for less than $2,000
verify properties
of route efficiently.
Hard to find optimal solution
Verification simple, finding optimal solution is hard
Other problems are similar
Pack trucks with barrels,
use minimal # trucks
Ideas?
Problems are the “same hardness”:
solve one efficiently, solve them all
Слайд 14
Are hard problems easy?
P = easy problems, NP
= “hard” problems
P stands for polynomial, like x2
or x3
NP stands for non-deterministic, polynomial
guess a good solution
Question: P = NP ?
if yes, a whole suite of difficult problems can be solved efficiently
if no, none of the hard problems can be solved efficiently
Problem posed in 1971, central to the field
Most computer scientists believe P ≠NP, this is arguably the most important unsolved problem in computer science
Слайд 15
C.A.R. (Tony) Hoare (b. 1934)
Won Turing award in
1980
Invented quicksort, but didn’t see how simple it was
to program recursively
Developed mechanism and theory for concurrent processing
In Turing Award speech used “Emporer’s New Clothes” as metaphor for current fads in programming
“Beginning students don’t know how to do top-down design because they don’t know which end is up”
Слайд 16
Creating a Program
Specify the problem
remove ambiguities
identify constraints
Develop algorithms,
design classes, design software architecture
Implement program
revisit design
test, code, debug
revisit
design
Documentation, testing, maintenance of program
From ideas to electrons
Слайд 17
From High- to Low-level languages
C++ is a multi-purpose
language, we’ll use it largely as an object-oriented language,
but not exclusively
Contrast, for example, with Java in which everything is a class
Contrast with Fortran in which nothing is a class
Compilers translate C++ to a machine-specific executable program
The compiler is a program, input is C++, output is an executable
What language is the compiler written in?
In theory C++ source code works on any machine given a compiler for the machine
C++ and other programming language are more syntactically rigid than English and other natural languages
Слайд 18
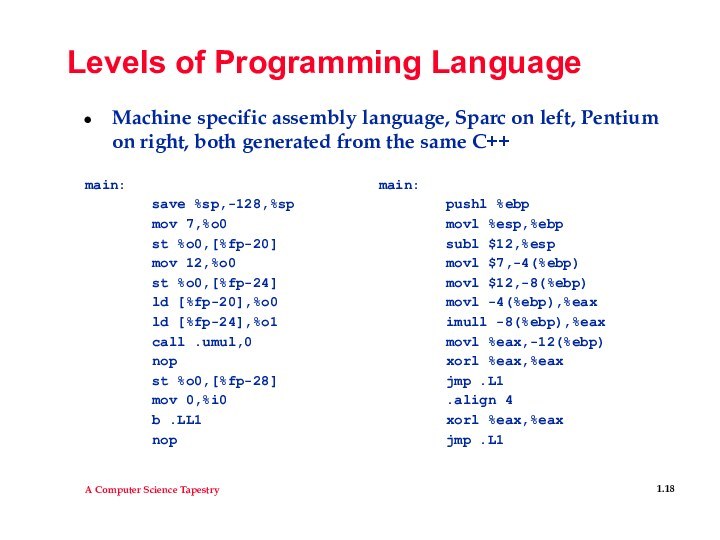
Levels of Programming Language
Machine specific assembly language, Sparc
on left, Pentium on right, both generated from the
same C++
main: main:
save %sp,-128,%sp pushl %ebp
mov 7,%o0 movl %esp,%ebp
st %o0,[%fp-20] subl $12,%esp
mov 12,%o0 movl $7,-4(%ebp)
st %o0,[%fp-24] movl $12,-8(%ebp)
ld [%fp-20],%o0 movl -4(%ebp),%eax
ld [%fp-24],%o1 imull -8(%ebp),%eax
call .umul,0 movl %eax,-12(%ebp)
nop xorl %eax,%eax
st %o0,[%fp-28] jmp .L1
mov 0,%i0 .align 4
b .LL1 xorl %eax,%eax
nop jmp .L1
Слайд 19
Alternatives to compilation
Some languages are interpreted, Scheme and
Java are examples
like simultaneous translation instead of translation of
written document. The same word may be translated many times
The interpreter is a program that translates one part of a source code at a time
The interpreter is machine specific, written in some programming language
JVM, the Java Virtual Machine
Like a PC or Mac but machine is virtual, written in software
Executes Java byte codes which are created from Java source
Like assembly language: between source code and executable
JVM must be written for each architecture, e.g., Linux, Windows, Mac, BeOS, ...
Слайд 20
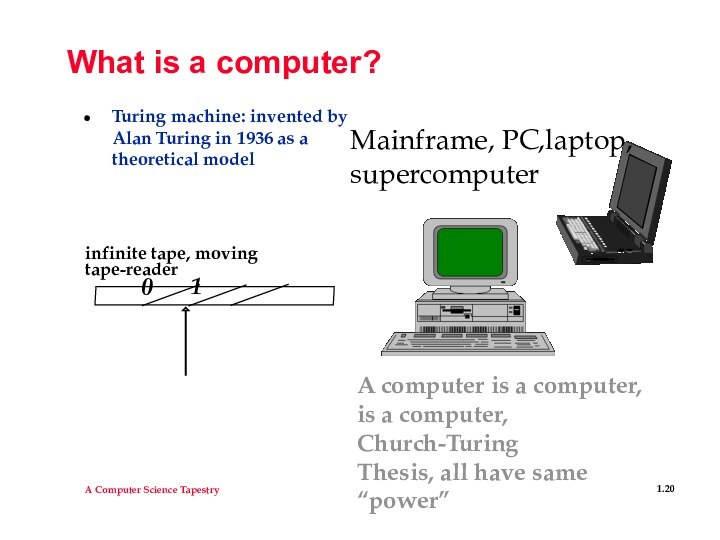
What is a computer?
Turing machine: invented by Alan
Turing in 1936 as a theoretical model
infinite tape, moving
tape-reader
0
1
Mainframe,
PC,laptop, supercomputer
A computer is a computer,
is a computer, Church-Turing
Thesis, all have same “power”
Слайд 21
Chips, Central Processing Unit (CPU)
CPU chips
Pentium (top)
G3 (bottom)
Sound,
video, …
Moore’s Law
chip “size” (# transistors) doubles every 12--18
months (formulated in 1965)
2,300 transistors Intel 4004, 7.5 million Intel Pentium II