- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему American descriptivism
Содержание
- 2. American Descriptivism 1. Basic ideas of American
- 3. Modern subject of Linguistics European approachArise out
- 4. American approach: Field methods - techniques for
- 5. E d w a r d
- 6. Edward Sapir’s Linguistic Conception FormalFunctionalLanguage unitsRadical (grammatical)
- 7. Leonard Bloomfield - the most outstanding representative
- 8. Bloomfield’s mechanistic approachThe main goal is to
- 9. Basic behaviouristic schemeS – R a stimulus
- 10. American structuralismAmerican structuralism is focused on formal
- 11. Bloomfield’s two top categories GrammarThe arrangement
- 12. The principle of immediate constituentsThe basic principle
- 13. Word as the smallest unit being a
- 14. A n t i m e n
- 15. DistributionalismAfter 1945It is based on the distribution
- 16. The crucial problem of distributional analysisThe positions
- 17. The crucial problem of distributional analysisForms identical
- 18. Pike’s theory of tagmemicsEtic view(distributionalism)Consist in refusing
- 19. Morphology in American Structural LinguisticsAdherents to American
- 20. Main contribution of structuralistsEach word has intricate
- 21. Скачать презентацию
- 22. Похожие презентации
















Слайд 2
American Descriptivism
1. Basic ideas of American Descriptivism.
2. Edward
Sapir’s linguistic conception.
Morphology in American structural Linguistics.
Слайд 3
Modern subject of Linguistics
European approach
Arise out of aims
and methods of the 19th century comparative philology with
its focus on written records, historical analysis and interpretation.American approach
Its pioneer was Franz Boas. Arose from preoccupations of American anthropologist, who established descriptions of the American Indian languages before they disappeared. Historical analysis was ruled out.
Слайд 4
American approach:
Field methods - techniques for the recording
and analysis of languages which the linguist himself could
not speak and which had not previously been committed to writing.- Antropological and ethnographical view – the attantion is paid to the life, habbits and “behaviour” of Indian tribes.
- Structuralistic view . Formed by Franz Boas : it is not necessary for all traditional categories to be present in all languages.
Mathematical methods – to formalize the analysis of the language and develop various models of grammatical description.
- Concentration on the form. The lexical meaning was disregarded.
Слайд 5 E d w a r d S
a p i r
The world of our experience must
be enormously simplified and generalized into a symbolic inventory – language signs are units having form (speech sounds) and meaning (elements of experience).Language is a dynamic system : “The feeling that our language is practically a fixed system is fallacious” [Language p.155]
“Eliminate society and the individual will never learn to talk”
“Language”
- the founder of Ethnolinguistics
Language has a certain norm – individual variations are swamped in or absorbed by major agreements.
Слайд 6
Edward Sapir’s Linguistic Conception
Formal
Functional
Language units
Radical (grammatical) elements and
sentences (finished sentence is a living sentence type, which
means that many sentences can be formed in relation to the same fundamental sentence pattern).Words
Слайд 7
Leonard Bloomfield -
the most outstanding representative of
American structuralism.
- “Introduction of the Study of Language” (1914)
-
“A set of postulates for the science of language” (1926)-- “Language” (1933) – generations of American linguists during the 30s-40s.
Слайд 8
Bloomfield’s mechanistic approach
The main goal is to put
Linguistics on scientific footing by scientific introduction, a perfect
description of a language.The methods of linguists should resemble those of natural sciences.
The ideal use of language is seen in Mathematics.
The explanations of different kinds are cause-and-effect sequences.
Слайд 9
Basic behaviouristic scheme
S – R a stimulus that
brings about a reaction
“Jack and Jill are walking down
a lane. Jill is hungry, sees an apple, and makes a noise with her larynx, tongue and lips. Jack vaults the fence, climbs the tree, takes the apple, and brings it to Jill, who eats it.”The scheme of this story is: S – r…s – R. Linguists should deal with the mediating part of the scheme (r….s).
Слайд 10
American structuralism
American structuralism is focused on formal analysis,
leaving the meaning facet aside. The analysis of meaning
is the weak point in language study, which is related to the limited human knowledge.This part of grammar was to be purely formal study, independent of semantics. On the other hand Bloomfield assumed that each linguistic form has a constant and definite meaning.
Слайд 11
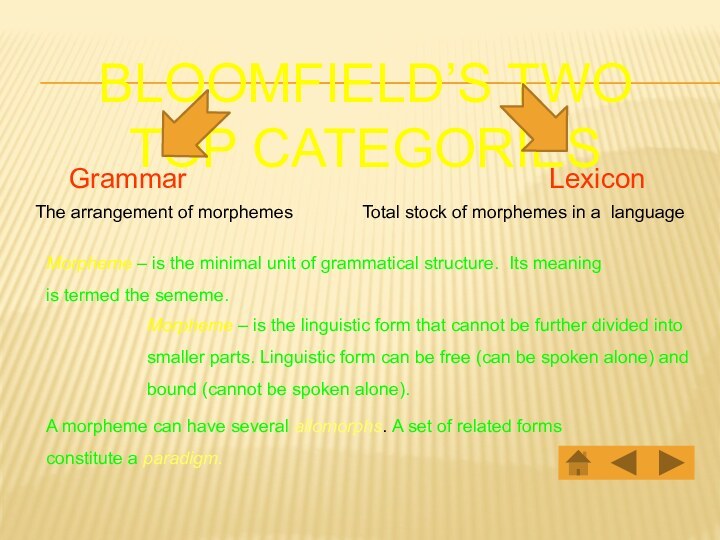
Bloomfield’s two top categories
Grammar
The arrangement of morphemes
Lexicon
Total stock
of morphemes in a language
A morpheme can have several
allomorphs. A set of related forms constitute a paradigm. Morpheme – is the linguistic form that cannot be further divided into smaller parts. Linguistic form can be free (can be spoken alone) and bound (cannot be spoken alone).
Morpheme – is the minimal unit of grammatical structure. Its meaning is termed the sememe.
Слайд 12
The principle of immediate constituents
The basic principle is
the division of each complex form into two, lower-level,
constituents.Poor John ran away.
IC: poor John & ran away.
Poor John.
IC: poor & John.
Away
IC: a & way
Слайд 13 Word as the smallest unit being a free
form.
Primary word
Consist of a single morpheme such as man,
boy, cut or contain more than one bound form: re-ceive, de-ceive.Compounds and derivations such as happy-go-lucky, down-to-earth
Secondary word
Слайд 14 A n t i m e n t
a l i s m
Mechanism of mentalism thesis: Speech
must be explained by the external conditions as well as internal one.A speech act is an instance of behavior of a particular type.
Speech is an explanation that cannot be immediately achieved.
Bloomfieldian Linguistics took as a point of departure the behavourists Psychology.
They say that human conduct is totally predictable on the basis of the situations in which it occurs.
Слайд 15
Distributionalism
After 1945
It is based on the distribution of
linguistic forms, which is the sum of the environments
in which the elements occurs.The distributionalist program arose indirectly out of the view of meaning as a domain of continuously variable and possibly unknowable details without verifiable internal organization.
Слайд 16
The crucial problem of distributional analysis
The positions taken
by the distributionalists:
Joos was actively interested in lexicology and
semantic structure;Bloch regarded meaning as a practical shortcut to the results best obtained through more laborious;
Trager was fully committed to excluding meaning from Linguistics altogether.
The problem was to decide whether forms occuring in the same environments were different or equivalent.
Слайд 17
The crucial problem of distributional analysis
Forms identical in
meaning would be mutually substitutable in all environments, and
thus would not differ in distribution;Forms differing in meaning are not mutually substitutable in all environments, and therefore differ in distribution;
Observation shows that different forms always differ somewhat in distribution, and therefore must differ somewhat in meaning;
A difference in form implies a difference in distribution and in turn a difference in meaning. There are thus no true synonyms.
Bloomfield’s view:
Слайд 18
Pike’s theory of tagmemics
Etic view
(distributionalism)
Consist in refusing all
hypotheses concerning the function of the events being reported
and in characterizing them only by means of spatio-temporal criteria.Consist in interpreting events according to their particular function in the particular world to which they belong.
Emic view
Слайд 19
Morphology in American Structural Linguistics
Adherents to American structural
school typically viewed linguistics not so much as a
“theory” of the language nature, but rather as a body of descriptive and analytical procedures.Linguistic analysis was expected to proceed by focusing selectively on one dimension of language structure at a time before tacking the next one.
Each dimention was formally referred to as a linguistic level.
The task was the separation of levels – first the pronunciation, then the word structure, then the sentence structure and finally the meaning of utterance.
Слайд 20
Main contribution of structuralists
Each word has intricate internal
structure – it consists of morphemes – the smallest
units of meaning and grammatical function.The structuralists introduced morphology as a separate sub-branch of Linguistics.