Слайд 2
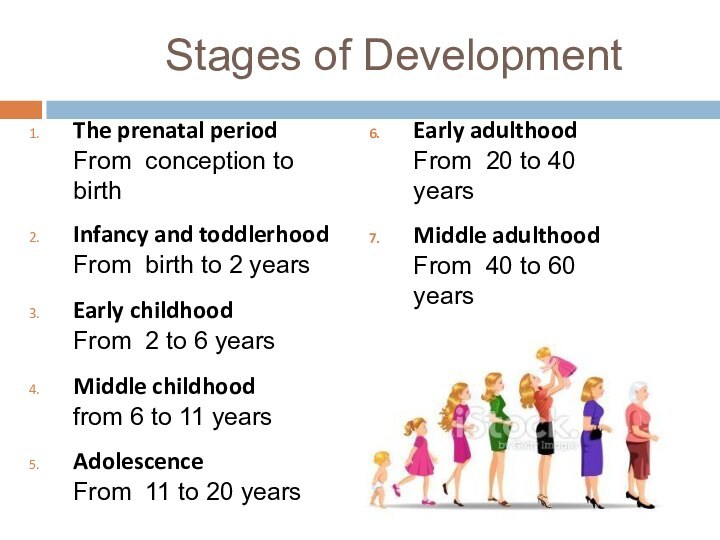
Stages of Development
The prenatal period
From conception to birth
Infancy
and toddlerhood
From birth to 2 years
Early childhood
From 2 to
6 years
Middle childhood
from 6 to 11 years
Adolescence
From 11 to 20 years
Early adulthood
From 20 to 40 years
Middle adulthood
From 40 to 60 years
Late adulthood
from 60 years
Слайд 3
Basic Issues
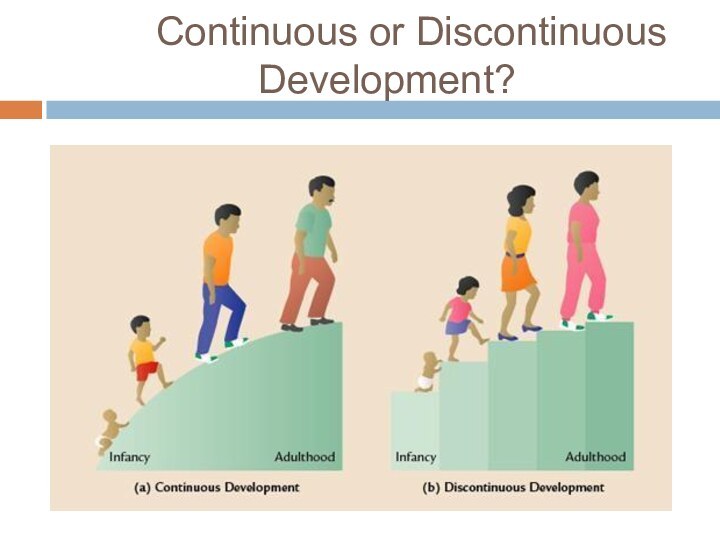
Is the course of development continuous or
discontinuous?
Is
there one general course of development that characterizes all
children, or are there many possible courses?
Are genetic or environmental factors more important in determining development?
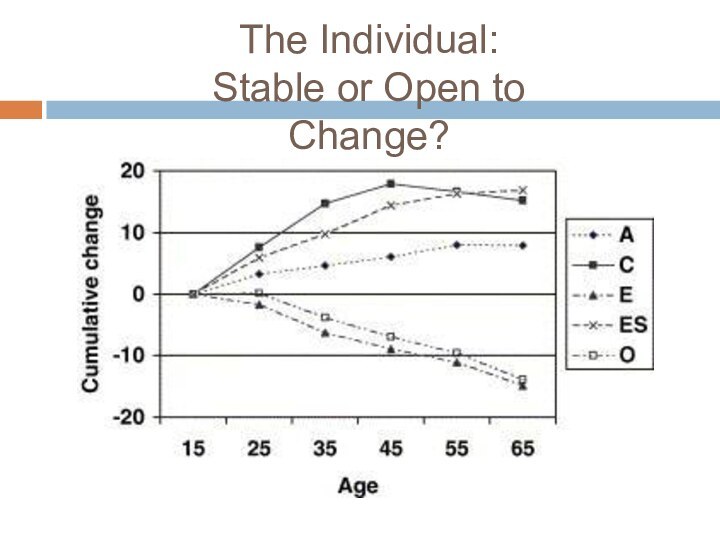
Do individual children establish stable, lifelong patterns of behavior in early development, or are they open to change?
Слайд 4
Continuous or Discontinuous Development?
Слайд 5
One Course of Development or Many?
Слайд 7
The Individual:
Stable or Open to Change?
Слайд 8
Some History
Medieval times: preformationism
(children = little adults)
Слайд 9
Some History
Reformation:
children are born evil, must be tamed
and civilized; harsh, restrictive child-rearing practices; bringing up
children as
an important obligation
Слайд 10
Some History
Enlightenment: the child as a tabula rasa
(John Locke)
or a noble savage (Jean-Jacques Rousseau); more
kindness and compassion in child-rearing
Слайд 11
Scientific Beginnings
Baby biographies (19th c)
Normative child studies (G.
Stanley Hall) → creating
a timetable of development (beginnings of
the 20th c)
The mental testing movement ( → the Stanford-Binet
Intelligence Scale)
The Psychoanalytic Perspective (development as a series of conflicts between biological drives and social expectations; mid-20th c)
Слайд 12
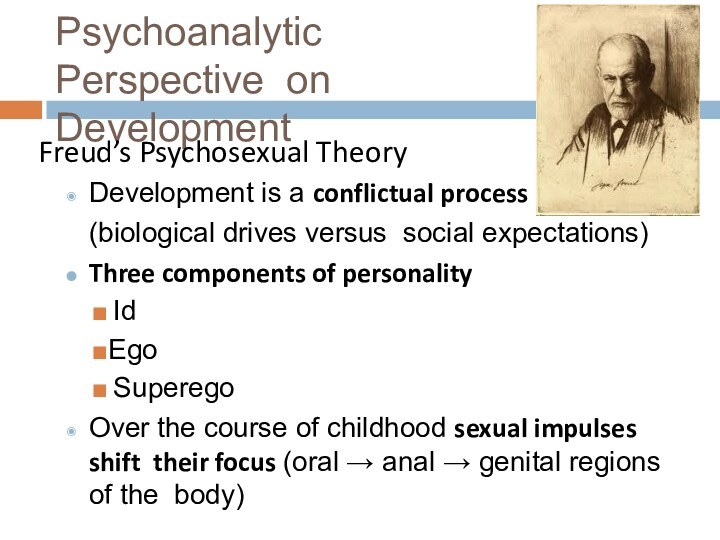
Psychoanalytic Perspective on Development
Freud’s Psychosexual Theory
Development is a
conflictual process
(biological drives versus social expectations)
Three components of personality
Id
Ego
Superego
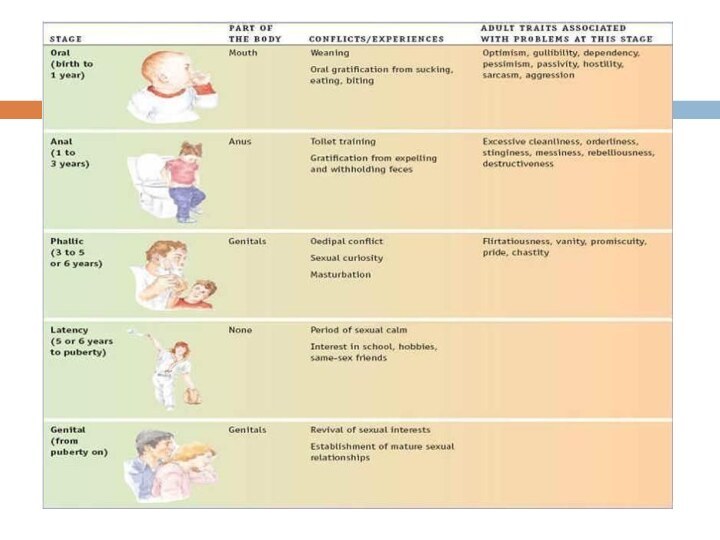
Over the course of childhood sexual impulses shift their focus (oral → anal → genital regions of the body)
Слайд 13
Psychoanalytic Perspective on Development
Freud’s contributions:
Highlighting the importance of
family relationships;
Stressing the role of early experience.
Criticism of Freud’s
theory:
Overemphasizing the role of sexual feelings in development;
Basing on sexually repressed
well-to-do adults;
No direct studies of children.
Слайд 15
Erik Erikson: Psychosocial Perspective
1902 (Frankfurt am Main) –
1994 (Harwich,
MA)
Jewish origin
Never met his biological father
Moved to Vienna
where he met Anna Freud, Sigmund’s daughter
Nazi pressures → moved to the US with
his wife and 2 sons
Positions at the University of California at Berkley and at Harvard
Combined classical psychoanalysis with anthropology
Specified the 8 stages of development
Childhood and Society (1950)
Слайд 16
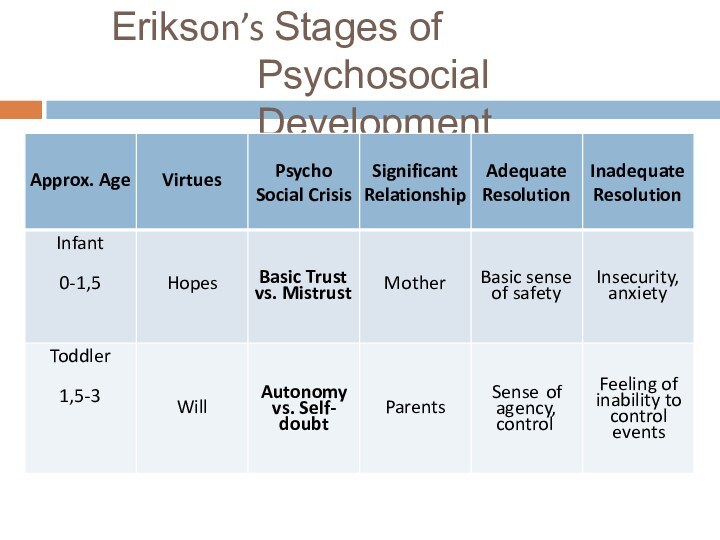
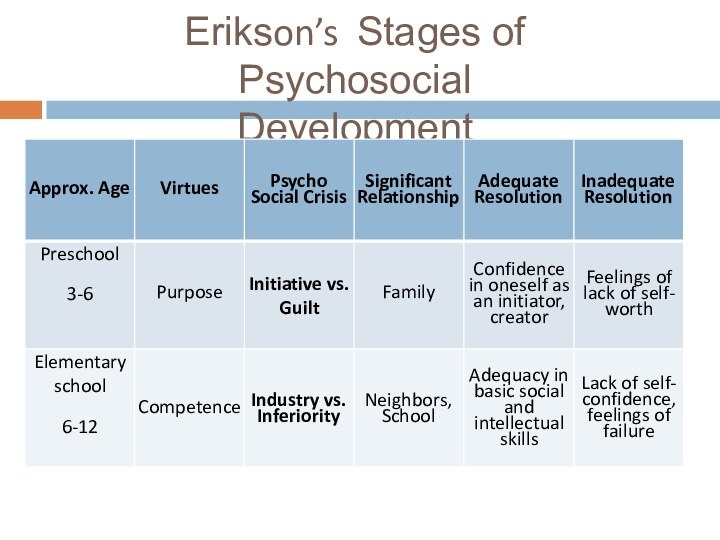
Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development
Слайд 17
Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial
Development
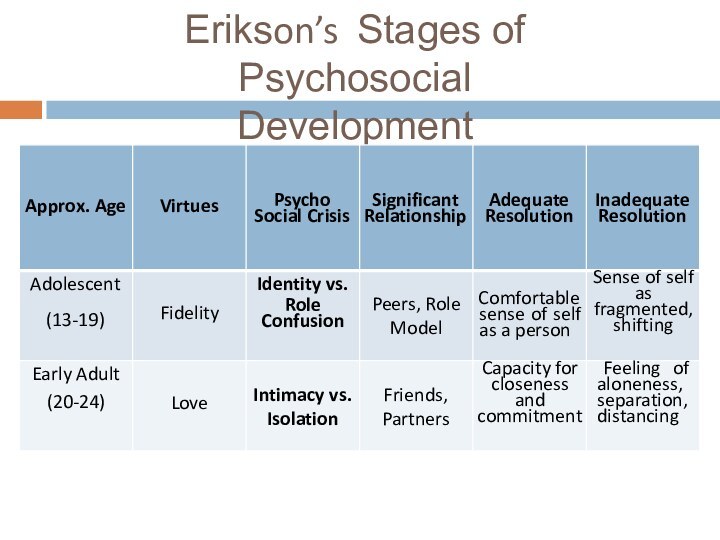
Слайд 18
Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial
Development
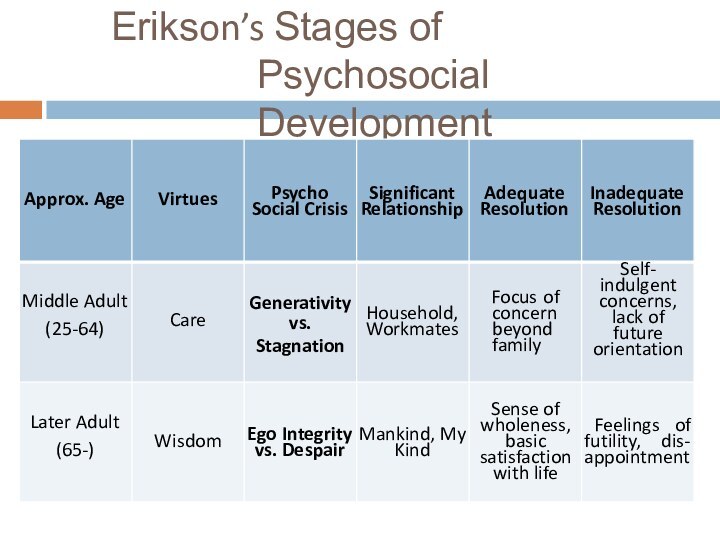
Слайд 19
Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development
Слайд 20
John Watson: Behaviorist Perspective
1913: “The Behaviorist
Manifesto
Applying the mechanisms
of classical conditioning to children
1928: Psychological Care of Infant
and Child – controversial views on childrearing
1920: the Little Albert
experiment
Слайд 21
B. F. Skinner: Behaviorist Perspective
The founding father of
operant conditioning
Inspired by John Watson’s ideas
but a more radical
behaviorist
Advocated behavioral engineering by means of different schedules of reinforcement and punishment
Слайд 22
Social Learning Theory
Grew out of behaviorism
a major force
in child developmental research by the 1950s
Albert Bandura: observational
learning (1977)
Слайд 23
Jean Piaget:
Cognitive-Developmental Theory
1896 – 1980 (Switzerland)
Very gifted in
his youth
Paris: teaching in a school for boys directed
by Alfred Binet
Observing the development of his own
three children
Director of the Interational Bureau of Education
Created the International Center for Genetic Epistemology in Geneva
The Origins of Intelligence in Children
(1952)
Children actively construct knowledge as they manipulate and explore their world.
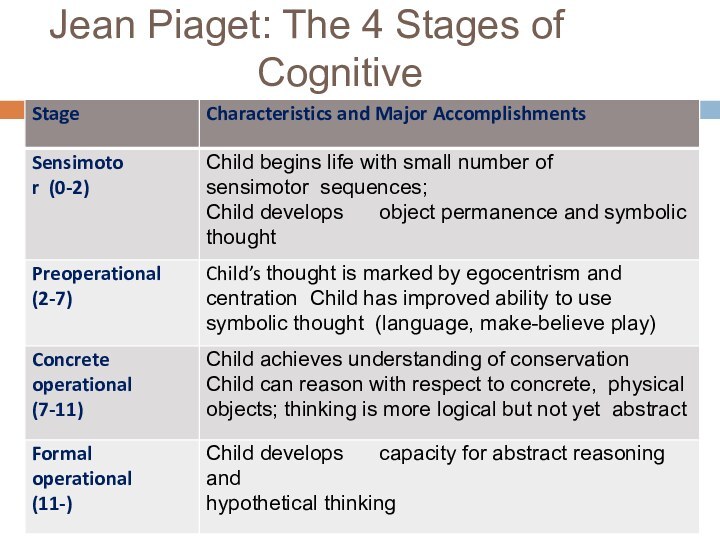
Слайд 24
Jean Piaget: The 4 Stages of Cognitive Development
Слайд 25
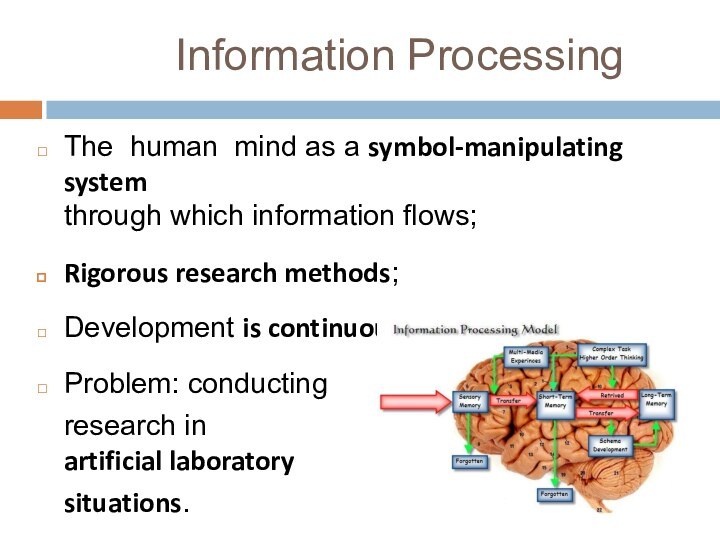
Information Processing
The human mind as a symbol-manipulating system
through
which information flows;
Rigorous research methods;
Development is continuous;
Problem: conducting
research in
artificial
laboratory situations.
Слайд 26
Ethology
Konrad Lorenz: imprinting
The idea of the sensitive
period;
John Bowlby:
applying ethological theory to the
understanding of the human infant.
Слайд 27
Lev Vygotsky: Sociocultural Approach
Studies on the cultural context
of
children’s lives;
Social interaction as a way of transmitting culture;
Development
as a socially mediated process, dependent on the support of adults and more competent peers (≠ Piaget);
Different cultures select different tasks for children’s learning;
Urie Bronfenbrenner: the ecological systems theory
(microsystem, mesosystem, exosystem, macrosystem)
Слайд 28
Research Methods Used in Child Psychology
Naturalistic observation
observation of
behavior in natural contexts
Structured observation
observation of behavior in a
laboratory
Self-reports
clinical interviews, structured interviews, questionnaires, tests
Psychophysiological methods
measuring the relationship between physiological processes and behavior
Case studies
combining various methods to study one individual
Слайд 29
Developmental
Research Designs
Longitudinal design
The same group studied at different
ages
Cross-sectional design
Groups of people differing in age are studied
at the same time
Longitudinal-sequential design
Two or more groups of participants born in
different years are studied at the same time
Слайд 30
Ethics in Research on Children
Typical ethical dilemmas:
To study
children’s willingness to separate from their caregivers, an investigator
asks mothers of 1- and 2- year-olds to leave their youngsters alone in an unfamiliar playroom; some children become very upset.
In a study on moral development, a researcher wants to assess children’s ability to resist temptation by videotaping their behavior without their knowledge. 7- year-olds are promised an attractive prize for solving a difficult puzzle, and they are told not to look at a classmate’s correct solutions which are deliberately placed at the back of the room.