- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Arguments and argumentation
Содержание
- 2. ArgumentFundamental building block of persuasionCollection of statements
- 3. Elements of ArgumentClaim/ThesisSupport/ProofInference (result/outcome/consequence)
- 4. Examples (claim): “The state should allow euthanasia
- 5. SupportIdea/set of ideas audience accepts as trueExample: “upon death terminally ill patient’s physical suffering ceases”
- 6. InferenceConnection between claim and supportMay be obvious
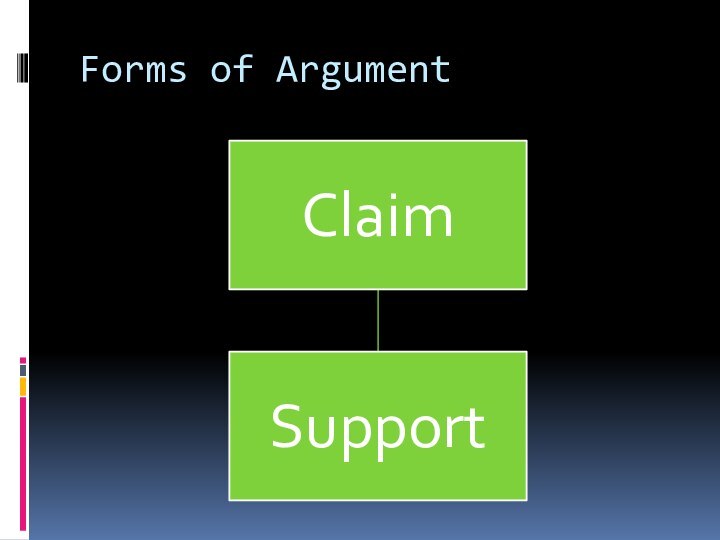
- 7. Forms of Argument
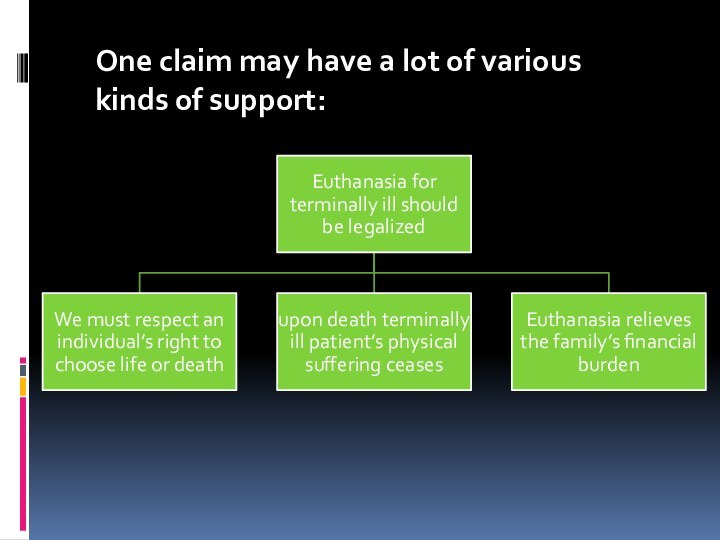
- 9. One claim may have a lot of various kinds of support:
- 10. Support components: Examples, facts, statistics, points of
- 11. Modes of ArgumentationDescriptiveRelationalEvaluative
- 12. Definitions/descriptive argumentationConcerns nature and definition of thingse.g.
- 13. Creating descriptive argumentationDifferentiation (from general class to
- 14. Relational ArgumentationRelationship between things/causal relationshipsExample: “Capital punishment deters crime expansion” “violence in mass media causes real violence”
- 15. Creating Relational ArgumentsReduction – from general to
- 16. Creating Relational ArgumentsAuthority – reference to people
- 17. Evaluative ArgumentationWhat is good/bad, desirable/undesirable, favorable/unfavourableExample: “TH
- 18. Creating Evaluative ArgumentsEvaluating components and comparing themE.g.:
- 19. Скачать презентацию
- 20. Похожие презентации
ArgumentFundamental building block of persuasionCollection of statements organized in a way to highlight/demonstrate connection between what is believed to be true and what should be accepted as true.















Слайд 4
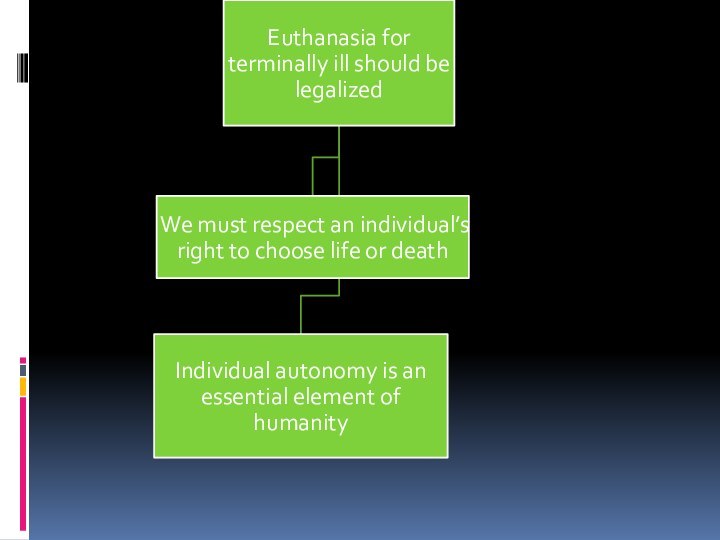
Examples (claim):
“The state should allow euthanasia for terminally
ill people”
Idea which is not yet accepted as true/proven
Not
an argument yet
Слайд 5
Support
Idea/set of ideas audience accepts as true
Example: “upon
death terminally ill patient’s physical suffering ceases”
Слайд 6
Inference
Connection between claim and support
May be obvious or
inferred directly
May have to emphasized
Example: euthanasia is desirable
because person will be relieved
Слайд 10
Support components:
Examples, facts, statistics, points of authority,
various sources such as books, magazines, journals, records, etc.
LOGIC!!!
Слайд 12
Definitions/descriptive argumentation
Concerns nature and definition of things
e.g. “euthanasia
– willful ceasing of death”
e.g. “euthanasia - murder”
e.g. “global
warming is increase of earth’s surface”
Слайд 13
Creating descriptive argumentation
Differentiation (from general class to the
rest of class)
Example (giving examples to illustrate how smth.
Functions or what smth/smn is, etc.)Authority (how an authoritative person or entity defines smth/smn.)
Analogies (comparing what needs to be defined to smth very similar)
Слайд 14
Relational Argumentation
Relationship between things/causal relationships
Example: “Capital punishment deters
crime expansion”
“violence in mass media causes real violence”
Слайд 15
Creating Relational Arguments
Reduction – from general to specific
or otherwise
E.g.: ^Harsher penalties will decline car accidents^
one would
be less likely to drive drunk if they knew that punishment would be a significant jail time, therefore harsher penalties are desirable.Analogies – comparison of the known to the unknown
E.g.: ^improve health care in the USA^
“look at health care in Canada and United Kingdom”
Слайд 16
Creating Relational Arguments
Authority – reference to people who
make credible assertions
E.g.: ^Global crisis is a worldwide disaster^
According
to Joseph. E. Stiglitz who is Nobel Prize winner in Economy Science, global crisis is indeed a disaster with severe consequences for the whole world….
Слайд 17
Evaluative Argumentation
What is good/bad, desirable/undesirable, favorable/unfavourable
Example: “TH fears
the rise of China”
Most resolutions are like this
(Value resolutions)
Слайд 18
Creating Evaluative Arguments
Evaluating components and comparing them
E.g.: “TH
fears the rise of China”
To evaluate: “rise of
China” and define “fear”To determine: what is bad (in this case):
E.g.: 1) increasing economic influence of China
2) political clout around the world
3) great modernizing military