- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Basic concepts of translation studies
Содержание
- 2. Issues to be discussedST and TT identity
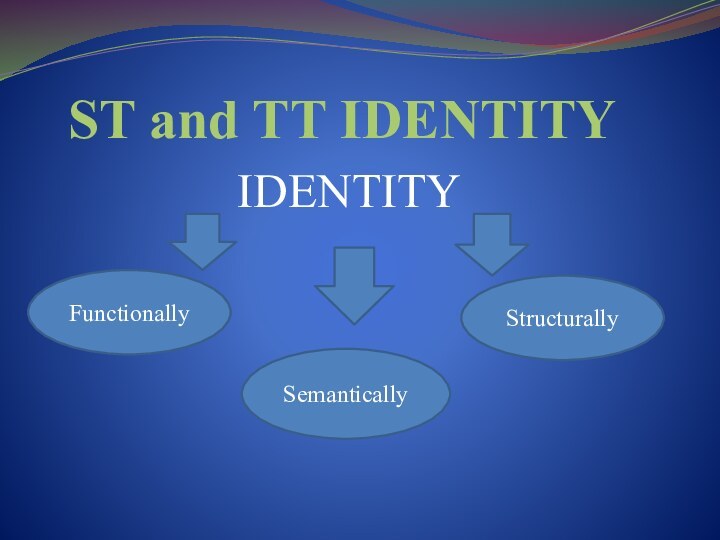
- 3. ST and TT IDENTITY IDENTITY FunctionallyStructurally Semantically
- 4. Minimal translation unitIn the element used by
- 5. Translatability – is a relative notion and
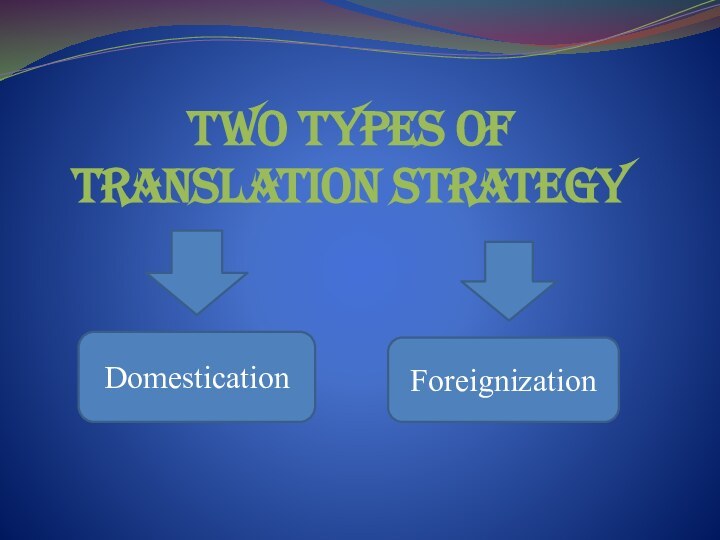
- 6. Two types of translation strategy Domestication Foreignization
- 7. Domestication is the strategy of
- 8. Adaptation – a set of translative interventions
- 9. Transformation – any change of the source
- 10. Universals of translation - Textual
- 11. Скачать презентацию
- 12. Похожие презентации
Issues to be discussedST and TT identity Minimal translation unitTranslatability( untranslatability)EquivalenceDomestication Adaptation Transformation Universals of translation Components of translation situation









Слайд 4
Minimal translation unit
In the element used by the
translator when working on the ST. It is the
smallest unit in the ST , which has it`s equivalent in TT.Phoneme
Morpheme
Word
Word combination
Sentence
Text





























