- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Globalization
Содержание
- 2. Globalization is a process of interaction and
- 3. IN OTHER WORDS….Globalization is the way that
- 4. РОРРОПРОПОПРПThe term globalization has been increasingly used
- 5. Economic globalizationEconomic globalization is the increasing economic
- 6. It means that…Economic globalization is how countries
- 8. PoliticsPolitical globalization is how many institutions and
- 10. In general, globalization may ultimately reduce the
- 11. But..As a response to globalization, some countries
- 12. Cultural globalizationCultural globalization is how culture is
- 14. ALSOReligious movements Christianity, Islam, Buddhism and more
- 15. MultilingualismMultilingualism is becoming a social phenomenon governed
- 17. International tourismGlobalization has made tourism a
- 19. International sportsGlobalization has continually increased international competition
- 21. International educationAccording to the United Nations Educational,
- 22. Скачать презентацию
- 23. Похожие презентации
Globalization is a process of interaction and integration among the people, companies, and governments of different nations, a process driven by international trade and investment and aided by information technology. This process has effects on the





















Слайд 3
IN OTHER WORDS….
Globalization is the way that local
or national ways of doing things become global, that
is, done together around the world. It is about economics or trade, technology, politics, and culture. People feel differently about globalization: some think it helps everyone while others think it hurts some people.
Слайд 4
РОРРОПРОПОПРП
The term globalization has been increasingly used since
the mid-1980s and especially since the mid-1990s.
But Globalization is
not new, though. For thousands of years, people—and, later, corporations—have been buying from and selling to each other in lands at great distances, such as through the famed Silk Road across Central Asia that connected China and Europe during the Middle Ages. Likewise, for centuries, people and corporations have invested in enterprises in other countries. In fact, many of the features of the current wave of globalization are similar to those prevailing before the outbreak of the First World War in 1914.
Слайд 5
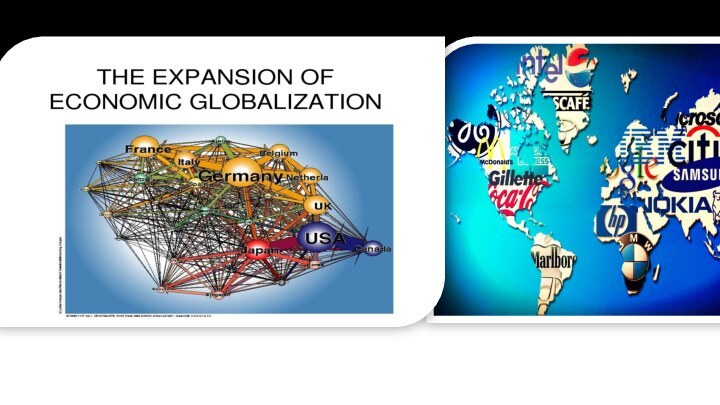
Economic globalization
Economic globalization is the increasing economic interdependence
of national economies across the world through a rapid
increase in cross-border movement of goods, service, technology and capital.Whereas the globalization of business is centered around the diminution of international trade regulations as well as tariffs, taxes, and other impediments that suppresses global trade, economic globalization is the process of increasing economic integration between countries, leading to the emergence of a global marketplace or a single world market. Depending on the paradigm, economic globalization can be viewed as either a positive or a negative phenomenon. Economic globalization comprises the globalization of production, markets, competition, technology, and corporations and industries. Current globalization trends can be largely accounted for by developed economies integrating with less developed economies by means of foreign direct investment, the reduction of trade barriers as well as other economic reforms and, in many cases, immigration.
Слайд 6
It means that…
Economic globalization is how countries are
coming together as one big global economy, making it
easier to buy and sell across countries. In the late 20th century, many countries agreed to lower tariffs, or taxes on goods that are imported from other countries. The way Internet and other communication technologies makes it easier for people to buy and sell products from around the world is an example of globalization. Herman E. Daly has said that there is an important difference between internationalization and globalization. Internationalization is about nations working together for the same goals. These are things like treaties, alliances, and other international agreements. Globalization is about making national borders less important for those who want to buy or sell things around the world.
Слайд 8
Politics
Political globalization is how many institutions and countries
now influence the whole world. The United Nations are
an example of globalization because most countries of the world are members of its Security Council. This means that they can make other countries follow their rules because if a country doesn't, they can sanction them. This means that the countries in the U.N will punish them by not talking or trading with them.Слайд 10 In general, globalization may ultimately reduce the importance
of nation states. Supranational institutions such as the European
Union, the WTO, the G8 or the International Criminal Court replace or extend national functions to facilitate international agreement Some observers attribute the relative decline in US power to globalization, particularly due to the country's high trade deficit. This led to a global power shift towards Asian states, particularly China, which unleashed market forces and achieved tremendous growth rates. As of 2011, the Chinese economy was on track to overtake the United States by 2025. Increasingly, non-governmental organizations influence public policy across national boundaries, including humanitarian aid and developmental efforts. Philanthropic organizations with global missions are also coming to the forefront of humanitarian efforts; charities such as the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Accion International, the Acumen Fund (now Acumen) and the Echoing Green have combined the business model with philanthropy, giving rise to business organizations such as the Global Philanthropy Group and new associations of philanthropists such as the Global Philanthropy Forum. The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation projects include a current multi-billion dollar commitment to funding immunizations in some of the world's more impoverished but rapidly growing countries. and hundreds of millions of dollars in the next few years to programs aimed at encouraging saving by the world's poor. The Hudson Institute estimates total private philanthropic flows to developing countries at US$59 billion in 2010.
Слайд 11
But..
As a response to globalization, some countries have
embraced isolationist policies. For example, the North Korean government
makes it very difficult for foreigners to enter the country and strictly monitors their activities when they do. Aid workers are subject to considerable scrutiny and excluded from places and regions the government does not wish them to enter. Citizens cannot freely leave the country.
Слайд 12
Cultural globalization
Cultural globalization is how culture is becoming
homogeneous, which means that people from all over the
world act in similar way. For example, a lot of people around the world wear T-shirts and jeans and watch Hollywood moviesCultural globalization has increased cross-cultural contacts
Слайд 14
ALSO
Religious movements Christianity, Islam, Buddhism and more recently
sects such as Mormonism, which have taken root and
influenced endemic cultures in places far from their originsThe diffusion of certain cuisines such as American fast food chains is a visible aspect of cultural globalization. The two most successful global food and beverage outlets, McDonald's and Starbucks, are American companies often cited as examples of globalization, with over 32,000 and 18,000 locations operating worldwide, respectively as of 2008.





























