Слайд 2
What is international business?
Exchange of capital or
goods or services between companies across national borders.
Sometimes
it is also called Cross-Border Business.
National Business= Domestic Business ≠ international Business
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 3
What can be exchanged in IB?
Goods ≡
Money
Technology ≡ Money
Services ≡ Money
Intellectual assets ≡ Money
Capitalistic assets
≡ Money
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 4
What is the difference between International Business and
International Economics ?
IE studies the “macroeconomic” nature of
international Business
IB studies the “micro-economic” nature of international Business
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 5
Why study International Business
To impress your future boy
or girl friend
To become rich quickly
To learn foreign
cultures
To work in foreign places
To speak foreign languages
To start an Internet Export Import Business buying cheap goods from China and selling them with a profit in France online- making tons of money without working much
Because of the nice professor
To help local companies to reap the profits of Internationalization
To help foreign companies to sell their goods in France
To please your parents
Because you want to help poor countries to develop
Слайд 6
What is Globalisation ?
Ongoing economic integration and growing
independency of countries worldwide on a macroeconomic point of
view.
13 000 000 000 000 USD exchanged annually between countries.
Substantial flow of capital, goods, ideas, technology around the world!
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 7
What is Globalisation
Ongoing economic integration and growing independency
of countries worldwide on a macroeconomic point of view.
READ
FINANCIAL TIMES AT THE LIBRARY OF ESC TO SEE HOW MACRO-EVENTS IN FOREIGN COUNTRIES AFFECT NATIONAL ECONOMIES !
http://www.ft.com/intl/global-economy
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 8
What is Globalisation
Financial crisis 2012 = Example for
Globalization
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 9
What are the key concepts in international Business
International
Trade = Export and Import
Exporting= Goods & Services against
Money
Importing= Sourcing =Money against Goods & Services
International investment = Money against assets
FDI = Acquisition of productive assets
Portfolio Investment = Acquisition of financial assets
http://www.ft.com/intl/global-economy
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 10
The Nature of Trade
Trade is growing very fast
, faster than GDP growth
For Belgium: Total annual value
of products trade (Export+Imports)/GDP= 150%
=== > (Exports+Imports)> GDP !!
For USA the ratio is about 20%. Why???
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 11
The state of international Business In Europe
http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistical-atlas/gis/viewer/
http://ec.europa.eu/trade/
file:///C:\Users\utilisateur\Dropbox\Yakeexport\Yakaexportcours\IB%20Introduction%20et%20economie%20internationale\KS-GI-10-002-EN.PDF
www.intracen.org
The
state of international Business In France
http://www.douane.gouv.fr/
The state of international
Business In Auvergne
http://lekiosque.finances.gouv.fr/Appchiffre/Etudes/Brochures/Reg_18.pdf
Introduction
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 12
The Nature of Trade
SERVICE versus PRODUCT TRADE
Services are
intangible.
25% of all trade is in Services
75 %
of all trade is in Products
Why is it difficult to export services?
Service companies have to make FDI in the countries to sell their services.
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 13
International Investment
Portfolio Investment= Passive ownership of foreign securities
for the purpose of financial returns. Generally Non-controlling.
Foreign Direct Investment= Active ownership of foreign productive assets such as factories the objective is to take operational control of the assets
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 14
FDI or Portfolio Investment?
Daimler is taking a participation
of 5% in a Swedish car maker Volvo
A Russian
company is buying 95% of the shares of GEFCO from PSA.
Toyota buys 100.000 kg of steel from a Chinese company for 100 Million JPY.
Your Father buys 5 Stocks of Google at the NYSE.
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 15
How does IB differ from Domestic Business
To the
usual risk of business we have to add on
the following risks:
Cross Cultural Risks
Cultural differences, Negotiation…
Commercial risks
Non-payment, competition,….
Currency Risks
Asset valuation, Currency exposure
Country Risks
Political risk
Foreign taxation, Corruption, Protectionism
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 16
Potential harm that arises from changes in the
price of one currency relative to another.
What currencies
to you know? USD, EUR, AUD, JPY,CAD, CNY,CHF,GBP….
Currency Risk
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 17
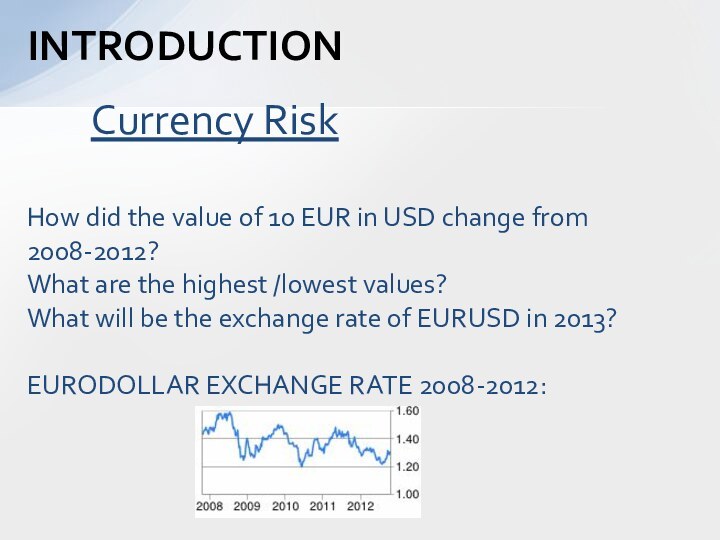
How did the value of 10 EUR in
USD change from 2008-2012?
What are the highest /lowest
values?
What will be the exchange rate of EURUSD in 2013?
EURODOLLAR EXCHANGE RATE 2008-2012:
Currency Risk
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 18
How can I learn more about the currency
market= Forex?
Currency Risk
INTRODUCTION
Слайд 19
Mercury the Roman god of trade.
HISTORY OF INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS
Слайд 20
History of globalization
Globalization is not new: trade always
existed.
Exchange of goods within the Roman Empire
Exchange of technology
in the middle ages
Слайд 21
History of globalization
Phases of globalization : Past
Industrialisation
in Great Britain, The Netherlands, USA
Rise of railroads and
road transport
Rise of Steel and electricity production
GATT after WWII
Слайд 22
History of globalization
Phases of globalization : Presence
BRICS, Emerging
Markets, Regional Integration
Technology: Internet
Container
Слайд 23
History of globalization
Phases of globalization : Future
Technology: Internet,
Knowledge transfer
WTO New Rules (Doha)
“Global consumer”
Improved transportation (Air,
Road, Railway)
New production technology
Further reduction of (non) tariff trade barriers
GDP Growth = Trade Growth
Слайд 25
What are the facilitators in IB ?
Banks
Insurance
Companies
UBIFRANCE (Government agencies)
Logistic service providers
Lawyers
Custom brokers
Слайд 26
What are the classical trade theories?
Mercantilism, Absolute Advantage
Principle, Comparative Advantage Priniciple
What is mercantilism?
With the rise of
nations came the idea that they should amass as much richness = Gold as they can. So they traded. If they have an trade surplus they increase their Gold stock. In case of a trade deficit their gold stock declined.
Why to we trade?
Слайд 27
What is the absolute advantage principle?
A country benefits
by producing the products in which it has an
absolute advantage.
Who invented it?
Adam Smith, Scotsman
Why to we trade?
Слайд 28
What is the comparative advantage principle?
It can be
beneficial for 2 countries to trade as long as
one is relatively more efficient at producing goods or services needed by the other. This is the basis theory of I-Trade.
Who invented it?
David Ricardo, Englishman
Why to we trade?
Слайд 29
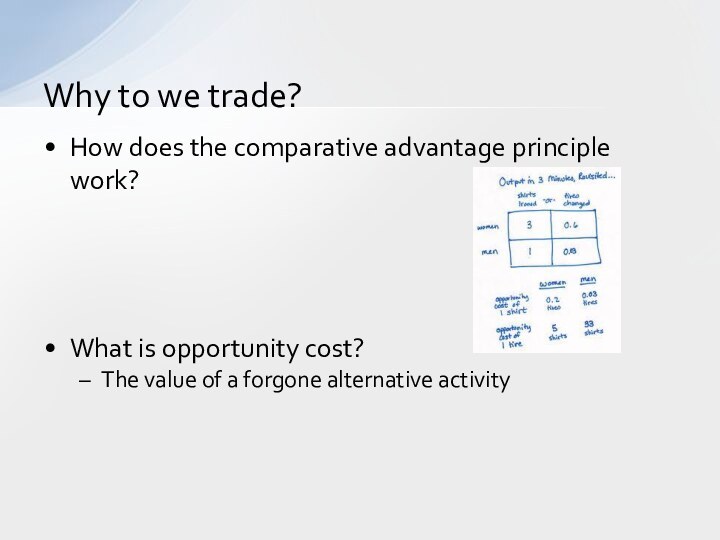
How does the comparative advantage principle work?
What is
opportunity cost?
The value of a forgone alternative activity
Why to
we trade?
Слайд 30
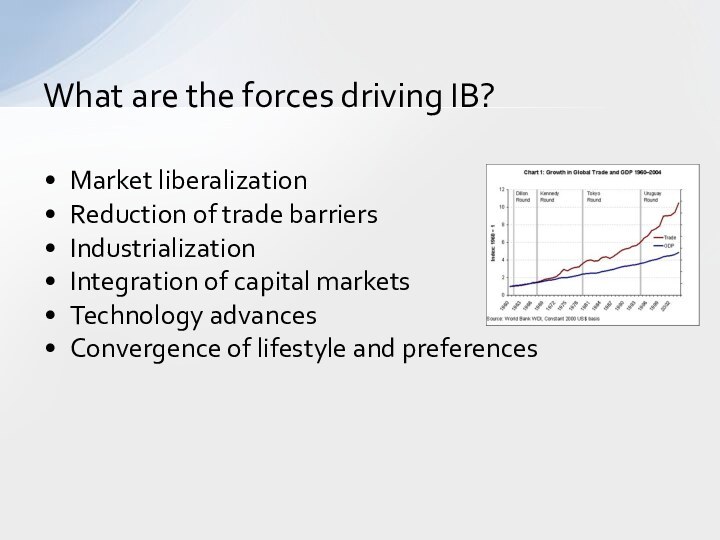
Market liberalization
Reduction of trade barriers
Industrialization
Integration of capital markets
Technology
advances
Convergence of lifestyle and preferences
What are the forces driving
IB?
Слайд 31
Why do companies internationalize?
To make more money by
increasing sales by FDI or exporting
To make more money
by reducing costs by global sourcing or FDI
To make money by selling Intellectual property
To “learn” or copy from competitors
To “follow” customers
To profit of EoS in the various parts of the Value Chain
To attack competitors on their home markets
Слайд 32
Who is participating in IB
MNE = Multinational Enterprise
SME
= Small and medium sized company
(< 500 employees)
BORN
GLOBAL FIRM: The success in local markets depends on the successful presence in international markets.
Слайд 33
How are the companies engaging in international business?
EXPORT
FDI
Collaborative
Agreements
Слайд 34
Value chain of the firm and globalization
Value chain:
sequence of value adding activities performed by the firm.
Слайд 35
Why are companies failing in IB?
Translation errors
Strategy
Production
Слайд 36
What is the export process like?
Export Diagnostics
Export Market
Selection
Market Study
Prospection
Sales/Negociation
Order intake
CRM
Слайд 38
COUNTRY EVALUATION AND SELECTION
Слайд 39
EVALUATION AND COUNTRY SELECTION
Chapter 1. The problem to
solve today
Chapter 2. Ready for export?
Chapter 3. Criteria's to evaluate
countries
Chapter 4. Researching for sources
Chapter 5. Completing the Matrix
Chapter 6. Analysis and Choice
Слайд 40
QUESTION:
“What can happen if people don’t
know about selecting and evaluating countries?“
Слайд 41
CHAPTER 1
THE PROBLEM TO SOLVE TODAY:
Our company is manufacturing goods and wants to export
as to increase its sales.
“Before engaging in selling and buying from abroad, managers need to set up an export operation. In order to do so they need to select the best adapted countries to start operations. The question is, what countries should we choose?”
Today you will learn how to establish a country selection matrix.
Слайд 42
CHAPTER 1
THE PROBLEM TO SOLVE TODAY:
Слайд 43
CHAPTER 1
THE PROBLEM TO SOLVE TODAY:
What kind of conditions should our matrix satisfy?
Fast to
put into place.
A logical approach.
No country should be forgotten
Слайд 44
CHAPTER 1
THE PROBLEM TO SOLVE TODAY:
What
are the advantages of engaging in export for a
company?
Advantage N°1: Increases sales revenues
Advantage N°2: Increases benefices by using economies of scale
Advantage N°3: Becoming less depended on home market
Слайд 45
CHAPTER 2
READY TO EXPORT?
What are in
your opinion the necessary conditions to start exporting?
Слайд 46
CHAPTER 2
READY TO EXPORT?
Production & Logistics
requirements
Capacity?
Storage capacity?
Lead times?
Customs?
Incoterms?
Packing?
Are the transport costs important?
Слайд 47
CHAPTER 2
READY TO EXPORT?
Finance
Investment financing?
Credit risk/payment
risks?
Currency exchange risks?
Слайд 48
CHAPTER 2
READY TO EXPORT?
Domestic Market
Growth market?
Sales
growth?
If sales decline: why?
Is the margin comfortable
Слайд 49
CHAPTER 2
READY TO EXPORT?
Communication
Site web in
English available?
Brochures available in English?
Слайд 50
CHAPTER 2
READY TO EXPORT?
Human Resources
English speaking
personnel available?
Competences concerning legal matters available?
Competences concerning export available?
Слайд 51
CHAPTER 2
READY TO EXPORT?
How to obtain
the information for the diagnostic export?
Internal questionnaire
Internal documents
Face to
Face interviewing
Observation
Слайд 52
CHAPTER 2
READY TO EXPORT?
Conclusion of export
diagnosis: :
-its weaknesses are too great and insurmountable. It must
avoid exporting;
-it presents some gaps, but these difficulties are surmountable.
It does not have any major weaknesses which prevent exporting. Export is possible in the short term.
Слайд 53
CHAPTER 3
CRITERIA’S TO EVALUATE COUNTRIES TO BE
TAKEN INTO CONSIDERATION.
Market growth & Market size
Ease and
compatibility of operations
Cost and Resource availability *
Risks
Слайд 54
CHAPTER 3
CRITERIA’S TO EVALUATE COUNTRIES TO BE
TAKEN INTO CONSIDERATION.
Market growth & Market size
Market
size (Population, GDP level, GDP per capita)
Growth of Gross Domestic Product ( GDP growth rate)
GDP per capita growth rate
Existence of a trading bloc?
Слайд 55
CHAPTER 3
CRITERIA’S TO EVALUATE COUNTRIES TO BE
TAKEN INTO CONSIDERATION.
Ease and compatibility of operations
Nearby location
–distance to domestic market
Share same language
Have similar market conditions as in home market
Слайд 56
CHAPTER 3
CRITERIA’S TO EVALUATE COUNTRIES TO BE
TAKEN INTO CONSIDERATION.
Cost and Resource availability *
Labor costs
Other factor costs: capital, labor, resources
Rare resources are available
Слайд 57
CHAPTER 3
CRITERIA’S TO EVALUATE COUNTRIES TO BE
TAKEN INTO CONSIDERATION.
Risks
Risks and uncertainty
Political risks
Payment risks
Legal
risks
Слайд 58
CHAPTER 4
RESEARCHING FOR SOURCES
Chapter 4. Researching for sources
CIA World Factbook
https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/Worldbank:
A must! The "World Fact Book", published
by the CIA, has extremely detailed information, by country, on the following subjects: geography, demography, politico-legal environment, economy, communication and transport infrastructure, transnational problems, etc. for most countries throughout the world. Indispensable when pre-selecting markets. Searches can be carried out by country or by theme.
Слайд 59
Chapter 4
RESEARCHING FOR SOURCES
Chapter 4. Researching for sources
Worldbank: www.worldbank.org
In addition to information on its publications and
reports, the World Bank site offers a "Data and Statistics" section. This allows highly-targeted searches on over 200 countries. These searches can be performed by country or by theme (population, literacy levels, education, health, environment, poverty, GDP, economy, industries, governments, infrastructure, etc.).
Слайд 60
CHAPTER 4
RESEARCHING FOR SOURCES
OECD http://www.oecd.org
The Organisation for
Economic Co-operation and Development offers all documents published since
1990, on-line (systematic and country reports, e-commerce, enterprise spirit, etc).
French and English
Слайд 61
CHAPTER 5
COMPLETING THE MATRIX
Assigning weights to criteria's
(0-5) for important criteria’s (0-3) for less important criteria's