Слайд 2
CLASSES AND OBJECTS
The main purpose of C++ programming
is to add object orientation to the C programming
language.
A class is used to specify the form of an object and it combines data representation and methods for manipulating that data into one neat package.
The data and functions within a class are called members of the class.
Слайд 3
CLASS ACCESS MODIFIERS
Data hiding is one of the
important features of Object Oriented Programming which allows preventing
the functions of a program to access directly the internal representation of a class type.
A class can have multiple public, protected, or private labeled sections. Each section remains in effect until either another section label or the closing right brace of the class body is seen.
public: Any class can access the features
protected: Any subclass can access the feature
private: No other class can access the feature
Слайд 4
CLASS ACCESS MODIFIERS
class Base {
public:
//
public members go here
protected:
// protected
members go here
private:
// private members go here
};
Слайд 5
THE PUBLIC MEMBERS EXAMPLE
A public member is accessible from anywhere
outside the class but within a program.
#include
using namespace
std;
class Line
{
public:
double length;
void setLength( double len );
double getLength( void );
};
Слайд 6
THE PUBLIC MEMBERS EXAMPLE CON…
// Member functions definitions
double
Line::getLength(void)
{
return length ;
}
void Line::setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
Слайд 7
THE PUBLIC MEMBERS EXAMPLE CON…
// Main function for
the program
int main( )
{ Line line;
//
set line length
line.setLength(6.0);
cout << "Length of line : " << line.getLength() <
// set line length without member function
line.length = 10.0; // OK: because length is public
cout << "Length of line : " << line.length < return 0; }
Length of line : 6
Length of line : 10
Слайд 8
THE PRIVATE MEMBERS
A private member variable or function cannot be
accessed, or even viewed from outside the class. Only
the class and friend functions can access private members.
By default all the members of a class would be private, for example in the following class width is a private member.
class Box
{ double width;
public:
double length;
void setWidth( double wid );
double getWidth( void );
};
Слайд 9
THE PRIVATE MEMBERS EXAMPLE
#include
using namespace std;
class Box
{
public:
double length;
void
setWidth( double wid );
double getWidth( void );
private:
double width;
};
// Member functions definitions
double Box::getWidth(void)
{
return width ;
}
Слайд 10
THE PRIVATE MEMBERS EXAMPLE CON…
void Box::setWidth( double wid
) {
width = wid;
}
int main( ) {
Box box;
// set box length without member function
box.length = 10.0; // OK: because length is public
cout << "Length of box : " << box.length <
// set box width without member function
// box.width = 10.0; // Error: because width is private
box.setWidth(10.0); // Use member function to set it.
cout << "Width of box : " << box.getWidth() < return 0; }
Length of box : 10
Width of box : 10
Слайд 11
THE PROTECTED MEMBERS EXAMPLE
A protected member variable or function is
very similar to a private member but it provided
one additional benefit that they can be accessed in child classes which are called derived classes.
#include
using namespace std;
class Box
{
protected:
double width;
};
Слайд 12
THE PROTECTED MEMBERS EXAMPLE CON…
class SmallBox:Box // SmallBox
is the derived class.
{ public:
void setSmallWidth( double wid );
double getSmallWidth( void );
};
// Member functions of child class
double SmallBox::getSmallWidth(void) {
return width ;
}
Слайд 13
THE PROTECTED MEMBERS EXAMPLE CON…
void SmallBox::setSmallWidth( double wid
) {
width = wid;
}
// Main function for
the program
int main( ) {
SmallBox box;
// set box width using member function
box.setSmallWidth(5.0);
cout << "Width of box : "<< box.getSmallWidth() << endl;
return 0;
}
Width of box : 5
Слайд 14
CLASS DEFINITIONS
When you define a class, you define
a blueprint for a data type. This doesn't actually
define any data, but it does define what the class name means, that is, what an object of the class will consist of and what operations can be performed on such an object.
A class definition starts with the keyword class followed by the class name;
Слайд 15
CLASS DEFINITIONS EXAMPLE
class Box
{
public:
double length; // Length of a box
double breadth; // Breadth of a box
double height; // Height of a box
};
Слайд 16
DEFINE C++ OBJECTS:
Box Box1;
// Declare Box1 of type Box
Box Box2;
// Declare Box2 of type Box
Слайд 17
ACCESSING THE DATA MEMBERS
#include
using namespace std;
class Box
{
public:
double length; // Length
of a box
double breadth; // Breadth of a box
double height; // Height of a box
};
Слайд 18
ACCESSING THE DATA MEMBERS CON…
int main( )
{
Box Box1; // Declare Box1
of type Box
Box Box2; // Declare Box2 of type Box
double volume = 0.0; // Store the volume of a box here
// box 1 specification
Box1.height = 5.0;
Box1.length = 6.0;
Box1.breadth = 7.0;
Слайд 19
ACCESSING THE DATA MEMBERS CON…
// box 2
specification
Box2.height = 10.0;
Box2.length = 12.0;
Box2.breadth = 13.0;
// volume of box 1
volume = Box1.height * Box1.length * Box1.breadth;
cout << "Volume of Box1 : " << volume <
// volume of box 2
volume = Box2.height * Box2.length * Box2.breadth;
cout << "Volume of Box2 : " << volume < return 0;
}
Volume of Box1 : 210
Volume of Box2 : 1560
Слайд 20
CLASS MEMBER FUNCTIONS
A member function of a class
is a function that has its definition or its
prototype within the class definition like any other variable.
class Box
{
public:
double length; // Length of a box
double breadth; // Breadth of a box
double height; // Height of a box
double getVolume(void);// Returns box volume
};
Слайд 21
CLASS MEMBER FUNCTIONS CON…
Method 1
class Box
{
public:
double length; // Length of
a box
double breadth; // Breadth of a box
double height; // Height of a box
double getVolume(void)
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
};
Method 2
double Box::getVolume(void)
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
Box myBox; // Create an object
myBox.getVolume();
// Call member function for the object
Member functions can be defined within the class definition or separately using scope resolution operator, ::.
Слайд 22
FULL EXAMPLE
https://ideone.com/n9IX03
Слайд 23
INHERITANCE
“C++ is Multi Inheritance, unlike Java is Single
inheritance”.
Inheritance allows us to define a class in terms
of another class, which makes it easier to create and maintain an application. This also provides an opportunity to reuse the code functionality and fast implementation time.
When creating a class, instead of writing completely new data members and member functions, the programmer can designate that the new class should inherit the members of an existing class. This existing class is called the base class, and the new class is referred to as the derived class.
Слайд 24
BASE & DERIVED CLASSES
A class can be derived
from more than one classes, which means it can
inherit data and functions from multiple base classes.
To define a derived class, we use a class derivation list to specify the base class(es). A class derivation list names one or more base classes and has the form:
class derived-class: access-specifier base-class
Where access-specifier is one of public, protected, or private.
“base-class” is the name of a previously defined class.
Слайд 25
FULL EXAMPLE
Consider a base class Shape and its derived class Rectangle:
https://ideone.com/dwJAOM
Слайд 26
ACCESS CONTROL AND INHERITANCE
A derived class can access
all the non-private members of its base class.
A derived
class inherits all base class methods with the following exceptions:
Constructors, destructors and copy constructors of the base class.
Overloaded operators of the base class.
The friend functions of the base class.
Слайд 27
TYPE OF INHERITANCE [ PUBLIC ]
Public Inheritance:
When deriving
a class from a public base class, public members of the base
class become public members of the derived class and protected members of the base class become protected members of the derived class.
A base class's privatemembers are never accessible directly from a derived class, but can be accessed through calls to the public and protected members of the base class.
Слайд 28
TYPE OF INHERITANCE [ PROTECTED AND PRIVATE ]
CON…
Protected Inheritance
When deriving from a protected base class, public
and protected members of the base class become protected members of the derived class.
Private Inheritance
When deriving from a private base class, public and protected members of the base class become private members of the derived class.
Слайд 29
MULTIPLE INHERITANCES EXAMPLE
https://ideone.com/yFSOrV
Слайд 30
FUNCTION OVERLOADING
An overloaded declaration is a declaration that
had been declared with the same name as a
previously declared declaration in the same scope, except that both declarations have different arguments and obviously different definition (implementation).
Function Overloading Example:
https://ideone.com/ktn9Ln
Слайд 31
POLYMORPHISM
The word polymorphism means having many forms. Typically, polymorphism occurs
when there is a hierarchy of classes and they
are related by inheritance.
C++ polymorphism means that a call to a member function will cause a different function to be executed depending on the type of object that invokes the function.
Example:
https://ideone.com/rGNTCc OR
Слайд 32
POLYMORPHISM [STATIC
RESOLUTION ]
Output of previous example:
WHY
!!!
The reason for the incorrect output is that the
call of the function area() is being set once by the compiler as the version defined in the base class. This is called static resolution of the function call, or static linkage - the function call is fixed before the program is executed. This is also sometimes called early binding because the area() function is set during the compilation of the program.
Parent class area
Parent class area
Слайд 33
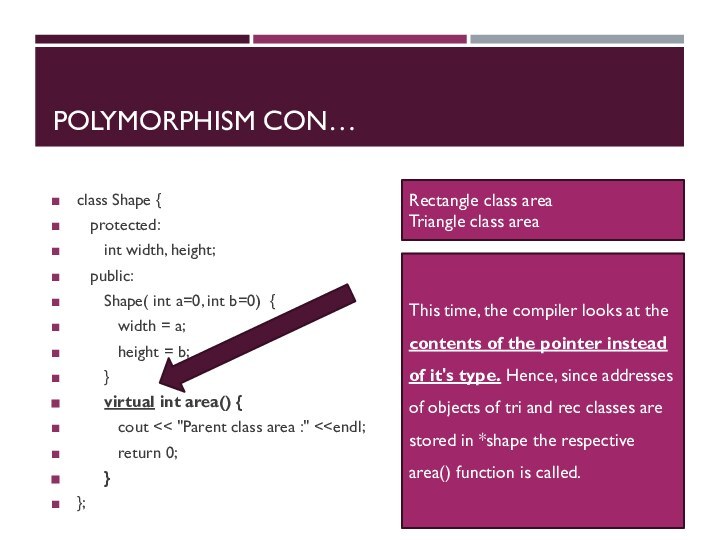
POLYMORPHISM CON…
class Shape {
protected:
int width, height;
public:
Shape( int
a=0, int b=0) {
width = a;
height = b;
}
virtual int area() {
cout << "Parent class area :" <
return 0;
}
};
Rectangle class area
Triangle class area
This time, the compiler looks at the contents of the pointer instead of it's type. Hence, since addresses of objects of tri and rec classes are stored in *shape the respective area() function is called.
Слайд 34
VIRTUAL FUNCTION
A virtual function is a function in
a base class that is declared using the keyword
virtual. Defining in a base class a virtual function, with another version in a derived class, signals to the compiler that we don't want static linkage for this function.
Слайд 35
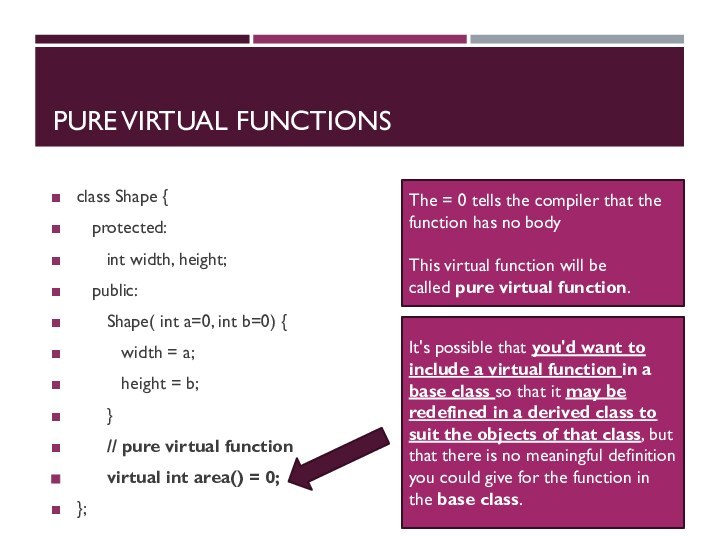
PURE VIRTUAL FUNCTIONS
class Shape {
protected:
int width, height;
public:
Shape(
int a=0, int b=0) {
width = a;
height = b;
}
// pure virtual function
virtual int area() = 0;
};
The = 0 tells the compiler that the function has no body
This virtual function will be called pure virtual function.
It's possible that you'd want to include a virtual function in a base class so that it may be redefined in a derived class to suit the objects of that class, but that there is no meaningful definition you could give for the function in the base class.
Слайд 36
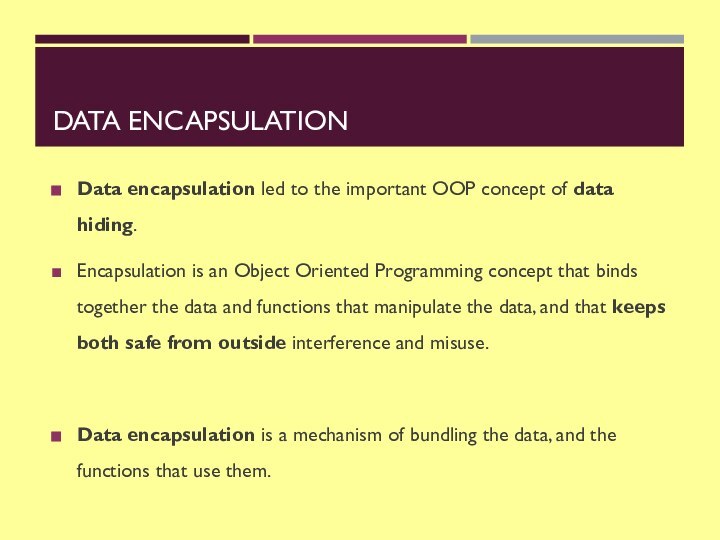
DATA ENCAPSULATION
Data encapsulation led to the important OOP
concept of data hiding.
Encapsulation is an Object Oriented Programming concept
that binds together the data and functions that manipulate the data, and that keeps both safe from outside interference and misuse.
Data encapsulation is a mechanism of bundling the data, and the functions that use them.
Слайд 37
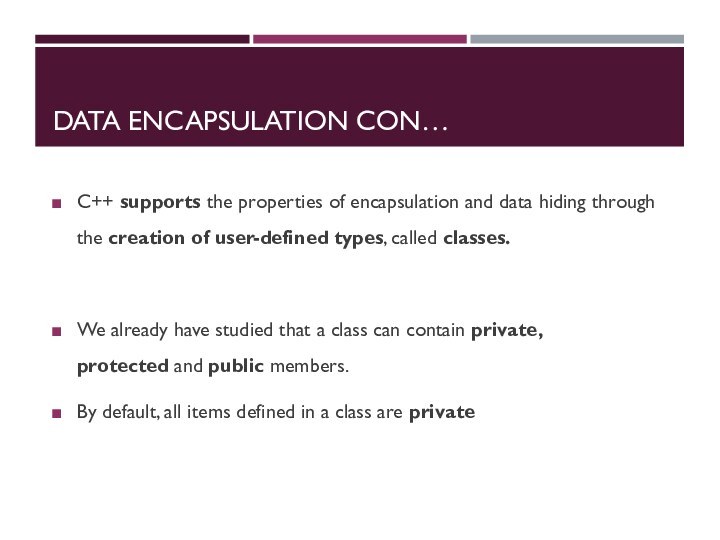
DATA ENCAPSULATION CON…
C++ supports the properties of encapsulation
and data hiding through the creation of user-defined types,
called classes.
We already have studied that a class can contain private, protected and public members.
By default, all items defined in a class are private
Слайд 38
DATA ENCAPSULATION CON…
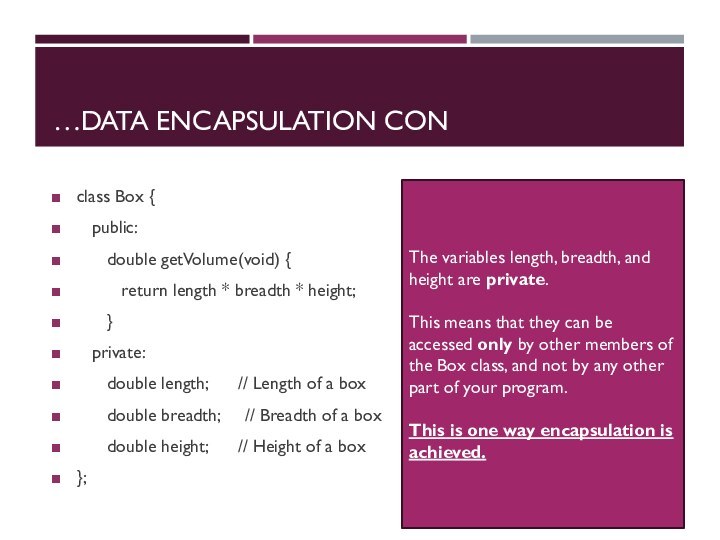
class Box {
public:
double getVolume(void) {
return
length * breadth * height;
}
private:
double length; // Length of a box
double breadth; // Breadth of a box
double height; // Height of a box
};
The variables length, breadth, and height are private.
This means that they can be accessed only by other members of the Box class, and not by any other part of your program.
This is one way encapsulation is achieved.
![Презентация на тему C++ [ OOP ] C++ [ OOP ]](/img/tmb/15/1458570/bea52d4c942ec6296a832ec096b0f435-720x.jpg)





















![lec12 TYPE OF INHERITANCE [ PUBLIC ]Public Inheritance:When deriving a class from a public base](/img/tmb/15/1458570/b10b5b6d15ddfb86a99e86fb3b28e2ee-720x.jpg)
![lec12 TYPE OF INHERITANCE [ PROTECTED AND PRIVATE ] CON…Protected InheritanceWhen deriving from](/img/tmb/15/1458570/34b63ec2abbb5059b7038389cf53fa2f-720x.jpg)


![lec12 POLYMORPHISM [STATIC RESOLUTION ]Output of previous example: WHY !!!The reason for](/img/tmb/15/1458570/8659a61c558595ca811a08551da412d9-720x.jpg)