- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему МЕТОДОЛОГИЯ РЕГИОНОВЕДЕНИЯthe methodsof regional science
Содержание
- 2. Методы региональных экономических исследованийБалансовый метод – составление регионального баланса для оптимального соотношения между отраслями рыночной специализации
- 3. The method of balanced estimates (regional material
- 4. GRAIN BALANCE (EXAMPLE)Alexander Baykov, The Development of the Soviet Economic System, CUP, 1946, p. 445
- 5. “The material balance is at the core
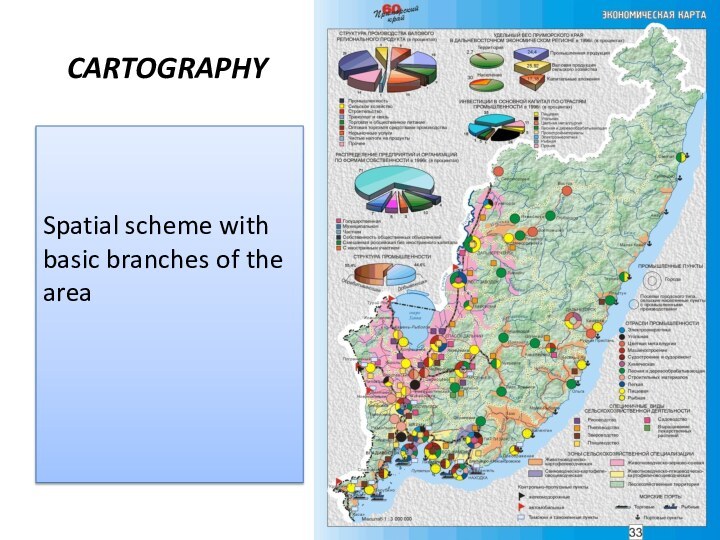
- 6. CARTOGRAPHYSpatial scheme with basic branches of the area
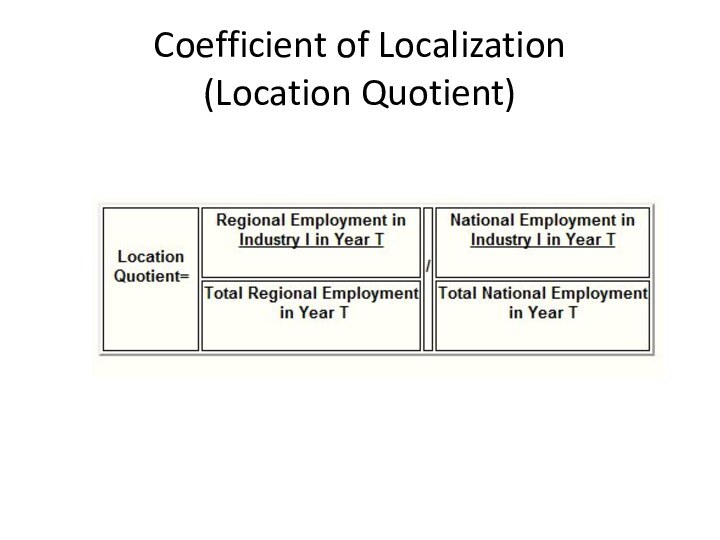
- 7. INDICATORSDetermining the “level of specialization” of an economic area based on the key indicatorsLocation QuotientSpecialization Quotient
- 8. Коэффициент локализации- отношение удельного веса данной отрасли
- 9. Coefficient of Localization (Location Quotient)A method of
- 10. Coefficient of Localization (Location Quotient)The coefficient is
- 11. Coefficient of Localization (Location Quotient)
- 12. Коэффициент локализации
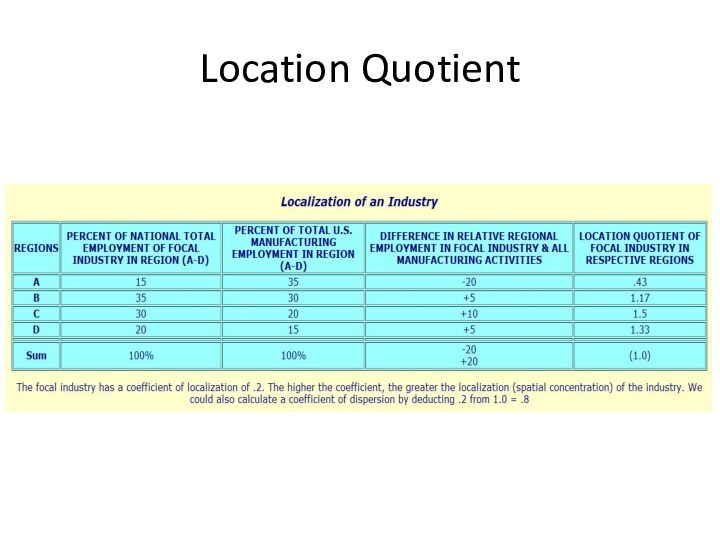
- 13. Location Quotient
- 14. Location Quotient ILQ < 1.0 = All
- 15. Location Quotient IIA LQ = 1.0 =
- 16. Location Quotient IIIA LQ > 1.0 =
- 17. Коэффициент душевого производства - исчисляется как отношение
- 18. Коэффициент душевого производства
- 19. Коэффициент межрайонной товарности
- 20. Коэффициент специализации
- 21. Скачать презентацию
- 22. Похожие презентации
Методы региональных экономических исследованийБалансовый метод – составление регионального баланса для оптимального соотношения между отраслями рыночной специализации


















Слайд 2
Методы региональных экономических исследований
Балансовый метод – составление регионального
баланса для оптимального соотношения между отраслями рыночной специализации
Слайд 3 The method of balanced estimates (regional material balances)
The main instrument in GOSPLAN planning system (Soviet Union
and other Eastern Bloc countries)
Слайд 4
GRAIN BALANCE (EXAMPLE)
Alexander Baykov, The Development of the
Soviet Economic System, CUP, 1946, p. 445
Слайд 5 “The material balance is at the core of
Soviet planning; it is the most operational (or bureaucratic)
of all balances in the sense that all its elements – output orders, import and export quotas, inventory changes and all allotments of materials to various consuming groups – hang on administrative decisions”J.M. Montias, Planning with Material Balances in Soviet-Type Economies, The American Economic Review, Vol. 49, No. 5, Dec., 1959