- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Product life cycle
Содержание
Stages of product life cycleA product is introduced among consumers, and if consumers perceive it as meeting their needs and want, it experiences a period of growth. Subsequently, it reaches the stage of maturity and when

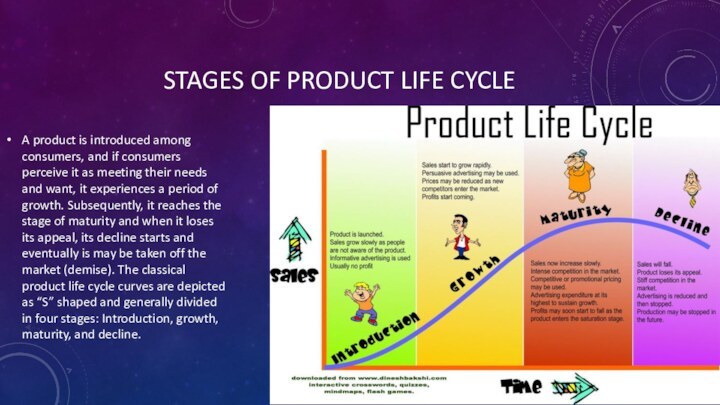
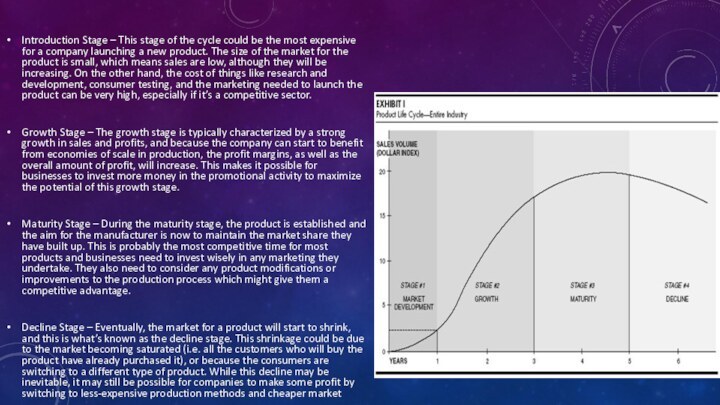


Слайд 3 Introduction Stage – This stage of the cycle
could be the most expensive for a company launching
a new product. The size of the market for the product is small, which means sales are low, although they will be increasing. On the other hand, the cost of things like research and development, consumer testing, and the marketing needed to launch the product can be very high, especially if it’s a competitive sector.Growth Stage – The growth stage is typically characterized by a strong growth in sales and profits, and because the company can start to benefit from economies of scale in production, the profit margins, as well as the overall amount of profit, will increase. This makes it possible for businesses to invest more money in the promotional activity to maximize the potential of this growth stage.
Maturity Stage – During the maturity stage, the product is established and the aim for the manufacturer is now to maintain the market share they have built up. This is probably the most competitive time for most products and businesses need to invest wisely in any marketing they undertake. They also need to consider any product modifications or improvements to the production process which might give them a competitive advantage.
Decline Stage – Eventually, the market for a product will start to shrink, and this is what’s known as the decline stage. This shrinkage could be due to the market becoming saturated (i.e. all the customers who will buy the product have already purchased it), or because the consumers are switching to a different type of product. While this decline may be inevitable, it may still be possible for companies to make some profit by switching to less-expensive production methods and cheaper market





























