- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Course content and mind maps
Содержание
- 2. KATHLEEN GRAVES’DESIGNING LANGUAGE COURSES 2002PENNY UR’S A COURSE IN ENGLISH LANGUAGE TEACHING 2012
- 3. LECTURE OUTLINELinguistic content of the course Conceptualizing
- 4. COURSE CONTENT (AFTER K. GRAVES)
- 5. FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: LINGUISTIC SKILLSPhonology: Individual sounds,
- 7. FOCUS ON COMMUNICATION: SITUATIONS AND FUNCTIONSSituations are
- 8. Situational or functional syllabus
- 9. TOPICS AND THEMESWhat the language is used
- 10. COMPETENCIESSituations + linguistic skills + functions A
- 11. SKILLSSpeaking: Inferring attitude, feeling, mood; using interactive
- 12. TASKSInteractions whose purpose is to get something
- 13. CONTENT Subject matter other than language itself
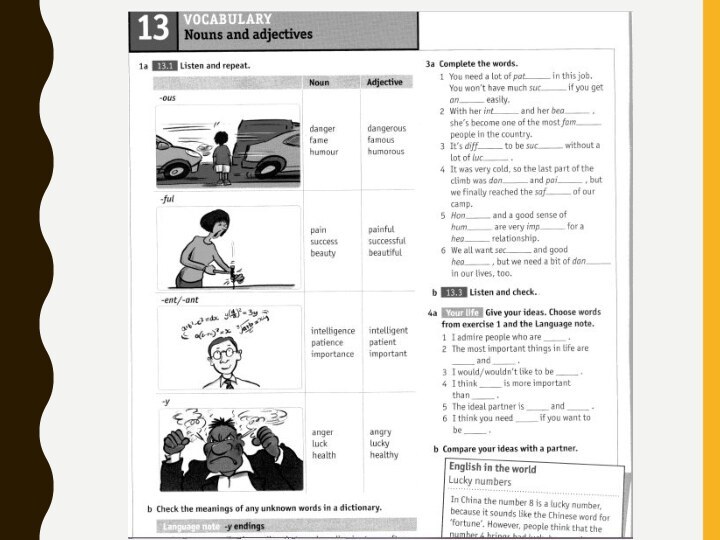
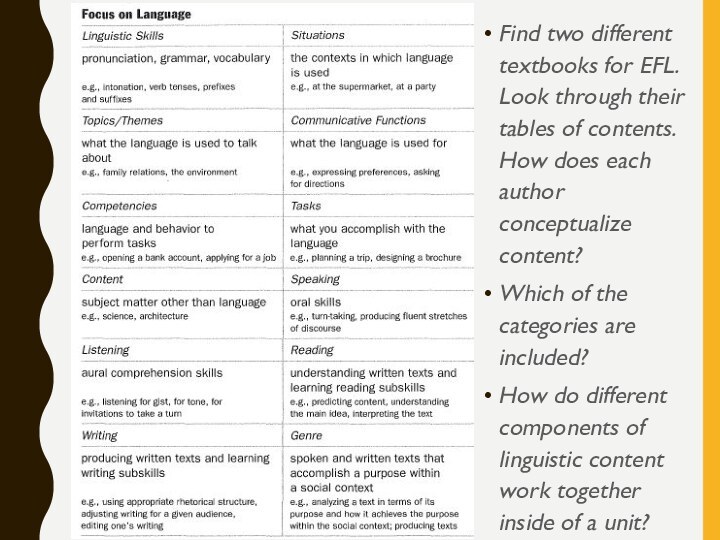
- 14. Find two different textbooks for EFL. Look
- 15. HOW TO CONCEPTUALIZE THE COURSEIf you are
- 19. NON-LINGUISTIC CONTENT Subject matter other than language
- 20. CULTURAL COMPONENTHome culture Culture of the (native)
- 21. SHOULD LITERATURE BE PART OF YOUR COURSE?Wide
- 22. UNDERLYING MESSAGES?SexismAgeism Social and cultural orientation
- 23. Скачать презентацию
- 24. Похожие презентации
KATHLEEN GRAVES’DESIGNING LANGUAGE COURSES 2002PENNY UR’S A COURSE IN ENGLISH LANGUAGE TEACHING 2012


















Слайд 2
KATHLEEN GRAVES’
DESIGNING LANGUAGE COURSES 2002
PENNY UR’S
A COURSE
IN ENGLISH LANGUAGE TEACHING 2012
Слайд 3
LECTURE OUTLINE
Linguistic content of the course
Conceptualizing the
content for your course
Non-linguistic content
Cultural component
Literature
Hidden messages
Слайд 5
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: LINGUISTIC SKILLS
Phonology: Individual sounds, words,
stress, rhythm and intonation
Grammar: Classifications and functions of words,
how words form phrases and sentencesVocabulary: Content words, word formation, inflections, meanings of prefixes and suffixes
Formal or structural syllabus
Слайд 7
FOCUS ON COMMUNICATION: SITUATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
Situations are the
contexts in which one uses language.
Typically include places
where one transacts business, such as the supermarket, or the travel, or places where one interacts with others such as at a partyCommunicative functions cover the types of transactions that will occur in the situation:
Suggesting, promising, apologizing, greeting, inviting, requesting, etc.
Слайд 9
TOPICS AND THEMES
What the language is used to
talk or write about
Personal: family, food, hobbies
Professional or
academic: employment, office etc.Sociocultural: education, political systems, elections, cultural customs etc.
Topical or thematical syllabus
Слайд 10
COMPETENCIES
Situations + linguistic skills + functions
A competency
attempts to specify and teach the language and behavior
needed to perform in a given situationHow to perform a job interview
How to book a flight
How to examine a patient
How to open a bank account
To perform in target language in the dominant culture
Слайд 11
SKILLS
Speaking: Inferring attitude, feeling, mood; using interactive strategies;
summarizing; paraphrasing.
Listening: Listening for detail, for gist, for global
understanding, inferring attitude, feeling, mood, listening for invitation to take turns.Reading: Predicting content, understanding the main idea, reading for detail, deducing meaning from context, note-taking, skimming etc.
Writing: Proofreading, editing, summarizing, paraphrasing, adjusting the writing to a specific audience or purpose etc.
Слайд 12
TASKS
Interactions whose purpose is to get something done
Task
can be for work purposes, for academic purposes, for
daily lifeTasks can be an end in themselves or a means to practice skills, perform functions, discuss topics
Some are real-life and some only have classroom application
Слайд 13
CONTENT
Subject matter other than language itself
Two
approaches:
For ESL: content-based syllabus will be based
on the content of other disciplines, like math, history, computer science, using English as a medium of instructionFor EFL, all types of non-linguistic content (see Penny Ur, 2012)
Слайд 14 Find two different textbooks for EFL. Look through
their tables of contents. How does each author conceptualize
content?Which of the categories are included?
How do different components of linguistic content work together inside of a unit?
Слайд 15
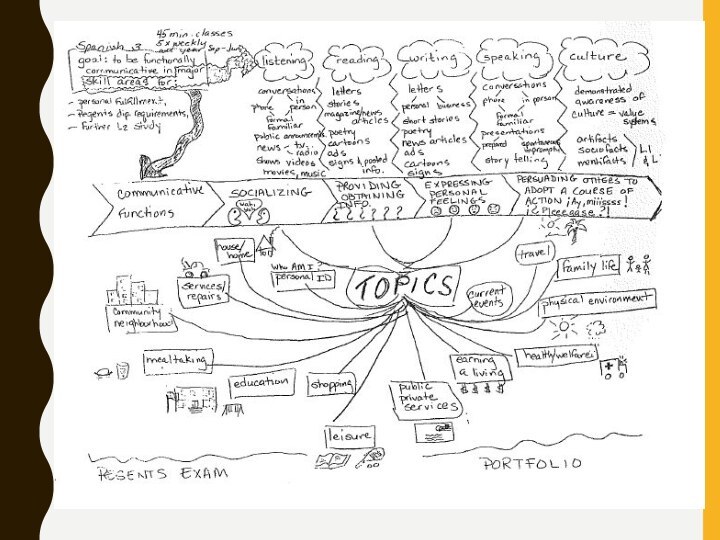
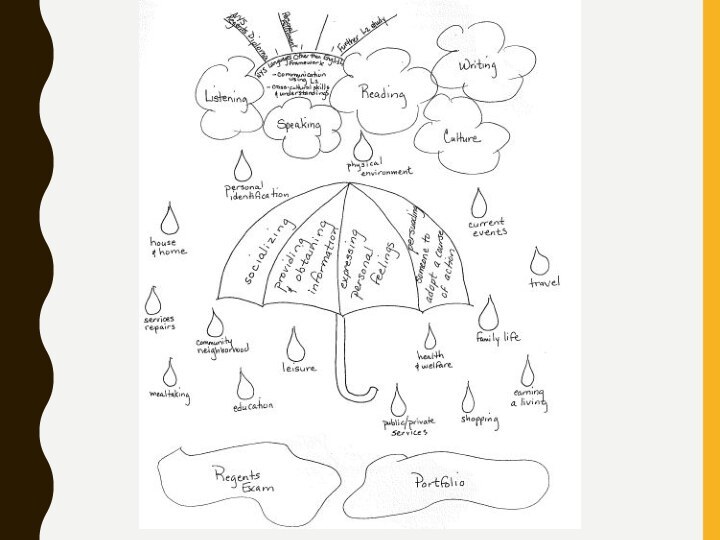
HOW TO CONCEPTUALIZE THE COURSE
If you are developing
a course from scratch, or for very specific learner
needs, you can useTables and grids
Mind-maps
Flow charts
Слайд 19
NON-LINGUISTIC CONTENT
Subject matter other than language itself
Study
the list of non-linguistic content and discuss which types
are more or less relevant for a language course in general, for the course that you are developing in particular.
Слайд 20
CULTURAL COMPONENT
Home culture
Culture of the (native) English-speaking
people
Cultures of other speech communities
Global cultural norms
In
the course units which you studied before, find elements of culture, if any?
Слайд 21
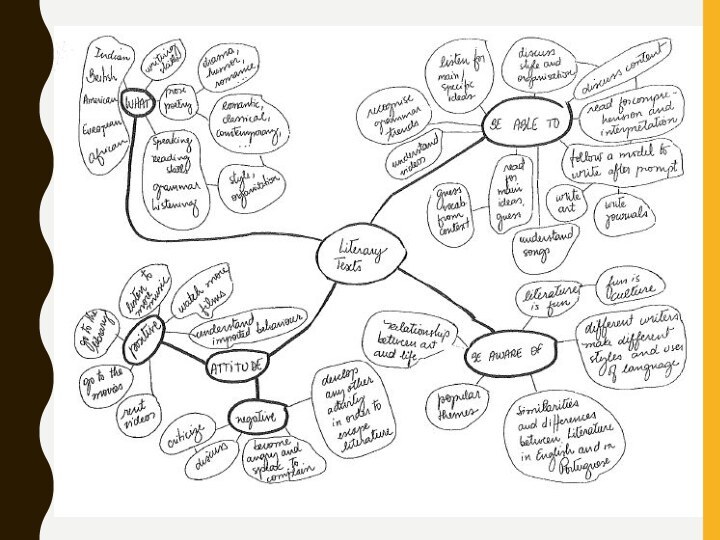
SHOULD LITERATURE BE PART OF YOUR COURSE?
Wide range
of authors and texts
But are they essential, or
desirable components of your course?What are the advantages and disadvantages of teaching literature as part of your language course?