Слайд 2
© Wiley 2010
Learning Objectives
Define the role of Business
Strategy
Explain how a Business strategy is developed
Explain the role
of Operations Strategy in the organization
Explain the relationship between business strategy and operations strategy
Describe how an operations strategy is developed
Слайд 3
© Wiley 2010
Learning Objectives
Identify competitive priorities for of
the operations function
Explain the strategic role of technology
Define productivity
and identify productivity measures
Compute productivity measures
Слайд 4
© Wiley 2010
The Role of Operations Strategy
Provide a
plan that makes best use of resources which;
Specifies the
policies and plans for using organizational resources
Supports Business Strategy as shown on next slide
Слайд 5
© Wiley 2010
Business/Functional Strategy
Слайд 6
© Wiley 2010
Importance of Operations Strategy
Essential differences between
operational efficiency and strategy:
Operational efficiency is performing tasks well,
even better than competitors
Strategy is a plan for competing in the marketplace
Operations strategy ensures all tasks performed are the right tasks
Слайд 7
© Wiley 2010
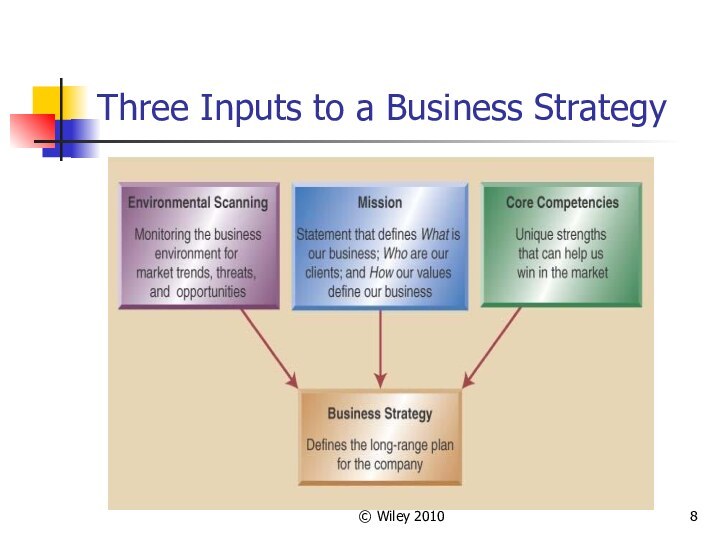
To Develop a Business Strategy
Consider these
factors and strategic decisions:
What business in the company in
(mission)
Analyze and understand the market (environmental scanning)
Identify the company strengths (core competencies)
Слайд 8
© Wiley 2010
Three Inputs to a Business Strategy
Слайд 9
© Wiley 2010
Key Examples
Mission: Dell Computer- “to
be the most successful computer company
in the world”
Environmental Scanning: political trends, social trends, economic trends, market place trends, global trends
Core Competencies: strength of workers, modern facilities, market understanding, best technologies, financial know-how, logistics
Слайд 10
© Wiley 2010
Developing an Operations Strategy
Operations Strategy: a
plan for the design and management of operations functions
is developed after the business strategy
focuses on specific capabilities which give it a competitive edge – competitive priorities
Слайд 11
© Wiley 2010
Operations Strategy – Designing the Operations
Function
Слайд 12
© Wiley 2010
Competitive Priorities- The Edge
Four Key Operations
Questions:
Will you compete on –
Cost?
Quality?
Time?
Flexibility?
All of the above? Some? Tradeoffs?
Слайд 13
© Wiley 2010
Competing on Cost
Offering product at a
low price relative to competition
Typically high volume products
Often limit
product range & offer little customization
May invest in automation to reduce unit costs
Can use lower skill labor
Probably uses product focused layouts
Low cost does not mean low quality
Слайд 14
© Wiley 2010
Competing on Quality
Quality is often subjective
Quality
is defined differently depending on who is defining it
Two
major quality dimensions include
High performance design:
Superior features, high durability, & excellent customer service
Product & service consistency:
Meets design specifications
Close tolerances
Error free delivery
Quality needs to address
Product design quality – product/service meets requirements
Process quality – error free products
Слайд 15
© Wiley 2010
Competing on Time
Time/speed one of most
important competition priorities
First that can deliver often wins the
race
Time related issues involve
Rapid delivery:
Focused on shorter time between order placement and delivery
On-time delivery:
Deliver product exactly when needed every time
Слайд 16
© Wiley 2010
Competing on Flexibility
Company environment changes rapidly
Company
must accommodate change by being flexible
Product flexibility:
Easily switch
production from one item to another
Easily customize product/service to meet specific requirements of a customer
Volume flexibility:
Ability to ramp production up and down to match market demands
Слайд 17
© Wiley 2010
The Need for Trade-offs
Decisions must emphasize
priorities that support business strategy
Decisions often required trade offs
Decisions
must focus on order qualifiers and order winners
Which priorities are “Order Qualifiers”?
Must have excellent quality since everyone expects it
Which priorities are “Order Winners”?
Dell competes on all four priorities
Southwest Airlines competes on cost
McDonald’s competes on consistency
FedEx competes on speed
Custom tailors compete on flexibility
Слайд 18
© Wiley 2010
Translating to Production Requirements
Specific Operation requirements
include two general categories
Structure – decisions related to the
production process, such as characteristics of facilities used, selection of appropriate technology, and the flow of goods and services
Infrastructure – decisions related to planning and control systems of operations
Слайд 19
© Wiley 2010
Translating to Production Requirements
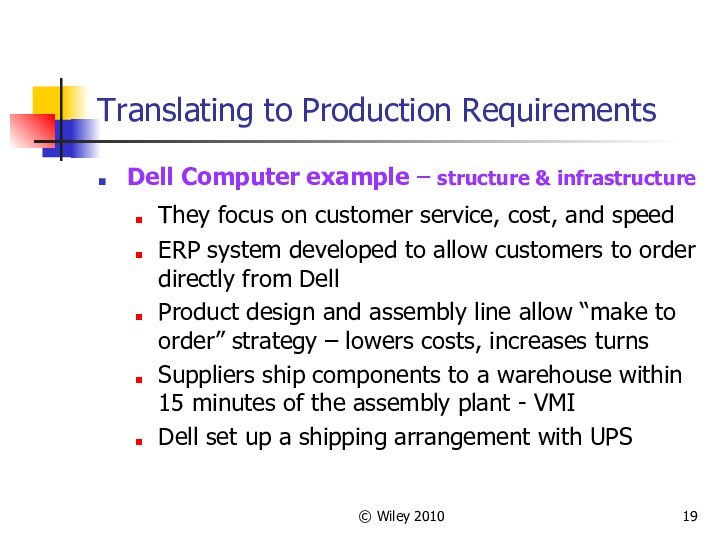
Dell Computer example
– structure & infrastructure
They focus on customer service, cost,
and speed
ERP system developed to allow customers to order directly from Dell
Product design and assembly line allow “make to order” strategy – lowers costs, increases turns
Suppliers ship components to a warehouse within 15 minutes of the assembly plant - VMI
Dell set up a shipping arrangement with UPS
Слайд 20
© Wiley 2010
Strategic Role of Technology
Technology should support
competitive priorities
Three Applications: product technology, process technology, and information
technology
Products - Teflon, CD’s, fiber optic cable
Processes – flexible automation, CAD
Information Technology – POS, EDI, ERP, B2B
Слайд 21
© Wiley 2010
Technology for Competitive Advantage
Technology has positive
and negative potentials
Positive
Improve processes
Maintain up-to-date standards
Obtain competitive advantage
Negative
Costly
Risks such
as overstating benefits
Слайд 22
© Wiley 2010
Technology for Competitive Advantage
Technology should:
Support competitive
priorities
Can require change to strategic plans
Can require change to
operations strategy
Technology is an important strategic decision
Слайд 23
© Wiley 2010
Measuring Productivity
Productivity is a measure of
how efficiently inputs are converted to outputs
Productivity = output/input
Total Productivity Measure
Total Productivity = $sales/inputs $
Partial Productivity Measure
Partial Productivity = cars/employee
Multifactor Productivity Measure
Multi-factor Productivity = sales/total $costs
Слайд 24
© Wiley 2010
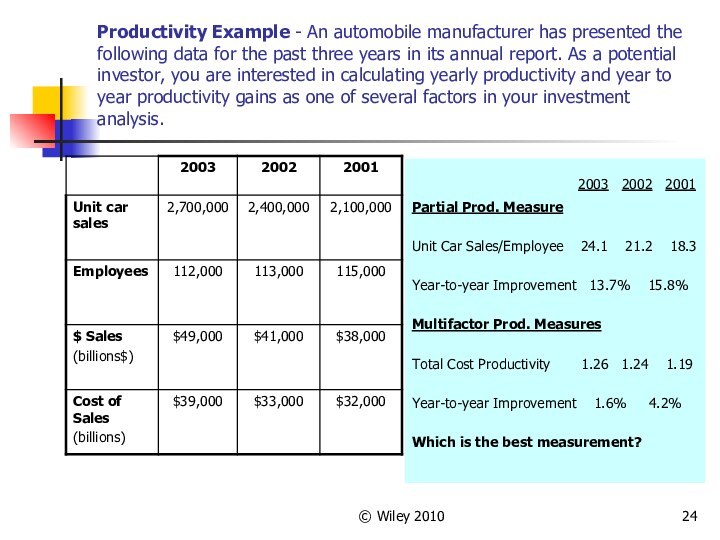
Productivity Example - An automobile manufacturer
has presented the following data for the past three
years in its annual report. As a potential investor, you are interested in calculating yearly productivity and year to year productivity gains as one of several factors in your investment analysis.
2003 2002 2001
Partial Prod. Measure
Unit Car Sales/Employee 24.1 21.2 18.3
Year-to-year Improvement 13.7% 15.8%
Multifactor Prod. Measures
Total Cost Productivity 1.26 1.24 1.19
Year-to-year Improvement 1.6% 4.2%
Which is the best measurement?
Слайд 25
© Wiley 2010
Interpreting Productivity Measures
Productivity measures must be
compared to something, i.e. another year, a different company
Raw
productivity calculations do not tell the complete story unless there are no major structure differences.
In the prior automobile business example, it is obvious that some major changes were taking place to yield 15.8% and 13.7% year-to-year cars/employee productivity improvements. What changes could improve car sales per employee? Automation? Out sourcing? Major re-design?
Слайд 26
© Wiley 2010
Interpreting Productivity Measures
Other productivity measure questions:
Is this partial productivity measurement enough to make an
investment decision?
Is the Total Cost Productivity measure a better reflection of year to year productivity at 4.2% and 1.6%. Why?
Should you also look at productivity measures for the two major competitors for comparison?
Productivity measure provides information on how the firm is doing relative to what is critical to the firm
Слайд 27
© Wiley 2010
Productivity, Competitiveness, and the Service Sector
Productivity
is a scorecard on effective resource use
A nation’s Productivity
effects its standard of living
US productivity growth averaged 2.8% from
1948-1973
Productivity growth slowed for the next 25 years to 1.1%
Productivity growth in service industries has been less than in manufacturing
Слайд 28
© Wiley 2010
Productivity and the Service Sector con’t
Measuring
service sector productivity is a unique challenge
Traditional measures focus
on tangible outcomes
Service industries primarily produce intangible outcomes
Measuring intangibles is challenging
Слайд 29
© Wiley 2010
Operations Strategy Across the Organization
Business strategy
defines long-term plan
Operations strategy support the business strategy
Marketing strategy
needs to fully understand operations capability
Financial plans in effect support operations activities.
Слайд 30
© Wiley 2010
Chapter 2 Highlights
Business Strategy is a
long range plan and vision. Each individual business function
develop needs to support the business strategy
An organization develops its business strategy by doing environmental scanning and considering its mission and its core competencies.
The role of operations strategy is to provide a long-range plan for the use of the company’s resources in producing the company’s primary goods and services.
The role of business strategy is to serve as an overall guide for the development of the organization’s operations strategy.
Слайд 31
© Wiley 2010
Chapter 2 Highlights con’t
The operations strategy
focuses on developing specific capabilities called competitive priorities.
There
are four categories of competitive priorities: cost, quality, time, and flexibility
Technology can be sued by companies to gain a competitive advantage and should be acquired to support the company’s chosen competitive priorities
Productivity is a measure that indicates how efficiently an organization is using its resources
Productivity is computed as the ratio or organizational outputs divided by inputs