- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Introduction to business. Lecture 3
Содержание
- 2. OutlineHow are businesses organised and structured?Major aims
- 3. How it is organised?Micro approach ‘black box’:
- 4. FirmTransaction costs: those incurred when making economic
- 5. Goals of the firmTraditional assumption: firms want
- 6. Principal-agent relationshipObjectives of managers: profits or other
- 7. Principal-agentPrincipal-agent problem in practice. Solutions:Reasonable compensation packageDirect
- 8. Business ethicsHow to measure commitment to business
- 9. Business ethicsBut in many cases right choice
- 10. Right legal structureThis decision is in most
- 11. Types of business organizationPrioprietorship (UK: sole trader)
- 12. PartnershipTwo or more people own the business
- 13. More on partnershipVery often partners draw up
- 14. Incorporated vs unincorporatedSole traders and partnerships are
- 15. CorporationA legal entity registered by a state,
- 16. Private limited companiesLimited liability (ltd) – a
- 17. Public limited companiesShares are bought and sold
- 18. Скачать презентацию
- 19. Похожие презентации
OutlineHow are businesses organised and structured?Major aims of businessHow to achieve these aims?Legal forms of businessBusiness ethics

















Слайд 3
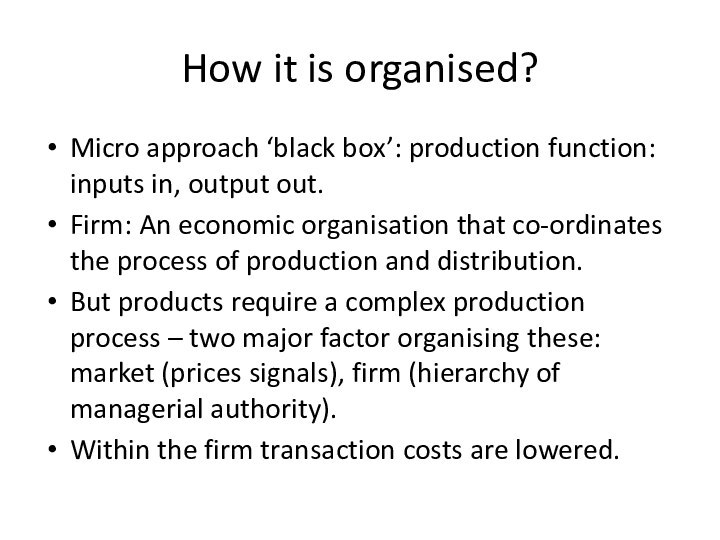
How it is organised?
Micro approach ‘black box’: production
function: inputs in, output out.
Firm: An economic organisation that
co-ordinates the process of production and distribution.But products require a complex production process – two major factor organising these: market (prices signals), firm (hierarchy of managerial authority).
Within the firm transaction costs are lowered.
Слайд 4
Firm
Transaction costs: those incurred when making economic contracts
in the marketplace
Reasons for transaction costs:
Uncertainty of contracts
Complexity
of contractsMonitoring contracts
Enforcing contracts
Therefore, for most goods, firm represents a superior way to organise production!
Слайд 5
Goals of the firm
Traditional assumption: firms want to
maximise profits.
Owners clearly interested in profits maximisation.
However maximisation is
a process of undertaking decisions on how much to produce, at what price etc.In many cases it is not up to owners to undertake these decisions – rather to managers.
Ownership ≠ control. In most cases modern company is legally separated from its owners.
Слайд 6
Principal-agent relationship
Objectives of managers: profits or other aims?
Principal-agent
problem: One where people (principals), as a result of
lack of knowledge (information), cannot ensure that their best interests are served by their agents.Asymmetric information: A situation in which one party has superior position with respect to the information (knows more than another).
Possible ways of solving: monitoring or incentives
Слайд 7
Principal-agent
Principal-agent problem in practice. Solutions:
Reasonable compensation package
Direct intervention
of shareholders
Threat of takeover
All this leads to increased stress
on business ethics!Business ethics: A company attitude and conduct toward its employees, customers, community and stock-holders.
Слайд 8
Business ethics
How to measure commitment to business ethics?
compliance to law
product safety
Fair employment practices
Fair marketing and selling
practicesLack of use of confidential info for personal profits
Community involvement
Lack of corruption
How to obey: code of ethical behaviour, various trainings
Слайд 9
Business ethics
But in many cases right choice is
unclear….
Consequences: bankruptcy, lack of trust, individual tragedies.
Are companies unethical
or just some of their employees? In most cases individuals are blamed, however in Arthur Andersen case otherwise.
Слайд 10
Right legal structure
This decision is in most cases
one of the earliest decisions to make. It affects:
Taxation/social
insurance the business paysThe record and accounts that have to be kept
The liability faced by the owner if the business fails
The sources avaiable to the business
The way decisions are made
Слайд 11
Types of business organization
Prioprietorship (UK: sole trader) –
a person is in business on his/her own behalf.
Usually small business, but may employ other people.(+) inexpensive, easy formation; less regulated, usually easier tax regime, business affairs are private, close relationship with customers, workload individualy tailored
(-) unlimited personal liability; difficulties in funding on larger scale, owner inability to handle all aspects of company activities, life of business limited to the life of individual who created it☹
Слайд 12
Partnership
Two or more people own the business (incl.
sleeping partners). Advantages similar to prioprietorship plus more capital
available (each partner bring some money), but each partner liable for business debt (from 2001 in UK limited liability partnerships allowed).Case: Arthur Andersen – each partner suffered from those who worked with Enron, WorldCom.
Слайд 13
More on partnership
Very often partners draw up a
Deed of Partnership which specifies key features like:
How much
of the finance each contributedHow the profits will be shared
How much control each partner has
How the partnership can be resolved
Слайд 14
Incorporated vs unincorporated
Sole traders and partnerships are unincorporated
Incorporation means that new legal entity is created, something
that exists as the law is concerned.With incorporated business the business itself exists, whereas with an unincorporated business the owner (or owners in case of partnership) is the business.
Слайд 15
Corporation
A legal entity registered by a state, separate
and distinct from its owners and managers, having unlimited
life, easy transferability of ownership and limited liability.(-) taxation – in most cases double: first on corporate level (corporate tax – Poland: CIT) next on personal level when paid out as dividend, more complicated start, lenders may view limited liability as a risk.
(+) Limited liability reduces investors’ risk – lower risk=higher value; growth opportunities due to easier access to capital; better liquidity due to facilitation of ownership transfer.
Слайд 16
Private limited companies
Limited liability (ltd) – a feature
of incorporated business which means that owners’ liability is
limited to the amount that have invested in the business.Popular form for family business and for relatively small and well established businesses
Generally shares can be sold privately and with the consent of the shareholders.
Слайд 17
Public limited companies
Shares are bought and sold publicly
(plc)
So, there is a market value
Initial sale of shares
called flotation or IPOLarger scale, usually requirements regarding minimum value of share capital
Separation of ownership and control
Regular detailed financial information have to be provided
Case: rising share price means that plc gets more money?