Access
TF TAVR
n = 179
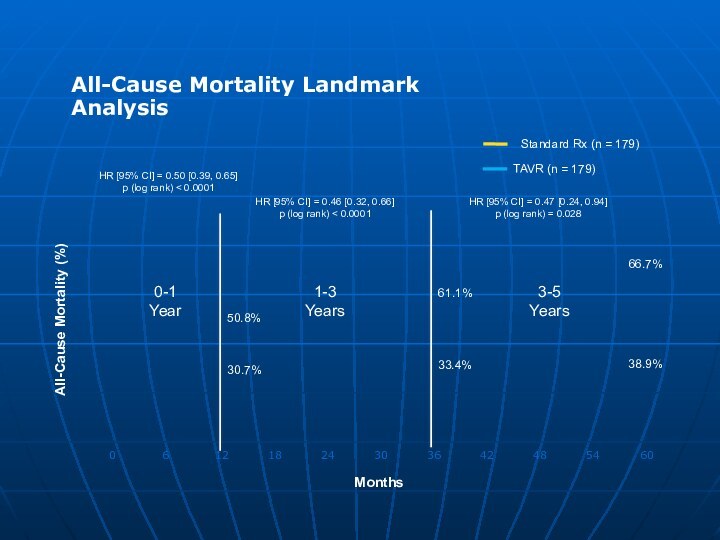
Primary Endpoint: All-Cause Mortality
Over Length
of Trial (Superiority)
1:1 Randomization
VS
Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis
Primary endpoint evaluated when all patients reached one year follow-up.
After primary endpoint analysis reached, patients were allowed to cross-over to TAVR.
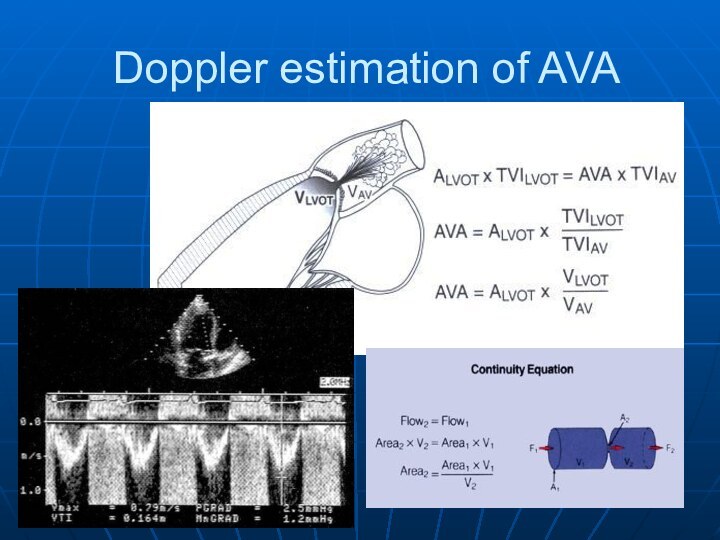
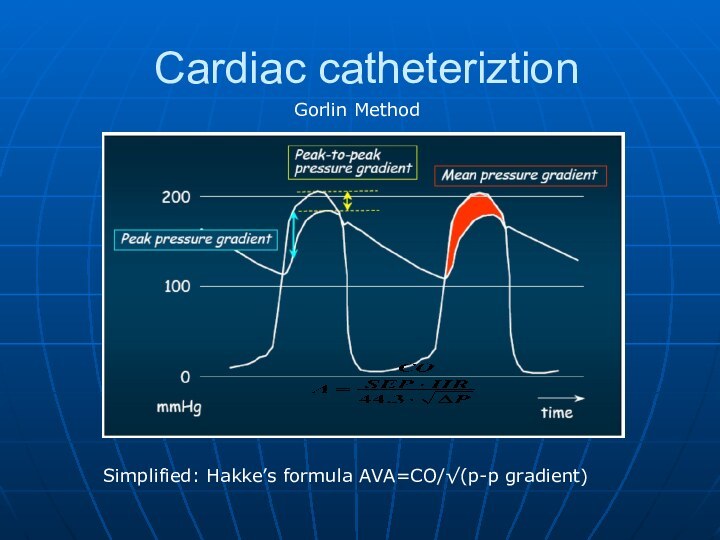
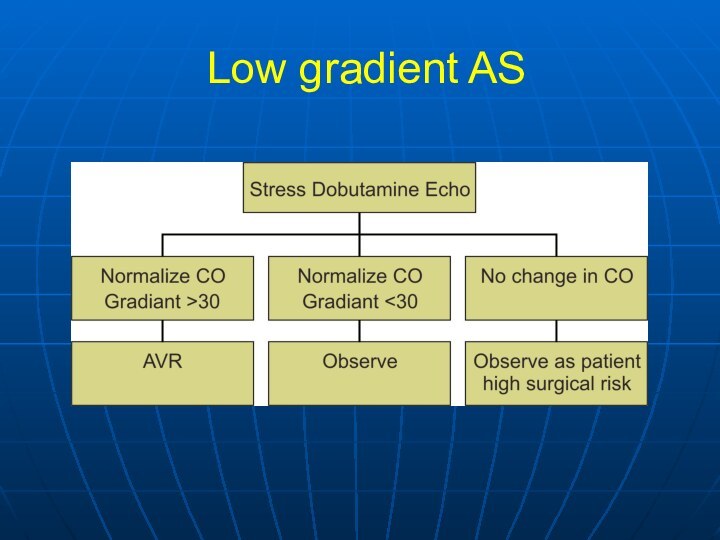
Severe Symptomatic AS with AVA< 0.8 cm2 (EOA index
< 0.5 cm2/m2), and mean gradient > 40 mmHg
or jet velocity > 4.0 m/s
Inoperable defined as risk of death or serious irreversible morbidity of AVR as assessed by cardiologist and two surgeons exceeding 50%.