after MI
mortality
morbidity with socioeconomic
burden for the patient, family & societyIntroduction
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть






















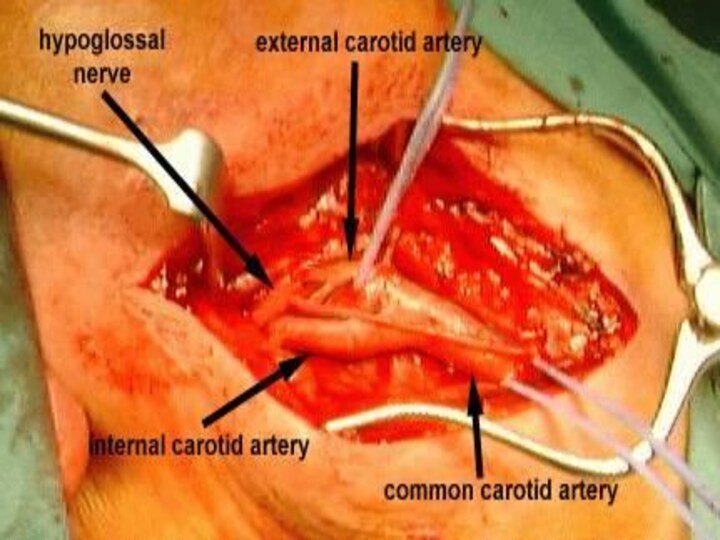












Introduction
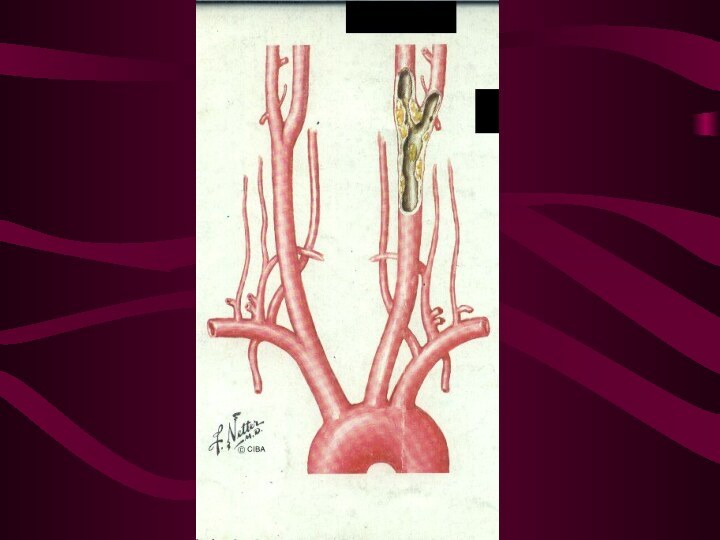
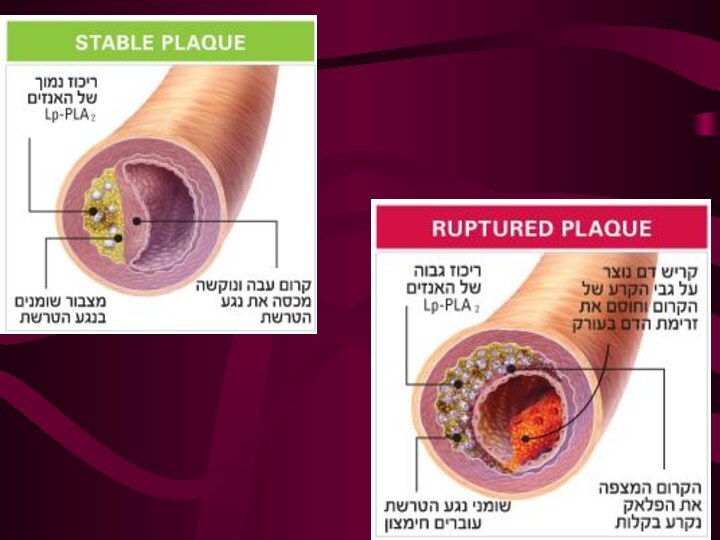
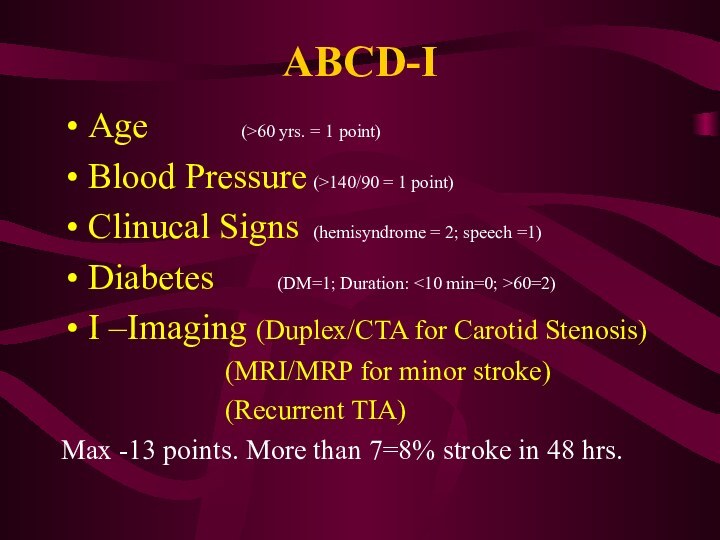
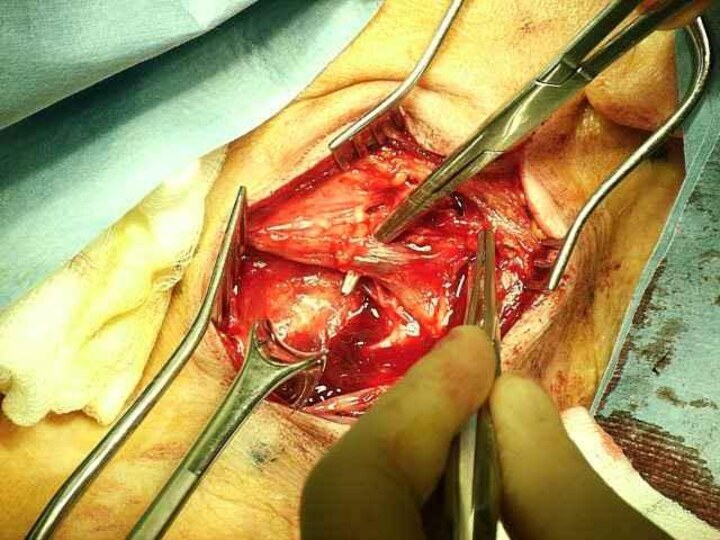
To date, definitely accepted criteria to identify "high-risk" patients for carotid endarterectomy (CEA) do not exist
CONCLUSIONS: Carotid endarterectomy is a safe procedure also in so-called high-risk subsets of patients. Severe comorbidites seem to affect only long-term survival.
Interim results from the lead-in phase of CREST show that the periprocedural risk of stroke and death after CAS increases with age in the course of a credentialing registry. This effect is not mediated by potential confounding factors.
… care should be taken when CAS is performed in older patient populations.