Слайд 2
Plan of the lecture
1. Definition of glomerulonephritis
2. Risk factors and etiology
3. Pathogenesis
4. Classification
5. Diagnostic criteria
6. Treatment and prophylaxis
Слайд 3
Glomerulonephritis (Gn): definition
Gn is heterogeneous group of inflammatory
immune-complex diseases predominantly of kidney glomerular apparatus with different
clinical and morphological presentation, course and outcome.
Слайд 4
Epidemiology
Glomerulonephritis take 3-4 place among all urinary tract
diseases;
Morbidity is more frequent in 3-12 years old, but
children of all ages can be affected. If glomerulonephritis occur after 10 years old it is more frequently chronic form or resistant for steroid therapy.
Слайд 5
Etiology
Any diseases that are caused by Streptococcal
infections of group A : 4, 6, 12, 18,
25, 49 strains (like angina, scarlet fever, piodermia);
Viral infections (adenoviral, flu, ЕСНО 9, Cocsakie, Varicella, epidemic parotitis);
Autoantibodies for mesangeal epithelial, basal, nuclear antigenes;
Noninfectious factors: overcooling, repeated vaccinations and serum medications injections, trauma, insolation, some medications that release autoantigenes;
Idiopathic (IgA-nephropathy, membranous-proliferative glomerulonephritis of I-II types).
Слайд 6
Pathogenesis
Main mechanism is immunopathologic reactions;
There are 2
main mechanisms: immunocomplex (in 80-85%) and autoimmune;
Слайд 7
Immuncomplex glomerulonephritis factors
Disturbances of immune complexes clearance from
circulation;
Compliment system pathology that leads to impairment of immune
complexes inhibition;
Disturbances of erythrocyte clearance of immune complexes due to pathology of CR1-receptors in erythrocytes;
Functional blockage of mononucleal phagocutes Fc-receptors in liver and spleen;
Excess of immune complexes formation with peculiar sizes and charge that capable connect with target organs and tissues
Слайд 8
Autoimmune mechanism of glomerulonephritis development differs from immunocomplex
process only by its initial steps. Effector process is
common due to:
Presence of common criss-cross antigenes of microorganisms (bacteria, viruses) and basal membrane and absence of tolerance;
Appearance of HLA complexes (DR2 и DR3)on glomerular basal membrane;
Kidney tissue damage and releasing of hidden antigenes or glomerular membranes dterminants that has no immune tolerance.
Слайд 9
The only necessary condition for glomerulonephritis development due
to autoimmune mechanism is specific immunodefficiancy with decreased function
of T-supressors.
Слайд 10
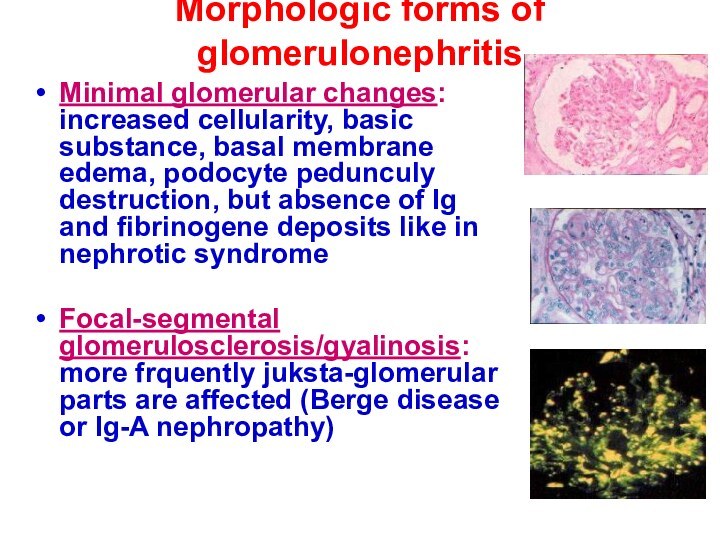
Morphologic forms of glomerulonephritis
Minimal glomerular changes: increased cellularity,
basic substance, basal membrane edema, podocyte pedunculy destruction, but
absence of Ig and fibrinogene deposits like in nephrotic syndrome
Focal-segmental glomerulosclerosis/gyalinosis: more frquently juksta-glomerular parts are affected (Berge disease or Ig-A nephropathy)
Слайд 11
Diffuse Gn (80% and more glomerulus are affected)
Membranous Gn: diffuse uniform capillary walls thickening in glomerulars
without cell proliferation and matrix increasing but with thorn development on basal membrane;
Diffuse proliferative
Mesangiocapillary Gn
Mesangeal proliferative Gn
Endocapillary proliferative
Fibroplastic Gn
Gn with semilunaris (crescentic) (subacute fast progressive Gn)
Слайд 12
Classification of primary glomerulonephritis
ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS:
Nephritic syndrome;
Isolated urinary syndrome;
Nephrotic
syndrome;
Nephrotic with hypertension and hematuria
Слайд 13
CHRONIC GLOMERULONEPHRITIS:
Hematuric form;
Nephrotic form;
Mixed form.
SUBACUTE (MALIGNANT) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Слайд 14
Process course activity
Acute Gn
Initial manifestation;
Swing period (2-4 weeks);
Period
of clinical regression (2-3 months).
Chronic Gn
Period of exacerbation;
Period of
partial remission;
Period of complete clinic-laboratory remission.
Слайд 15
Kidney functioning condition
Acute Gn
Without impairment;
With kidney functioning impairment;
Acute
kidney failure.
Chronic Gn
Without impairment;
With kidney functioning impairment;
Chronic kidney failure.
Слайд 16
NEPHRITIC SYNDROME
Morbidity is frequent at 5-12 y old;
Streptococcal
diseases of oral cavity and skin as a rule
precede 2-4 weeks before Gn onset;
Onset of Gn is sudden with intoxication signs like head ache, malaise, nausea
Слайд 17
Paleness of skin (due to angiospasm)
Loin pains (
due to kidney capsule distention because of parenchyma edema)
Moderate
edema of face, low extremeties;
Слайд 18
Cardio-vascular abnormalities- tachycardia;
Arterial hypertension;
Oliguria can occur;
Hematuria (micro or
macrohematuria);
Слайд 19
Proteinuria not more than 1-2 g/l per day;
Frequently moderate anemia, ESR elevation, leucocytosis ( if infectious
focus is present) can be present
Dysproteinemia, ASL”O” more than 250 IU, hyperfibrinogenemia;
Kidney function insufficiency can be present
Слайд 20
Isolated urine syndrome
Onset is steady without any subjective
symptoms and extrarenal signs. There are only urine changes
like hematuria, moderate proteinuria, cylindruria
Слайд 21
NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
Typical for preschools (1,5-5 y old)
Frequently family
history has allergologic anamnesis;
Слайд 22
Onset is steady with edema development that can
be excessive. Edema can be peripheral, cavitary, and very
significant like anasarka. Sudden onset is possible.
Слайд 23
Olyguria
Significant proteinuria more than 3 g/l per
day.;
Blood tests – hypoproteinemia predominantly due to hypoalbuminemia, high
hyperlipidemia and cholesterolemia, hyperfibvrinogenemia;
ESR is elevated to 50-70 mm/h
NВ
!
BP is normal, hematuria isn’t present, kidney function failure isn’t typical
Слайд 25
Standards of lab testing
Obligatory lab studies
Common blood test
+thrombocyte count;
Biochemical tests (proteinogram, cholesterol, creatinine, urea etc.);
Common urine
tests;
Daily diuresis with daily protein loss;
Nechiporenko test;
Zimnitsky urine test;
Immune tests (ASL-O, CIC, IgM, IgA, compliment system).
Слайд 26
Specifying tests (if necessary))
Blood electrolites ( in stimulated
urination, corticosteroid treatment)
Liver tests (especially in cytotoxic drugs treatment)
Glucose
tests (corticosteroid treatment);
Coagulative tests (desaggrigant, anticoagulative therapy, DIC -syndrome);
Daily proteinurea ( in case of protein losses);
Creatinine clearance (if kidney function is impaired);
Uroleucogram and bacterial culture tests of urine (if leucocyteurea is present).
Слайд 27
Additional lab tests
Of blood
Antibodies to glomerular basal
membrane and neutrophyl cytoplasm (ANCA);
Lipidogram;
Acidic-basic ratio;
Kidney functioning tests;
Fibrin products
degradation (protaminesulphate and ethanol tests);
Antinuclear antibodies, LE-cells;
HLA-typing;
Markers of hepatite testing;
Etc..
Urine
Osmolality testing
В-2-microglobuline studying
Lysozyme detection
Throat
Streptococus smears
Microscopy of buccal washings
Stool
Coprogram
Слайд 28
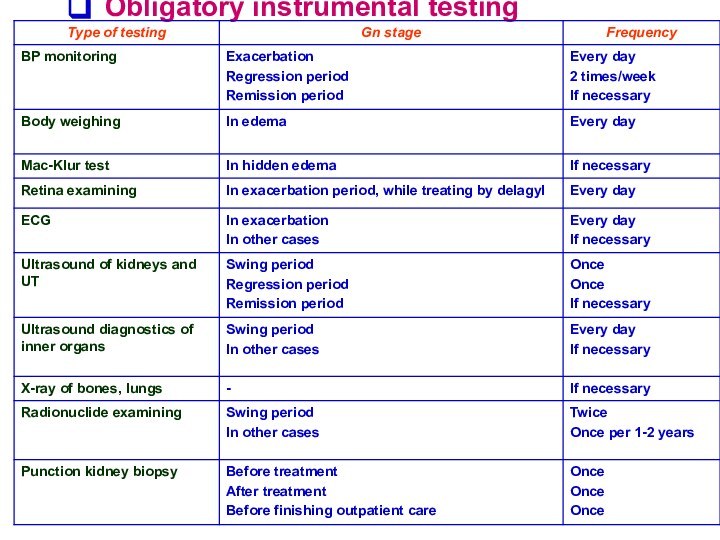
Obligatory instrumental testing
Слайд 29
Glomerulonephritis treatment
Regimen is strictly bed type only if
extrarenal symptoms are present like edema, hypertension, olygouria, macrohematuria
Слайд 30
Diet
Is dependant on edema arterial hypertension and
functional kidney capacity. During acute period salt (NaCl) must
be excluded, fluids and animal proteins must be restricted. All these demands are taken into account in diet N7 (Pevzner)
Слайд 31
Medications:
а) etiologic (if infection as initializing factor is
proved or chronic focus of infection is present-antibiotic treatment
(preferably penicillines);
Слайд 32
b) pathogenic (the main goal is to eradicate
antigen from organism and supress antibody production)
Plasmopheresis or hemasorbtion
(if creatinine, urea level, hyperfibrinogenemia and circulated immune complexes (CIC) are increased
Слайд 33
disaggregants (curantil, ticlid) for 3-4 weeks 2-5 mg/kg
per day, than 1/2 of this dosage for 1-3
month;
anticoagulants (heparin 50-150 IU/kg 4 times per day with blood coagulation tests control (Lee-White test);
Слайд 34
Corticosteroids 1,5-2mg/kg per day, prednisolon for 8 weeks
than cyclic treatment with 1/2 of initial dosage with
steady decreasing of it for 2,5-5 mg once per 1,5 - 2 month;
Cytostatics (leukeran 0,2 mg/kg per day for 6-8 weeks, than 1/2 of initial dosage for 6-8 months).
Слайд 35
Antihypertension, antiproteinuric, antisclerotic drugs :
Angitensin converting enzyme inhibitors
(ACEI) –enalapril, lysinopril – 5-40 mg/day; Angiotensin receptor blockers
(ARB) - (candesar, telmisartan)
Ca channel blockers- diltiazem
в) syndrome therapy: diuretics (trifas,lasycs,hypothiazid,verospironi).
Слайд 36
Outpatient care
After acute glomerulonephritis clinical-laboratory remision children must
be for 5 years under outpatient medical care
Слайд 37
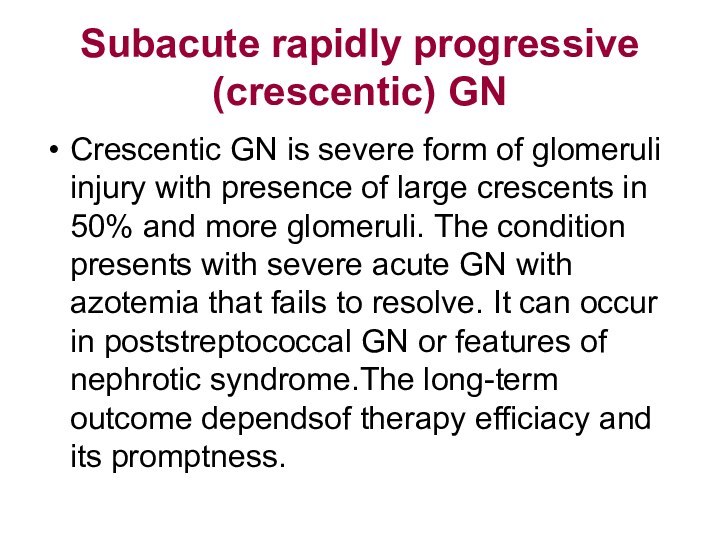
Subacute rapidly progressive (crescentic) GN
Crescentic GN is severe
form of glomeruli injury with presence of large crescents
in 50% and more glomeruli. The condition presents with severe acute GN with azotemia that fails to resolve. It can occur in poststreptococcal GN or features of nephrotic syndrome.The long-term outcome dependsof therapy efficiacy and its promptness.
Слайд 38
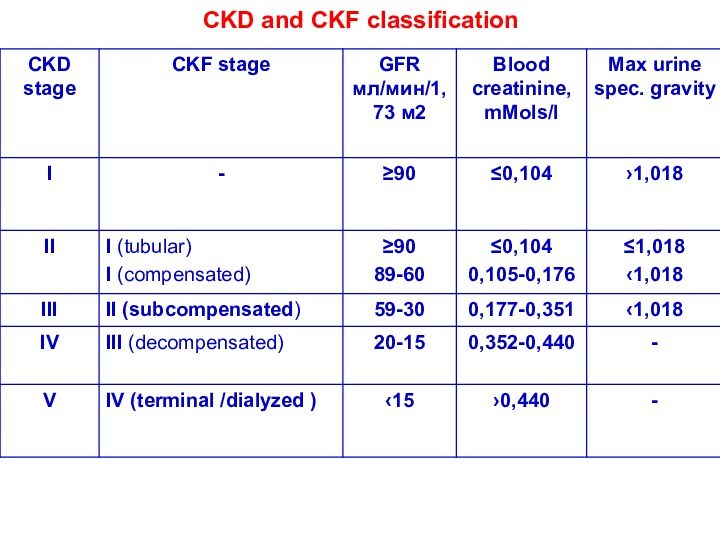
Chronic kidney diseases
From 2003 concept “Chronic kidney disease”
was introduced to children nephrology
Criteria of CKD:
Lesion of kidneys
more than 3 months with structural or functional features with or without glomerular filtration rate decreasing and manifested by one or several symptoms listed below:
Urine test or blood test changes;
Visualizing changes during special examinings;
Biopsy changes.
Glomerular filtration rate less than 60 ml/min or 1,73 м2 for 3 months with or without other kidney damages.
Слайд 39
CKD can be independent diagnose or summerized one;
Like:
CKD
CKD:
chronic glomerulonephritis, hematuric form, clinic-lab remission period.
Diagnosting of CKD
is performed independently to causative disease.
In this situation we suppose further process progression even without glomerular filtration rate decreasing
Слайд 40
Risk factors for CKD development
CKD induced factors
Diabetes mellitus
1, 2 type;
Arterial hypertension;
Autoimmune diseases;
Urinary tract infection;
Nephrocalcinosis;
Toxic medication influences.
Слайд 41
Factors induced CKD progression
High level of proteinurea or
arterial hypertension;
Insufficient glycemia level control;
Smoking.
Risk factors of CKD end-point
Low
dialyze access;
Temporary vessel access;
Anemia;
Low level of albumin;
Late dialyze treatment.
Слайд 42
Glomerular filtration rate
GFR less than 60 ml/min –
can be developed due to CKF without clinical- lab
symptoms of kidney disease.
GFR less than 60 ml/min means that more than 50% of nephrones has been destroyed, but creatinine level can be in the highest normal level.
Слайд 43
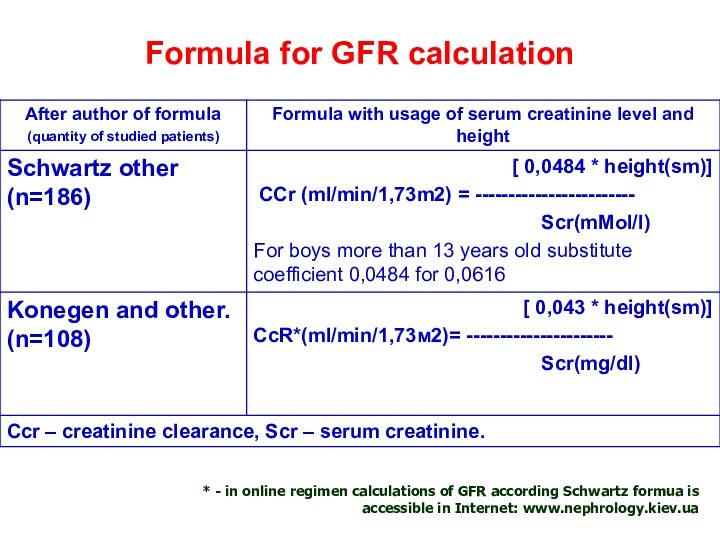
Formula for GFR calculation
* - in online regimen
calculations of GFR according Schwartz formua is accessible in
Internet: www.nephrology.kiev.ua
Слайд 44
Hystologic types of CKD
Proliferative GN ( mesangial prolifirative
GN, crescentic GN, membranoproliferative GN)
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Membranous nephropathy with
diffuse thickening of glomerular basement membrane
Слайд 45
CKD treatment
There is no specific treatment for chronic
GN.
Steroids and immunosuppressive drugs can only retard development
of renal sclerosis and progression to chronic renal failure
Слайд 46
Chronic kidney failure
is stable irreversible progressive
kidney function disorder due to different diseases manifested by
endogene createnine clearence decreasing more than 20ml/min 1,73 m, serum createnine more than 0,177 mmol/sec, urea more than 5,8 mmol/l
(4 European Congress of pediatritians-nephrologists Recommendations, Dublin, 1971)
Слайд 48
2.Total kidney failure
Serum createnine content 0,17 –0,44 mmols/l:
Glomerulopathies: Hypertension, hemorrhagic syndrome, acidosis, decreasing of glomerular filtration
rate and tubular functions
Tubulapathies: osteopathies, anemia, acidosis, glomerular filtration rate and tubular function limitation
Serum createnine level is 0,44-0,88 mmol/l in first group disturbancies of inner organ functioning, in tubulopathies both inner organs functioning and hemorrhagic syndrome will be present
If createnine concentration is more than 0,88 mmoll/l symptoms of uremia will be present. This is End Stage Renal Disease, olygoanuric stage
Слайд 49
Chronic kidney failure (CKF) etiology
Glomerulopathies: Primary glomerular dieases,
immuneglobuline A nephropathies, membrane-proliferative glomerulonephritis
Glomerulopathies associated with systemic diseases
– diabetus mellitus, amyloidosis, SLE, hemolytic-uremic syndrome
Tubularinterstitial disease:reflux-nepohropathies with pyelonephritris, sarcoidosis, toxic nephropathies
Inherited diseases: cystic, Alport syndrome
Hypertension
Kidney vascular disesases
Obstructive uropathies
Слайд 50
CKF syndromes and reasons of their development
Failure to
growth and development – hypostature, malnutrition, sexual development retardation
due to kidney dysembryogenesis, nephrosclerosis, protein and vitamin defficiency, azotemia, acidosis
Uremia - astenia, anorexia, psychoneurologic disorders, gastroentherocolitis, pericarditis due to retention of nitrogenic metabolites and impaired filtration, enhanced catabolism
Water and electrolite balance disorder –edema, hyperkaliemia, hypocalciemia, hyponatriemia due to glomerulo-tubular dysbalance and impaired electrolyte transport
Metabolic acidosis - nausea, vomiting, dyspnea due to impaired ammonia- acid filtration, exhausting buffer reserve
Слайд 51
Arterial hypertension - head ache, hypertonic crises, retinopathy
due to enhanced Pg production and water –electrolyte dysbalance
Osteodystrophy
– pains in bones, X-ray and morphologic changes due to impaired VitD metabolites synthesis and hyperparathyroidism
DIC syndrome – Hemorrhagic lesions in different organs and tissues due to impaired thrombus formation, rheology, coagulative disorders
Immune-deficience –frequent viral and bacterial infections, septic complications due to protein deficiency, hormonal dysbalance
Слайд 52
Diet in CKF
Diet N 7 : moderate limitation
in protein, salt (not more than 0,4 g/day). Restrict
meat, fish, cottage cheese
May eat potato, oils, eggs, sour-cream, bread, pasta
Day quantity of proteins 0,6 до 1,7 mg/kg per day
In 3-4 grade of CKF protein intake mustn’t exceed - 0.5 g/kg per day
Essential amino-acids can be used as food additives (ketosteril – 1 trabl/kg per day)
Слайд 53
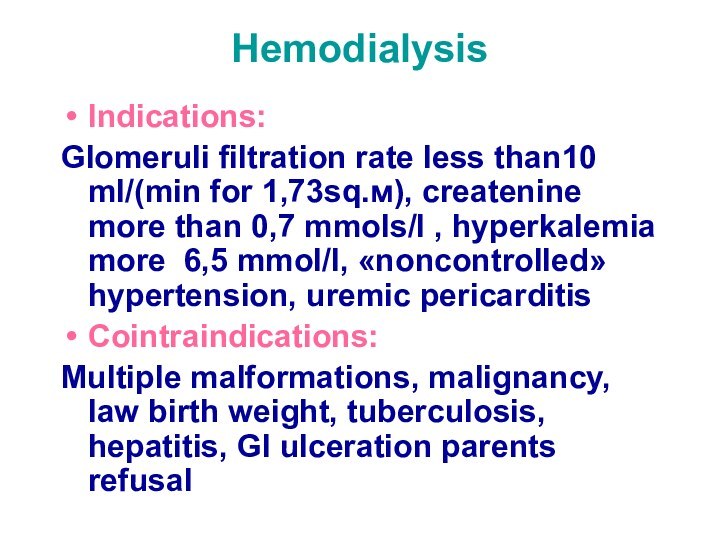
Hemodialysis
Indications:
Glomeruli filtration rate less than10 ml/(min for 1,73sq.м),
createnine more than 0,7 mmols/l , hyperkalemia more 6,5
mmol/l, «noncontrolled» hypertension, uremic pericarditis
Cointraindications:
Multiple malformations, malignancy, law birth weight, tuberculosis, hepatitis, GI ulceration parents refusal
Слайд 54
Indications for kidney transplantation terminal kidney failure stage
Contraindications
: mental diseases, malignancies, sepsis, chronic purulent lung diseases,
systemic vasculitius, reflux-nephropathy, ulcer stomach diseases, polyserositis, severe uncontrolled hypertension