- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Intoxication by agricultural chemical poisonings
Содержание
- 2. DefinitionPesticides (Latin pestis is a plague, contagion,
- 3. Where Are Pesticides Used? Forests to control
- 4. Where Are Pesticides Used?Aquatic sites to control
- 5. Main groups of pesticides1. Insecticides – substances
- 6. 4. Herbicides – for destroying weeds5. Bactericides
- 7. Classification of pesticides according the chemical structure:1.
- 8. Classification of pesticides according the chemical structure:6.
- 9. AerialAir blast sprayerEnclosed cabBackpack wandBoom sprayerAgriculture Pesticide Applications
- 10. Agriculture JobsOrchard thinnerMixer loaderFlaggerPicker
- 11. 90% of pesticides used today are synthetic
- 12. ROUTES OF EXPOSURESource: EPA Protect Yourself from
- 13. The pesticide cyclePesticide use has helped increase
- 14. Intoxication by phosphorus organic connections.
- 15. Organophosphate poisoninghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Organophosphate_poisoning
- 16. Organophosphates are used in:Pesticides sprayed and dusted
- 17. Chemical names for organophosphates active ingridientsMethyl parathionEthyl parathionMalathionDiazinonFenthionDichlorvosChlorpyrifosTrichlorfonparathionDichlorvosChlorpyrifosMalathionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Organophosphate_poisoning
- 18. Pathophysiology2007 Pediatric Environmental Health Specialty Unit (PEHSU), Department of Environmental & Occupational Health Sciences.University of Washington opchild@u.washington.edu
- 19. Common causes of OP poisoningInhalation The agricultural
- 20. IngestionConsumption of domestic drinking water stored in
- 21. Absorption and ingestionFailure to wash hands after
- 23. http://blog.ecosmart.com/index.php/2008/09/19/the-history-of-pesticides/Clinical pictureSymptoms of acute OP poisoning develop
- 24. Commonly reported early symptomsHeadacheNauseaDizzinessHypersecretion (sweating and salivation)Muscle twitchingWeaknessTremorsIn coordinationVomitingAbdominal crampsDiarrheaParalysis http://www.extension.org/pages/17854/symptoms-of-pesticide-poisoning
- 25. Clinical picture Basic symptoms of the acute poisoning
- 26. Muscarinic effects (result of excitation of M-
- 27. Nicotinic effects (excitation of M- cholinoreceptions and
- 28. CNS Effects (toxic influence of acetilcholine on
- 29. The types and severity of cholinesterase inhibition
- 30. The easy form of acute intoxication- tachycardia
- 31. At middle degree of severity of acute
- 32. The heavy (comatose) form of intoxication meets
- 33. Chronic poisonings by phosphorus organic connections it
- 34. TreatmentAntidote therapy - cholinolitics and reactivates of
- 35. Intoxication by arsenic connections
- 36. Arsenic (As)Chemistry:extremely complex because it can exist
- 37. Sources of As smelting of gold, silver, copper,
- 38. Arsenic (As)pharmacokinetics and dynamics:absorbed via inhalation, ingestion
- 39. Arsenic Toxicity Mechanismsbinds to sulfhydryl groups (and
- 40. The catarrhal form of acute intoxicationappear from
- 41. Gastrointestinal format the casual hit of poison
- 42. Chronic intoxicationmeets in persons, which long time
- 43. Arsenic poisoninghttp://manbir-online.com/diseases/arsenic.htmTypical findings are skin and nail changes,
- 44. http://manbir-online.com/diseases/arsenic.htm
- 45. Diagnostic criteria of Chronic arsenicosis.1. At least
- 46. Dermatological criteria and grading of severity of chronic arsenic toxicityhttp://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/arsenicun4.pdfGuha Mazumder , (In press)
- 47. LABORATORY FINDINGS When acute arsenic poisoning is suspected,
- 49. TreatmentVomiting should be induced in the alert
- 50. Intoxication by chlorine organic connections.
- 51. Chlorinated hydrocarbon (organochlorine) insecticides, solvents, and fumigants
- 52. 5 groups of organochlorines insecticidesDichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and
- 53. http://www.prn.usm.my/old_website/mainsite/bulletin/1996/prn10.html
- 54. http://wa.water.usgs.gov/pubs/fs/fs170-96/images/fs-170-96_foodchain.gif
- 55. Mechanism of toxicityToxicity in humans is largely
- 56. Clinical presentationCNS excitation and depression are the
- 57. Physical findingsPhysical examinations findings depends on type
- 58. Skin absorption or inhalationEar, nose, and throat irritationBlurred visionCoughAcute lung injury (ALI)DermatitisPhysical findingshttp://emedicine.medscape.com/article/815051-overview#a0104
- 59. Chronic exposure (meets in persons who constantly
- 60. Pulmonary - Increased A-a gradient, hypoxemiaCardiovascular -
- 61. Prehospital CareDermal decontamination is a priority. Remove
- 62. TreatmentGI DecontaminantActivated charcoal is emergency treatment in
- 63. Bile acid sequestrantsThese binding agents are used
- 64. BenzodiazepinesMainstay of treatment for hydrocarbon insecticide–induced seizures.Lorazepam
- 65. AnticonvulsantsClass Summary. Additional options include pentobarbital or
- 66. Intoxication by mercury organic connections.
- 67. They are high enough bactericidal and fungicides
- 68. The organic mercury compounds are of great
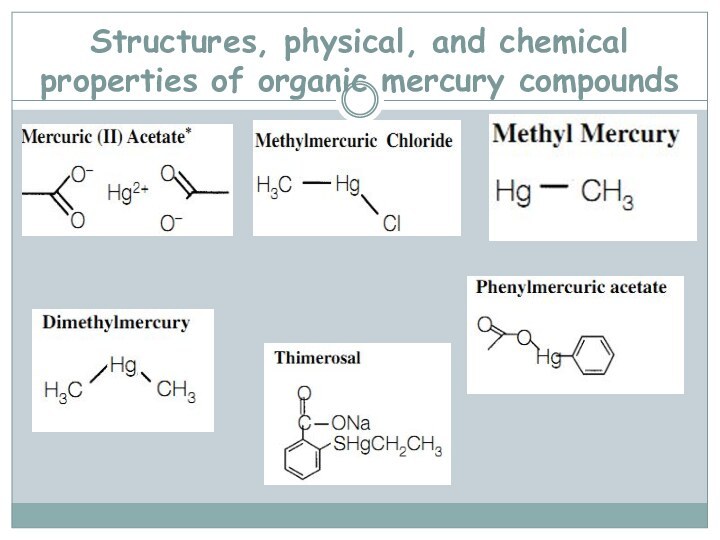
- 69. Structures, physical, and chemical properties of organic mercury compounds
- 71. Mechanism of mercury toxicityMolecular mechanisms of mercury
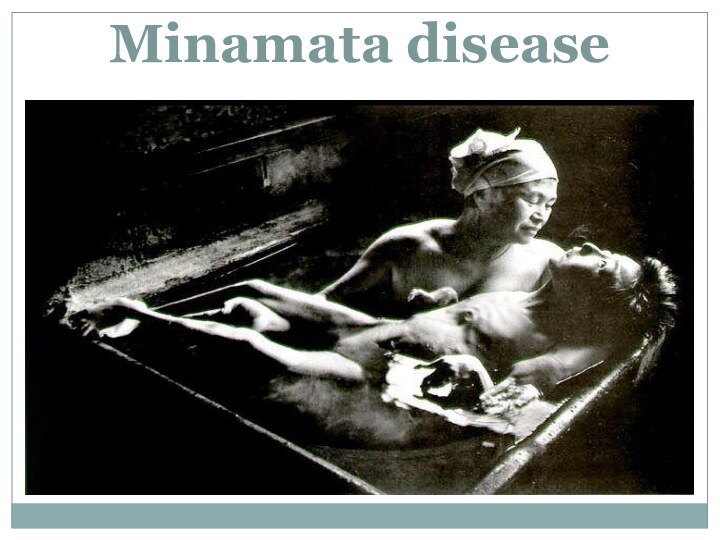
- 72. Minamata disease
- 73. Clinical presentationAtaxiatremors unsteady gait illegible handwriting, slurred
- 74. A diagnosis we put when we have
- 75. Treatment- To wash a stomach and enterosorbtion;-
- 76. Скачать презентацию
- 77. Похожие презентации



























































Слайд 3
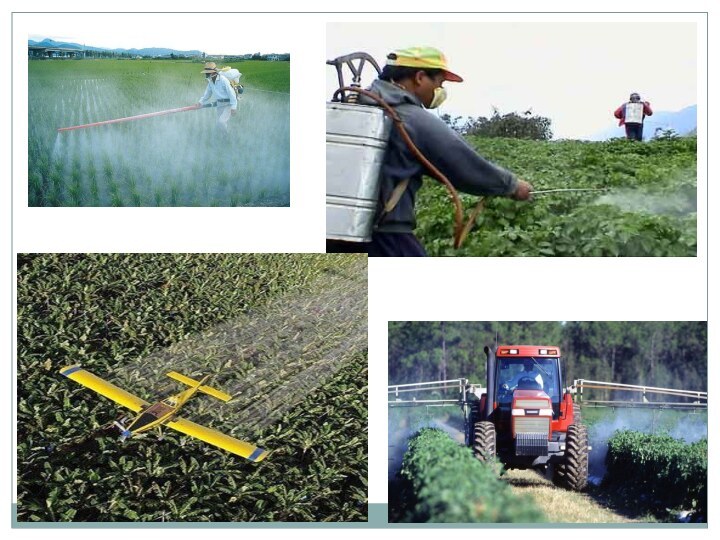
Where Are Pesticides Used?
Forests to control insects
and under-story vegetation;
Landscapes, parks, and recreational areas to control
weeds, insects, and disease pests;Rights-of-way along railroads and under electric wires to control vegetation;
Houses, schools, and commercial and office buildings to control insects, rodents, and fungi;
Boat hulls to control fouling organisms;
Слайд 4
Where Are Pesticides Used?
Aquatic sites to control mosquitoes
and weeds
Wood products to control wood-destroying organisms
Food preparation areas
to control insects and rodentsHuman skin to kill or repel insects
Household pets to control fleas and ticks
Livestock to control insects and other pests.
Слайд 5
Main groups of pesticides
1. Insecticides – substances which
are used for a fight against insects
2. Fungicides –
for treating of plants from mycotic diseases3. Defoliants – preparations which are used for the delete of leaves of plants
Слайд 6
4. Herbicides – for destroying weeds
5. Bactericides –
against bacteria
6. Acaracides – for destroying of the mites
7.
Rodenticides – against rodents8. Ovicides – against larvae and caterpillar
Main groups of pesticides
Слайд 7
Classification of pesticides according the chemical structure:
1. Chlorine
organic connections (chloridan, heptachlor, chlorten, polychlorpinen).
2. Phosphorus organic connections
(karbofos, chlorofos, metaphos, thiophos).3. Mercury organic connections (granosan, mercuran, mercur- gexan).
4. Connections of arsenic (arsenat sodium, arsenat calcium, parisian greenery).
5. Derivates of carbamic acid (bethanol, carbin, sevin and other).
Слайд 8
Classification of pesticides according the chemical structure:
6. Cyanides
(cyanic acid, cyanamid of calcium).
7. Preparations of copper (burgundy
liquid, blue vitriol).8. Sulphur and its connections (colloid sulphur, sulphuric anhydride, ground sulphur).
9. Preparations of vegetable origin (anabasine, nicotine, piretrum).
Слайд 9
Aerial
Air blast sprayer
Enclosed cab
Backpack wand
Boom sprayer
Agriculture Pesticide Applications
Слайд 12
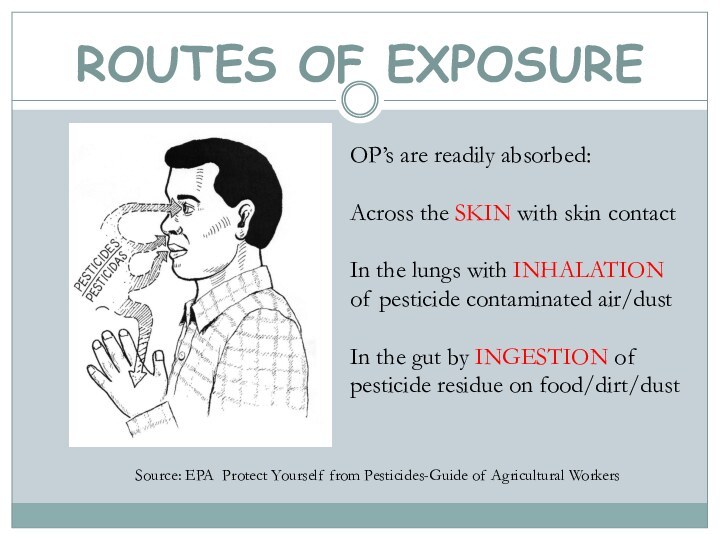
ROUTES OF EXPOSURE
Source: EPA Protect Yourself from Pesticides-Guide
of Agricultural Workers
OP’s are readily absorbed:
Across the SKIN with
skin contactIn the lungs with INHALATION of pesticide contaminated air/dust
In the gut by INGESTION of pesticide residue on food/dirt/dust
Слайд 13
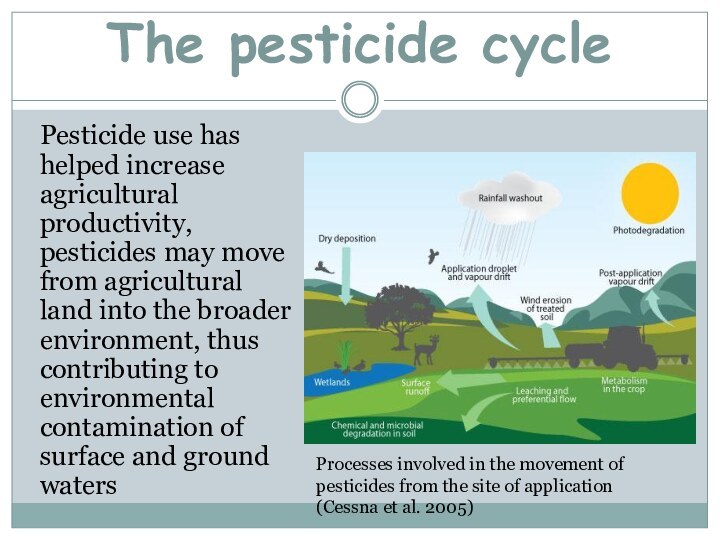
The pesticide cycle
Pesticide use has helped increase agricultural
productivity, pesticides may move from agricultural land into the
broader environment, thus contributing to environmental contamination of surface and ground watersProcesses involved in the movement of pesticides from the site of application (Cessna et al. 2005)
Слайд 16
Organophosphates are used in:
Pesticides sprayed and dusted onto
cereals, fruit and vegetables
De-wormers and systemic ‘pour-ons’ applied to
farm animalsFly sprays and vaporizing strips used in industrial, commercial and domestic premises
Flea collars and treatment for pests
Anti-lice shampoo
Слайд 17
Chemical names for organophosphates active ingridients
Methyl parathion
Ethyl parathion
Malathion
Diazinon
Fenthion
Dichlorvos
Chlorpyrifos
Trichlorfon
parathion
Dichlorvos
Chlorpyrifos
Malathion
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Organophosphate_poisoning
Слайд 18
Pathophysiology
2007 Pediatric Environmental Health Specialty Unit (PEHSU), Department of
Environmental & Occupational Health Sciences.University of Washington opchild@u.washington.edu
Слайд 19
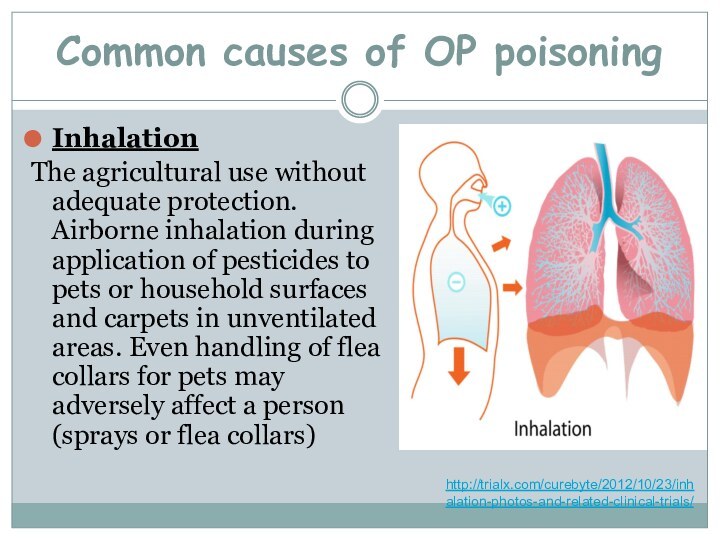
Common causes of OP poisoning
Inhalation
The agricultural use
without adequate protection. Airborne inhalation during application of pesticides
to pets or household surfaces and carpets in unventilated areas. Even handling of flea collars for pets may adversely affect a person (sprays or flea collars)http://trialx.com/curebyte/2012/10/23/inhalation-photos-and-related-clinical-trials/
Слайд 20
Ingestion
Consumption of domestic drinking water stored in contaminated,
discarded poison containers
Consumption of fruit and vegetables that have
been treated with pesticides, and not washed properlyCommon causes of OP poisoning
http://toolboxes.flexiblelearning.net.au/demosites/series3/315/resources/ohs/hazards/08hazardoussubstances.htm
Слайд 21
Absorption and ingestion
Failure to wash hands after handling
pesticides or pet flea and tick control products
Common causes
of OP poisoninghttp://nasdonline.org/document/196/Fact7/d000145/preventing-agricultural-chemical-exposure-a-safety-program-manual.html
Слайд 23
http://blog.ecosmart.com/index.php/2008/09/19/the-history-of-pesticides/
Clinical picture
Symptoms of acute OP poisoning develop during
or after exposure, within minutes to hours, depending on
the method of contact. Exposure due to inhalation results in the fastest appearance to toxic symptoms, followed by the gastrointestinal route and, finally, the dermal route.
Слайд 24
Commonly reported early symptoms
Headache
Nausea
Dizziness
Hypersecretion (sweating and salivation)
Muscle twitching
Weakness
Tremors
In
coordination
Vomiting
Abdominal cramps
Diarrhea
Paralysis
http://www.extension.org/pages/17854/symptoms-of-pesticide-poisoning
Слайд 25
Clinical picture
Basic symptoms of the acute poisoning by
phosphorus organic pesticides are owing to muscarinic action, nicotinic
action and by the central action of acetilcholine.
Слайд 26
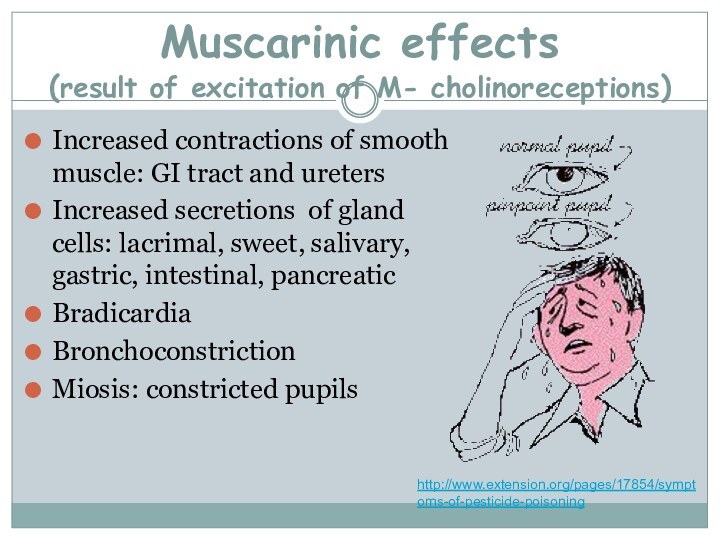
Muscarinic effects
(result of excitation of M- cholinoreceptions)
Increased contractions
of smooth muscle: GI tract and ureters
Increased secretions of
gland cells: lacrimal, sweet, salivary, gastric, intestinal, pancreaticBradicardia
Bronchoconstriction
Miosis: constricted pupils
http://www.extension.org/pages/17854/symptoms-of-pesticide-poisoning
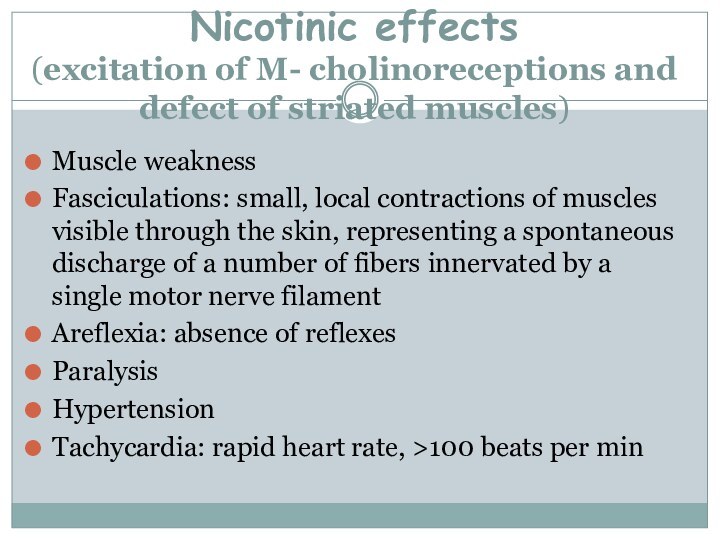
Слайд 27 Nicotinic effects (excitation of M- cholinoreceptions and defect of
striated muscles)
Muscle weakness
Fasciculations: small, local contractions of muscles visible
through the skin, representing a spontaneous discharge of a number of fibers innervated by a single motor nerve filamentAreflexia: absence of reflexes
Paralysis
Hypertension
Tachycardia: rapid heart rate, >100 beats per min
Слайд 28 CNS Effects (toxic influence of acetilcholine on the cortex
of cerebrum and medulla)
Confusion
Seizures
Oppression and paralysis of vitally important
centers of medullaСлайд 29 The types and severity of cholinesterase inhibition symptoms
depend on:
Toxicity of pesticide
Amount of pesticide involved in the
exposureRoute of exposure ( inhalation is fastest, followed by ingestion, then dermal)
Duration of exposure
Слайд 30
The easy form of acute intoxication
- tachycardia which
later changes on bradycardia, and raises the arterial blood
pressure;- the decrease of cholinesterase is marked in blood;
- a disease at the easy form of motion is finished, as a rule, by convalescence.
Слайд 31 At middle degree of severity of acute intoxication
to the symptoms of previous stage addition;
- a fever with
increase of temperature of body to 40 ºC, excitation which later changes for depression, feeling of fear, appears inadequate reaction on external irritants;- headache increases, appears expressed salivation and tearing, hyperhidrosis, a muscle weakness grows;
- violation of breathing shows up by hard inhalation and exhalation, with mass of dry whistling and moist large vesicles, little vesicles and vesicular rales;
- appear the signs of oxygen insufficiency, tachycardia which changes on bradycardia, decrease of arterial blood pressure, a heart is extended, tones are quiet;
Слайд 32 The heavy (comatose) form of intoxication meets rarely,
sometimes it finished lethally. In the clinic of heavy
form distinguish three stages: excitation, convulsive and paralytic.Management of a patient with severe organophosphorus poisoning in a Sri Lankan district hospital.
www.thelancet.com Vol 371 February 16, 2008
Слайд 33 Chronic poisonings by phosphorus organic connections it is
needed to differentiate with astenovegetative neuroses, myocardial dystrophy. By
an important laboratory index which confirms the diagnosis of acute intoxication there is decrease of activity of cholinesterase to 50 % and anymore.
Слайд 34
Treatment
Antidote therapy - cholinolitics and reactivates of cholinesterase:
at the easy form of intoxication intramuscular enter 1-2
ml of 0,1 % to solution of atropine; at middle and heavy degrees intoxications intensive atropinisation is conducted. Once intramuscular enter 3-5 ml of 0,1 % solution of atropine, and then pass introduction of atropine to supporting. Injections repeat oneself each 5-6 minutes to stopping of muskarinic symptoms and appearance of signs of overdose of atropine (dryness of mycoses, expansion of pupils).Respiratory support is given as necessary. Gastric decontamination should be considered only after the patient has been fully resuscitated and stabilised. Patients must be carefully observed after stabilisation for changes in atropine needs, worsening respiratory function because of intermediate syndrome, and recurrent cholinergic features occuring with fat-soluble organophosphorus
Слайд 36
Arsenic (As)
Chemistry:
extremely complex because it can exist in
metallic form, can be in trivalent and pentavalent state
(charge of 3+ or 5+), and can be organic or inorganicwidely distributed in nature (variety of forms)
Environmental fate:
found in surface and groundwater through runoff
accumulates in plants if soil conditions are right
bioaccumulates in aquatic ecosystems (so fish consumption is a source)
From: Klaassen et al., Chap. 19, Philp, Chap. 6
Слайд 37
Sources of As
smelting of gold, silver, copper, lead
and zinc ores
combustion of fossil fuels
agricultural uses as herbicides
and fungicides, as insecticides for staining of seed, destroying the pests of garden cultures, rice fields, malarial mosquito maggots and for a fight against rodentscigarette smoke
occupational: largest source is manufacture of pesticides and herbicides
Слайд 38
Arsenic (As)
pharmacokinetics and dynamics:
absorbed via inhalation, ingestion and
dermal exposure
mimics phosphate in terms of uptake by cells
Detoxified
by methylation: decreased rates lead to increased toxicity (individual susceptibility)Can cross placenta
accumulates in liver, kidney, heart and lung - later in bones, teeth, hair, etc.
half-life is 10 hr, excretion via kidneys
From: Klaassen et al., Chap. 19, Philp, Chap. 6
Слайд 39
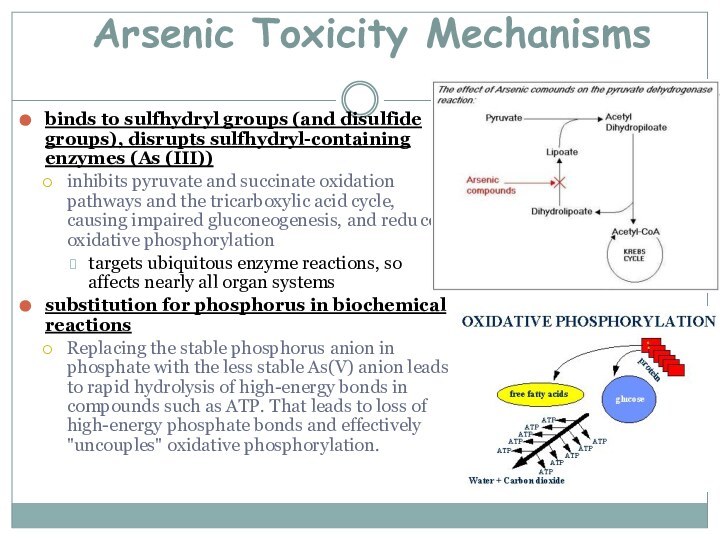
Arsenic Toxicity Mechanisms
binds to sulfhydryl groups (and disulfide
groups), disrupts sulfhydryl-containing enzymes (As (III))
inhibits pyruvate and succinate
oxidation pathways and the tricarboxylic acid cycle, causing impaired gluconeogenesis, and redu ced oxidative phosphorylationtargets ubiquitous enzyme reactions, so affects nearly all organ systems
substitution for phosphorus in biochemical reactions
Replacing the stable phosphorus anion in phosphate with the less stable As(V) anion leads to rapid hydrolysis of high-energy bonds in compounds such as ATP. That leads to loss of high-energy phosphate bonds and effectively "uncouples" oxidative phosphorylation.
Слайд 40
The catarrhal form
of acute intoxication
appear from the hit
of the aerosol of arsenic on the mycoses of
eyes and breathing organs.- appearance of weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomit, by sweetish taste in a mouse, feeling of fear, shaking, and painful cramps;
- there are an irritation and sharp hyperemia of mucosas of overhead respiratory tracts and eyes that shows up burning of eyes, tearing, cold, sneezing, edema of mucus of nose, cough, sometimes with hemoptysis and pain in thorax;
- the signs of heart insufficiency, astenovegetative syndrome, and also symptoms of defect of gastrointestinal tract, appear later.
Слайд 41
Gastrointestinal form
at the casual hit of poison in
a gastrointestinal tract.
metallic taste appears in a mouth,
dryness, swallowing, incessant vomit (the masses of vomits have a garlic smell), acute abdomen pain, diarrhea. the amount of urine diminishes;
the loss of liquid conduces to acute dehydration of organism;
an acute weakness, dizziness, develops, sometimes fainting fit, decrease the temperature of body and arterial blood pressure goes down, the collapse state develops;
Слайд 42
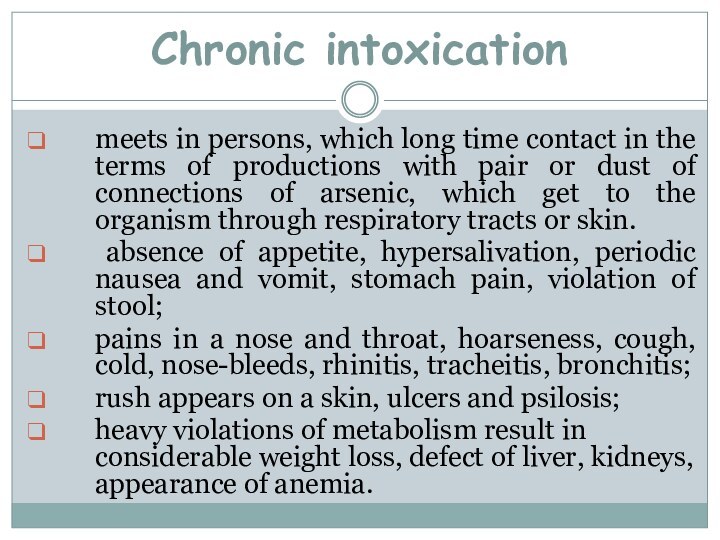
Chronic intoxication
meets in persons, which long time contact
in the terms of productions with pair or dust
of connections of arsenic, which get to the organism through respiratory tracts or skin.absence of appetite, hypersalivation, periodic nausea and vomit, stomach pain, violation of stool;
pains in a nose and throat, hoarseness, cough, cold, nose-bleeds, rhinitis, tracheitis, bronchitis;
rush appears on a skin, ulcers and psilosis;
heavy violations of metabolism result in considerable weight loss, defect of liver, kidneys, appearance of anemia.
Слайд 43
Arsenic poisoning
http://manbir-online.com/diseases/arsenic.htm
Typical findings are skin and nail changes, such
as hyperkeratosis, hyperpigmentation, exfoliative dermatitis, and Mees’ lines (transverse white striae of
the fingernails); sensory and motor polyneuritis manifesting as numbness and tingling in a “stocking-glove” distribution, distal weakness, and quadriplegia; and inflammation of the respiratory mucosa.Epidemiologic evidence has linked chronic consumption of water containing arsenic at concentrations in the range of 10 to 1820 ppb with vasospasm and peripheral vascular insufficiency culminating in “blackfoot disease - a gangrenous condition affecting the extremities.Chronic arsenic exposure has also been associated with a greatlyelevated risk of skin cancer and possibly of cancers of the lung, liver (angiosarcoma), bladder, kidney, and colon
Слайд 45
Diagnostic criteria of Chronic arsenicosis.
1. At least 6
months exposure to arsenic levels of greater than 50
mg/L or exposure of high arsenic level from food and air.2. Dermatological features characteristic of chronic arsenicosis.
3. Non carcinomatous manifestations : Weakness, chronic lung disease, non cirrhotic portal fibrosis of liver with/without portal hypertension, peripheral neuropathy, peripheral vascular disease, non pitting edema of feet/ hand.
4. Cancers : Bowens disease, Squamous cell carcinoma, Basal cell carcinoma at multiple sites, occurring in unexposed parts of the body.
5. Arsenic level in hair and nail above 1 mg/kg and 1.08 mg/kg respectively and/or arsenic level in urine, above 50 mg/L (without any history of taking seafood).
http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/arsenicun4.pdf
Guha Mazumder , (In press)
Слайд 46 Dermatological criteria and grading of severity of chronic
arsenic toxicity
http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/arsenicun4.pdf
Guha Mazumder , (In press)
Слайд 47
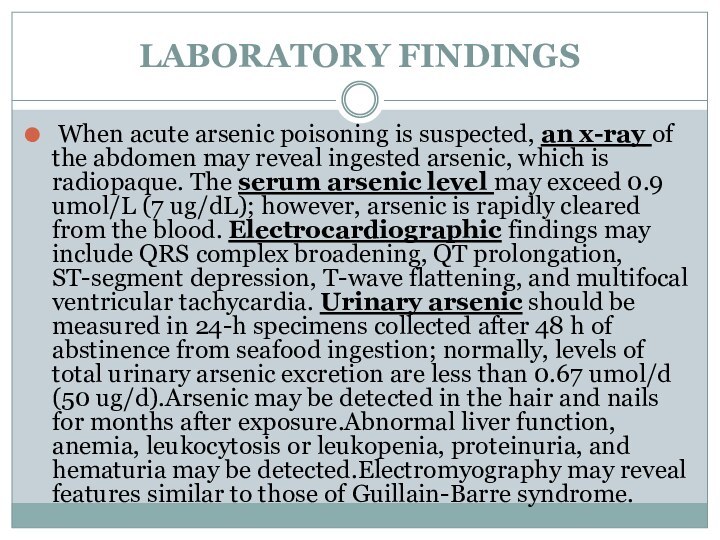
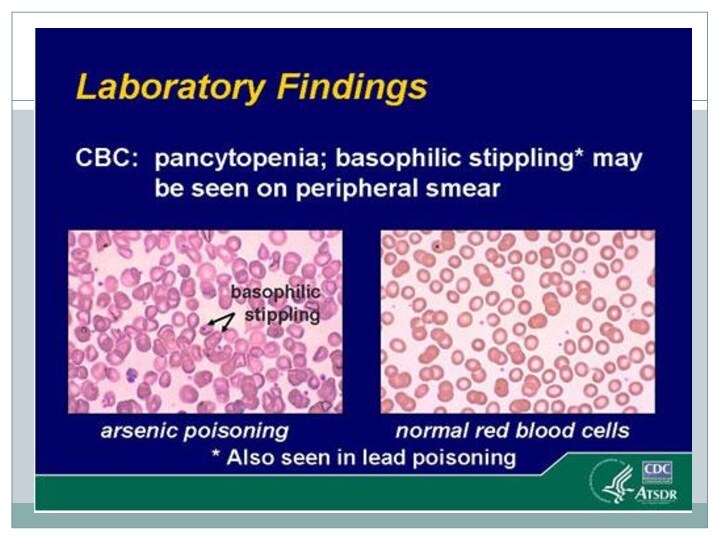
LABORATORY FINDINGS
When acute arsenic poisoning is suspected, an
x-ray of the abdomen may reveal ingested arsenic, which
is radiopaque. The serum arsenic level may exceed 0.9 umol/L (7 ug/dL); however, arsenic is rapidly cleared from the blood. Electrocardiographic findings may include QRS complex broadening, QT prolongation, ST-segment depression, T-wave flattening, and multifocal ventricular tachycardia. Urinary arsenic should be measured in 24-h specimens collected after 48 h of abstinence from seafood ingestion; normally, levels of total urinary arsenic excretion are less than 0.67 umol/d (50 ug/d).Arsenic may be detected in the hair and nails for months after exposure.Abnormal liver function, anemia, leukocytosis or leukopenia, proteinuria, and hematuria may be detected.Electromyography may reveal features similar to those of Guillain-Barre syndrome.
Слайд 49
Treatment
Vomiting should be induced in the alert patient
with acute arsenic ingestion.
Gastric lavage may be useful; activated
charcoal with a cathartic (such as sorbitol) may be tried.Aggressive therapy with intravenous fluid and electrolyte replacement in an intensive-care setting may be life-saving.
Dimercaprol is the chelating agent of choice and is administered intramuscularly at an initial dose of 3 to 5 mg/kg on the following schedule: every 4 hr for 2 days, every 6 hr on the third day, and every 12 hr thereafter for 10 days. (An oral chelating agent may be substituted). Succimer is sometimes an effective alternative, particularly if adverse reactions to dimercaprol develop (such as nausea, vomiting, headache, increased blood pressure, and convulsions). In cases of renal failure, doses should be adjusted carefully, and hemodialysis may be needed to remove the chelating agent-arsenic complex. Arsine gas poisoning should be treated supportively with the goals of maintaining renal function and circulating red-cell mass.
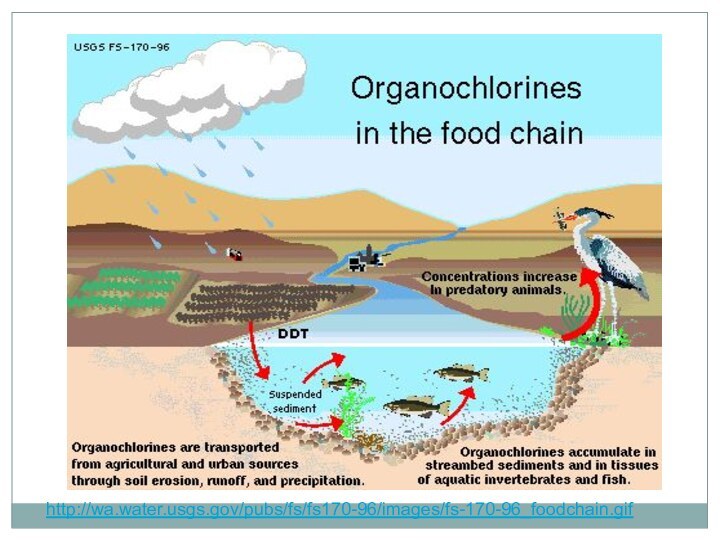
Слайд 51 Chlorinated hydrocarbon (organochlorine) insecticides, solvents, and fumigants are
widely used around the world. This class comprises a
variety of compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, and chlorine. These compounds can be highly toxic, and the overwhelming majority have been universally banned because of their unacceptably slow degradation and subsequent bioaccumulation and toxicity.[1]Among the more notable, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) is an organochlorine pesticide and its invention won Paul Müller the 1948 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
Слайд 52
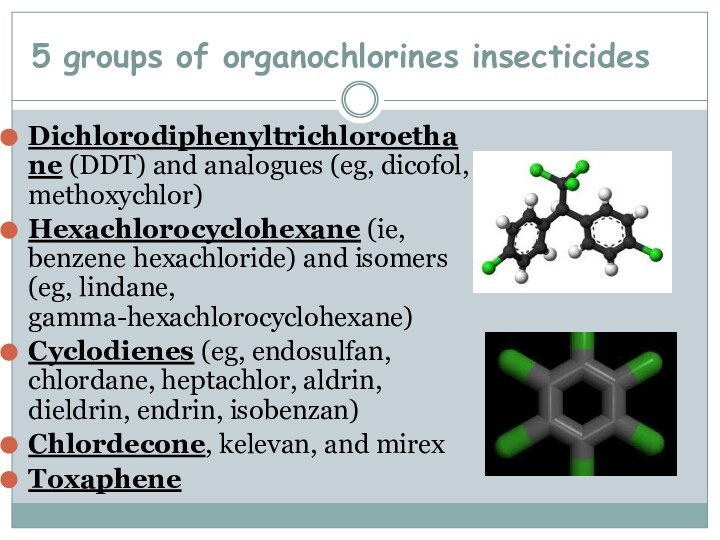
5 groups of organochlorines insecticides
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and analogues
(eg, dicofol, methoxychlor)
Hexachlorocyclohexane (ie, benzene hexachloride) and isomers (eg,
lindane, gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane)Cyclodienes (eg, endosulfan, chlordane, heptachlor, aldrin, dieldrin, endrin, isobenzan)
Chlordecone, kelevan, and mirex
Toxaphene
Слайд 55
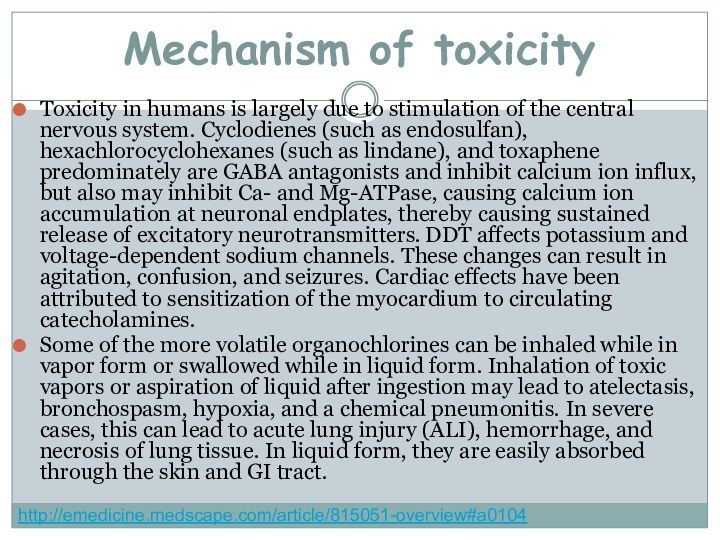
Mechanism of toxicity
Toxicity in humans is largely due
to stimulation of the central nervous system. Cyclodienes (such
as endosulfan), hexachlorocyclohexanes (such as lindane), and toxaphene predominately are GABA antagonists and inhibit calcium ion influx, but also may inhibit Ca- and Mg-ATPase, causing calcium ion accumulation at neuronal endplates, thereby causing sustained release of excitatory neurotransmitters. DDT affects potassium and voltage-dependent sodium channels. These changes can result in agitation, confusion, and seizures. Cardiac effects have been attributed to sensitization of the myocardium to circulating catecholamines.Some of the more volatile organochlorines can be inhaled while in vapor form or swallowed while in liquid form. Inhalation of toxic vapors or aspiration of liquid after ingestion may lead to atelectasis, bronchospasm, hypoxia, and a chemical pneumonitis. In severe cases, this can lead to acute lung injury (ALI), hemorrhage, and necrosis of lung tissue. In liquid form, they are easily absorbed through the skin and GI tract.
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/815051-overview#a0104
Слайд 56
Clinical presentation
CNS excitation and depression are the primary
effects observed from organochlorine toxicity; therefore, the patient may
appear agitated, lethargic, intoxicated, or even unconscious. Organochlorines lower the seizure threshold, which may precipitate seizure activity. Initial euphoria with auditory or visual hallucinations and perceptual disturbances are common in the setting of acute toxicity. Patients may have pulmonary complaints or may be in severe respiratory distress. Cardiac dysrhythmias may complicate the initial clinical presentation.Other symptoms include the following:
Pulmonary - Cough, shortness of breath
Dermatological - Skin rash
Gastrointestinal - Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain
Nervous system - Headache, dizziness, or paresthesias of the face, tongue, and extremities
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/815051-overview#a0104
Слайд 57
Physical findings
Physical examinations findings depends on type of
exposure
Ingestions
Nausea and vomiting
Confusion, tremor, myoclonus, coma, and seizures
Respiratory depression
or failureUnusual odor - Toxaphene may have a turpentine-like odor. Endosulfan may have a sulfur odor
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/815051-overview#a0104
Слайд 58
Skin absorption or inhalation
Ear, nose, and throat irritation
Blurred
vision
Cough
Acute lung injury (ALI)
Dermatitis
Physical findings
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/815051-overview#a0104
Слайд 59 Chronic exposure (meets in persons who constantly contact
with chlorine organic connections: workers of compositions and enterprises
from the production of chemical poisonings)Anorexia
Hepatotoxicity
Renal toxicity
CNS disturbances
Skin irritation
Physical findings
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/815051-overview#a0104
Слайд 60
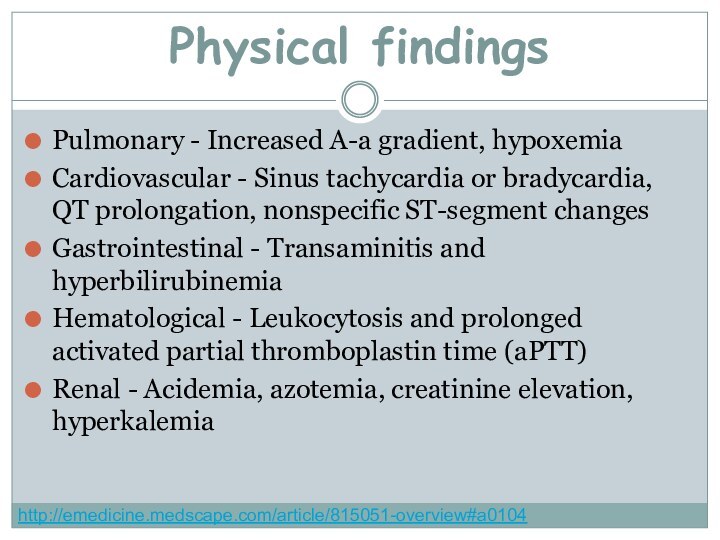
Pulmonary - Increased A-a gradient, hypoxemia
Cardiovascular - Sinus
tachycardia or bradycardia, QT prolongation, nonspecific ST-segment changes
Gastrointestinal -
Transaminitis and hyperbilirubinemiaHematological - Leukocytosis and prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
Renal - Acidemia, azotemia, creatinine elevation, hyperkalemia
Physical findings
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/815051-overview#a0104
Слайд 61
Prehospital Care
Dermal decontamination is a priority. Remove clothes.
Wash
skin with soap and water.
Provide oxygen and supportive care
as necessaryGI decontamination and elimination
Слайд 62
Treatment
GI Decontaminant
Activated charcoal is emergency treatment in poisoning
caused by drugs and chemicals. The network of pores
present in activated charcoal adsorbs 100-1000 mg of drug per gram of charcoal. It does not dissolve in water.For maximum effect, administer within 30 minutes of ingesting poison.
Multiple dose activated charcoal (MDAC) may be administered at 10-20 g q2-4h without a cathartic
Слайд 63
Bile acid sequestrants
These binding agents are used in
the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and have been noted to
bind certain lipid-soluble drugs and enterohepatically recycled drugs.Cholestyramine forms a nonabsorbable complex with bile acids in the intestine, which, in turn, inhibits enterohepatic reuptake of intestinal bile salts.
Treatment
Слайд 64
Benzodiazepines
Mainstay of treatment for hydrocarbon insecticide–induced seizures.
Lorazepam (Ativan)
Rate
of injection should not exceed 2 mg/min. May be
administered IM if unable to obtain IV access.Midazolam (Versed)
Used as alternative in termination of refractory status epilepticus. Because water soluble, takes approximately 3 times longer than diazepam to peak EEG effects. Thus, clinician must wait 2-3 min to fully evaluate sedative effects before initiating procedure or repeating dose.
Diazepam (Valium)
Depresses all levels of CNS (eg, limbic and reticular formation), possibly by increasing activity of GABA.
Treatment
Слайд 65
Anticonvulsants
Class Summary. Additional options include pentobarbital or propofol
for seizure control if status epilepticus does not respond
to benzodiazepines or phenytoin or fosphenytoin.Treatment
Слайд 67
They are high enough bactericidal and fungicides characteristics
and at staining does not have a negative influence
on a corn, seed of vegetable and technical crops of bobs. That’s why they are basic pesticides that are used for staining of seed.Слайд 68 The organic mercury compounds are of great interest
today because they are often found in the food
chain and have been used to inhibit bacterial growth in medications. Organic mercury is also found in fungicides and industrial run-off.
Слайд 71
Mechanism of mercury toxicity
Molecular mechanisms of mercury genotoxicity.
Mercury compounds enter the cell through plasmatic membrane or
transport proteins (grey cylinder). (1) Inside the cell, they may produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) which react directly with DNA or, indirectly, induce conformational changes in proteins responsible for the formation and maintenance of DNA (DNA repair enzymes, proteins of microtubules). Mercury compounds may be also able to bind directly to: (2) DNA molecules, forming mercury species-DNA adducts, (3) “zinc fingers” core of DNA repair enzymes (white large arrow), affecting their activity and (4) microtubules, avoiding mitotic spindle formation and chromosome segregation.
Слайд 73
Clinical presentation
Ataxia
tremors
unsteady gait
illegible handwriting, slurred speech
erythema
of the palms and soles
edema of the hands and
feet,desquamating rash, hair loss, pruritus
tachycardia, hypertension, photophobia, irritability, anorexia, insomnia,
poor muscle tone, and constipation or diarrhea.
Слайд 74 A diagnosis we put when we have special
clinical picture and information of anamnesis, which specify on
a contact with mercury organic connections. The important diagnostic sign of intoxication is a presence of mercury in blood, urine, and at heavy intoxications – in a cerebrospinal liquid.
Слайд 75
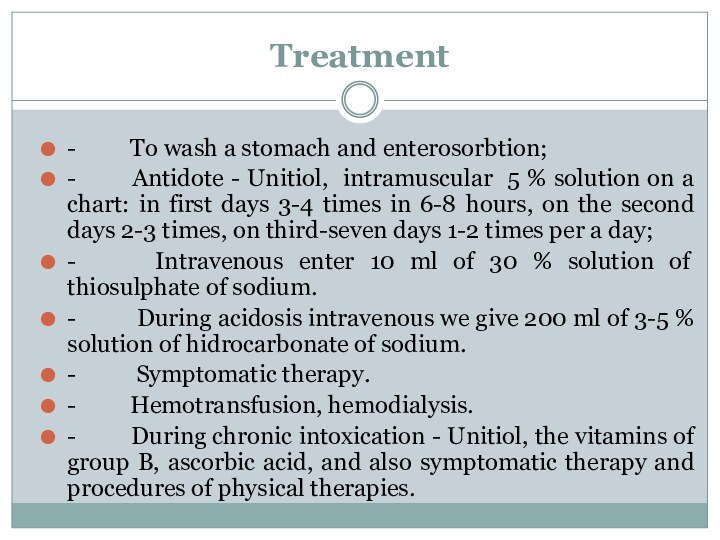
Treatment
- To wash a stomach and enterosorbtion;
- Antidote
- Unitiol, intramuscular 5 % solution on a chart:
in first days 3-4 times in 6-8 hours, on the second days 2-3 times, on third-seven days 1-2 times per a day;- Intravenous enter 10 ml of 30 % solution of thiosulphate of sodium.
- During acidosis intravenous we give 200 ml of 3-5 % solution of hidrocarbonate of sodium.
- Symptomatic therapy.
- Hemotransfusion, hemodialysis.
- During chronic intoxication - Unitiol, the vitamins of group B, ascorbic acid, and also symptomatic therapy and procedures of physical therapies.