- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Obstetric procedures
Содержание
- 2. Content:Procedures for fetal prenatal diagnosis:Ultrasound.Amniocentesis.Chorion villous sampling.Fetal blood sampling.External cephalic version.Operative vaginal delivery:Forceps.Ventouse.Cesarean section.
- 3. Ultrasound:Types:Tran abdominal.TransvaginaGuidelines for first trimester:Location of gestational
- 4. Guide for second and third trimesters:Fetal life
- 5. Amniocentesis:Def: it is a technique for withdrawing
- 6. Gestation age: from 11 to
- 7. Chorionic villus sampling:Dif: small samples of the
- 8. Indications (CVS):Maternal age : 35 yo at
- 9. Fetal blood sampling (cordocentesis)Indication:Assessment and treatment of
- 10. Complications: (cordocentesis )
- 11. Operative vaginal delivery:Forceps: Parts: Blade.( cephalic
- 12. Cont. Forceps:Classification:Outlet forceps.Low forceps.Midpelvic forceps.High forceps.Indications for
- 13. Pre-requisites for forceps application:Head engaged.Vertex presentation.Known position.Fully
- 14. Complication of forceps:Lacerations and episiotomy.Urinary dysfunction .Rectal
- 15. Vacuum Extraction (Ventouse):Types:Metal cup vacuum.Soft cup vacuum
- 16. Cont. complication of ventouse:7. Macrosomia.8. Recent scalp
- 17. Cesarean Delivery (C/S):Indications:Labor dystosia.Fetal distress.Breech presentation.Multiple gestations.
- 18. Technique of c/s:Skin incision:Vertical incision.Transverse incision (
- 19. Cnt. Indecation of classical c/s:3.Some cases Placenta
- 20. Complications of cesarean section:Increase maternal mortality &morbidity :Increase maternal death.Bleeding. Infections.DVT.Adhesions.Pain.
- 21. Vaginal birth after prior cesarean:Benefit:Short stay at
- 22. Cont. VBAC:LSCS.Institute ER C/S with anest &physician immd. Available.NO contraindications for vag. Delivery.No other uterine scare.
- 23. External cephalic version :
- 24. Cont. ECV :AGOC recommendation ECV shoud be
- 25. Cont. Contraindications ECV :3. No reassuring CTG.4.
- 26. Скачать презентацию
- 27. Похожие презентации
Content:Procedures for fetal prenatal diagnosis:Ultrasound.Amniocentesis.Chorion villous sampling.Fetal blood sampling.External cephalic version.Operative vaginal delivery:Forceps.Ventouse.Cesarean section.






















Слайд 2
Content:
Procedures for fetal prenatal diagnosis:
Ultrasound.
Amniocentesis.
Chorion villous sampling.
Fetal blood
sampling.
Слайд 3
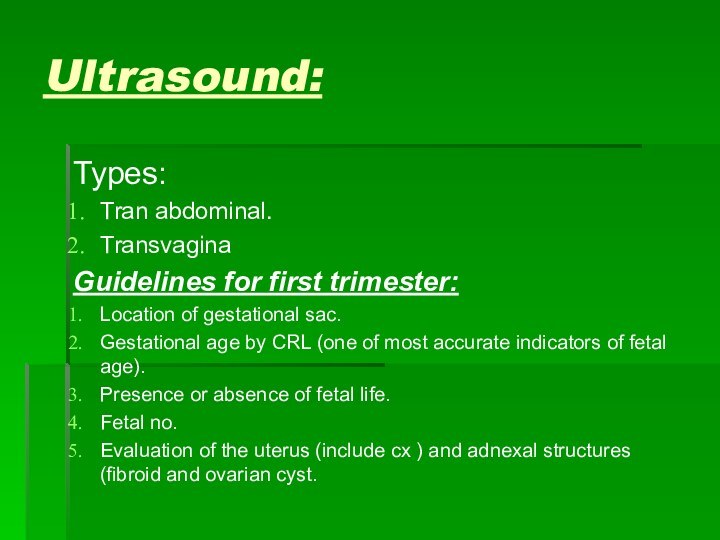
Ultrasound:
Types:
Tran abdominal.
Transvagina
Guidelines for first trimester:
Location of gestational sac.
Gestational
age by CRL (one of most accurate indicators of
fetal age).Presence or absence of fetal life.
Fetal no.
Evaluation of the uterus (include cx ) and adnexal structures (fibroid and ovarian cyst.
Слайд 4
Guide for second and third trimesters:
Fetal life ,
number , and presentation.
An estimate of the amount of
amniotic fluid (< > N) .Placenta location.
Assessment of gestation age.
Evaluation of the uterus and adnexal path.
Fetal anatomy.
Слайд 5
Amniocentesis:
Def: it is a technique for withdrawing amniotic
fluid from the uterine cavity using a needle via
atransabdominal approach.Indications
Diagnostic indications ex. Prenatal genetic studies.
Ass. Fetal lung maturity.
Fetal infection.
Degree of hemolytic anemia.
Blood or platete type.
NTD
coaglopath.
Therapeutic procedure.( remove excess fluid ).
Hemoglobinopath.
Слайд 6
Gestation age:
from 11 to term.
Complications:
Rupture
of membranes .
Fetal injury (direct ,indirect ).
Infection . (
hepatitis ,toxo , CMV, HIV,).Fetal loss 0.5 -1 %. (significantly affected by maternal age ).
Amnionitis 1/1000.
Cont. Amniocentesis:
Слайд 7
Chorionic villus sampling:
Dif: small samples of the placenta
are taken sent for genetic analysis , provides preliminary
cytogenetic results within 48h and final culture result within 7 days.Time: 10 -12 weeks .
Complications : similar to amniocentesis .
Approach:
1.Transcervical.
2.transabdominal. ( depend on placenta site ) .
Contraindications:
1.Vag. Bleeding.
2.Active genital tract infection.
3.Extreme ante – or retroflexed uterus.
Слайд 8
Indications (CVS):
Maternal age : 35 yo at delivery
.
Previous child with non- disjunctional chromosome abn.
Parent is carrier
of balanced translocation or other chromosome disorder.Both parents are carriers of autosomal recessive disease.
Women who are carriers of a sex – linked disease .
Positive first – trimester screen for trisomy 21 or 18 .
Слайд 9
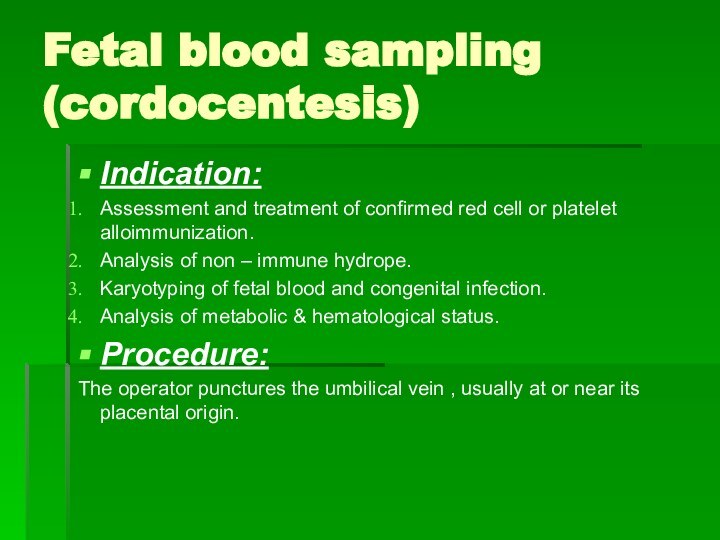
Fetal blood sampling (cordocentesis)
Indication:
Assessment and treatment of confirmed
red cell or platelet alloimmunization.
Analysis of non – immune
hydrope.Karyotyping of fetal blood and congenital infection.
Analysis of metabolic & hematological status.
Procedure:
The operator punctures the umbilical vein , usually at or near its placental origin.
Слайд 10 Complications: (cordocentesis )
As amniocentesis.
Cord hematoma.
Cord vessel bleeding.
Fetal – maternal hemorrhage.
Fetal
bradycardia.Fetal death.
Слайд 11
Operative vaginal delivery:
Forceps:
Parts:
Blade.( cephalic ,pelvic
curve )
Shank.
Lock. (sliding lock , English lock )
Handle.
Function of
forceps:Traction.
Rotation.
Both.
Слайд 12
Cont. Forceps:
Classification:
Outlet forceps.
Low forceps.
Midpelvic forceps.
High forceps.
Indications for forceps:
Heart
disease , pulmonary inj. Or compromise.
Intrapartum infection.
Exhaustion.
Prolonged second stage
of labour.Certain neurological condition.
Non- reassuring CTG.
Prolapsed cord , premature separation of placenta.
Слайд 13
Pre-requisites for forceps application:
Head engaged.
Vertex presentation.
Known position.
Fully dilated
cx.
Mb ruptured.
Role out CPD.
Local or regional anesthesia.
Bladder should be
empty.Expert operator.
Слайд 14
Complication of forceps:
Lacerations and episiotomy.
Urinary dysfunction .
Rectal &
anal dysfunction.
Febrile morbidity.
Low Apgar score.
Cephalohematoma.
Caput.
Facial nerve injury.
Fetal truma (
Erb palsy ,fratured clavicle ).Retinal hemorrhage.
Слайд 15
Vacuum Extraction (Ventouse):
Types:
Metal cup vacuum.
Soft cup vacuum (silastic
cup ).
Indications &prerequisites:
as forceps.
Contraindications:
Inexperience.
Inability to ass. Fetal
position.High station.
Suspicion of CPD.
Non vertex presentations.
Fetal coagulopathy.
Слайд 16
Cont. complication of ventouse:
7. Macrosomia.
8. Recent scalp blood
sampling.
Vacuum extraction is reserved for fetus 34 weeks or
older.Complications:
Scalp lacerations & bruising.
Subgaleal hematoma.
Cephalohematomas.
Intracranial hemorrhage.
Neonatal jaundice.
Subconjuctival hemorrhage.
Clavicular fracture.
Слайд 17
Cesarean Delivery (C/S):
Indications:
Labor dystosia.
Fetal distress.
Breech presentation.
Multiple gestations. Prior
c/s.
Utrine segments:
Upper uterine segment .(active seg. ) contacts ,retracts
,expels fetus ,mainly muscular.Lower uterine segment .( passeve seg. ) dilate ,expande ,thinned –out . Fibromuscular .
So lower & upper seg. Differ anatomically & physiologically.
Слайд 18
Technique of c/s:
Skin incision:
Vertical incision.
Transverse incision ( pfannenstiel
incision ).
Uterine incisions:
Lower uterine segment transversely incision.
Lower uterine segment
vertical incision (may be used).Upper uterine segment vertical incision ( classical incision) . Rare.
Indications for classical c/s :
Can not expose lower seg.
Transverse lie ,large fetus ,rup. Mb.
Слайд 19
Cnt. Indecation of classical c/s:
3.Some cases Placenta previa
(ant.) .
4. Some cases small ,breech ,premature .
5. Some
cases massive obesity when upper seg. Accessible.Advantage of LSCS:
Easier to repair .
Less likely to rupture during subsequent pregnancy .
Dose not promote adherence of bowel or momentum at the incision line .
Less bleeding .
Слайд 20
Complications of cesarean section:
Increase maternal mortality &morbidity :
Increase
maternal death.
Bleeding.
Infections.
DVT.
Adhesions.
Pain.
Слайд 21
Vaginal birth after prior cesarean:
Benefit:
Short stay at hospital.
Less
blood loss .
Fewer transfusion.
Fewer infections.
Fewer DVT.
Risk of VBAC:
Uterine rupture.
Hysterectomy.
Increase
morbidity .(b.tran.).Fetal death or damage.
Слайд 22
Cont. VBAC:
LSCS.
Institute ER C/S with anest &physician immd.
Available.
NO contraindications for vag. Delivery.
No other uterine scare.
Слайд 23 External cephalic version : (
ECV )
Definition: It is a procedure by which an
obstetrician turns the baby from the breech to the cephalic position by manipulating the baby through the maternal abdomen .The procedure increases the chance of cephalic presentation at onset of labor and decreases the rate of cesarean delivery.
Слайд 24
Cont. ECV :
AGOC recommendation ECV shoud be available
and offered to women with breech presentation at term
.Risk : Discomfort , ERC/S , Transient bradycardia is less common ,placental abruption , premature labor .
Cost : cost-effective .
Contraindications :
Indications for c/s .
Rupture membranes .
Слайд 25
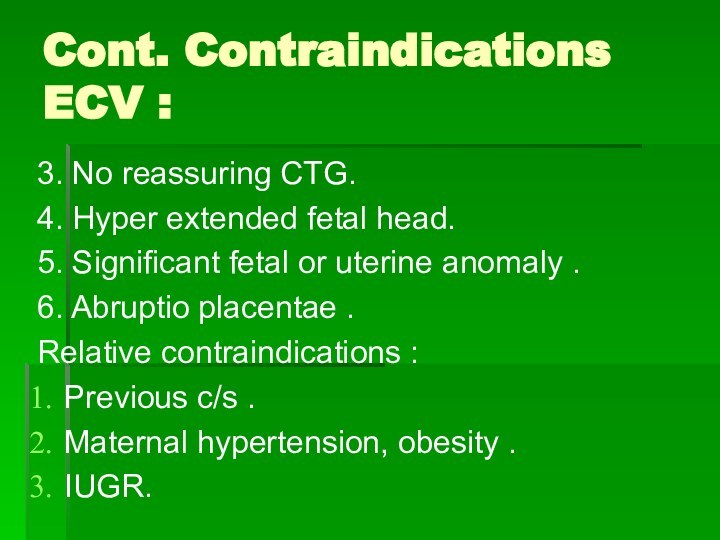
Cont. Contraindications ECV :
3. No reassuring CTG.
4. Hyper
extended fetal head.
5. Significant fetal or uterine anomaly
.6. Abruptio placentae .
Relative contraindications :
Previous c/s .
Maternal hypertension, obesity .
IUGR.