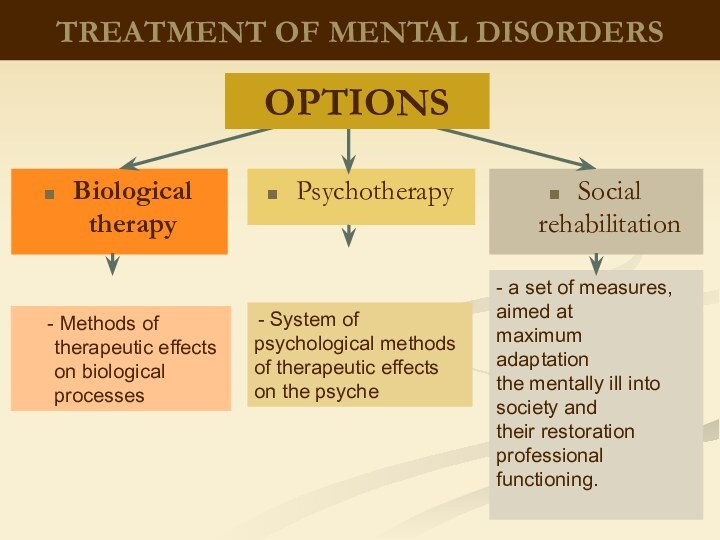
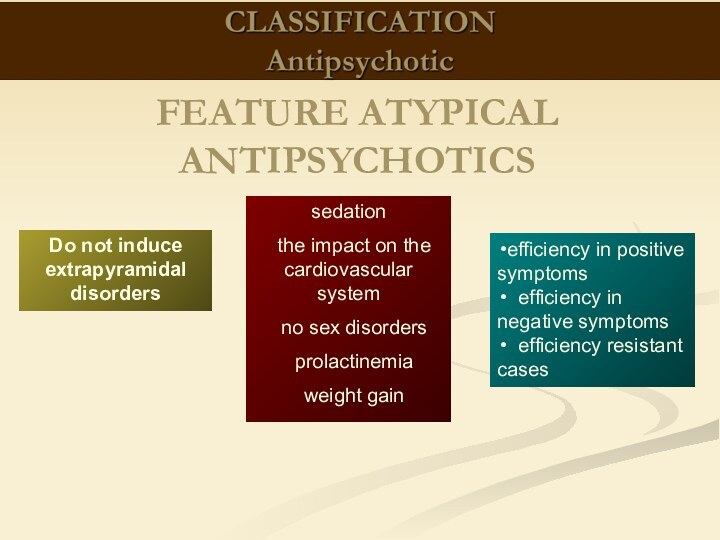
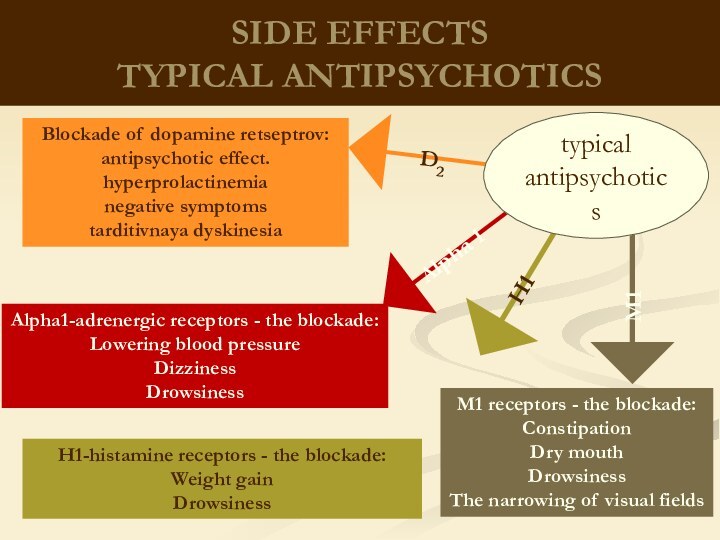
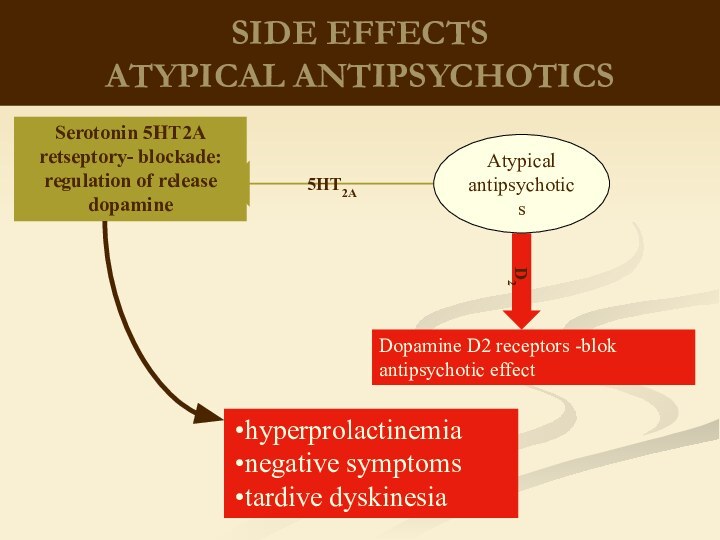
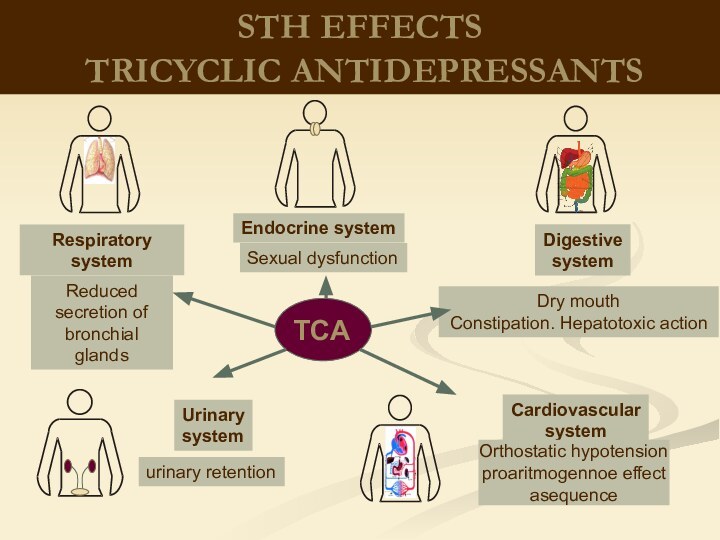
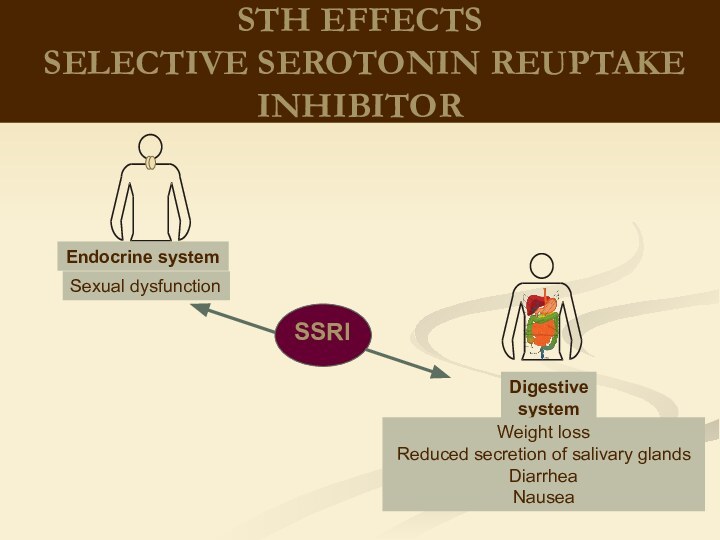
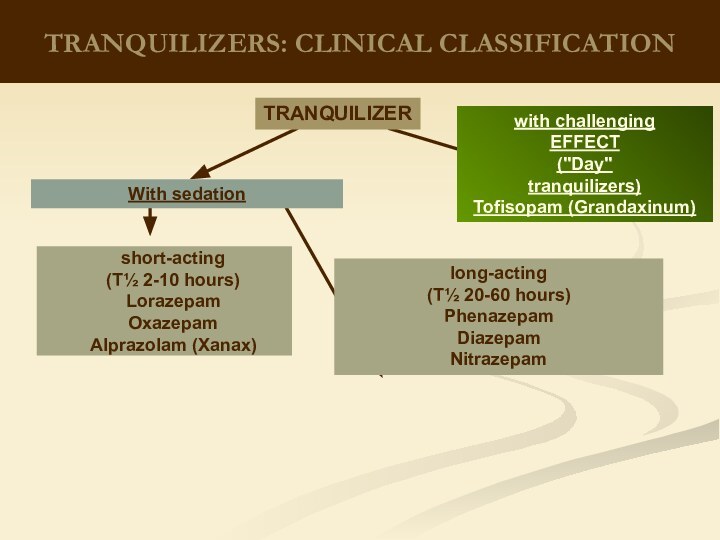
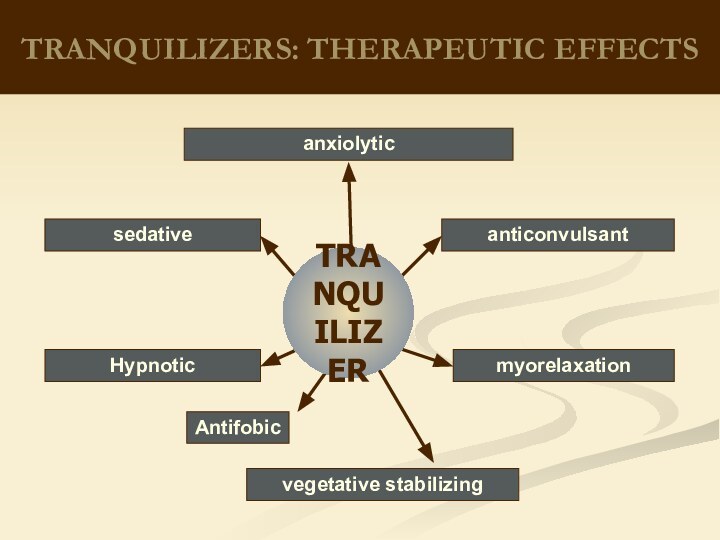
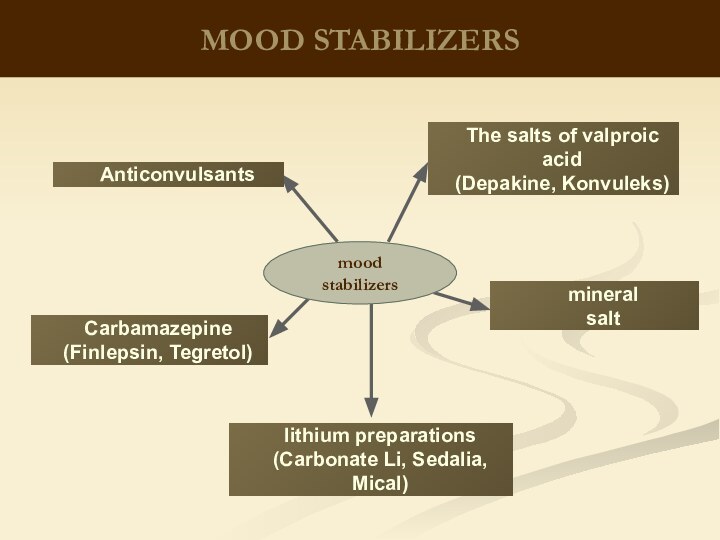
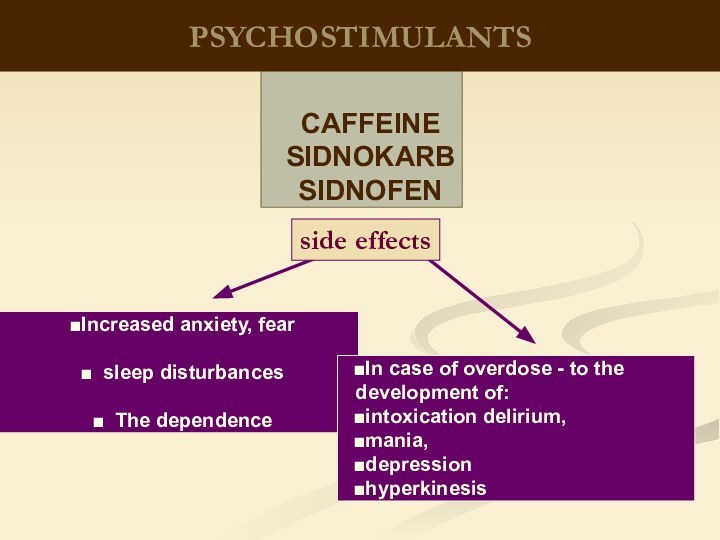
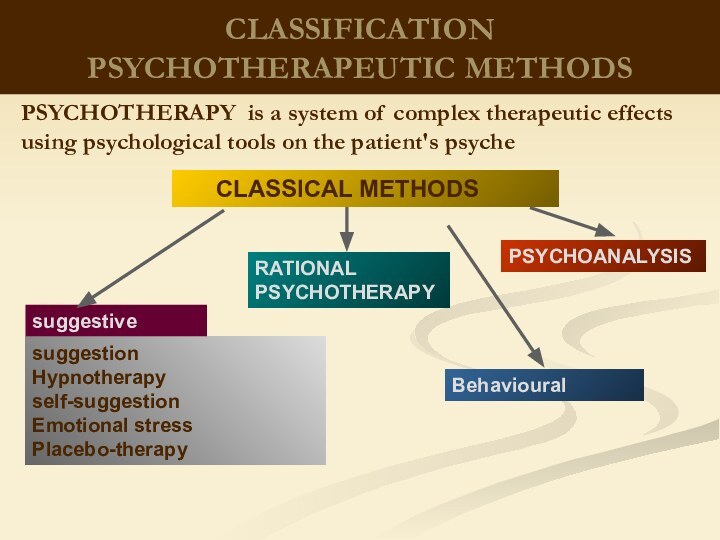
therapeutic effects on biological processes
System of psychological methods
of therapeutic effects on the psyche- a set of measures,
aimed at
maximum
adaptation
the mentally ill into society and
their restoration
professional
functioning.
OPTIONS