Слайд 2
Surgery
Radiation therapy
Drug therapy-anti-cancer drugs:
- cytotoxic drugs
- hormone therapy
- cytokines,
- targeted therapy: monoclonal antibodies & “small molecules”
Drug that protect against side effects of chemotherapy
Anti-cancer treatment modalities
Слайд 3
Palliative
Increased survival
Symptom relief/Improved quality of life
Curative
Adjuvant/Neoadjuvant (induction chemotherapy)
Disease
free survival (DFS) as end point in adjuvant chemotherapy
Goals
of cancer chemotherapy
Слайд 4
Adjuvant:
-Breast cancer
-Colon cancer (Dukes` C2; i.e.
positive regional
lymph nodes)
Neoadjuvant:
-Osteogenic sarcoma
- Gastric Adenocarcinoma
Adjuvant/neoadjuvant chemotherapy with proven efficacy
Слайд 5
Groups of cytotoxic drugs and
mechanism of action
Слайд 6
Alkylating Agents & Platinum Analogs
Antimetabolites
Topoisomerase (I,II) interactive agents
Antimicrotubule
Agents
Major Groups of Cytotoxic Drugs
Слайд 7
The parent drug (prodrug) is activated to form
an “active drug”, which has an alkylating group.
The “active
drug”, which is positively charged, binds covalentely to various macromolecules at nucleophylic sites.
The biological effect results mainly from alkylation of DNA bases (particularly the electron-rich N-7 position of guanine) and formation of DNA adducts.
Alkylating agents
Слайд 8
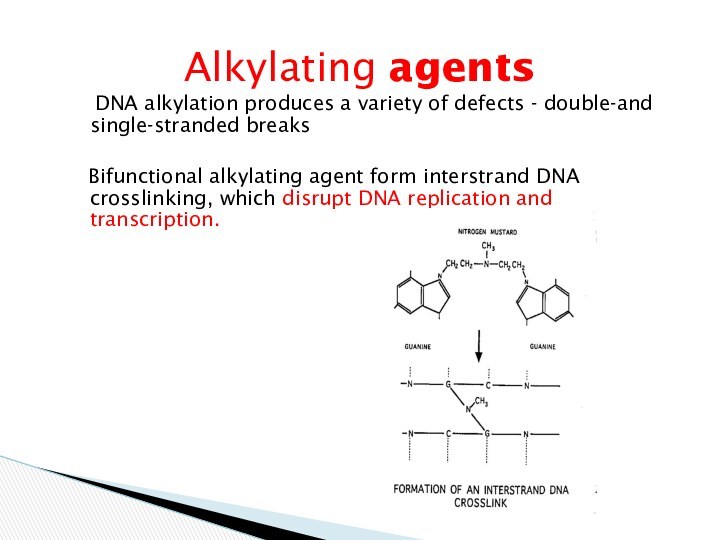
DNA alkylation produces a variety of
defects - double-and single-stranded breaks
Bifunctional alkylating agent
form interstrand DNA crosslinking, which disrupt DNA replication and transcription.
Alkylating agents
Слайд 9
Cyclophopsphamide (cytoxan)
Ifosfamide
The prodrug is activated by CYT-P-450
dependent
metabolism in the liver.
Chlorambucil (leukeran)
Commonly used alkylating agents
Слайд 10
Nausea and vomiting are dose-related:
> 90% for
>1500 mg/m2,
60-90% for 750-1500 mg/m2,
30-60% for
750 mg/m2 or oral;
Myelosuppression
Hemorrhagic cystitis (up to 40%) with high-dose and/or long term therapy - severe, potentially fatal
Alopecia (40-60%);
Side Effects of Cyclophosphamide
Слайд 11
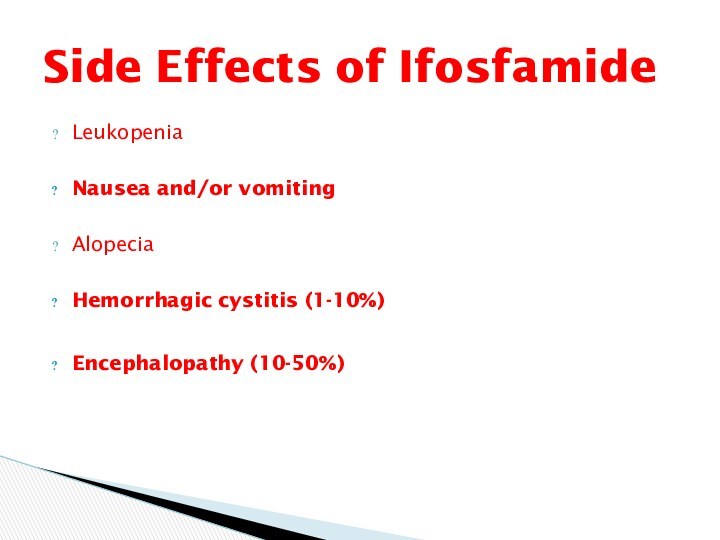
Leukopenia
Nausea and/or vomiting
Alopecia
Hemorrhagic cystitis (1-10%)
Encephalopathy (10-50%)
Side Effects
of Ifosfamide
Слайд 12
Cisplatin -
Curative in testicular
cancer and very active in ginecologic, GI, GU,
Head and neck, lung cancers
Carboplatin
Ovarian, lung cancer
the difference between the cisplatin and carboplatin molecules is in the leaving groups
Oxaliplatin
Colorectal cancer
Platinum analogs
Слайд 13
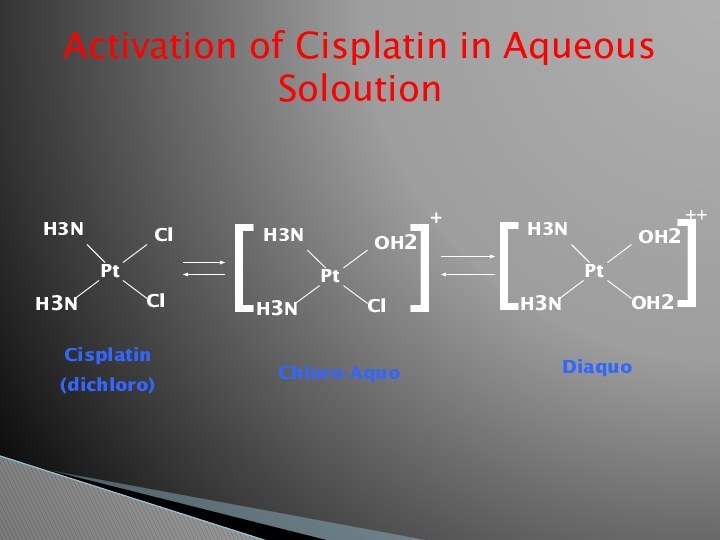
Activation of Cisplatin in Aqueous Soloution
Слайд 15
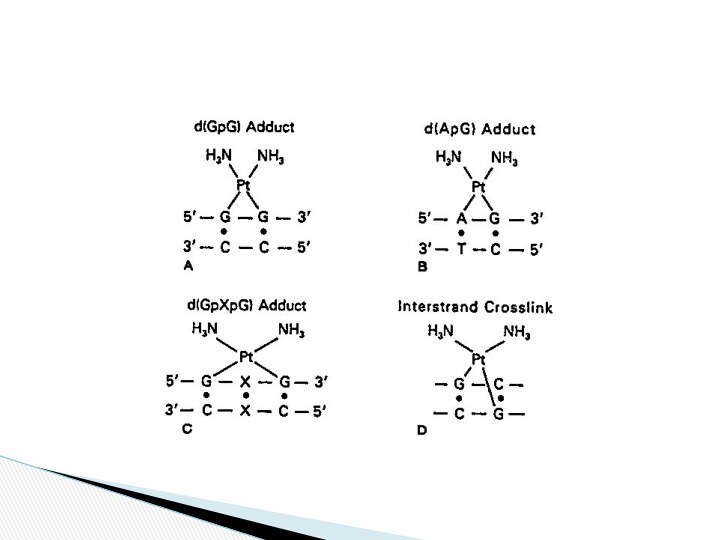
This platinum-DNA adduct is repaired by the nucleotide
excision repair (NER)
pathway
Слайд 16
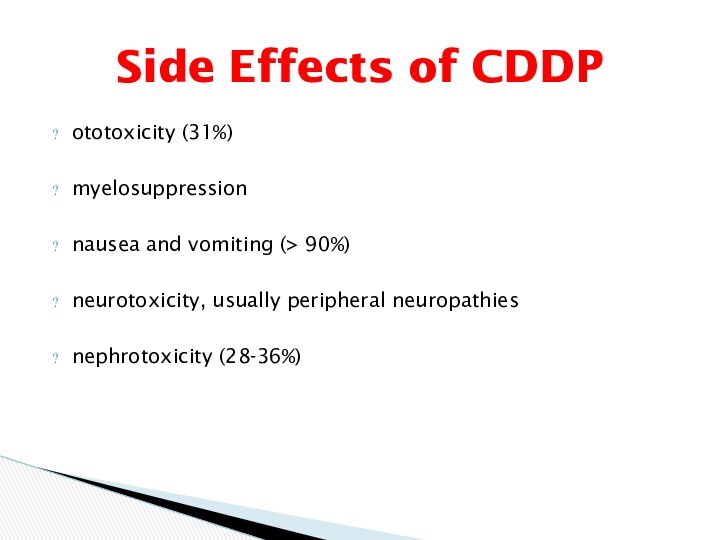
ototoxicity (31%)
myelosuppression
nausea and vomiting (> 90%)
neurotoxicity, usually peripheral neuropathies
nephrotoxicity (28-36%)
Side Effects of
CDDP
Слайд 17
Carboplatin
Myelosuppression
Nausea and vomiting
Oxaliplatin
neuropathy, sensory
Myelosuppression
Side Effects
Слайд 18
Antimetabolites
Antimetabolites are antineoplastic agents that are structurally and
chemically similar to naturally occurring compounds, required for synthesis
of purines, pyrimidines, and nucleic acids.
These drugs interfere with DNA synthesis by competitive inhibition of a key enzyme in the purine or pyrimidine synthesis pathway or by incorporation into the DNA or RNA molecules.
Слайд 19
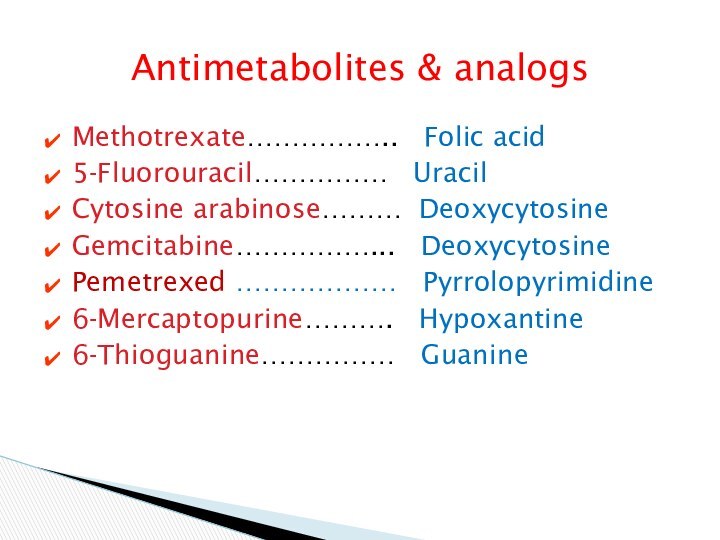
Antimetabolites & analogs
Methotrexate…………….. Folic acid
5-Fluorouracil…………… Uracil
Cytosine
arabinose……… Deoxycytosine
Gemcitabine……………... Deoxycytosine
Pemetrexed ……………… Pyrrolopyrimidine
6-Mercaptopurine………. Hypoxantine
6-Thioguanine……………
Guanine
Слайд 20
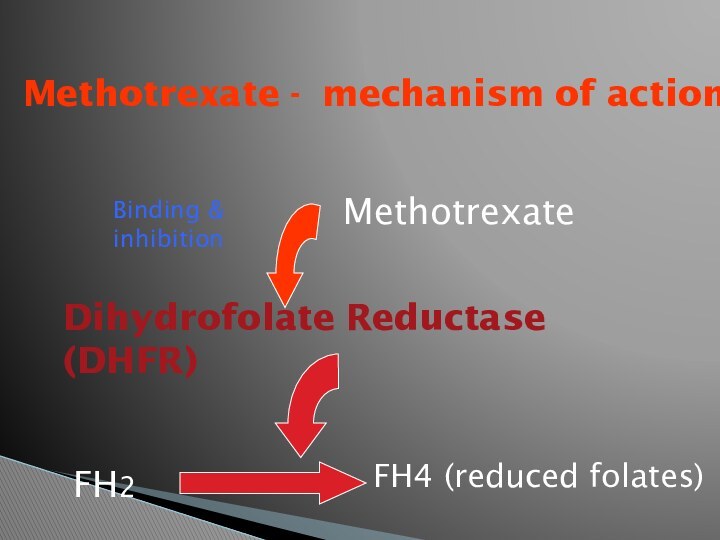
Methotrexate - mechanism of action
Methotrexate
Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR)
Binding &
inhibition
FH2
FH4 (reduced folates)
Слайд 21
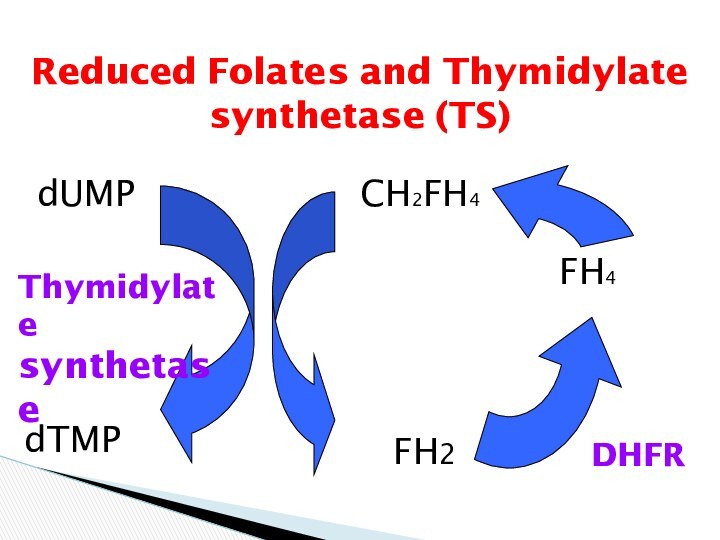
Reduced Folates and Thymidylate synthetase (TS)
Слайд 22
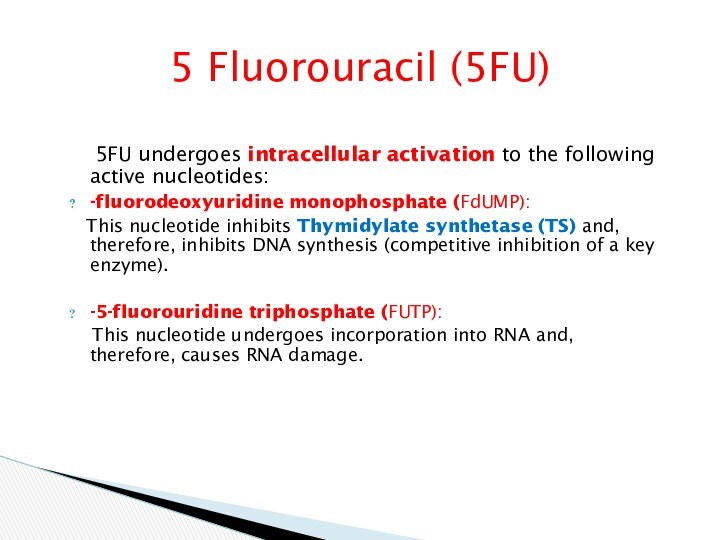
5 Fluorouracil (5FU)
5FU undergoes intracellular activation
to the following active nucleotides:
-fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate (FdUMP):
This nucleotide inhibits Thymidylate synthetase (TS) and, therefore, inhibits DNA synthesis (competitive inhibition of a key enzyme).
-5-fluorouridine triphosphate (FUTP):
This nucleotide undergoes incorporation into RNA and, therefore, causes RNA damage.
Слайд 23
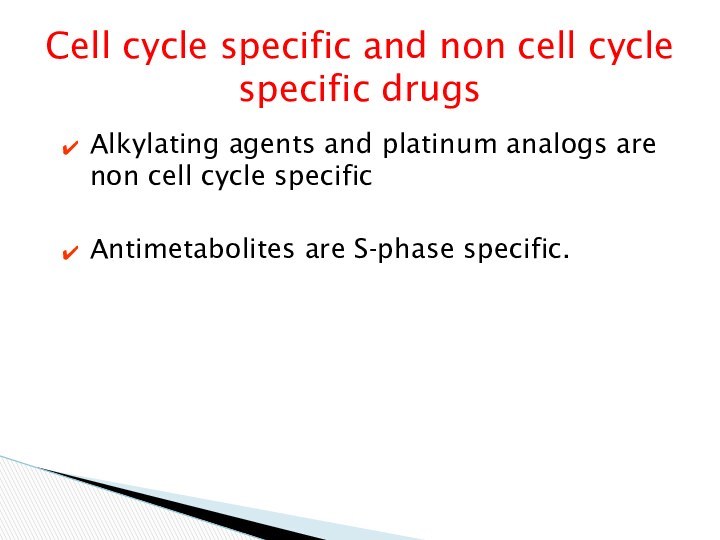
Cell cycle specific and non cell cycle specific
drugs
Alkylating agents and platinum analogs are non cell cycle
specific
Antimetabolites are S-phase specific.
Слайд 24
Tubulin Binding Agents
Vinca Alkaloids:
Vincristine (Oncovin)
Vinblastine
Vinorelbine (Navelbine)
Taxanes:
Paclitaxel
(Taxol)
Docetaxel (Taxotere)
Слайд 26
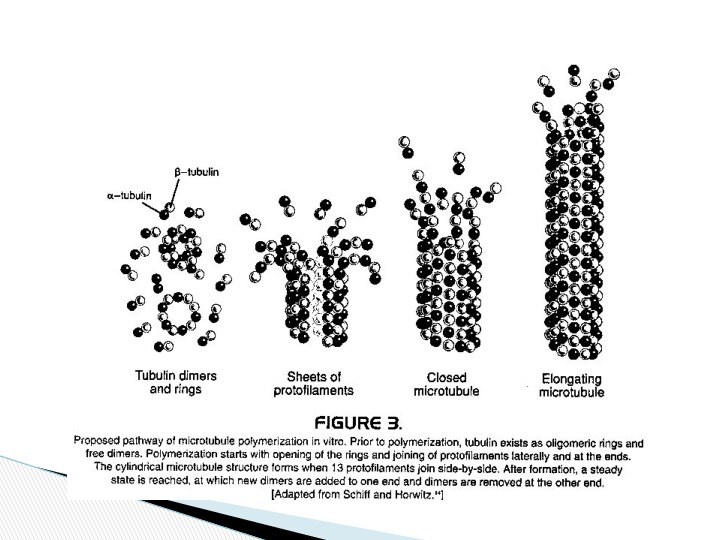
Vinca Alkaloids
Mechanism of action:
binding to specific
site on tubulin with prevention of polymerization, inhibition of
microtubule assembly and mitotic spindle formation (leading to metaphase arrest)
Слайд 27
Mechanism of
action of taxanes
Bind to polymerized tubulin
(beta subunit of microtubules)
Binding is reversible and stabilize the
microtubules against depolymerization (induce tubular polymerization), thereby disrupting normal microtubule dynamics (halts mitosis) and lead to arrest at G2/M phase.
Слайд 29
Hormone therapy in breast cancer: antiestrogens and aromatase
inhibitors
2/3 of all post-menopausal breast cancers are hormone-sensitive, expressing
estrogen- and/or progesterone-receptors (ER/PgR)
Estrogens can stimulate cancer growth through binding to specific nuclear estrogen receptors (ER)
Cancer regression can be achieved by
Blocking estrogen receptors with an antiestrogen such as tamoxifen,faslodex
Effectively suppressing estrogen synthesis with aromatase inhibitors such as letrozole (femara) or anastrazole (arimidex) –through blocking conversion of androstenedione to estrone .
Non steroidal=Type II=reversible:
Anastrazole (Arimidex)
Letrozole (Femara)
Steroidal=Type I=irreversible:
Exemestane (Aromasin)
Слайд 31
Rituximab (Mabthera)
Rituximab is a genetically engineered
chimeric murine/human monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen.
Active as single agent in CD-20 positive NHL and synergistic with chemotherapy in NHL.
Слайд 33
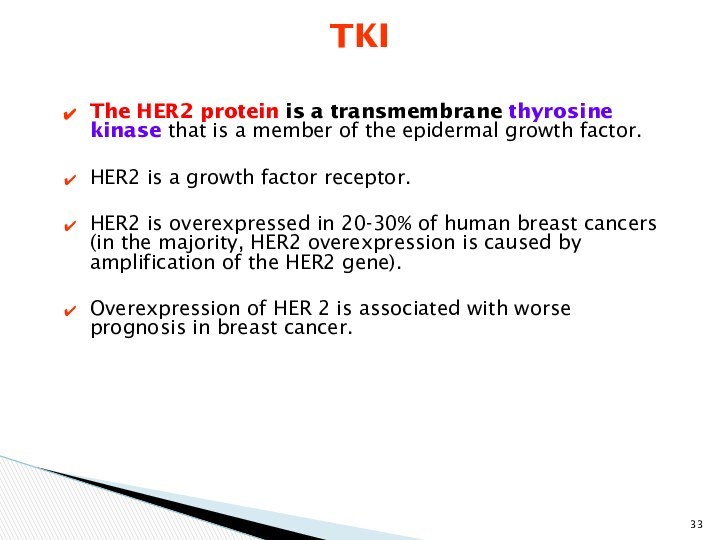
TKI
The HER2 protein is a transmembrane thyrosine kinase
that is a member of the epidermal growth factor.
HER2
is a growth factor receptor.
HER2 is overexpressed in 20-30% of human breast cancers (in the majority, HER2 overexpression is caused by amplification of the HER2 gene).
Overexpression of HER 2 is associated with worse prognosis in breast cancer.
Слайд 34
Trastuzumab (Herceptin)
A recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody that binds
with the extracellular domain of the HER2 cell-surface receptor,
thereby inhibiting the growth of breast tumor cells that overexpress HER2.
It is active in breast cancer only in HER 2 positive pts, especially in combination with chemotherapy, both in metastatic disease and as adjuvant therapy in HER 2 positive tumors.
Слайд 35
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) as a target
Слайд 36
EGFR
EGFR is a 170-kd transmembrane receptor. It has
a tyrosine kinase activity.
It has an extracellular ligand-binding domain,
a transmembrane segment and intracellular component.
When EGF (i.e. the ligand) binds to the extracellular domain, receptors dimers are formed with activation of the extracellular tyrosine kinase domain.
This results in autophosphorylation of downsream molecules with activation of multiple cellular functions including prpliferation and survival.
EGFR is often overexpressed (and is often mutated) in human tumors, thus there is a good rationale for trying to inhibit the EGFR.
Слайд 37
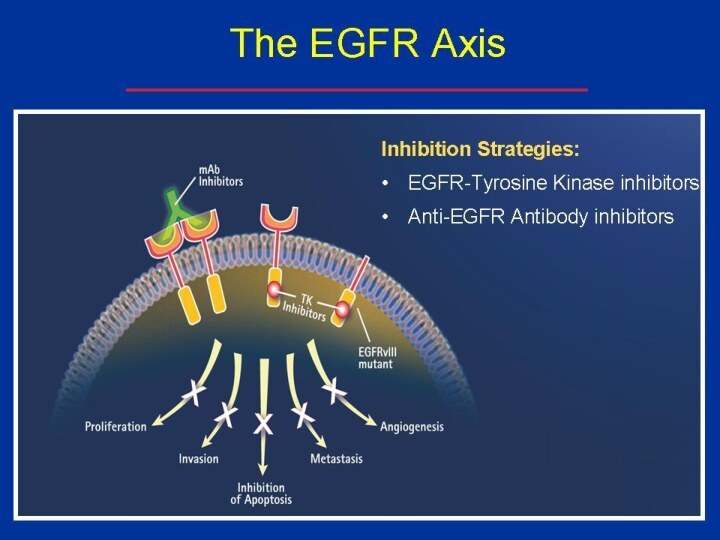
EGFR inhibitors
Monoclonal antibodies: bind to the extracellular domain
of the receptor. Example: Cetuximab (Erbitux),Panitumumab (vectibix).
Small molecules: bind
to the intracellular domain of the receptor.
example: Erlotinib (Tarceva).
Слайд 40
Avastin (Bevacizumab)
VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) , a
diffusible glycoprotein produced by normal and neoplastic cells ,has
been shown to have central role in the control of angiogenesis and to be essential for the development of tumor vasculature. VEGF (=ligand) binds to VEGF receptor.
Bevacizumab (Avastin) is a humanized anti- (VEGF) monoclonal antibody. It prevents VEGF to bond to its receptor, and therefore, has an antiangiogenic effect.
Слайд 41
Sunitinib (Sutent) –bind to intracellular domain VEGFR
Слайд 42
К наиболее распространенным побочным действиям циклофосфамида относятся все,
кроме:
1. миелосупрессия
2. геморрагический цистит
3. кардиальная токсичность
4. энцефалопатия
Вопросы:
Слайд 43
Химиотерапевтическое лечение в онкологии применяется как:
1.паллиация (симптоматическое лечение)
2.
куративное лечение (излечение)
3. предоперационное лечение
4. все верно
Слайд 44
Основной препарат, используемый в лечении рака яичек (Testicular
Cancer):
1. Паклитаксел (Таксол)
2. Метотрексат
3. Цисплатин
4. Флюроурацил (5FU)
Слайд 45
К ингибиторам ароматазы относятся все перечисленные препараты, кроме:
1.Тамоксифен
2.Летрозол
3.Фазлодекс
4.1,3
5.Экзаместен