a comparative look at
a firm’s capabilities.
• What are
the firm’s strengths?• What are the firm’s weaknesses?
• How do these strengths and weaknesses compare
to competitors?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть

























• What are the firm’s weaknesses?
• How do these strengths and weaknesses compare
to competitors?
Internal analysis helps a firm:
• assumes that a firm’s resources and capabilities
are the primary drivers of competitive advantage
and economic performance
• used to help firms achieve competitive advantage
and superior economic performance
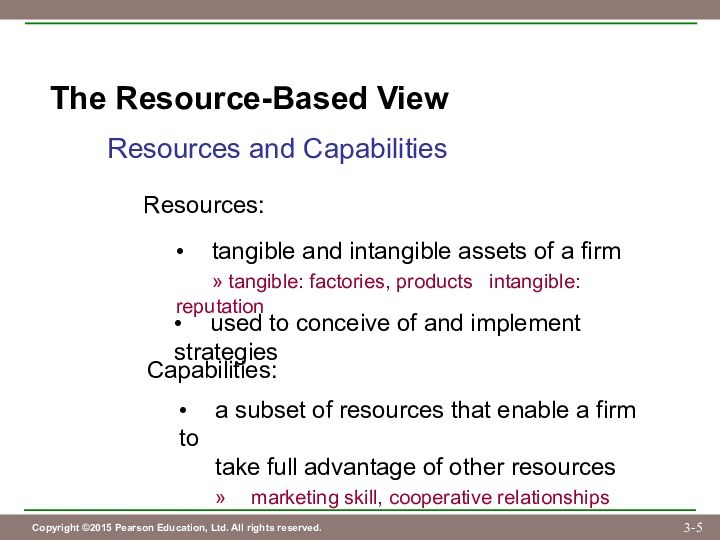
Capabilities:
• a subset of resources that enable a firm to
take full advantage of other resources
» marketing skill, cooperative relationships
• Organizational (reporting structures, relationships)
» Some resources may not spread from firm to
firm easily.
• if other firms can’t imitate these resources
without incurring high costs, then…
• the firm possessing the valuable resources
will likely gain a sustained competitive advantage
Resource Heterogeneity
• Managers of a firm could take resources that seem
homogeneous and “bundle” them to create
heterogeneous combinations.
• Competitive advantage typically stems from several
resources and capabilities “bundled” together.
then the firm can expect to enjoy a sustained
competitive advantage.
Applying the Tool
• Each question is considered in a comparative
sense (competitive environment).
• The practical: Does the resource result in an
increase in revenues, a decrease in costs, or
some combination of the two? (Levi’s reputation
allows it to charge a premium for its Docker’s pants)
• If a resource is not rare, then perfect competition
dynamics are likely to be observed (i.e., no
competitive advantage, no above normal profits).
• Thus, there may be other firms that possess the
resource, but still few enough that there is scarcity
(several pharmaceuticals sell cholesterol-lowering
drugs, but the drugs are still scarce—look at prices).
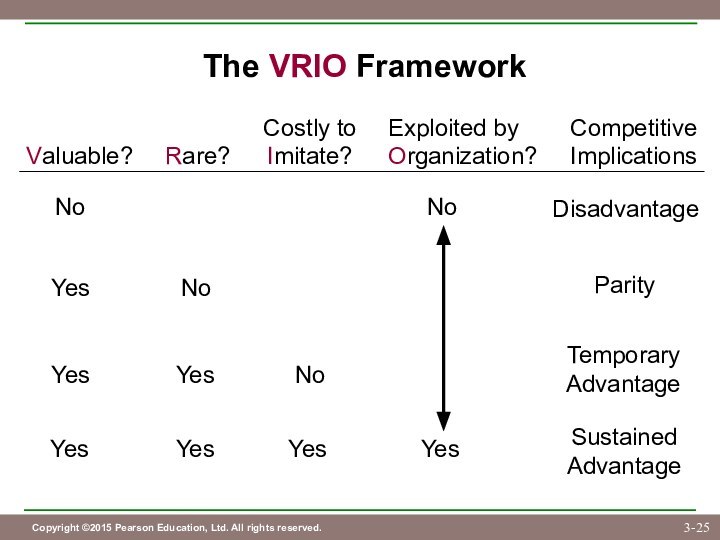
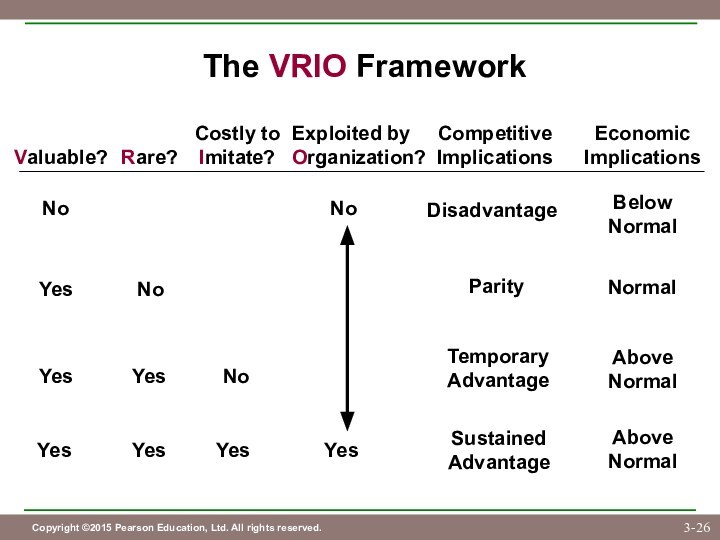
Competitive Parity
Valuable and Rare
Competitive Advantage
(at least temporarily)
» Intangible resources are usually more
costly to imitate than tangible resources.
(Harley-Davidson’s styles may be easily
imitated, but its reputation cannot.)
» A sustained competitive advantage will last
only until a duplicate or substitute emerges.
If a firm has a competitive advantage, others
will attempt to imitate it. (Razor scooters
were a big hit and others quickly imitated them.)
• Bundles of resources fog these causal
links.
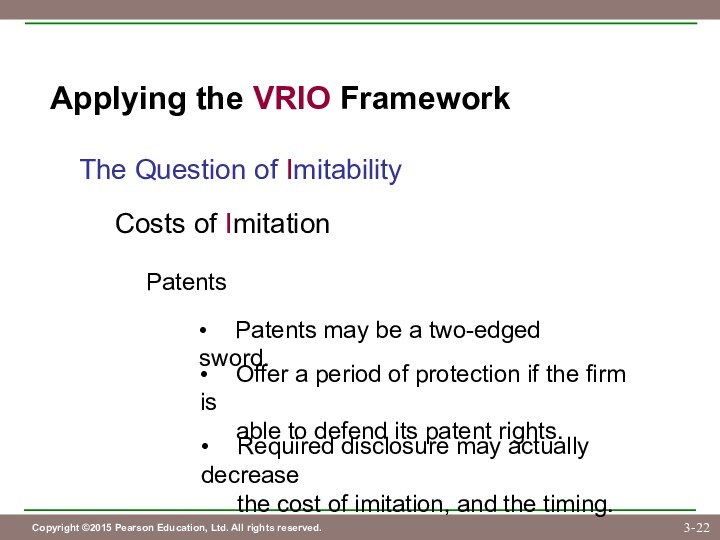
• Required disclosure may actually decrease
the cost of imitation, and the timing.
Temporary
Competitive Advantage
Valuable, Rare, and
Costly to Imitate
Sustained
Competitive Advantage
(if Organized appropriately)
• Examples: formal and informal reporting structures,
management controls, compensation policies,
relationships, and so on
• These structure and control mechanisms complement
other firm resources—taken together, they can help a
firm achieve sustained competitive advantage.
(3M Company)
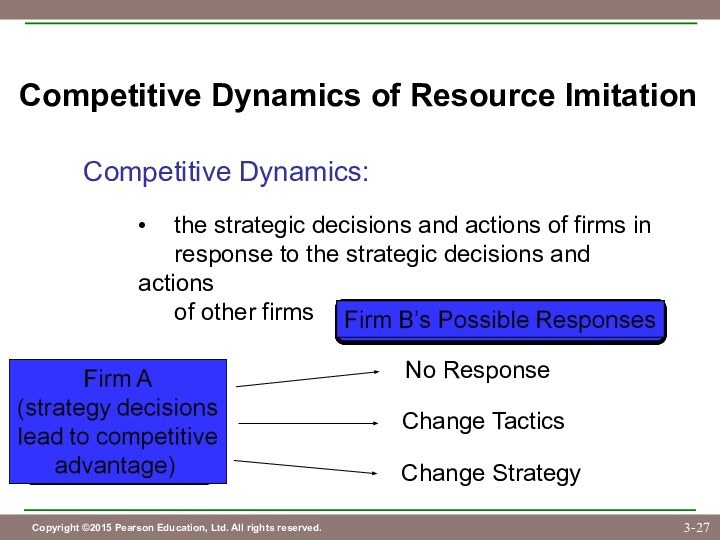
No Response
Change Tactics
Change Strategy
• it does not have the resources and capabilities
to mount an effective response
• it wants to reduce or manage rivalry in the
market through tacit collusion
• a fundamental change
in a firm’s theory
• may be necessary if
current strategy
becomes obsolete
• a mimetic change may
achieve parity, but not
advantage
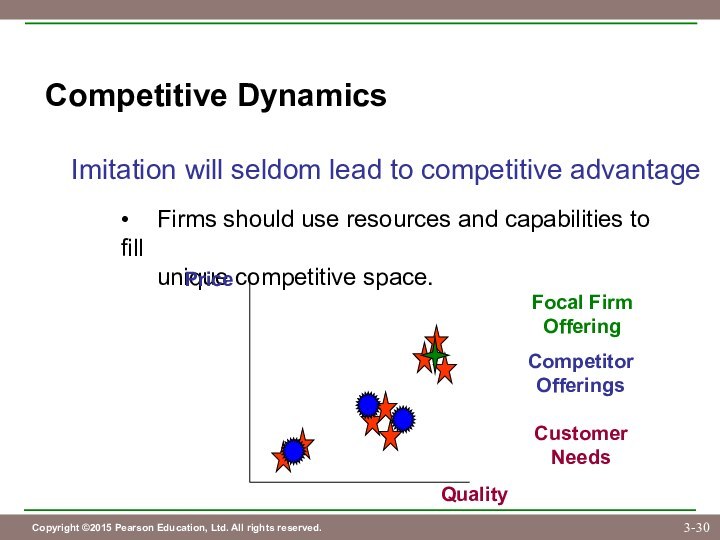
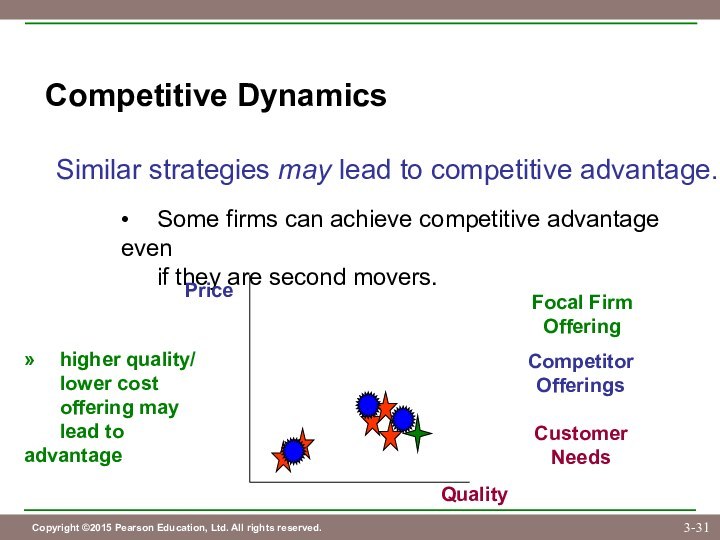
Customer
Needs
Competitor
Offerings
Price
Quality
Focal Firm
Offering
» higher quality/
lower cost
offering may
lead to advantage
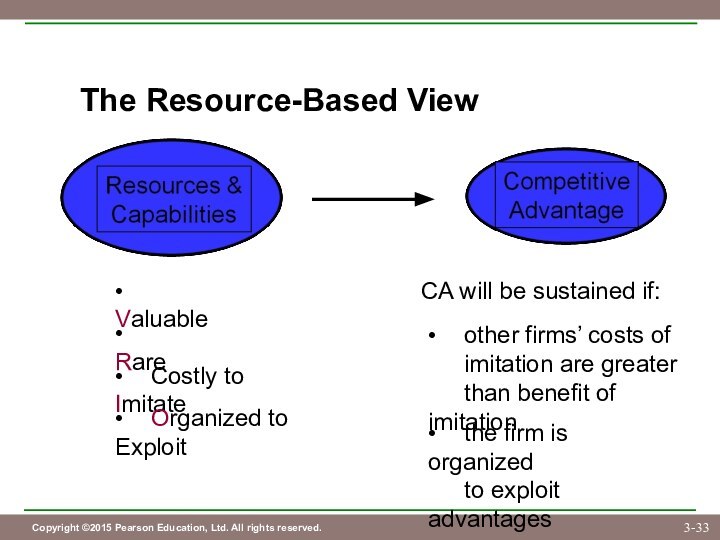
• Competitive advantage stems from resources
and capabilities that meet the VRIO criteria.
• the firm is organized
to exploit advantages
VRIO Framework Helps Managers Recognize
Sources of Competitive Advantage