Слайд 2
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
* Explain why race and ethnicity are
important in understanding marriages and families
* Describe the characteristics
of and variations among African American families
* Describe the characteristics of and variations among American Indian families
* Describe the characteristics of and variations among Latino families
* Describe the characteristics of and variations among Asian American families
Слайд 3
AFRICAN AMERICAN FAMILIES
As of 2014, the population was
45.7 million
Estimates indicate by 2060 the population to
exceed 74 million
That projection would be about 17.9% of the nation’s total population
Location:
New York highest population (3.8m)
Texas had the largest increase
D.O.C. had the highest percentage, followed by Mississippi
Cook County (Chicago) had the largest population of any county in 2014
Schaefer p. 153
Слайд 4
FAMILY STRUCTURE
Shift in the life of married-couple families
reflected in various social and economic developments
Postponement of marriage
High
divorce and separation rates
Low remarriage rates
Male unemployment
Out-of-wedlock births
Many single parents
Слайд 5
FIGURE 4.3 - WHERE U.S. CHILDREN LIVE, BY
RACE AND ETHNICITY, 2012
Notes: The “all other” includes American
Indian and Alaska Native children, but there are no current data on their percentage. For all groups, most of the children living with neither parent live with one or more grandparents. “Two parents” includes children living with parents who are and aren’t married to each other.
Sources: Based on U.S. Census Bureau, Current Population Survey, 2012. 2012, November, Table C3.
Слайд 6
CONT’D FAMILY OVERVIEW
27-28% live below the poverty
line
More single-parents
Challenges (overloads)
Extended families
Egalitarian
Conflict Perspective
Racial Socialization
Overloads:
Emotional – neglecting
the parent’s needs for the child’s
Responsibility – income
Task – too much to do
Слайд 7
GENDER ROLES
Egalitarian family pattern - Both men and
women share equal authority
Division of domestic work is not
equal
African American families are often stereotyped as matriarchal.
Cause of instability in black marriages
Expectation from men to do more of the traditionally female domestic tasks
Слайд 8
STRENGTHS OF THE AFRICAN AMERICAN FAMILY
Strong kinship bonds
Ability
to adapt family roles to outside pressures
Strong work ethic
despite recessions and unemployment
Determination to succeed in education
Unwavering spirituality that helps them cope with adversity
Слайд 9
AMERICAN INDIAN FAMILIES
In 2014, 5.4 million, 2% of
U.S. population (39% is under 24).
The number of
states with 100,000 or more American Indian and Alaska Native residents, alone or in combination, in 2014. These states were California, Oklahoma, Arizona, Texas, New York, New Mexico, Washington, North Carolina, Florida, Michigan, Alaska, Oregon, Colorado, Pennsylvania and Minnesota.
566 -- The number of federally recognized Indian tribes in 2015.
Speak 169 languages
Navajo is the largest tribe
Слайд 10
FAMILY STRUCTURE
Living arrangements
Large extended households
Nuclear families
Divorced parents
Single-parent families
No
distinction between blood relatives and relatives by marriage
Слайд 11
FAMILY STRUCTURE
In 2011, there were almost 558,000
AIAN family households: 57 percent were married couples, 32
percent were mother-only, and 11 percent were father-only families.
Living in an extended family provides many resources, such as assistance with child care, money, transportation, and emotional and moral support.
Can result in stress too
Слайд 12
GENDER ROLES
Nonexistent in contemporary American Indian families
Both husbands
and wives feel equally competent in solving family problems
and coping with everyday issues
Research indicates, mothers spent significantly more time than did fathers in cleaning, food-related work, and child care responsibilities.
Compared with fathers in other cultural groups, the Navajo fathers’ involvement in household labor and child-related tasks was high.
Слайд 13
ELDERS AND GRANDPARENTS
Important to a child’s care, upbringing,
and development
Contribute to a family’s cohesiveness and stability
Elders serve
as mentors and advisors and reinforce cultural norms, values, and roles
Children are taught to respect their elders because old age is viewed as a badge of honor
Badge of honor - A sign that one has done the right things and has pleased the creator.
Elders have traditionally played a central role in a family’s decision making.
Elders deal with an increasing number of issues ranging from poverty to poor health and minimal access to services in both urban and reservation areas.
Слайд 14
STRENGTHS OF THE AMERICAN INDIAN FAMILY
Relational bonding -
Core behavior that is built on widely shared values
Respect
Generosity
Sharing across the tribe, band, clan, and kin group
Spirituality sustains the family’s identity and place in the world
American Indians have made considerable economic progress by insisting on self-determination and the rights of tribes to run their own affairs.
Слайд 15
LATINO FAMILIES
Latinos are the largest racial-ethnic group.
Latinos trace
their roots to the Spanish and Mexican settlers who
founded cities in the Southwest before the arrival of the first English settlers on the East Coast.
Others are recent immigrants or children of the immigrants who arrived in large numbers at the beginning of the twentieth century.
Слайд 16
FIGURE 4.5 - U.S. LATINOS BY ORIGIN, 2010
Note:
Central American includes countries such as El Salvador, Honduras,
and Guatemala; South American includes countries such as Argentina, Bolivia, and Venezuela.
Source: Based on Ennis et al., 2011, Table 1.
Слайд 17
FAMILY STRUCTURE
68 percent of Latino children live in
two-parent families
Latino couples born in the United States are
more likely to divorce
More out-of-wedlock births, particularly among adolescents
Children may live with relatives than only with parents
Acculturation, particularly in low-income neighborhoods, may result in Latino adolescents’ higher rates of delinquency and crimes.
Слайд 18
GENDER ROLES
Change in response to job opportunities and
new family policies, and as people approach retirement
Having and
raising children is the core focus of life
Fathers are more likely to supervise and restrict their children’s TV viewing
Mothers teach cultural values to their children
Слайд 19
FAMILISM AND EXTENDED FAMILIES
Familism - Family relationships in
which sharing and cooperation take precedence over one’s personal
needs and desires
Extended family members
Constitute of relatives, godparents, and even close friends
Exchange a wide range of goods and services
Слайд 20
FAMILISM AND EXTENDED FAMILIES
For Latinos, familism and the
extended family have traditionally provided emotional and economic support.
They
believe relatives are more important than friends.
Familism depends on the family’s origin.
Helps new immigrants to cope with the everyday stresses of discrimination, unemployment, and learning to survive in a different culture
Reduces parental conflict and increased nurturing parenting that, in turn, increased the likelihood of children doing well in school.
Some Mexican Americans practice chain migration
Chain migration - Those already in the United States find employment and housing for other kin who are leaving Mexico.
Слайд 21
STRENGTHS OF THE LATINO FAMILY
Resilient and adaptive
Hard working
Give
more importance to religion
Are more likely to give than
to receive financial support from their families
Слайд 22
ASIAN AMERICAN FAMILIES
In 2015 20 million
CB recognizes
47 groups
California and NY have highest population
The diverse origins
mean that there are vast differences in languages and dialects, religions, cuisines, and customs.
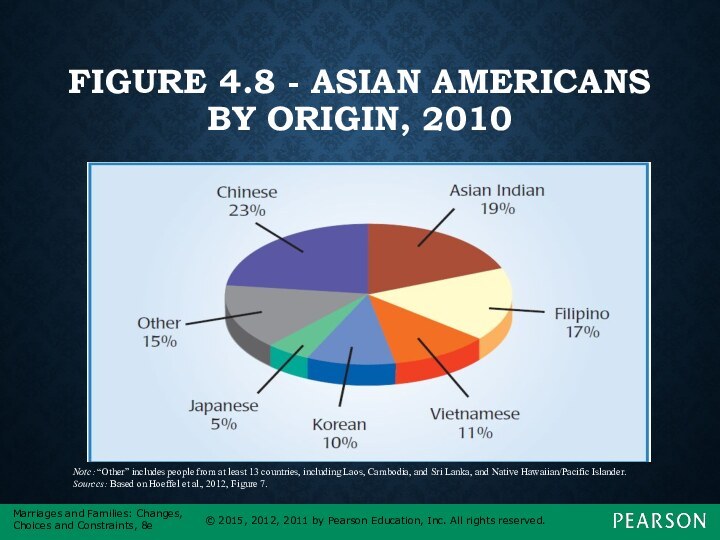
The largest groups of Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders are as follows:
Chinese Americans
Filipino Americans
Asian Indians
Vietnamese Americans
Korean Americans
Japanese Americans
Other Asian Americans
Слайд 23
FIGURE 4.8 - ASIAN AMERICANS BY ORIGIN, 2010
Note:
“Other” includes people from at least 13 countries, including
Laos, Cambodia, and Sri Lanka, and Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander.
Sources: Based on Hoeffel et al., 2012, Figure 7.
Слайд 24
FAMILY STRUCTURE
Vary widely depending on:
Country of origin
Time of
arrival
Past and current immigration policies
Whether the families are immigrants
or refugees
Parents’ original socioeconomic status
Most Asian American children grow up in two-parent homes
Слайд 25
MARRIAGE AND GENDER ROLES
Highest marriage rates and the
lowest divorce rates
Gender roles - Traditional in most families
and vary by:
Social class
Country of origin
Length of residence in the United States