Слайд 2
Denys Correll
Executive Director
International Council on Social Welfare
C/O
NIZW International Centre
P.O. Box 19152
3501 DD Utrecht
The Netherlands
Phone 31
30 2306 336 Fax 31 30 2306 540
Email icsw@icsw.org Website: www.icsw.org
Слайд 3
What I will cover
Global influences on social
policy and social programmes
Example of the world bank influence
Three
schools of thought on globalization
Areas of social governance reform
How we have moved from public sector universal provision to private sector and safety nets
UN and finally ICSW
Слайд 4
Global Influences
Financial Institutions – World Bank, International Monetary
Fund, World Trade Organisation
United Nations, the UN secretariat and
the UN social agencies eg UNDP
Other non UN agencies eg International Labour Office, OECD
The “Gs” G7, G20, G77 etc
Слайд 5
World Bank and IMF
Having enormous influence on national
governments
Evolving philosophies but believe in welfare pluralism i.e. state
is not the only or even the primary financier and provider of social services
1990s WB into social paternalism
2000 social liberalism and corporatization
2004 World Development Report - making services work for the poor
Слайд 6
Tension in the World Bank
Two competing philosophies emerging
Making
services work for the poor means making services work
for everybody while ensuring poor have access
Alternative view is that public spending benefits the rich and should be refocused on the poor
But other reports still emphasise privatisation
Слайд 7
World Bank and Health Care
Policy of welfare pluralism
especially in health
1987 WB publication “Financing Health Services in
Developing Countries”
Increase the amount patients pay
Develop private health insurance
Expand participation of the private sector in health care
Слайд 8
World Bank and Pensions
1994 report “Averting the Old
Age Crisis”
Governments needing loans from WB or IMF forced
into structural adjustment
WB committed to “three pillars”
Minimal public pension
Contributory privatised pension
Private savings
But not enough emphasis on governments protecting consumer interests
Слайд 9
Three Schools of thought on Globalization
Globalization has a
very significant impact on welfare states through increasing dominance
of the market economy.
Internationalization means demise of nation-state autonomy
Reduces national policy options
Weakens labour movement
Expansion of trade creates unemployment and increases inequality
Слайд 10
Three Schools of thought on Globalization
2. Globalization has
an effect upon welfare states but these effects are
mediated through national institutional structures and policy responses
Some welfare states are more compatible to competitiveness than others and adapt
Слайд 11
Three Schools of thought on Globalization
3. Globalization is
having relatively little impact on the welfare state
Changes are
occurring for other reasons
Erosion of the welfare state is due to ideology rather than globalization
Domestic factors are causing change eg demography, technology and changes to family structures
Слайд 12
Areas of Social Governance Reform
World Commission on the
Social Dimension of Globalization
Call for global tax authority
Reform of
UN including Economic and Social Commission
Involvement of civil society in UN
Involvement of civil society in the Bretton Woods institutions (World Bank, IMF,WTO)
Слайд 13
Universalism to Safety Nets
Globalization as we know it
took shape in the 1980s and 1990s
Related to neoliberal
policies typified by President Regan and Prime Minister Thatcher
Era of anti public provision discourse
Слайд 14
New politics
Social programmes were characteristic of the 19th
and 20th centuries
Late 20th and early 21st centuries beginning
of the retrenchment of the welfare state or welfare reduction
The politics of retrenchment is different to the politics that created the welfare state
Extending benefits to large numbers is very different to taking benefits away
Слайд 15
New politics
Retrenchment politics characterised by political shift to
the right, economic changes and the increasing costs of
the welfare state
“typically treacherous because it imposes tangible losses on concentrated groups of voters in return for diffuse and uncertain gains” (Pierson – The new politics of the welfare state)
Слайд 16
Retrenchment policies
Main goal is to dismantle existing
universal programmes
Globalization of policy and capital has reduced economic
tools and independence of national governments
Not worried about political unpopularity
Use techniques of incremental and technical reforms which limits the emergence of opposition
Power of organised labour and left parties has diminished
Слайд 17
UN Commission for Social Development
2004 priority theme
was public sector effectiveness
Commission emphasised the crucial role of
the public sector in the provision of equitable, adequate and accessible social services for all to meet the needs of the entire population
Contrast with the minimalist approach of the millennium development goals – basic education, basic health, basic income etc
Слайд 18
UN Commission for Social Development
ICSW’s submission to the
Commission argued that an effective public sector is the
single most important determinant of good governance
ICSW defined public sector in terms of the functions it exercises
It is not a question of who does what but who takes responsibility for access and equity
ICSW argued that the state must ensure universal and equitable access to quality services – education, nutrition, health care, water and sanitation
Слайд 19
ICSW
NGO which works and advocates at global and
regional level
Mission is to relieve poverty
Gains its knowledge from
its members
Members are organisations involved in social welfare and social development in about 70 countries
Conveys the knowledge gained from members to global and regional institutions
Expanding membership into eastern Europe
Слайд 20
Questions
To what extent are you aware of the
influence of global and regional bodies in your country?
What influence do you think external organisations are having on your governments?
In what areas of social policy are they having an influence?
What role can you see NGOs having in influencing directions in social policy?
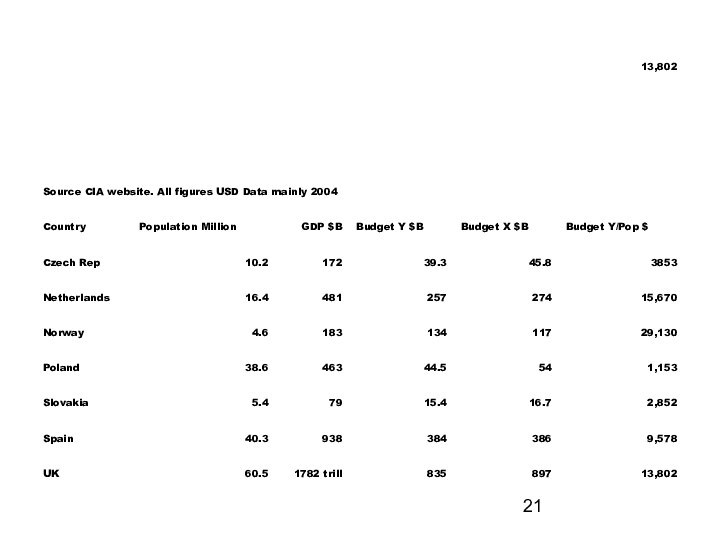
Слайд 22
Public goods and welfare benefits
Public goods – rail,
gas, electricity, water, sanitation and housing subject to privatisation
Welfare
benefits – services include health and education subject to privatisation
Welfare benefits – cash transfers subject to means testing (targeting) and changes in eligibility rules
Слайд 23
Areas of global activity
Global public goods eg tax
agreements, global alliances on vaccines and immunization
Global social regulation
eg global labour standards and in emerging international markets including private health and education
Global social rights eg Human Rights Commission, migrants, illegal trafficking.
Слайд 24
Obstacles to Reform
Southern resistance to Northern reform proposals
Suspicion
or opposition to Northern neoliberalism
National sovereignty
Growth in
strength of regional groupings of governments
Conditionality imposed by global institutions