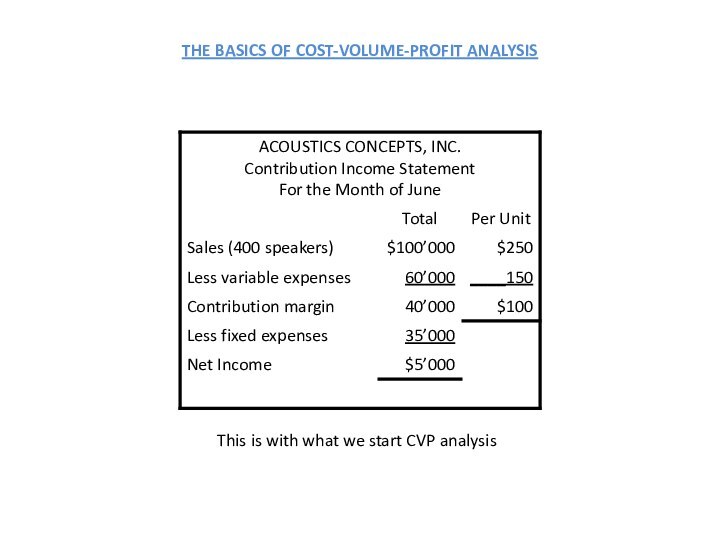
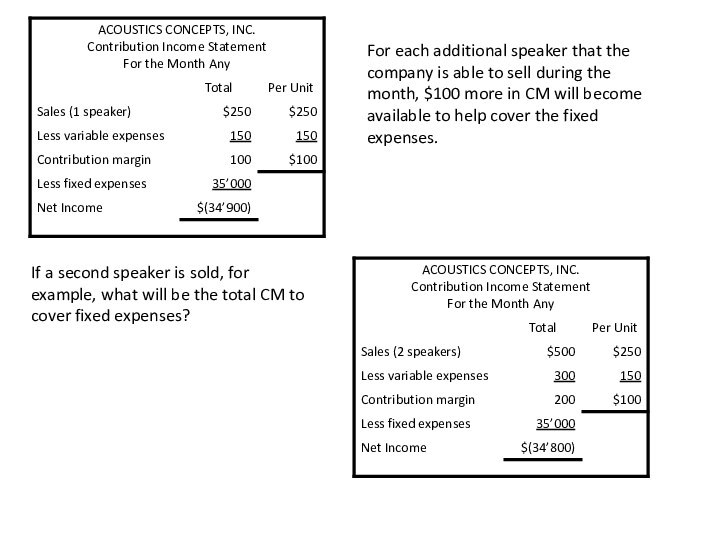
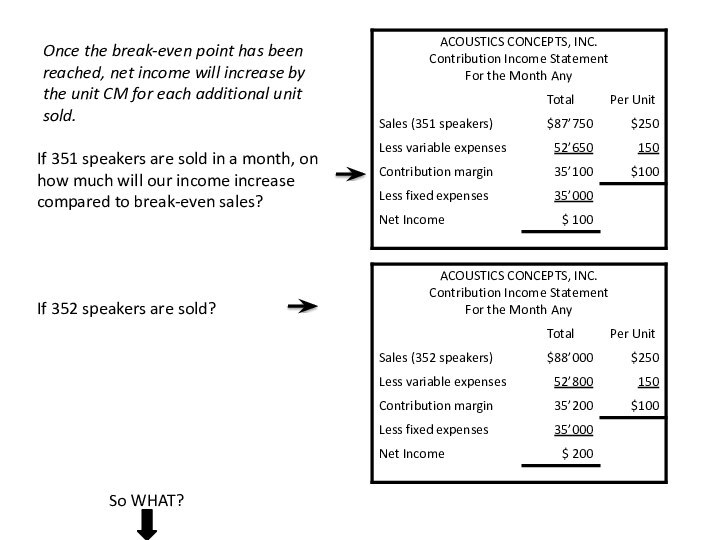
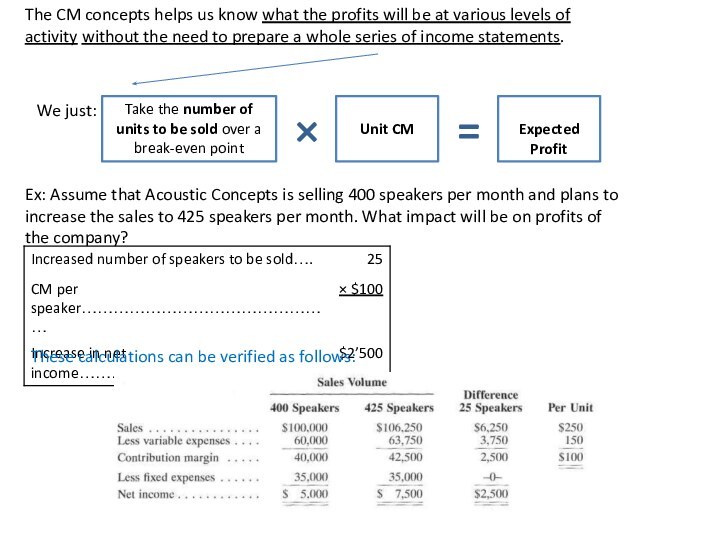
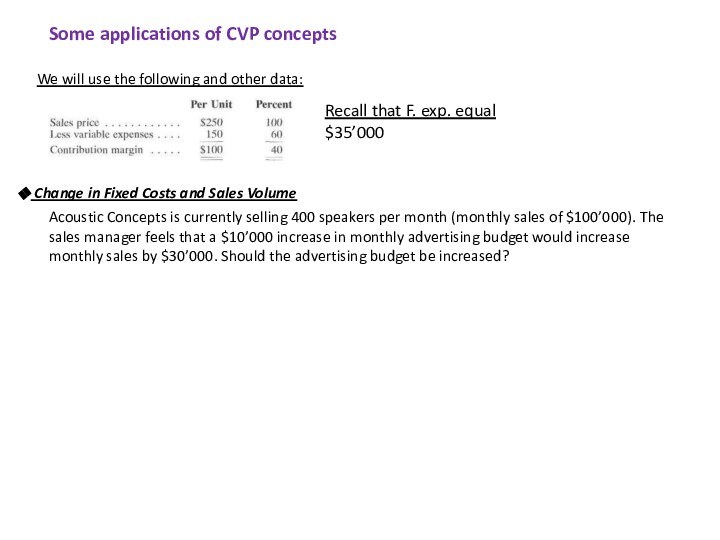
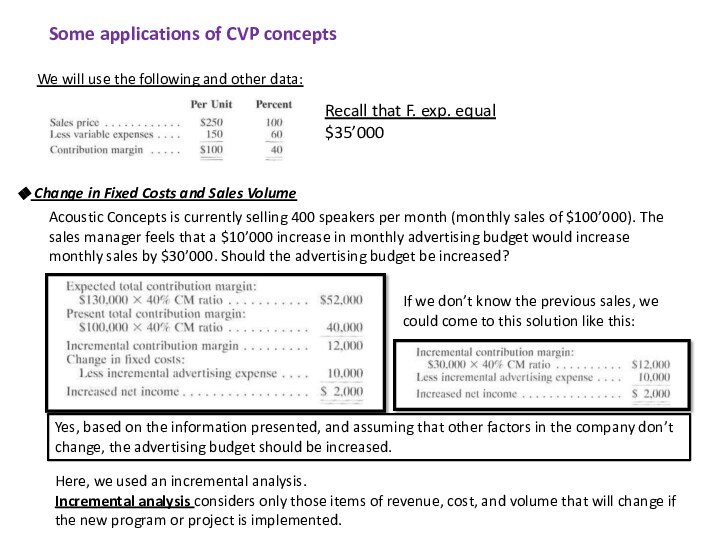
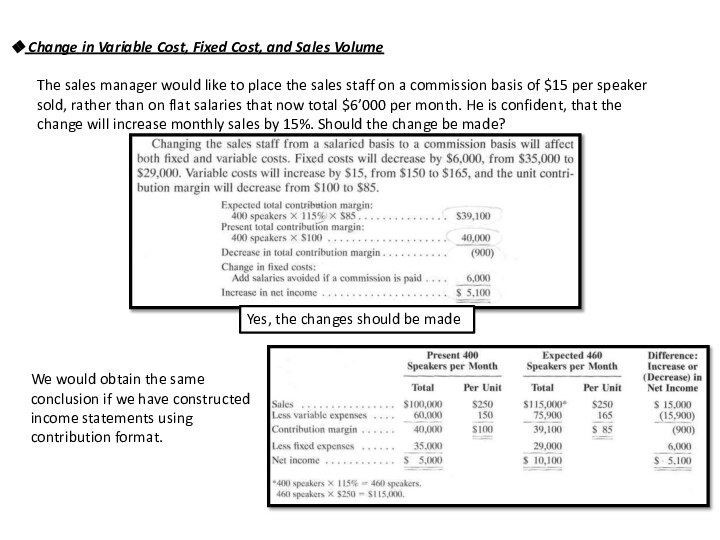
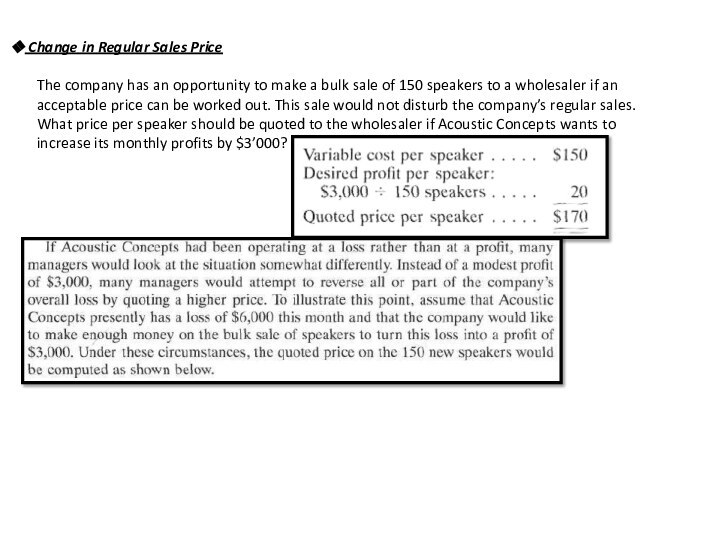
following and other data:
Recall that F. exp. equal $35’000
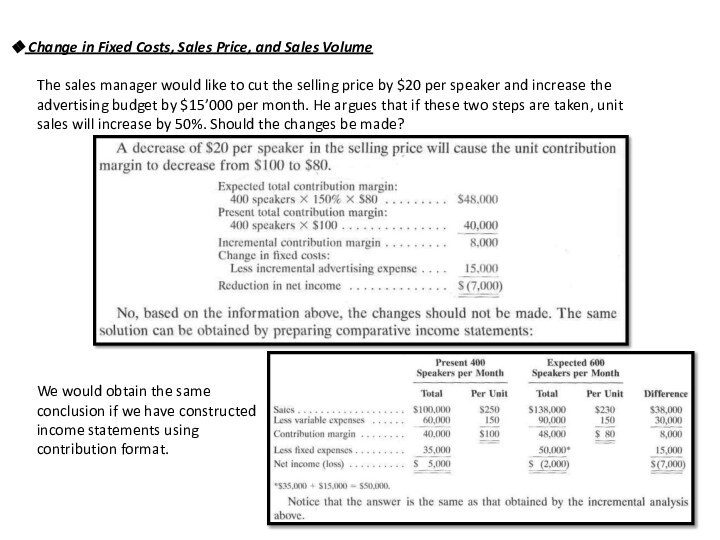
Change in Fixed Costs and Sales Volume
Acoustic Concepts is currently selling 400 speakers per month (monthly sales of $100’000). The sales manager feels that a $10’000 increase in monthly advertising budget would increase monthly sales by $30’000. Should the advertising budget be increased?
If we don’t know the previous sales, we could come to this solution like this:
Here, we used an incremental analysis.
Incremental analysis considers only those items of revenue, cost, and volume that will change if the new program or project is implemented.
Yes, based on the information presented, and assuming that other factors in the company don’t change, the advertising budget should be increased.