Слайд 2
Drilling Fluid Function
Drilling Fluid Function
1.Transport cutting and dispose
to surface - The drilling fluid brings the drilled
material to the ground surface
either by mud rheology and velocity
Слайд 3
Drilling Fluid Function
2. Clean drill bits – As
drilling fluid exits the bit jets, fluid velocity removes
cutting from the bit teeth and bit body.
This prevents bit
ball up situation.
Слайд 4
Drilling Fluid Function
3. Provide hydrostatic pressure to control
well while drilling –Hydrostatic pressure provided from drilling fluid
is the primary well control. Mud weight should be high enough
to control formation pressure while drilling.
P=0.052*MW*TVD
Psi=0.052*ppg*ft
Слайд 5
Drilling Fluid Function
4. Prevent excessive mud loss -
While drilling, clay particle will form a thin layer
over porous zones called “mud cake” or “filter cake”. Mud cake acts as barrier to prevent excessive drilling fluid loss into formation and provides wellbore stability..
Слайд 6
Drilling Fluid Function
5. Prevent formation damage by using
reservoir drill-in fluid – While drilling long reach zone
in horizontal wells, the special drilling fluid will be utilized in order to prevent formation damage.
Слайд 7
Drilling Fluid Function
6. Provide hydraulic pressure to
down hole assembly (BHA)- as mud motor, measuring
while
drilling (MWD),
logging while drilling (LWD), etc
– Without enough hydraulic power,
down hole tool will not be properly
operated, hence, drilling fluid plays
essential role to provide power to
sophisticated down hole tool.
Слайд 8
Drilling Fluid Additives
There are many drilling fluid additives
which are used to either change the mudweight(density) or
change its chemical properties .
1.Weighting Materials:
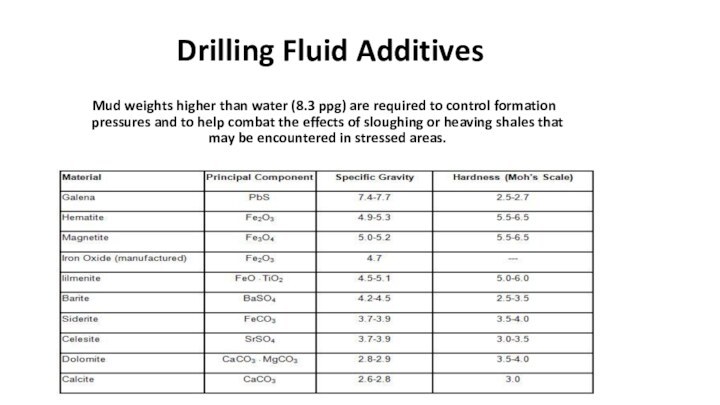
Weighting materials (densifiers) are compounds that are dissolved or suspended in drilling fluid to increase its density. They are used to control formation pressures and to help combat the effects of sloughing or heaving shales that may be encountered in stressed areas.
Any substance that is denser than water and that does not adversely
affect other properties of the drilling fluid can
be used as a weighting material
Слайд 9
Drilling Fluid Additives
Mud weights higher than water
(8.3 ppg) are required to control formation pressures and
to help combat the effects of sloughing or heaving shales that may be encountered in stressed areas.
Слайд 11
Air drilling
Advantages:
Higher penetration rates
Better hole cleaning
Less formation damage
Disadvantages:
Air
cannot support the wellbore stability
Doesn’t provide enough pressure
Слайд 12
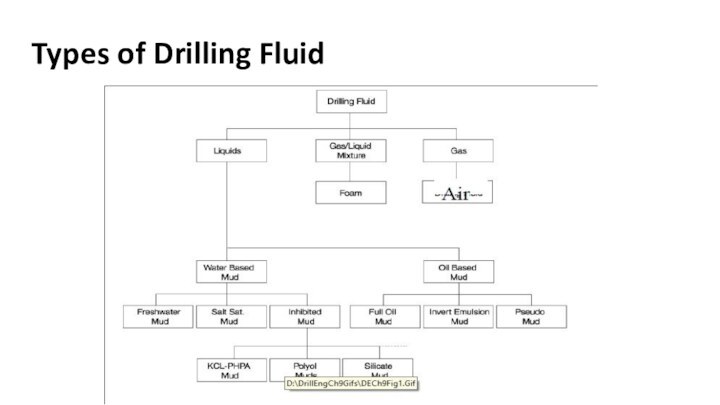
Types of drilling Fluid
Three types of drilling mud
are in common use:
water-base mud
oil-base mud
Gas based fluids
Water
Base Mud
This fluid is the mud in which water is the continuous phase. This is the most common drilling mud used in oil drilling.
The following designations are normally used to define the classifications of water base drilling fluid
Слайд 13
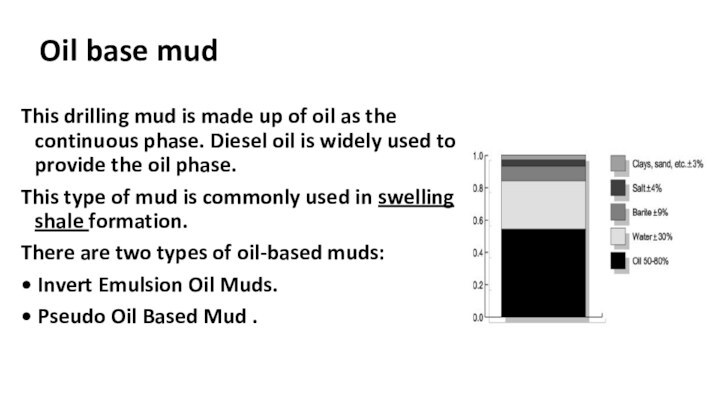
Oil base mud
This drilling mud is made up
of oil as the continuous phase. Diesel oil is
widely used to provide the oil phase.
This type of mud is commonly used in swelling shale formation.
There are two types of oil-based muds:
• Invert Emulsion Oil Muds.
• Pseudo Oil Based Mud .
Слайд 14
Advantages of Oil Based Mud
• The oil base
mud is good for high temperature environment because the
base fluid is oil.
• It is good for drilling into shale formation because it does not react with formation clay causing shale instability.
• It typically creates thin mud cake. This is really good because you can reduce risk for pipe stuck situation.
• It can be treated and reused. Using this mud for long run can reduce overall drilling mud cost.
• Oil base as external phase is good lubricant so it greatly reduce drilling torque.
Слайд 15
Disadvantages of OBM
Environmental concern – Oil base mud
is considered as toxic waste therefore it cannot be
disposed directly into land, river, or ocean
People Heath – This mud has hazardous vapors which will cause health problem to personnel who working with it in both short and long term.
Cost – Mud cost of this system is higher than water base mud in terms of cost per barrel.
Gas kick detection – Gas kick is very difficult to identify because gas is soluble in oil. You may take kick but you will be able to see pit gain or flow increase at the first time.
Equipment – Rubber parts is easily deteriorated by oil base.
Слайд 16
Density
((Any accepted terminology that indicates the weight
per unit volume of drilling fluid))
-Pounds per gallon (ppg).
-Pounds
per cubic feet (pcf).
-Gram per cubic centimeter (g/cc).
-Kilogram per liter (kg/l).
Слайд 17
Density
Mud weight is measured in the field
using a mud balance, as shown in Fig..
Слайд 18
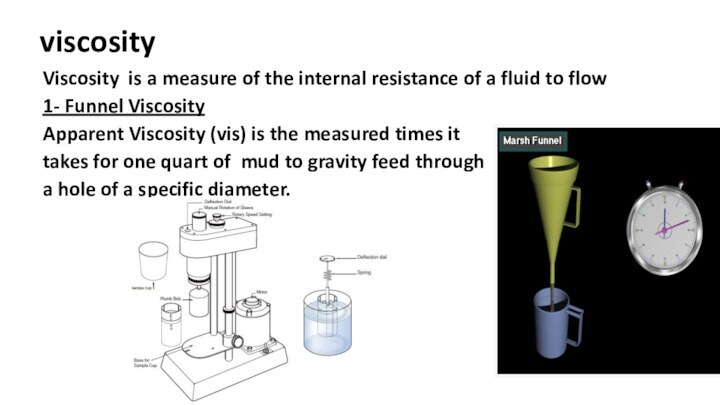
viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the internal
resistance of a fluid to flow
1- Funnel Viscosity
Apparent Viscosity
(vis) is the measured times it
takes for one quart of mud to gravity feed through
a hole of a specific diameter.
Слайд 19
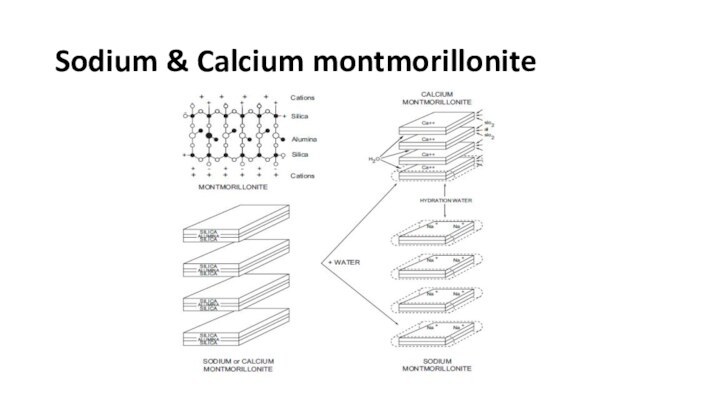
Clay Chemistry
Expandable Clays which absorb water so that
they are called hydrophilic. (such as montmorillonite clays)
Non-expandable Clays,
they will not absorb water so they are called hydrophobic (such as illite)
Слайд 20
Sodium & Calcium montmorillonite
Слайд 21
Viscosity Control additives to WBM
Native clays
Wyoming Bentonite
To reduce
the viscosity of the mud:
Reduce the solids content
Reduce the
number of particles per unit volume
Neutralize the attractive forces between the particles. (Using thinners)