- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Ecosystem
Содержание
- 2. Ecosystem
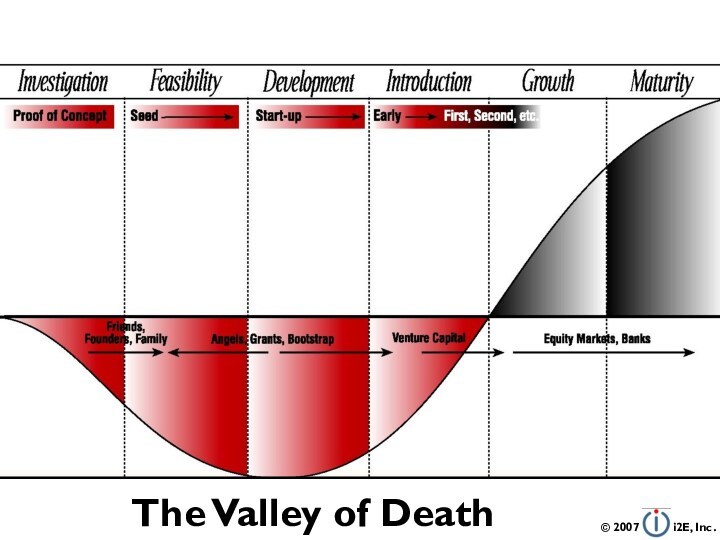
- 3. The Valley of DeathThe Capital Lifecycle
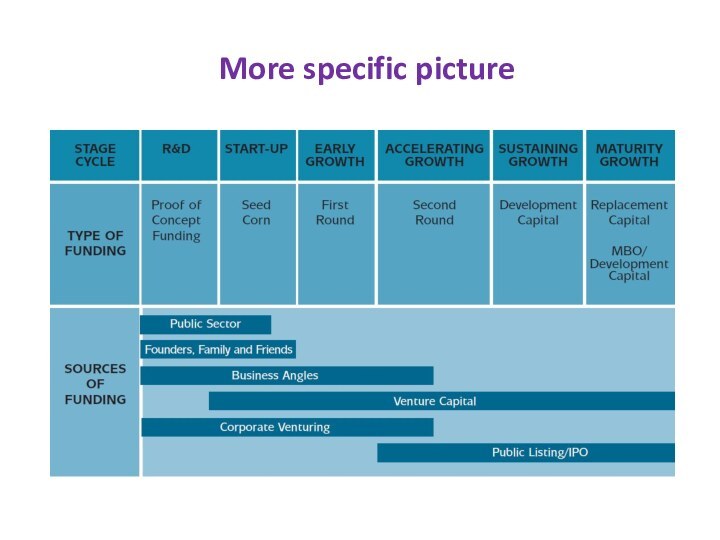
- 4. More specific picture
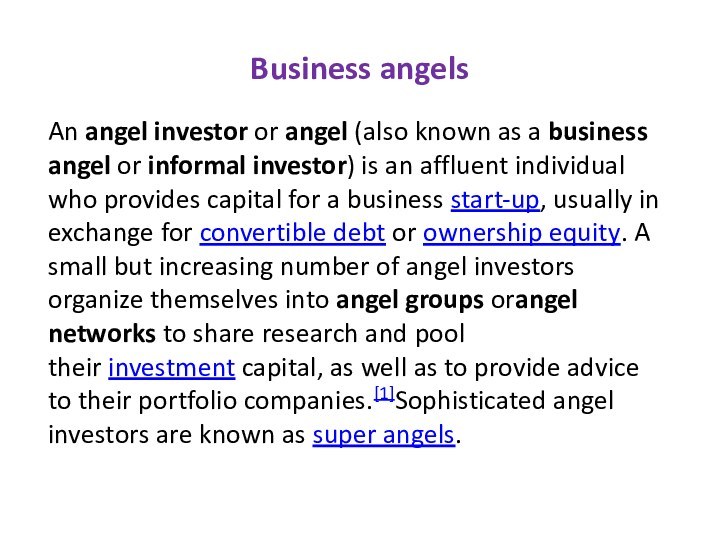
- 5. Business AngELSWikipediahttp://www.go4funding.com/articles/angel-investors/types-of-angel-investors.aspx
- 6. Business angelsAn angel investor or angel (also known as a business angel or informal
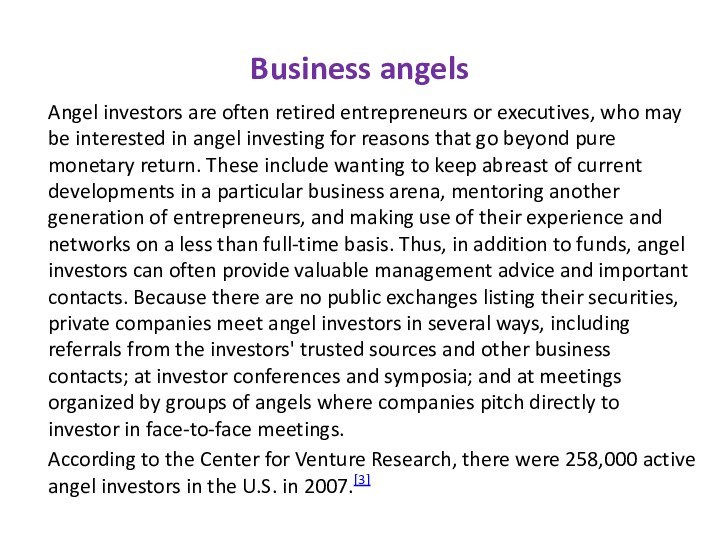
- 7. Business angelsAngel investors are often retired entrepreneurs
- 8. Business angelsFive reasons people become business angels:I
- 9. Smart moneyDefinition of 'Smart Money‘Cash invested or
- 10. Angel categoriesCore angels- These investors are individuals with
- 11. Angel categoriesHigh-tech angels- These investors may have less
- 12. Angel categoriesReturn on investment (ROI) angels- These investors are
- 13. Angel typesCorporate angels- These individuals are former business
- 14. Angel typesEntrepreneurial angels- These people are successful angel
- 15. Angel typesEnthusiast angels- These angels are older (age
- 16. Angel typesMicromanagement angels: These individuals are considered to
- 17. Angel typesProfessional angels- These angels are professionally employed
- 18. Angel speciesHead angels (aka “lead dogs”)-These people are
- 19. Angel speciesIntentional angels (aka “dark angels”)-These angels will
- 20. Angel speciesFemale angel organizations- In a male-dominated field,
- 21. Angel speciesVenture capitalists who are also angel investors
- 22. Скачать презентацию
- 23. Похожие презентации
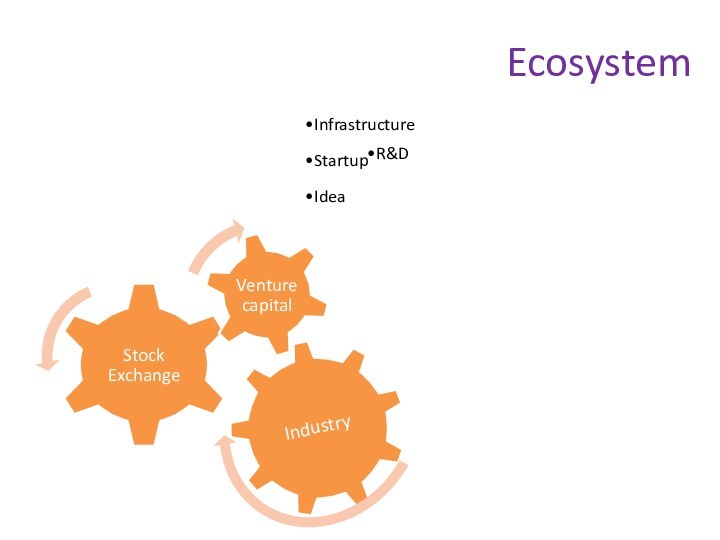
Ecosystem














Слайд 5
Business AngELS
Wikipedia
http://www.go4funding.com/articles/angel-investors/types-of-angel-investors.aspx
Слайд 6
Business angels
An angel investor or angel (also known as a business angel or informal investor)
Слайд 7
Business angels
Angel investors are often retired entrepreneurs or
executives, who may be interested in angel investing for
reasons that go beyond pure monetary return. These include wanting to keep abreast of current developments in a particular business arena, mentoring another generation of entrepreneurs, and making use of their experience and networks on a less than full-time basis. Thus, in addition to funds, angel investors can often provide valuable management advice and important contacts. Because there are no public exchanges listing their securities, private companies meet angel investors in several ways, including referrals from the investors' trusted sources and other business contacts; at investor conferences and symposia; and at meetings organized by groups of angels where companies pitch directly to investor in face-to-face meetings.According to the Center for Venture Research, there were 258,000 active angel investors in the U.S. in 2007.[3]
Слайд 8
Business angels
Five reasons people become business angels:
I must
share, I must give back a.k.a. Spirit of the
ValleyThis has to be done!
I am looking for a project to get contracted later
I am looking for a project to invest
Welcome to the club
Fifty thousand dollars on a
handshake
Слайд 9
Smart money
Definition of 'Smart Money‘
Cash invested or wagered
by those considered to be experienced, well-informed, "in-the-know" or
all three. Although there is little empirical evidence to support the notion that smart-money investments perform any better than non-smart-money investments do, many speculation methods take such influxes of cash very seriously.
Слайд 10
Angel categories
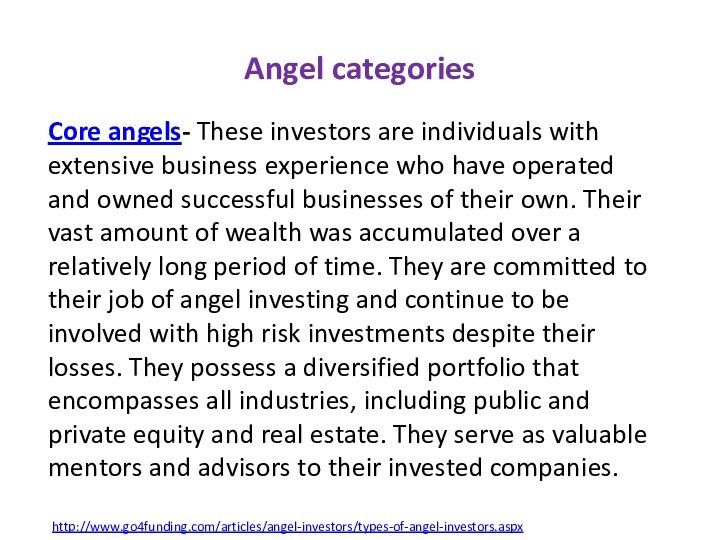
Core angels- These investors are individuals with extensive
business experience who have operated and owned successful businesses
of their own. Their vast amount of wealth was accumulated over a relatively long period of time. They are committed to their job of angel investing and continue to be involved with high risk investments despite their losses. They possess a diversified portfolio that encompasses all industries, including public and private equity and real estate. They serve as valuable mentors and advisors to their invested companies.http://www.go4funding.com/articles/angel-investors/types-of-angel-investors.aspx
Слайд 11
Angel categories
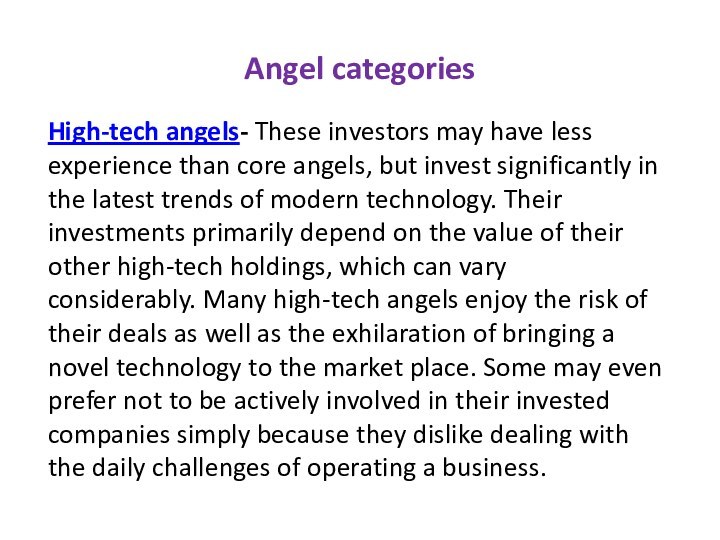
High-tech angels- These investors may have less experience
than core angels, but invest significantly in the latest
trends of modern technology. Their investments primarily depend on the value of their other high-tech holdings, which can vary considerably. Many high-tech angels enjoy the risk of their deals as well as the exhilaration of bringing a novel technology to the market place. Some may even prefer not to be actively involved in their invested companies simply because they dislike dealing with the daily challenges of operating a business.
Слайд 12
Angel categories
Return on investment (ROI) angels- These investors are primarily
concerned with the financial reward of high-risk investments. Their
motivation behind investing is their perception of what other angels gross income may be. ROI angels tend to stay away from investing when market performance is poor and emerge once the market shows stability and improvement. They view each of their investments as another company added to their diversified portfolio and rarely become actively involved in the invested companies.
Слайд 13
Angel types
Corporate angels- These individuals are former business executives
from large corporations who have been downsized, have taken
early retirement, or have been replaced. Even though profitability of their investment is their overall goal, they also seek personal opportunity when investing, claiming that they are looking for an investment opportunity when, in reality, they are really looking for a job. For instance, many corporate angels are known to invest in one company and seek a paid position, which is often part of the business deal. They are also known to have about $1 million in cash and may invest as much as $200,000 in a company. Many can be extremely controlling once they obtain their desired position in the invested company.
Слайд 14
Angel types
Entrepreneurial angels- These people are successful angel investors
who own and operate their own businesses. Their steady
flow of income allows them to make more higher-risk investments and provide a larger amount of capital for start-ups. Entrepreneurial angels tend to make adequately-sized investments anywhere from $200,000 to $500,000 and are known for investing more money into the same company as the business progresses. They enjoy the personal fulfillment of assisting entrepreneurs launch a successful start-up and rarely take an active role in managing a company.
Слайд 15
Angel types
Enthusiast angels- These angels are older (age 65
and up) businessmen who are independently wealthy before their
investments. They often invest small amounts of capital (between $10,000 to a few hundred thousand dollars) in several different enterprises and view investing as a mere hobby. They also do not take an active role in management.
Слайд 16
Angel types
Micromanagement angels: These individuals are considered to be
serious investors. Even though many are born wealthy, the
majority of these angels have acquired their success and wealth through their own independent and strategic efforts. They often demand a board position and are known to impose the same strategies they have used with their own companies towards their invested companies. Micromanagers will usually invest anywhere between $100,000 and $1 million for each endeavor. Rarely do these angels seek an active management role, but tend to emerge and be more actively involved when their invested companies do not do well.
Слайд 17
Angel types
Professional angels- These angels are professionally employed as
physicians, lawyers, accountants, etc. who invest in companies in
their related field. Professional angels invest in several companies at the same time, and their capital contributions range anywhere from $25,000 to $200,000 per investment. They may also provide services to their invested company (legal, accounting or financial) at a discounted rate, but may be unpleasant to deal with and impatient at times when it comes to their investments. Professional angels are of tremendous value for initial needed capital and rarely make follow-on investments.
Слайд 18
Angel species
Head angels (aka “lead dogs”)-These people are true
angel leaders who bring together and advocate other angel
investors to a specific deal. These head angels enjoy being the first in a deal and leading others to an investment opportunity.Mentor angels (aka “guardian angels”)-These individuals serve as advisors and mentors to their invested companies. Providing insight to a young company and mentoring entrepreneurs to achieve success is more valuable to them than monetary rewards.
Generational angels (aka “silver spoons with silver wings”)-These investors are the second generation offspring of successful families. They are typically younger than the average angel investor, but have acquired a significant amount of business expertise from working in the family business.
Слайд 19
Angel species
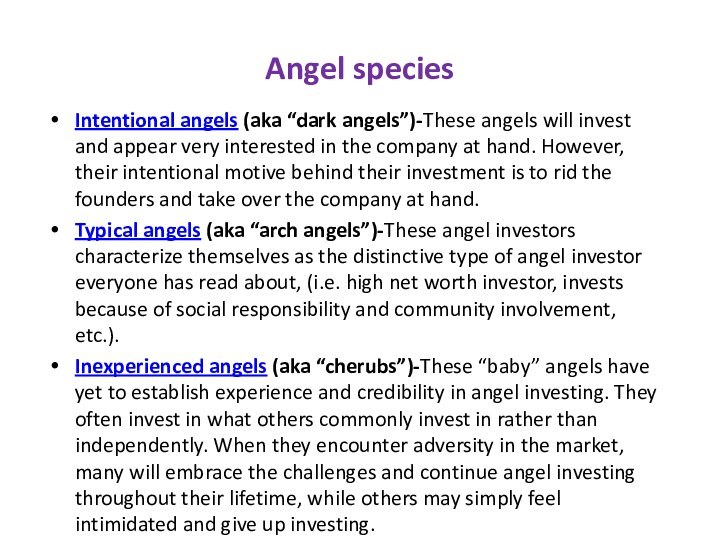
Intentional angels (aka “dark angels”)-These angels will invest
and appear very interested in the company at hand.
However, their intentional motive behind their investment is to rid the founders and take over the company at hand.Typical angels (aka “arch angels”)-These angel investors characterize themselves as the distinctive type of angel investor everyone has read about, (i.e. high net worth investor, invests because of social responsibility and community involvement, etc.).
Inexperienced angels (aka “cherubs”)-These “baby” angels have yet to establish experience and credibility in angel investing. They often invest in what others commonly invest in rather than independently. When they encounter adversity in the market, many will embrace the challenges and continue angel investing throughout their lifetime, while others may simply feel intimidated and give up investing.
Слайд 20
Angel species
Female angel organizations- In a male-dominated field, there
has been the emergence of women angel investor groups.
Female angel networks primarily focus on the educational facet of investing and advocate deal flow. Often times, female angel syndicates focus on a variety of industries, not necessarily companies managed by or owned by women.Here also come LGBT, People of Color, People with Disability, etc.





























