Слайд 2
History of Coca-Cola
John Pemberton created the first soft
drink in the United States in 1886 in Atlanta,
Georgia
John Pemberton was a pharmacist in Atlanta
He stirred up a fragrant, caramel-colored liquid
When it was done he took it to Jacobs’ Pharmacy and sold it for 5 cents a bottle
Слайд 3
Company Mission and Vision
Mission:
To refresh the world..
To inspire
moments of optimism and happiness..
To create value and make
a difference
Vision:
2020 Vision: It creates a long-term destination for our business and provides us with a "Roadmap" for winning together with our bottling partners
Слайд 4
Vision
Steps to accomplish sustainable and quality growth:
People:
Be a great place to work where people are
inspired to be the best they can be
Portfolio: Bring to the world a portfolio of quality beverage brands that anticipate and satisfy peoples desires and needs
Partners: Nurture a winning network of customers and suppliers, together we create mutual, enduring value
Слайд 5
Vision
Planet: Be a responsible citizen that makes a
difference by helping build and support sustainable communities
Profit: Maximize
long-term return to shareholders while being mindful of our overall responsibilities
Productivity: Be a highly effective, lean and fast-moving organization
Our winning culture makes the 2020 vision possible.
Слайд 6
Company Goals
Beverage Benefits
Invest more than $50 million in
research by 2015
Active Healthy Living
Support at least one physical
activity program in every country in which we operate by the end of 2015
Community
Give back at least 1% of our operating income annually to help develop and sustain communities around the world.
Energy Efficiency and Climate Protection
Grow our business, but not our system wide carbon emissions from our manufacturing operations through 2015, compared with a 2004 baseline
Слайд 7
Company Goals
Sustainable Packaging
Recover 50% of the equivalent bottles
and cans used annually by 2015
Water Stewardship
Replenish to nature
and communities an amount of water equivalent to what is used in our finished beverages by 2020
Workplace
Achieve a 98% performance level for Company-owned and -managed facilities upholding the standards set in our Workplace Rights Policy by 2015
Слайд 8
Company Values
Leadership: The courage to shape a better
future
Collaboration: Leverage collective genius
Integrity: Be real
Accountability: If it is
to be, it's up to me
Passion: Committed in heart and mind
Diversity: As inclusive as our brands
Quality: What we do, we do well
Слайд 9
External Analysis: Specific Environment
Current Rivalry Among Firms
Main competitors
are PepsiCo, Dr. Pepper Snapple Group, and Walmart (Sam’s
Choice)
Leader in Industry
Brand Loyalty
Potential Entrant Opportunities
Large capital requirements
No potential entrants
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Very low power
Слайд 10
External Analysis: Specific Environment
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Limited suppliers
due to three dominant companies in industry
Few suppliers, more
power
Substitute Products
Fruit drinks, energy drinks, sport drinks, and bottled water
Becoming more popular with more health/ weight issues
Слайд 11
External Analysis: General Environment
Economic Opportunities
Bad economy, but good
for beverage industry
Soft drinks can be small luxury items
Economic
Threats
With bad economy had to stop or slow down production to make up for losses
Demographic Opportunities
Younger generation
Demographic Threats
Marketing to younger generations
Слайд 12
External Analysis: General Environment
Sociocultural Opportunities
Diverse products
Sociocultural Threats
Marketing in
diverse countries
Political- Legal Opportunities
Introduction of “slim can”
Political-Legal Threats
Government regulation
of soft drinks and children
Слайд 13
External Analysis: General Environment
Technological Opportunities
“Smart” Vending Machine
Plastic rather
than glass
Technological Threats
Labeling process under scrutiny by FDA
Amount of
Lycopene
Слайд 14
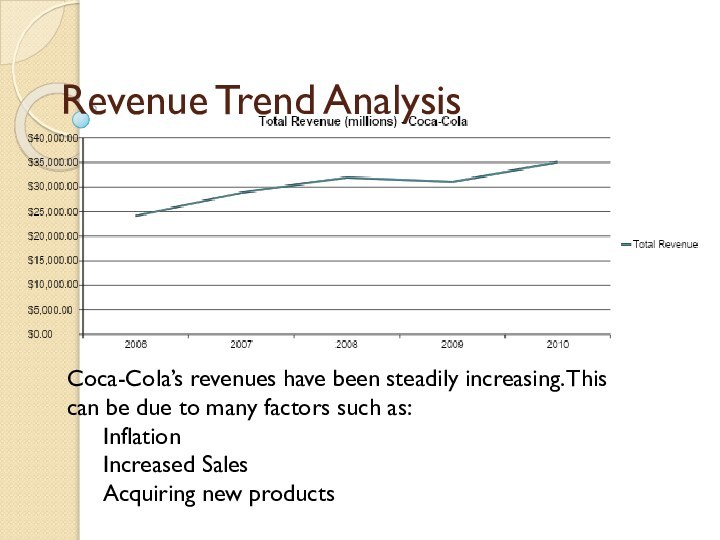
Revenue Trend Analysis
Coca-Cola’s revenues have been steadily increasing.
This can be due to many factors such as:
Inflation
Increased Sales
Acquiring new products
Слайд 15
Net Income Trend Analysis
Along with revenues, net income
has also been steadily increasing. This can be due
to the same factors as revenue, and also a decreased cost of goods sold and a decreased selling and administrative expenses.
Слайд 16
Important Ratio’s
Liquidity Ratio – 1.166
Ease of meeting short
term obligations
Profit Margin – 33.63%
For every dollar in sales,
Coke takes in about .33 cents in retained earnings.
Return on Equity – 38.09%
For every dollar that investors invest, Coke generates about .38 cents in profit.
Слайд 17
Financially Compared to the Industry
Coke Inventory Turnover –
13.25
Industry – 10.26
Coke has a higher inventory turnover because
of higher demand for products.
Coke Profit Margin – 33.68%
Industry – 6.67%
Cokes generates about 5 and a half times more profit, which highly exceeds the industry profit margin.
Return on Equity – 38.09%
Industry – 14.05%
Our investors dollars go further in our company than they would in a competitors company.
Слайд 18
Market Performance
Responsible Marketing Policy
Coke does not market to
an audience that is 35% children under 12 years
of age.
This applies to all areas of marking from TV commercials to internet advertisements.
“Kurt the Crate”
Germany
Inspires consumers to buy a variety of Coke products and transport them in a reusable crate.
Слайд 19
Marketing Performance
Successful marketing has lead to:
More than 500
sparkling and still beverages
Company portfolio includes 15 billion dollar
brands such as: Diet Coke, Fanta, Sprite, Coke-Zero, & more.
Marketing territory is in more than 200 countries
Serving beverages at a rate of 1.7 billion per day
Слайд 20
Human Resources
Exciting job areas such as:
Aviation
Because Coke
marketed in over 200 countries, Coke employs company pilots
to fly up scale private planes.
Innovation
Opportunity to create the next best thing
And much more common
career areas.
Слайд 22
Key Success Factors
Success depends on the amount of
brand loyalty and the amount of advertising.
The more a
company advertises the more revenue it receives. It works in a cyclical process and each is dependent on the other.
New products need large amounts of promotion so that the public is informed about the product.
Market share gained by one competitor is given up by another.
Слайд 23
Cost Position of Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola products sell at a
premium compared to other soft drinks. Although the premium
is marginal in the eyes of consumers, it makes a large difference from a corporate standpoint.
It is rumored that Coke products will increase in the near future due to rising commodity costs, like corn, because Coke uses high-fructose corn syrup as a sweetner.
Слайд 24
Economic Characteristics
Growth Rate shown to have increased by
19% in 2007
Unit Case Volume Growth increased by 6%,
growing from $24,088 to $28,857
Net Operating Growth increased by 20% from $6,308 to $7,552
Operating Income Growth was 15% from $5,080 to $5,981
(All Above Numbers In Millions)
Слайд 25
Ease Of Entry Into Industry
Very low, but not
impossible
High overhead and starting costs
No patents for producing carbonated
beverages
Ex. Wal-Mart
Слайд 26
What Forces Drive Change in Industry
Environmental Sustainability
Competition
Innovation
Слайд 27
Strongest/Weakest Competitive Position in Market
Coke at approximately $164,400,497
Pepsi
at $127,598,367
Dr. Pepper group $10,727,926
(Numbers in Thousands)
Слайд 28
Competitive Forces within Industry
Brand Name loyalty
Substitutes
New Entrants
Suppliers
Слайд 29
Keys to Success
Marketing(right demographics and message)
Philanthropy
Innovation(Freestyle, Flavors)
Слайд 30
Future Products
“Cokes with a Kick!”
Captain Morgan and Coke
Smirnoff
and Coke
Jack and Coke